AP Micro - Unit 5
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
what are factors and what is considered when making decisions to employ them?
Factors: Resources (land, labor, capital)
considerations: productivity of the factor, cost of the factor (rent, wages, interest), price of the good/service
labor market supply and demand def.
supply = willing and able workers
demand = many firms with jobs
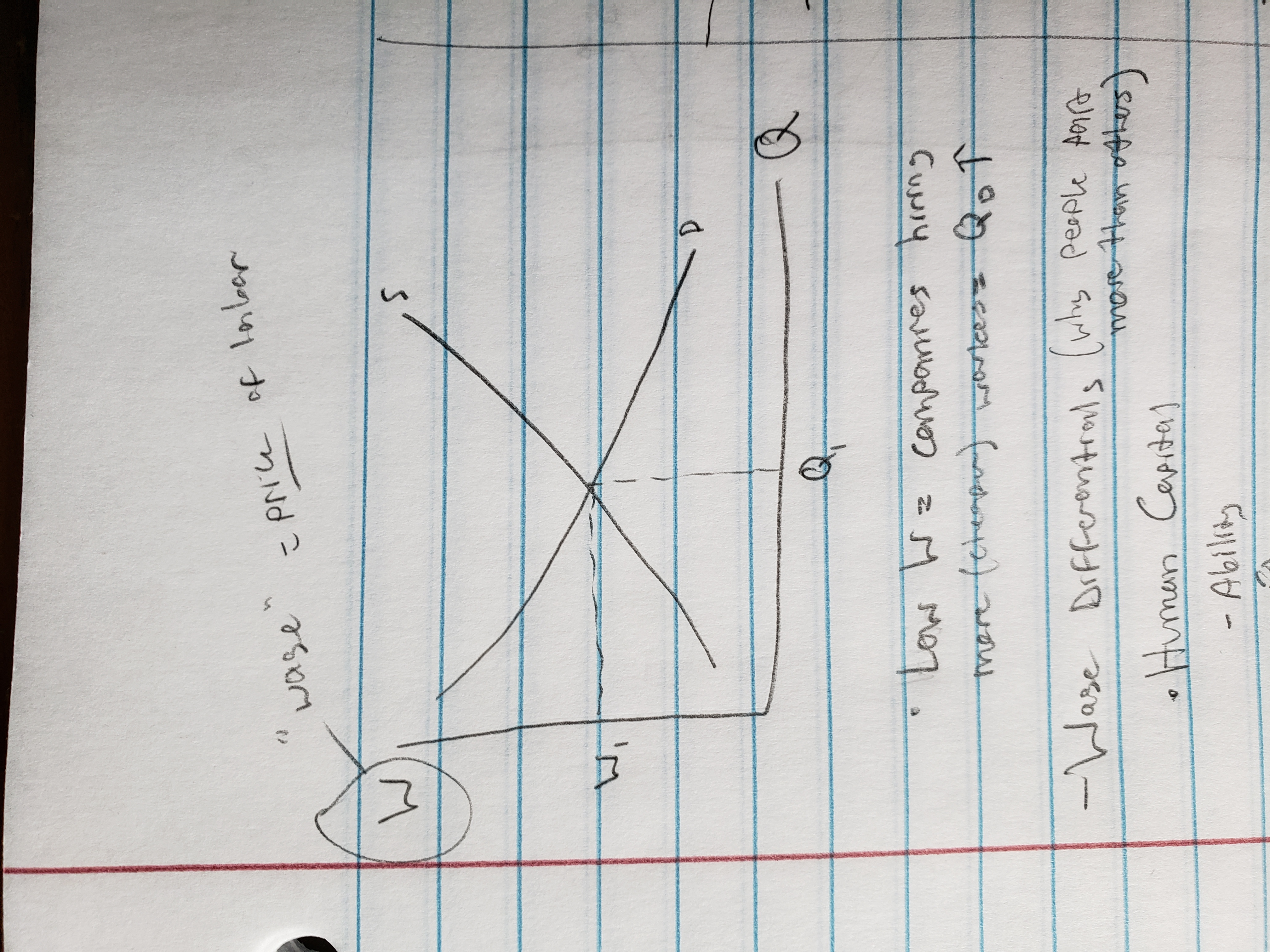
wage differentials (why people paid more than others)
Human capital
ability
education
training
networking
discrimination
luck
how minimum wage affects labor market
overall
creates unemployment
labor welfare increases
stops monopsonies

determinants of factor demand
derived demand
driven by product demand
productivity of resource (Marg. Product)
better resources
education / training
technology
better prod. = more of good made = more workers needed
price of product (P)
P ^ = Qs ^ = Dfactor ^
related goods
changes in the price of complementary resources
determinants of factor supply
immigration, emigration
age distribution (mandatory retirement, large old population will decrease supply)
working conditions (willingness dec., supply dec.)
education (able dec., supply dec.)
preferences for leisure
availability of substitute resource
automation, AI
harder to replace = S increases
marginal revenue product (MRP)
change in total revenue / change in resource quantity
marginal resource cost (MRC)
change in total resource cost / change in resource quantity
what is the optimal amount of a resource?
MRP >= MRC
(in perfect competition only: MP * P = MRP) (b/c price is constant)
labor market graph
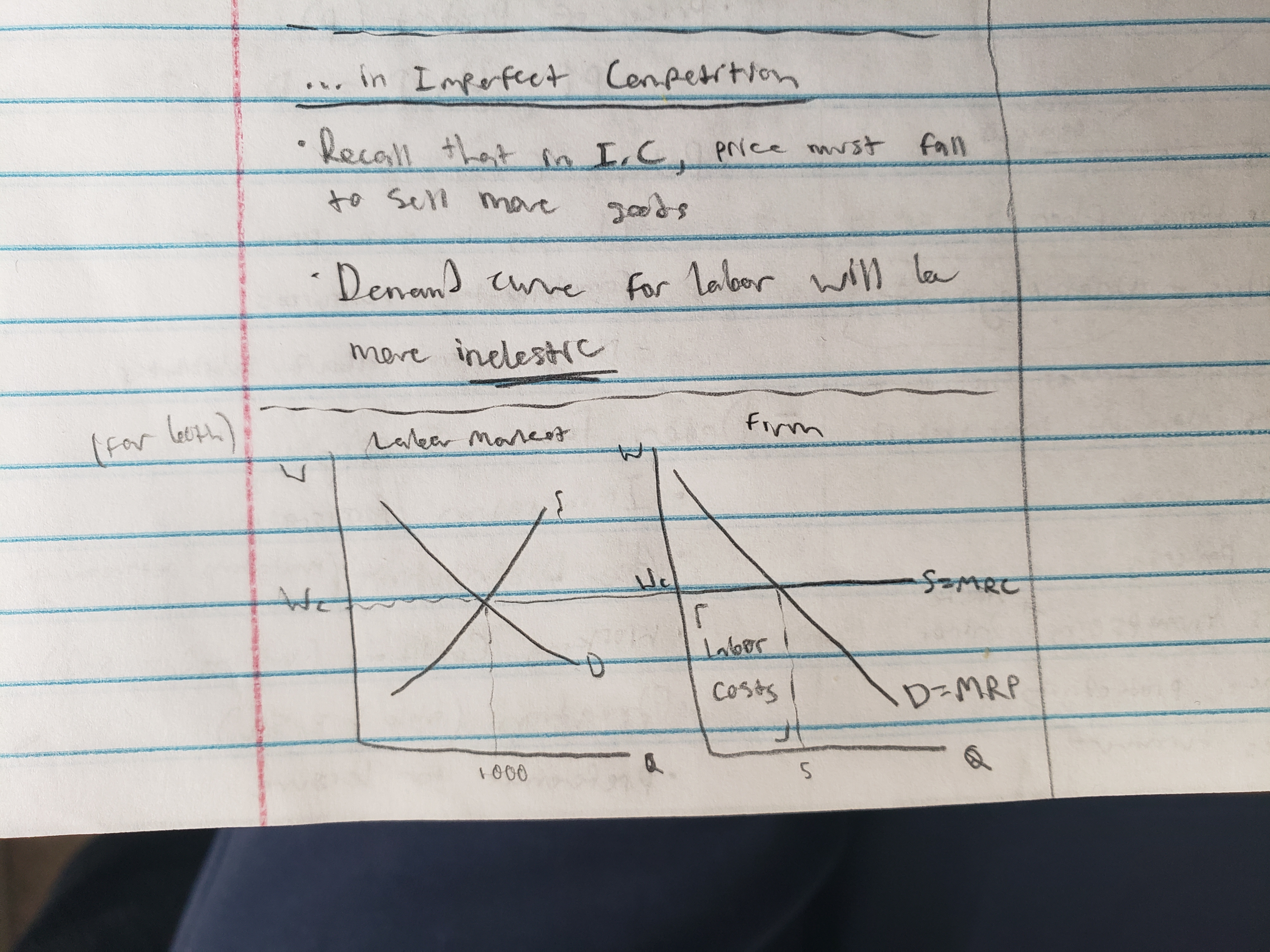
optimal combination of resources
All resources are variable
last dollar spent on each resource yields the same marginal product
MP(L) / P(L) = MP (C) / P(C)
where L = labor and C = capital
If MP/P for capital larger, then we will form more capital, fire more labor with lowest MP until MP/Ps are equal
diminishing returns, more capital decreases its marginal product, and less labor increases its marginal product
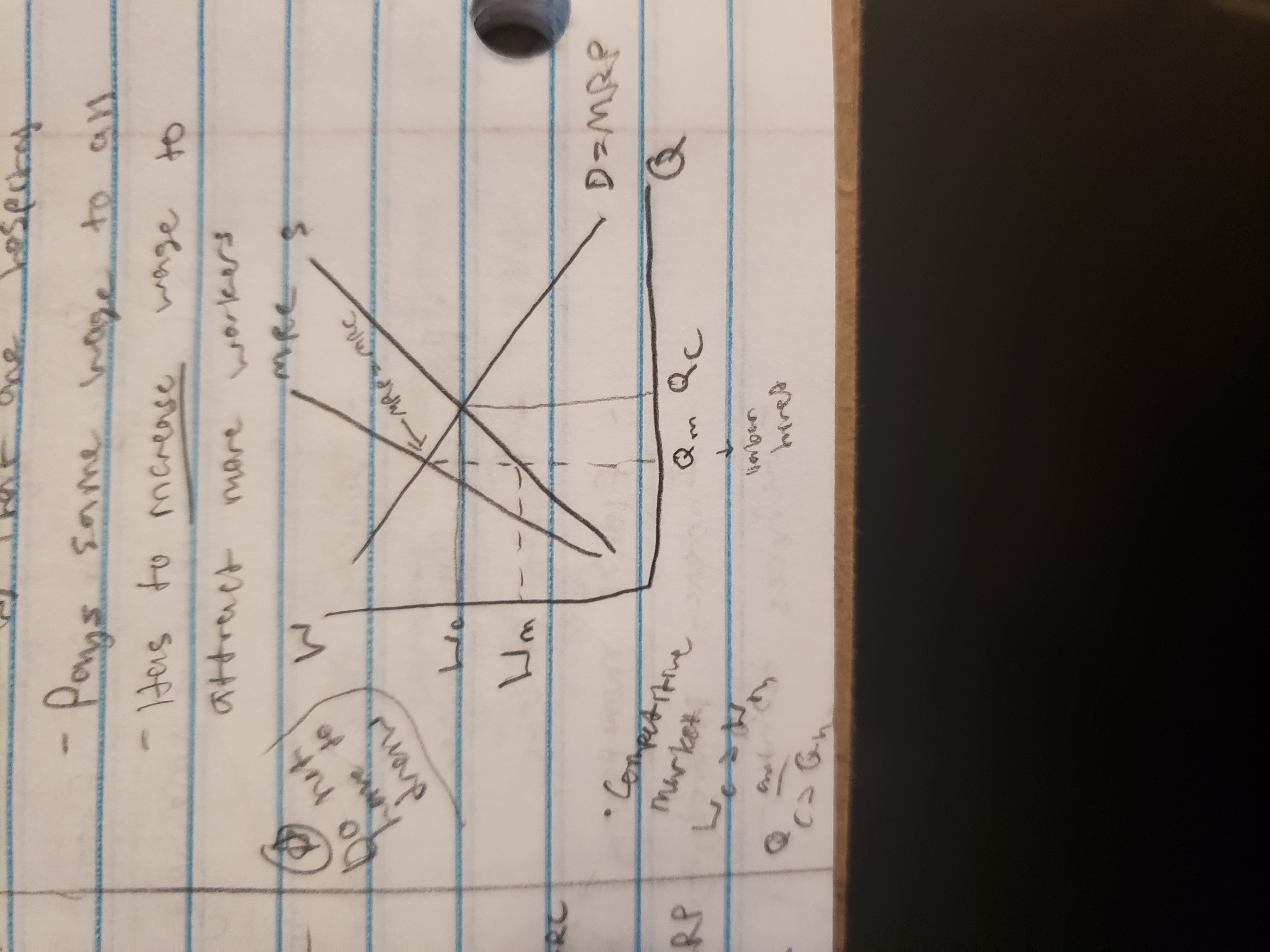
monopsonistic markets
single buyer for a type of labor
“wage maker”
ex) The only hospital in a sparse rural area, if you’re a doctor, you can only get a job with that hospital
pays same wage to all
has to increase wage to attract more workers