Projectile motion
1/6
Earn XP
Description and Tags
YOU MOSTLY NEED TO DO PRACTICE QUESTIONS
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
define projectile
object where only force is gravity
assumptions made in projectile motion
no air resistance, gravity is constant, there is no friction (if being rolled off a cliff), no rotational motion, etc
how to solve projectile qs
consider horizontal and vertical components separately —> only common measurement is time
—> horizontal = constant velocity (no acceleration)
—> vertical = constant acceleration down
DIRECTION IS VERY IMPORTANT
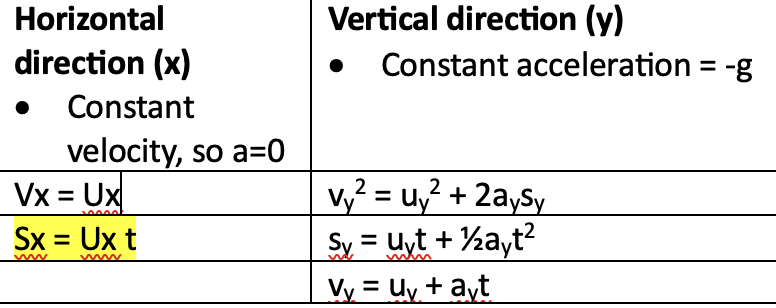
equations
key notes:
at max point vy=0 but vx is constant
for a full parabola, time of flight is 2 times the time to max height —> due to symmetry
use the equations to solve for any unknowns
gravity is -9.8m/s/s
can decompose launch angle to x and y
u = initial v= final
NOTE: IF A BALL IS DROPPED VERTICALLY WHILST A BALL IS THROWN HORIZONTALLY, (when Ux is same for both), they will land at the same time
Influence of variable on projectile
Ux
Uy
Sy
g
U
launch angle
determines range + shape
determines max height + time of flight
same Uy, they have the same Vy
the same time of flight, the same max height (assuming that the projectile was dropped from the moving object)
are always in line with each other vertically (when the projectile hits the ground, the object that dropped it will be directly above it)
Increasing acceleration decreases the range, and max height, and time of flight
Increasing the launch velocity increases maximum height, time of flight, and range
angle:
Optimum Launch angle for range is 45
Optimum launch angle for max height is 90°
proof for optimum range
use v=u+at for vertical components, rearrange for t
sub t=(v-u)/a in for Sx=Ux t
v and u are the same quantity but opposite signs so = -2v
use double angle rule so 2sinWcosW = sin2W, and sin2W greatest when 2W=90 W=45
questions involving stroboscope
gaps = time interval
use scale measure distance and fine Ux —> convert scale to real life
no. of images missing = distance of missing images ÷ distance between one image