Patho- Inflammation & Immune System
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Pathophysiology Exam 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
body’s mechanisms for self
innate immune system, inflammation, adaptive immune syst, chronic inflammation
innate immunity
the first line of defense—the natural defenses in place at birth protecting against pathogens and environmental stressors (fast acting)
- includes physical(skin), mechanical (peeing), and biochemical mechanisms (tears)
physical barriers
part of innate immunity
- contains Epithelial Cells (which are tightly bound, line the surface of the skin+GI tract, and prevent pathogens penetrating deeply)
- inhibits pathogen growth because of the low temperature of skin + low pH of the skin & stomach
mechanical barriers
part of innate immunity- the mechanisms for clearing pathogens from the surfaces of epithelial cells
- ex: vomiting, urination, and goblet cells secreting mucous trapping pathogens
biochemical barriers
part of innate immunity- the substances synthesized by and secreted by epithelial cells designed to trap or destroy pathogens
- ex: Antimicrobial Fatty Acids+ Lactic Acids (secreted by sebaceous glands), Antimicrobial peptides (secreted by epithelial cells), and Lysozyme (part of perspiration, tears, and saliva)
opportunistic infection
normally: bacteria and fungi colonize the surfaces of the body, are nonpathogenic, and compete for resources+ space
- but under __ __, the immune system suppressed growth of normal flora, leading to this risk
lactobacillus
common component of vaginal microbiome, produces hydrogen peroxide and lactic acid (to inhibit growth of pathogens
- w/o __, candida albicans grows and forms thrush
true
(T/F) urination flushes bacteria out and disrupts adhesion BUT there is increased risk of bacterial growth if there is: Short Urethra, Reflux/Retrograde Flow, Obstruction
respiratory tract
part of the innate immunity-
- Mucociliary blanket lining nose+upper resp tract traps microbes.
- Goblet cells secrete mucus+trap microbes.
- Cilia move trapped microbes to throat to be expelled/swallowed.
- Alveolar macrophages destroy microbes that reach the lungs.
gastrointestinal tract
part of the innate immunity-
- Gastric acid destroys pathogens in stomach.
- Viscous mucus coats gut and traps pathogens.
- Pancreatic enzymes & bile destroy organisms.
- IgA from mucosa neutralizes microbes.
- Normal flora outcompete pathogens
inflammation
second line of defense and programmed response to tissue injury
- integrated system of humoral and cellular responses to: Limit tissue damage, Destroy pathogens, Initiate adaptive immune system, and Begin healing
endothelial cells
cell of inflammation- layers of cells lining blood vessels
functions: release nitric oxide to promote vasodilation
- release inflammatory mediators (interleukins, prostaglandins) to regulate cellular changes
- control cellular movement through __ layer
- release tissue factor in response to injury
mast cells
cell of inflammation- cells that lie in connective tissue near blood vessels
- when activated they Degranulate or release inflammatory meditators (histamine) (immediate reaction) or Synthesize new inflammatory mediators (delayed rxtion)
neutrophils
first phagocytic cell to arrive during inflammation. function is the phagocytosis of pathogens
eosinophils
cell of inflammation: functions: Defend against parasites/worms and regulate changes with allergic reactions
dendritic cells
link btwn innate and adaptive immune syst. functions as antigen-presenting cells to initiate adaptive immunity
- mildly phagocytic
monocyte/macrophage
functions as antigen-presenting cells to initiate adaptive immunity and clear pathogens and debris form injured tissue/wounds
- mono in blood → macro in tissue
histamine
first inflammatory mediatory released and produced by mast cells
responsible for- Vasodilation, ↑ Vascular Permeability, and Bronchoconstriction
bradykinin
chem mediator of inflammation- initiated by activation of Factor XII(hageman factor)
- function: Vasodilation , ↑ Vascular Permeability, Bronchoconstriction, and Pain
clotting factors
chem mediators of inflammation- induces the clotting cascade-chain of events that lead to production of Prothrombin →Thrombin→ Fibrin
complement proteins
chem mediators of inflammation- plasma proteins
function in inflammation
- vascular permeability and promote chemotaxis
function in immune system
- act as opsonins and facilitate phagocytosis, and as membrane attack complex
COX Pathway
cyclooxygenase pathway- metabolizes arachidonic acid metabolites
- produces Prostaglandins which promote bronchoconstriction and vasodilation and Thromboxane which promotes platelet aggregation
Lipoxygenase pathway
metabolizes arachidonic acid metabolites
- produces leukotrienes and promotes bronchoconstriction and ↑ capillary permeability
interleukins
chem mediators of inflammation- proteins produced mainly by lymphocytes and macrophages
- function- recruit+activate leukocytes (WBCs) and induces acute-phase responses of systemic inflammation (fever, ↑ HR, anorexia, ↑ neutrophils, ↑ cortisol)
- associated with tumor necrosis factor
interferons
chem mediators of inflammation- enhances defense against viruses and interferes w viral replication by inhibiting DNA/RNA synthesis
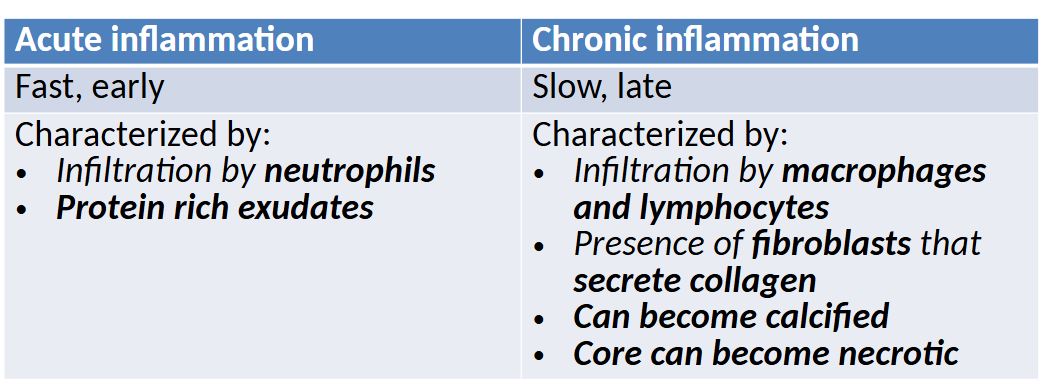
acute inflammation
early, shortterm and self-limiting, occurs b4 adaptive immunity
- designed to remove injurious agent and limit damage extent
- neutrophils dominate at first
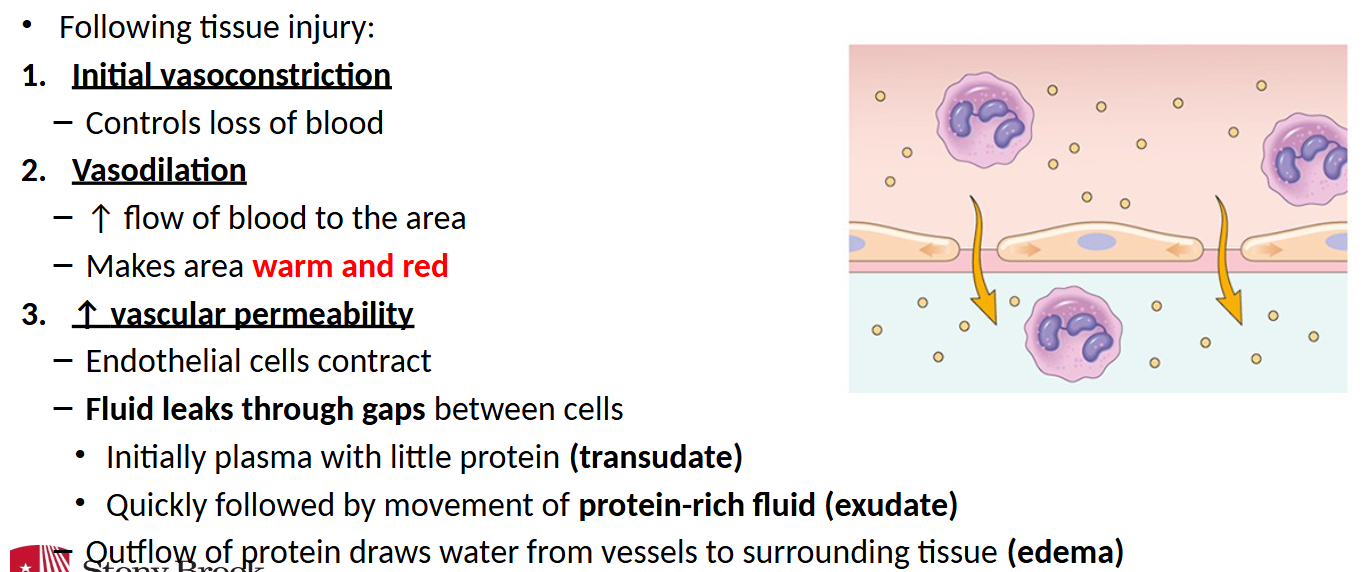
vascular response (acute inflammation)
chronic inflammation
late, long-term, and self-perpetuating—results from recurrent inflammation/infections or processes that dont induce an adequate acute response
- commonly macrophages and lymphocytes
acute vs chronic
exudate
protein rich fluid, types:
- Serous (early stages of inflammation) – Watery/yellow w/ little protein or cellular component
- Fibrinous (advanced inflammation) – ↑ protein/fibrin content
- Purulent/suppurative – grey, large amounts of leukocytes and pus– Lesions may be walled-off (cysts/abscess)
- Hemorrhagic/sanguinous – Exudate is filled with erythrocytes
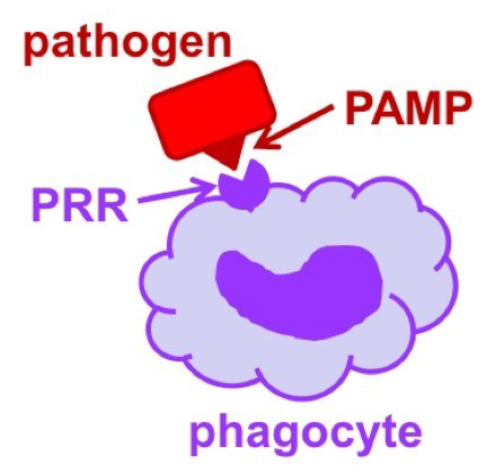
pattern recognition receptors
how leukocytes recognize pathogens:
- __ __ __ are molecules on the surface of phagocytic cells that recognize PAMPs (pathogen-associated molecular patterns) on the surface of pathogens
- PRR attachment to PAMPS stimulates the phagocytic cell and phagocytosis
opsonization
how leukocytes recognize pathogens:
__ are soluble molecules that bind to the surface of pathogens (like sprinkles). phagocytic cells bind to __ on the surface and this activates phagocytosis
local
__ manifestations of inflammation occur as the result of vasodilation and increased vascular permeability
- Vasodilation→ Heat and Redness
- ↑Capillary Permeability→ Swelling and Pain
Systemic
__manifestations of inflammation characterized by:
Fever (early response induced by IL-1 acting on hypothalamus), Leukocytosis (↑leukocytes to fight infection), and Plasma Protein Synthesis (fibrinogen, prothrombin, clotting factors, etc. produced by liver)
adaptive immunity
third line of defense— slow process designed to create a specialized immune response against a pathogen (end product may remain in body)
- cell-mediated by T-lymphocytes
- humoral: mediated by antibodies produced by plasma cells
major histocompatibility complex
glycoproteins on the surface of cells responsible for antigen presentation and they help immune syst differentiate native cells from foreign cells
- MHC II on APCs: activate CD4+ to become T-helper cells
- MHC I on all nucleated cells activate CD8+ to become cytotoxic T cells
B Lymphocytes
type of lymphocyte when activate, it differentiates into plasma cells and make antibodies
T lymphocytes
type of lymphocytes with 2 types:
- CD4+ _ _: converts into T-helper cells and regulates adaptive immune system and creates memory
- CD8+ _ _: convert into cytotoxic T cells and release reactive oxygen species and enzymes to destroy infected cells
humoral immunity
immune response mediated by antibodies
- Primary Immune Response- First exposure to an antigen→ slow to develop→ results in memory B cells
- Secondary Immune Response- Subsequent exposure to antigen, much quicker
IgG
Most abundant immunoglobulin/antibody-75%
- arrives late after infection is gone but stays for the rest of ur life, the only one that crosses placenta, promotes lysis of infected cells
IgA
immunoglobulin/antibody
- common in mucous membranes and secretions, provides local immunity
IgM
immunoglobulin/antibody- first to appear in response to antigen (when u first get sick)
- promotes agglutination of organisms for lysis/phagocytosis
IgD
immunoglobulin/antibody- on B cells and required for B cell maturation
IgE
immunoglobulin/antibody- reacts to inflammation, allergic responses, parasites/worms
- binds to Fc receptors on mast cells releasing histamine
active immunity
immunity developed by vaxx or having the disease—body is exposed to antigen and develops its OWN immunity, longterm
- host immune syst responds by creating antibodies to antigen
passive immunity
received immunity from another, short-term
-ex: fetus is protected by IgG of mother (hyperimmune serum-IVIg)
type 1 hypersensitivity
hypersensitivity- IgE-mediated + immediate + atopic
- sensitization: IgE is produced→ binds to mast cells
- re-exposure: Allergen binds to IgE bound to mast cells → histamine release
- effects: bronchoconstriction, vasodilation, ↑ capillary permeability
1. Primary/initial phase – onset 5-30 min (Vasodilation, vascular leakage, and smooth muscle contraction)
2. Secondary/late phase – 2-8 hrs after initial phase (Continued vasodilation, infiltration w/ eosinophils etc., and eosinophils promote tissue damage)
type 2 hypersensitivity
“Antibody-mediated” hypersentivity– Mediated by IgM or IgG directed against target antigens
– Location of the target antigen defines the response
ex:
1. Antibody binding to cell-surface antigen causes cell destruction (ABO/Rh incompatibility)
2. Antibody binding to cell receptors activates cell (Graves disease)
3. Antibody binding to cell receptor prevents cell activation (myasthenia gravis)
type 3 hypersensitivity
“immune complex-mediated” hypersensitivity– Antigen/antibody complexes formed in bloodstream
– Complexes are eventually deposited in vascular endothelium or extravascular tissue
– Activates complement and initiates inflammation
type 4 hypersensitivity
“T-cell-mediated” delayed hypersensitivity (no antibodies involved)
sensitization: APCs after processing antigen activate T-cells →produce memory T-cells
re-exposure:
– recruitment + activation of memory T-cells
– Cytotoxic T-cells and phagocytic cells (recruited by other t-cells) destroy tissue
DIRECT transplant rejection
pathway when donor APCs present donor MHC directly to recipient T cells, triggering a fast immune attack, primarily through CD8+ cell killing and CD4+ cytokine-driven inflammation and antibody production
INDIRECT transplant rejection
pathway where recipient APCs process the donor antigen. recipient T cells (CD4&CD8) are activated when facing donor(foreign) MHC → Cytotoxic CD8+ kill foreign tissue and CD4+ conducts 3 functions..
transplant rejection types
Hyperacute: v rare– Immediate + occurs if someone was pre-sensitized – recipient antibodies react w/ antigens on the graft and create a type II hypersensitivity
Acute: 7-10 days — recipient T lymphocytes interact with APCs in grafted tissue (DIRECT)– T helper lymphocytes of host do the 3 things...
Chronic: Delayed (months/years)– Gradual proliferation & fibrosis of vascular smooth muscle → occlusion and organ dysfunction
graft vs host disease
cells w/ functional immunity are transplanted into someone who is immunocompromised →the grated tissue rejects the recipient (often bone marrow transplant)
autoimmune disorders
Tolerance is the ability of the immune syst to differentiate self vs. non-self
— Central tolerance: apoptosis of autoreactive T cells (removed in thymus) and B cells (in bone marrow)
— Peripheral tolerance: eliminates autoreactive cells that escape
Failure of tolerance → __ disorder
heredity, gender, environment
factors linked to autoimmune diseases
lupus
systemic __ erythmatosus. females>
— Caused by B cell overactivity & faulty T cell regulation
— antinuclear, antiphospholipid and antiplatelet antibodies form immune complexes
— Type III hypersensitivity → tissue damage
Symptoms: fatigue, joint pain, rash, renal disease, anemia
tissue regeneration
type of tissue repair—replacement of damaged w cells of the same types.
— complete returns to normal structure+function - takes 2 yrs
fibrous tissue repair
type of tissue repair— normal tissue replaced w connective tissue, scar often forms
— occurs if: extensive damage, not capable of regeneration, abscess/granuloma develops, fibrin persists in area
inflammatory phase
phase prepping wound for healing
— vasoconstriction followed by vasodilation, fibrin mesh forms, influx of macrophages+neutrophils→ clean the wound of debris
proliferative phase
wound healing 2cd phase— 2-3 days of injury
— clot is replaced by normal/scar tissue. macrophages release growth factor→ stimulates angiogenesis, fibroblasts create granulation tissue, epithelial cells formed at edge, wound contraction
remodeling phase
3rd phase of wound healing— 3 weeks after-2yrs
— structure of scar changes, vascularity↓, new collagen by fibroblasts, lysis of old collagen, wound contraction cont.
keloid
raised scar due to excessive collagen production. genetic predisposition and common among AA
primary intention
faster method of wound healing— suture wound. less tissue damage this way and less shrinkage needed.
secondary intention
slower method of wound healing—pressure ulcer/burn. greater tissue damage and heals from bttm up. more shrinkage required