Thermodynamics Quiz
1/29
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
kinetic molecular theory
matter is made up of tiny particles that are always in motion; particles move faster as the temperature increases and transfer energy during collisions
states of matter
solid, liquid, gas
phase diagram
shows the phase of a molecule according to the pressure and temperature of the environment
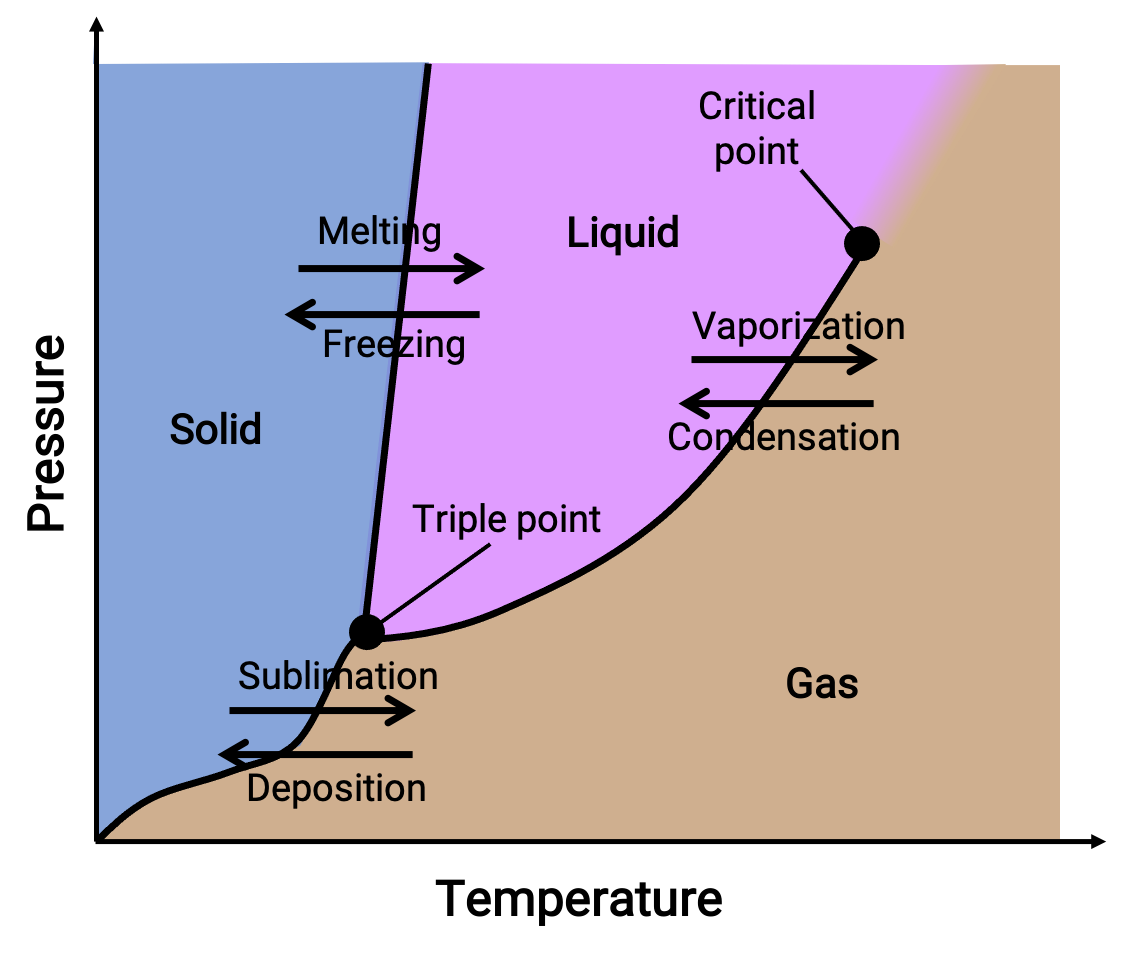
triple point
point where all 3 states of matter exist in equilibrium
critical point
point where the substance can no longer be distinguished between a liquid and a gas; exists as a supercritical fluid
melting
change from solid to liquid
freezing
change from liquid to solid
vaporization
change from liquid to gas
condensation
change from gas to liquid
sublimation
change from solid to gas
deposition
change from gas to solid
endothermic
reaction or change that absorbs heat
which phase changes are endothermic
melting, boiling, sublimation
exothermic
reaction or change that releases heat
what phase changes are exothermic
freezing, condensing, deposition
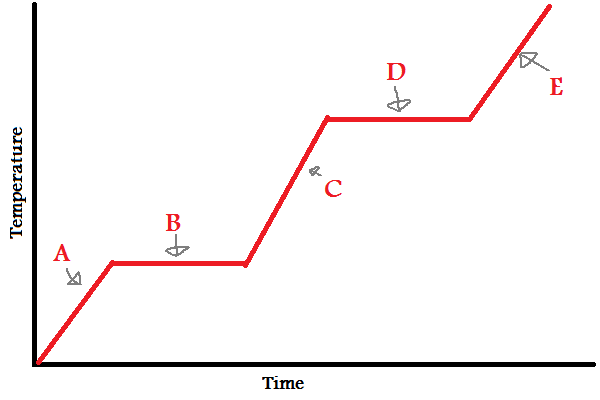
what formula is used for A, C, and E
q = mcΔT
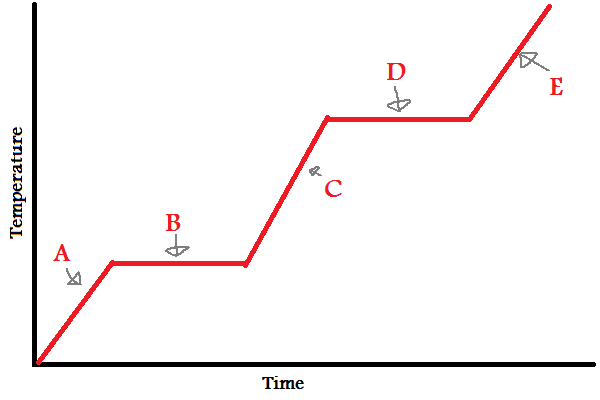
what formula is used for B and D
q = mΔH°
when to use q = mcΔT, q = mΔH°
use q = mcΔT as temperature increases, use q = mΔH° when a phase change occurs
why doesn’t the temperature change during a phase change?
the added heat is being absorbed to break the IMFs between molecules rather than increasing kinetic energy
what does q represent
heat in J or kJ
what does m represent
mass in grams or moles
what does c represent
the specific heat of a substance
what does ΔT represent
change in temp (final temp - starting temp)
specific heat
heat required to raise the temperature of the unit mass of a given substance by one degree
heat of fusion (ΔHf)
amount of energy required for a substance to melt
heat of vaporization (ΔHv)
amount of energy required for a substance to vaporize
calorimetry
process of measuring the amount of heat released/absorbed during a chemical reaction
calorimeter
device used to measure the absorption or release of heat
why is styrofoam used as a calorimeter?
it is an excellent insulator, meaning that minimal heat will escape the system
if in calorimetry, the metal released 100J of energy, how much energy did the water absorb?
100J (heat loss = heat gained)