ecawns market failure
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
-VE EXT AND PETDQQD (+ve and -ve)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
what is market failure
failure of the free market to allocate resources efficiently
-ve ext?
spillover costs to third parties who are not directly involved in the consumption/production of the good or service itself
MEC
additional cost to third parties (con/prod) ++ unit of g/s
MSC
MPC + MEC
MSC>MPC
over allocation
ext (PETDQQD) P
priv benefit and cost
ext (PETDQQD) E
externalities → what isit
ext (PETDQQD) T
third parties - who?
ext (PETDQQD) D
divergence
—> presence of MEC/B create divergence between MSC/B and MPC/B
—> (MSC><MPC)
—> diagrammatically, MS curve lie above MP by amt of ME
—> assuming no ( ) ext, MP=MS
ext (PETDQQD) Qp
left to free market, firms prod/consumers consume Qp units
MPB=MPC, only consider priv costs and benefits
ext (PETDQQD) Qs
-social optimal lvl of prod/cons = Qs units
- msb=msc
- QP>QS, over production/consumption + over allocation of resources
-QP<QS< under
ext (PETDQQD) Dwl
Deadweight loss
at Qp, MSC>MSB/MSB>MSC
add more to costs/benefits
from Qp to Qs units, TSC>TSB/ TSB>TSC
welfare loss to society when output not prod at social optimal lvl
market failure —> Qp is allocative ineff, social welfare NOT maximised
ext (PETDQQD) conc
ext costs/benefits not factored in decision making
distortion of price signals
price mech fail to bring socially optimal allocation of resources
over allocation
(Govt Int) —> -ve ext (4)
indirect taxes
rules and regulations
tradable pollution permits
key SG transport policies
-ve ext: indirect taxes (use)
generate ext costs on third parties
make prod/con internalise the -ve ext
-ve ext: indirect tax —> for producers (8pt)
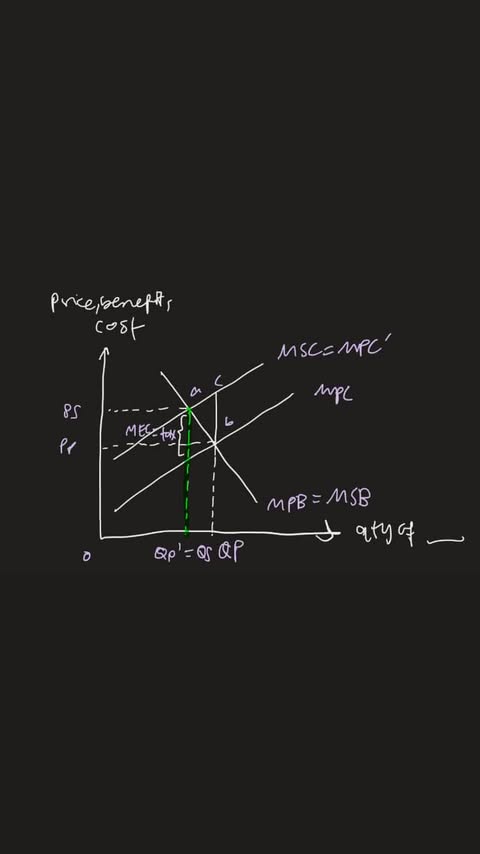
levy indirect tax = MEC @ QS (social opt)
increase in MPC, force producers internalise MEC to third parties
increase shift of MPC curve by amt of tax (MPC to MPC’)
new QP’ (mpc=mpc’) coincide with QS (msb=msc)
fall in prod from Qp to Qp’ —> eliminate dwl
reduce -ve ext —> incentivise both con and prod to reduce + internalise
allocative eff
social wf
-ve ext: indirect tax —> consumers
govt levy
thru producers —> pass to consumers in terms of higher prices
directly at consumers
indirect tax —> govt unintended conseq
opp cost of implementation
inequity (PED)
indirect tax —> govt intended conseq
1 . revenue from tax (address ext damages from prod/cons of g/s)
loss aversion (pain of losing > pleasure of gaining)
indirect tax —> govt limitations (4)
info gap
high admin costs —> unsustainable in long term
uncertainty and time lag
sunk cost fallacy
indirect tax —> govt limitations - info gap
over/under est of MEC
-over: govt levy excessively high tax
mpc higher than msc
wf loss >gi
govt failure
-under:
tax rate lower than necessary
new mpc lower than msc
indirect tax —> govt limitations- high admin
manpower and resources (monitoring)
indirect tax —> govt limitations- time lag
-govt need time to determine amt of ext costs
-prod and con need to fully respond to the dis incentives
indirect tax —> govt limitations- sunk cost
time and money alr invested, too much to quit
-ve ext - rules and regulations (types) 3
quota
ban
production/consumption methods
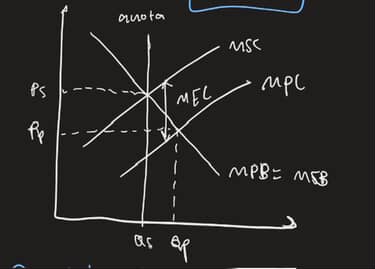
-ve ext - rules and regulations - quotas
def: legal limits on output/pollution lvl
set at QS (prevents c/p beyond that lvl)
yay allocative eff
for pollution:
limit amt of emissions
directly limits ext cost generated
red mec and msc
qs increase, reduce extent of overproduction and wf loss
-ve ext - rules and regulations - bans
2 types
mechanism
complete + partial
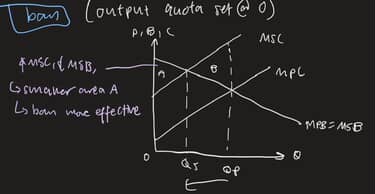
def: output quota set at 0
def
social optimal when MEC very large
MSB intersect MSC —> social opt qty QS @/close to 0
no prod/cons
eradicate all -ve ext + benefits generated from p/c of g/s
area A: wf loss (MSB>MSC for output between 0 and Qs)
A<B (initial wf loss)
NOTE: better to ban when extent of MEC vv large —> social welfare improves overall
-ve ext - rules and regulations - productn/consumptn methods
ext cost decrease
social optimal qty QS increase to QS1
closer to Q- (QSQP to QS1QP)
reduce extent of overconsumption and dwl
increase allocative eff
-ve ext - rules and regulations
-ve ext - rules and regulations - govt considerations - limitations
info gap
—> govt dk lvl of penalty/consequence harsh enough to deter firms
—> bans: mec not significant
high admin costs —> unsustainable
—> inspection, monitoring, prosecution
-ve ext - rules and regulations - govt considerations - unint conseq
high costs to firms
(firms incurring increasing pollution abatement costs —> same limit on emissions as lower ones)
trade off with macroeconomic aims
(chase firmsaway to other countries cuz penalty too harsh)
opp cost of implementation
-ve ext - rules and regulations - govt considerations - intended con
laws compel ppl to take action
certain and faster outcomes
-ve ext: tradable pollution permits (def)
govt issue firms with permits on max lvl of pollution they are allowed to emit (set quotas)
→ firms buy and sell to eachother in carbon market
-ve ext: tradable pollution permits - example
European Union Emissions Trading System (EU ETS)
—> cap and trade principle
—> price det by mkt dd and ss of such permis
pollution abatement costs exceed current permit price
—> cheaper to buy more permits than reduce pollution lvl
firms facing lower pollution abatement costs
—> sell permits + reduce pollution
-ve ext: tradable pollution permits - outcome
cleaner production techniques
avoid increase cop, yay revenue
ext cost reduced
msc shift downwards towards MPC in long run
reduce DWL
-ve ext: tradable pollution permits - govt considerations - limitations
info gap
high admin costs
increased pollution in certain regions
—> one region buy permit from another
—> lower non material SES
-ve ext: tradable pollution permits - govt considerations - unintended conseq
trade off with macro aims
opp cost
-ve ext: tradable pollution permits - govt considerations - unintended conseq - trade off
-need purchase permits
—> increase firm COP
→ decrease in investment, employment and econ growth
—> if heavy polluting firms find permits to costly, might relocate
-ve ext: tradable pollution permits - govt considerations - unintended conseq - opp cost
increase admin cost outweigh benefit from reducing extent of mf (govt failure)
opp cost: implementation and enforcement financed thru reduction of spending in other areas
wf loss for 1 market > wf gain for other market —> GOVT FAILURE
-ve ext: tradable pollution permits - govt considerations - intended conseq
incentives (r&r no incentive to futher reduce emissions once they meet the limit by govt)
lower total cost
more certain outcome
key sg transport policies - govt int (2)
target problem on market of road usage
target problem of rising car ownership
key sg transport policies - govt int - road usage
reduce congestion and pollution —> TAXES
electronic road pricing (ERP)
diagram;
indirect tax=MEC @ Qs
increase MPC by amt of indirect tax
increase cost of road usage, motorists compelled to internalise ext
mpc shift to mpc’, traffic vol reduced to Qs, decrease congestion
decrease amt of emissions, decrease pollution
@Qs, dwl eliminated
allocative eff (MSB=MSC)
key sg transport policies - govt int - rising car ownership
reduce congestion and pollution
quota: vehicle quota system (VQS)
tax: additional registration fee (ARF)