Introduction to Geography and Economic Activities: Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Sectors
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
What is economic geography?
The study of how people earn their living, how livelihood systems vary by area, and how economic activities are spatially interrelated and linked.
What are the primary activities in economic geography?
Agriculture, gathering industries, and extractive industries.
What are secondary activities in economic geography?
Activities that add value to materials by changing their form or combining them into more useful commodities, including manufacturing and processing.
What do tertiary activities provide?
Services to the primary and secondary sectors and goods and services to the general community and individuals.
What are the three major types of economic systems in the early 21st Century?
Subsistence economies, market (commercial) economies, and planned economies.
What characterizes subsistence economies?
Goods and services are created for the use of the producers and their kinship groups, with little exchange of goods.
How are goods and services distributed in market economies?
Through competitive markets where price and quantity are determined by supply and demand forces.
What defines planned economies?
Goods and services are distributed through governmental agencies that control both supply and price.
What is the agricultural continuum?
The range from subsistence to traditional (intermediate) to advanced (modern) farm economies.
What are the two chief types of subsistence agriculture?
Extensive subsistence agriculture and intensive subsistence agriculture.
What is extensive subsistence agriculture?
Agriculture that uses large areas of land with minimal labor input per hectare, resulting in low product per land unit and population densities.
What is intensive subsistence agriculture?
Agriculture that involves small land holdings with great amounts of labor per acre, resulting in high yields per unit area and population densities.
What is nomadic herding?
The controlled movement of livestock solely dependent on natural forage, requiring the greatest amount of land area per person sustained.
What is transhumance?
Seasonal movement to exploit locally varying pasture conditions.
What is shifting cultivation?
A form of agriculture practiced in warm wet tropical climates where plots are cleared and burned, cultivated until fertility is lost, then shifted to a new site.
What percentage of the world's population is involved in intensive subsistence agriculture?
About 25%.
What are two paths to increased food production?
Expanding the land area under cultivation and increasing crop yields from existing farmlands.
What challenges exist in expanding the land area under cultivation?
Most suitable land is already cultivated, and millions of hectares are lost annually due to soil erosion, salinization, and urbanization.
What is the significance of agricultural employment in developing countries?
Employment in agriculture is steadily declining as economies develop.
What is the impact of the economic crisis that began in 2007 on global hunger?
It reversed a 30-year trend of reduced global hunger, leading to over 1.0 billion undernourished people.
What factors influence livelihood patterns in economic geography?
Physical environment, cultural considerations, technological development, political decisions, and economic factors of demand.
What is the role of transportation in economic development?
Transportation is crucial for the allocation of labor force among economic activities and contributes to overall development.
What is the criticism of assessments of stages of development?
They are frequently criticized for Western market economy biases.
What is the 'Big Push' theory in development?
A theory proposing that significant investment in infrastructure and human capital is necessary to transition from subsistence to industrial economies.
What is the primary goal of expanding crop production?
To increase crop yields from existing farmlands.
What are the key inputs increased during the Green Revolution?
Water, fertilizer, pesticides, herbicides, and labor.
What does the term 'Green Revolution' refer to?
A complex of seed and management improvements designed to increase agricultural output.
What are some negative consequences of the Green Revolution?
Displacement of traditional agriculture, loss of food security, nutritional diversity, salinization, and groundwater depletion.
What is one major issue with the benefits of the Green Revolution?
Unequal spatial distribution of benefits and declining gains in many areas.
What is Von Thünen's model of agricultural location?
A model analyzing human activity patterns based on distance to a market town and land use intensity.
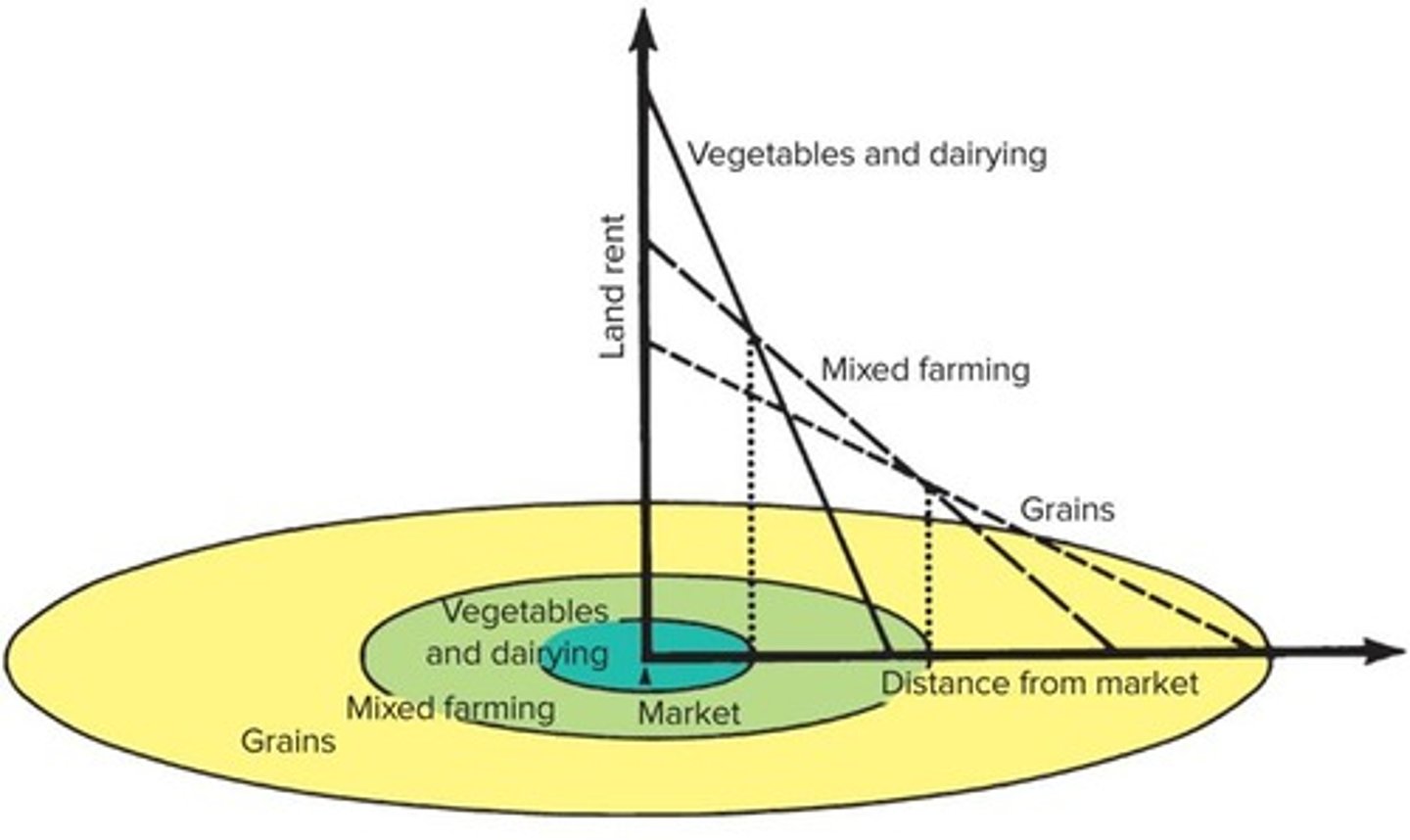
What are the rings in Von Thünen's model used for?
To represent different land uses based on their rent values and distance from the market.
What characterizes intensive commercial agriculture?
Production of high-yield crops with high market value per unit of land.
What is extensive commercial agriculture?
Larger farm units on cheaper land, typically farther from markets.
What is Mediterranean agriculture known for?
Special crops like grapes, olives, and oranges, often developed in climates far from markets.
What does sustainable agriculture aim to address?
Negative effects of industrialized agriculture, including environmental impact and food quality.
What are the primary sources of fish supply?
Inland catch, fish farming, and marine catch.
What is a significant challenge facing commercial marine fishing?
Overfishing and pollution of coastal waters.
What are the disadvantages of aquaculture?
Pollution from fish waste, disease transfer to wild stocks, and depletion of wild fish stocks for feed.
What factors influence mining and quarrying production decisions?
Quantity available, ore richness, distance to markets, and land acquisition costs.
What has changed in traditional export patterns between developed and less-developed countries?
Raw materials from less-developed countries have decreased while manufactured goods from developed countries have increased.
What is the 'tragedy of the commons' in relation to fishing?
The overuse of shared resources leading to depletion and environmental degradation.
What has been the trend in the number of farms since 2002?
A reduction in the number of farms, with a rise in small farms due to consumer demand for organic and local food.
What role does government play in commercial agriculture?
Governmental involvement includes regulations, subsidies, and support for agribusiness.
What is the significance of contractual arrangements in agriculture?
They facilitate specialization and interdependence between producers and buyers.
What is the impact of agricultural practices on rural populations?
Industrialized agriculture has led to depopulation of rural areas.
What is the fastest growing sector of the world food economy?
Aquaculture (fish farming).
What are the characteristics of plantation crops?
Large agricultural holdings, often foreign-owned, dedicated to one or two export crops, typically in tropical regions.
What is the relationship between agricultural practices and food security?
Intensive agricultural practices can lead to loss of food security and nutritional diversity.
What does Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) indicate?
PPP indicates the relative value of currencies and the purchasing power of income across different countries.
What is the range of GNI per capita (PPP) in 2019?
Ranges from 0 to 124190 US dollars.
Which regions have a high Purchasing Power Parity?
North America, Europe, the Middle East, Australia, Russia, and Japan.
What was the percentage of primary workers in the United States in 1850?
66% of the workforce.
What significant change occurred in the sectoral allocation of labor in the U.S. from 1850 to 2018?
The percentage of primary workers decreased from 66% in 1850 to 1% in 2018.
What is a key measure of economic development related to transportation?
Accessibility.
How does lack of accessibility affect subsistence economic areas?
It slows modernization and hinders participation in the world market.
Where are most undernourished children located according to the 2018 data?
Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia.
What agricultural regions are known for naturally fertile soils?
The corn and wheat belts of North America, Ukraine, southern Siberia, and rice-producing regions of India and Southeast Asia.
What is shifting cultivation, or swidden agriculture?
A practice that maintains soil fertility through traditional methods in tropical climates.
What does intensive subsistence agriculture involve?
High labor input, often with crops like rice requiring careful management of water levels.
What is the significance of von Thünen's model?
It illustrates how land use intensity decreases with increasing distance from the market.
What types of crops are grown closest to the market according to von Thünen's model?
Perishable commodities like fruits and vegetables.
What is the trend in commercial agriculture in the U.S.?
It uses intensive methods to produce large volumes of uniform products at low prices.
What is the impact of overfishing on marine fisheries near the U.S. coastline?
It has contributed to the depletion of fish stocks in those coastal waters.
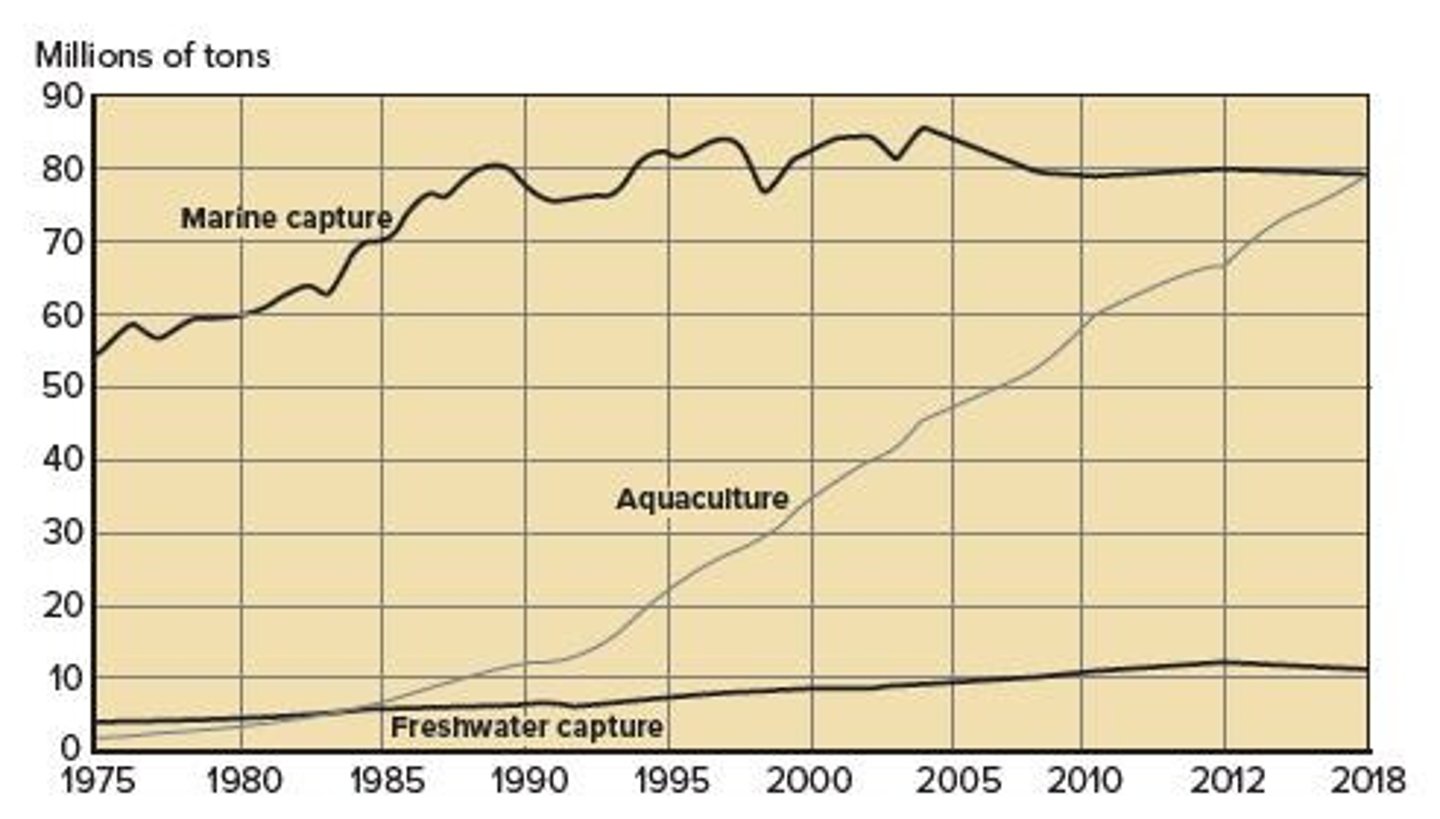
What is the trend in marine capture from 1975 to 2018?
Marine capture increased from 56 million tons in 1975 to 80 million tons in 2018.
What are the primary activities related to agriculture?
Includes subsistence agriculture, commercial agriculture, and various forms of crop production.
What is the role of livestock ranching in agriculture?
It primarily caters to urban markets in industrialized countries.
What influences the specialized crops of plantation agriculture?
Physical geographic conditions and historical colonial control.
What is the process of preparing a swidden plot?
Vegetation is hacked down, and the field is planted, with stumps and trees left in the clearing.
What is the significance of the Great Plains in U.S. agriculture?
It is known for concentrated animal-feeding operations and intensive commercial agriculture.
What are the characteristics of intensive subsistence rice farming?
Requires arduous hand labor and careful water management for optimal crop yield.

What does the graph of harvest in millions of tons from 1975 to 2018 show?
It shows growth in marine capture, agriculture, and freshwater harvest over the years.
What are the challenges faced by isolated areas in advanced economies?
They suffer price disadvantages due to high transportation costs.
What percentage of the U.S. workforce was in the tertiary sector by 2018?
79% of the workforce.