bio 109- CHAPTER 6- enzymes and energy
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
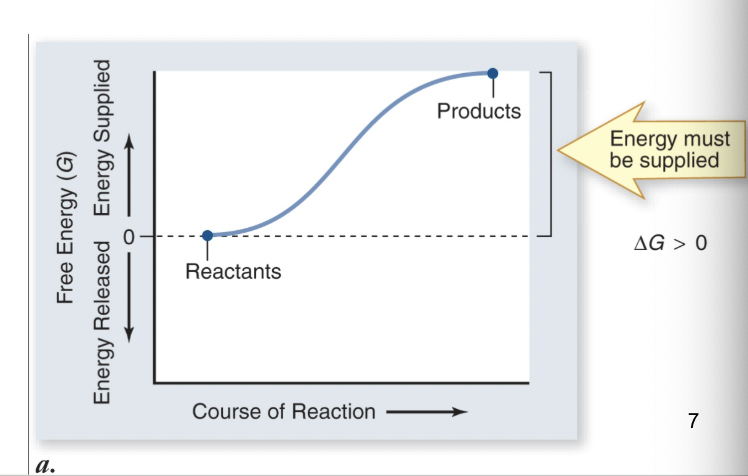
endothermic
energy of products > substrates (net energy input)
products have more energy than substrates
potential energy is higher disorder is lower
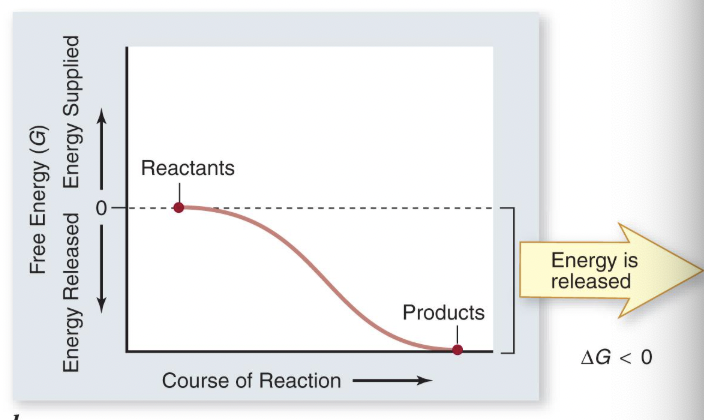
exothermic
energy of substrates > products (net energy output)
products have less energy than substrates
potential energy is lower disorder is higher
will happen on their own (may require activation energy)
anabolic
substrates built up into larger molecules
catabolic
substrates broken down into smaller molecules
activation energy
energy required to start an exothermic reaction
destabilize existing bonds (ex gas in a car)
reaction speed depends on energy in the system
lower activation energy = more kinetic energy left for reaction
enzyme
biological catalyst (usually a protein, some are RNA)
most are proteins (some are RNA)
shape of active site determine function
what do chemical reactions involve
forming or breaking chemical bonds
substrates (reactants)
molecules at start of reaction
products
molecules at end of the reaction
what is the first law of thermodynamics
energy cannot be created or destroyed
total amount of energy in the universe remains constant
only changes between kinetic and potential
during each conversion some energy given off as heat (kinetic energy)
what is the second law of thermodynamics
disorder (entropy) is continuously increasing
matter breaks to release energy

metabolism
total of all chemical reactions in an organism
anabolic reactions
use energy to build bigger molecules
catabolic reactions
release energy by breaking down molecules
what can exothermic reaction speed be increased by
1) increasing kinetic energy (heating)
2) decreasing activation energy (catalyst)
what are the three things speed of reaction is influenced by
1) temperature (more collisions between substrates)
2) concentration of substrates and products (mass action)
3) catalysts
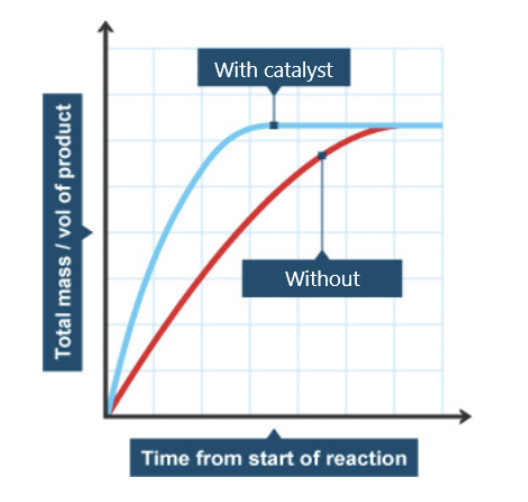
catalysts
stress bonds or increase meeting of substrates
low activation energy = high kinetic energy = high speed of reaction
does not alter the amount of product
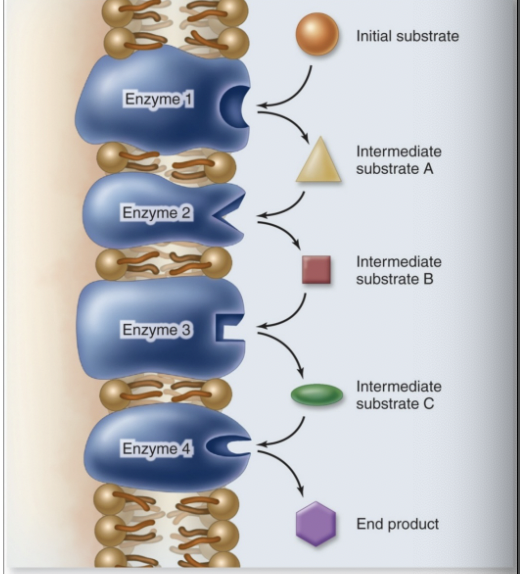
biochemical pathways
multiple reactions occur in a sequence
product of one reaction is substrate for the nect
promity = efficiency
reedback inhibition
products of pathway binds to an allosteric site on first enzyme
shuts down pathway so raw materials and energy are not wasted