Economics HSC Topic 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/337
Last updated 7:56 AM on 11/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
338 Terms
1
New cards
What are the key indicators of globalisation?
-Trade
-Financial Flows
-Investment flows
-TNCs
-Migration and the division of labour
-Technology, Transport and Communication
-Financial Flows
-Investment flows
-TNCs
-Migration and the division of labour
-Technology, Transport and Communication
2
New cards
Define Globalisation
Refers to the increasing level of integration between different economies and the increased impact of international influences on economic activity
3
New cards
What is Gross World Product (GWP)?
The sum of total output of goods and services by all economies in the world over a period of time.
4
New cards
What is the World Trade Organisation (WTO)?
An organisation of 164 members countries that implements and advances global trade agreements and resolves trade disputes between nations.
5
New cards
Who are the two main drivers of global financial flows?
Speculators and Currency Traders. According to the Bank of International Settlements Triennial Survey, only a small share of the money being shifted around is for trade and investment purposes. Most is for speculative purposes (short term profits from currency and asset price movements). Hedge funds and International investment banks run this.
6
New cards
International Monetary Fund (IMF)
An international agency that consists of 189 members and oversees the stability of the global financial system. Its major functions are to ensure stability of exchange rates, exchange rate adjustment and convertibility.
7
New cards
What is the main negative impact of global financial flows?
Speculative behaviour can create significant volatility in foreign exchange markets and domestic financial markets as speculators operate with a herd mentality.
Speculative activity is much to blame for the financial crises in East Asia 1997.
Speculative activity is much to blame for the financial crises in East Asia 1997.
8
New cards
What is Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)?
The movement of funds between economies for the purpose of establishing a new company or buying a substantial proportion of shares in an existing company (10% or more). Generally considered to be a long-term investment and the investor normally intends to play a role in the management of the business.
9
New cards
Transnational Corporations (TNCs)
Global companies that dominate global product and factor markets. They have production facilities in at least two countries and are owned by residents of at least two countries. They play a vital role in global investment flows and governments offer benefits (tax) to have them set up locally.
10
New cards
What are some examples of technology integrating economies?
1. Developments in freight technology such as standardised shipping containers and cargo tracking
2. Cheaper and more reliable international communications through broadband
3. Powerful computer and communications networks that allow money to move around the world for investment and trade
4. Mobile internet access changing structure of retail industries and education
5. Advances in high speed rail networks allows greater mobility between economies as well as increased tourism.
2. Cheaper and more reliable international communications through broadband
3. Powerful computer and communications networks that allow money to move around the world for investment and trade
4. Mobile internet access changing structure of retail industries and education
5. Advances in high speed rail networks allows greater mobility between economies as well as increased tourism.
11
New cards
What is the International Division of Labour?
How the tasks in the production process are allocated to different people in different countries around the world
12
New cards
Outline trends in movements of the international division of labour
OECD reports that proportion of migrants leaving developing countries to high income economies has increased form 36% to 51% in the past 2 decades. Also, smaller advanced economies see their skilled workers leave for bigger developed countries. Hong Kong and Ireland lose 1/3-1/2 uni graduates. The same thing happens with businesses themselves, in search of the most efficient and cost effective labour (Brain Drain).
13
New cards
Offshoring
Producers operating a global supply chain with production facilities in several countries.
14
New cards
What is the International Business Cycle?
Fluctuations in the level of economic activity in the global economy over time. Driven by global GDP.
15
New cards
What are International Factors That Strengthen The International Business Cycle?
1. Trade Flows
2. Investment Flows
3. Transnational Corporations
4. Commodity Prices
5. International Organisations
2. Investment Flows
3. Transnational Corporations
4. Commodity Prices
5. International Organisations
16
New cards
Regional Business Cycle
The fluctuations in the level of economic activity in a geographical region of the global economy over time.
17
New cards
Comparative Advantage
The economic principle that nations should specialise in the areas of production in which they have the lowest opportunity cost
18
New cards
Opportunity Cost
Represents the alternative use of resources. Often referred to as the "real" cost, it represents the cost of satisfying one want over an alternative want. This is also known as the economic cost.
19
New cards
Free Trade
A situation where there are no artificial barriers to trade imposed by government for the purpose of shielding domestic producers from foreign competitors. Based off the principle of comparative advantage.
20
New cards
Advantages of free trade
1. Greater variety of g & s
2. Lower consumer prices
3. Greater efficiency
4. Higher standards of living
2. Lower consumer prices
3. Greater efficiency
4. Higher standards of living

21
New cards
Outline the disadvantages of free trade

22
New cards
Define Mercantilism
States that countries should use heavy protectionist methods to maximise their exports and minimise their imports, thus achieve trade surplus and an inflow of wealth in the form of gold and silver. (Adam Smith argued against this form of economics, as he stated it would produce inflation). The implementation of this in modern times is Neomercantilism.
23
New cards
Define Absolute Advantage
States that achieving an increase in a nation's wealth requires the removal of protection and encouraging specialisation in those products in which the economy has an absolute advantage. An economy has an absolute advantage if it can produce a greater quantity of a product with a given level of resources than another economy is able to. Argued it would improve standard of living. HOWEVER, it suggests that countries that are unable to produce any product with an absolute advantage (e.g. to poor production techniques), have no basis for trade.
24
New cards
Can an economy consume at a point beyond its PPF
Yes, by specialising in the production of goods and services in which the economy has a comparative advantage and trading with another economy, there will be a greater amount of goods and services in the global economy.
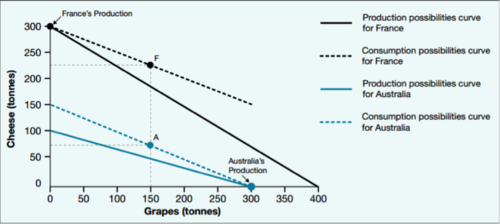
25
New cards
Define Terms of Trade
Determines the consumption possibilities curve (on the PPF), and measures the price level of an economy's exports relative to the price of its imports. Terms of trade index calculated as export price index divided by import price index. Gains from trade, (a form of economic profit).
26
New cards
What happens if the terms of trade improves?
An economy is able to purchase more imports with a given quantity of exports.
27
New cards
What happens if the terms of trade deteriorates?
The economy can purchase fewer imports with eh same level of exports (this is a form of purchasing power)
28
New cards
Define Protection
The government policies that give domestic producers an artificial advantage over foreign competitors such as tariffs on imports, import quotas and subsidies.
29
New cards
Outline the reasons for protectionist barriers
1. Assist infant industries
2. Protecting industries from overseas firms dumping goods
3. Reducing unemployment
4. Self-sufficiency in certain items, defence
5. Some argue that producers should be protected form competition with countries that produce goods with low-cost labour (developing countries). They should protect living standards of workers in high income countries.
6. Environmental factors, such as environmental harm involved in the production of certain goods makes certain industries less competitive in advanced economies with higher environmental laws.
2. Protecting industries from overseas firms dumping goods
3. Reducing unemployment
4. Self-sufficiency in certain items, defence
5. Some argue that producers should be protected form competition with countries that produce goods with low-cost labour (developing countries). They should protect living standards of workers in high income countries.
6. Environmental factors, such as environmental harm involved in the production of certain goods makes certain industries less competitive in advanced economies with higher environmental laws.
30
New cards
Why should a government only provide temporary assistance/protection to industries?
Because if protectionist policies are not removed, there will be no incentive for the industry to reach a level of efficiency that would enable it to compete without protection. We don't want them to become too reliant on government otherwise they are a waste of resources.
31
New cards
Define Dumping
The practice of exporting goods to a country at a price lower than their selling price in their country of origin. This may be to dispose of large production surpluses or to establish a market position in another country. These low prices are usually temporary. It is the only reason for protectionist policies that is widely accepted by economists.
32
New cards
What could the result of dumping be?
Local firms forced out of business, causing loss in a country's productive capacity and higher unemployment.
33
New cards
How many dumping complaints have been lodged with the WTO sine 1995?
More than 5000, India an US responsible for highest number. Australia has lodged a lot, 320.
34
New cards
In 2018 how many anti-dumping measures were in force globally and what items were they trying to protect?
By 2018, there were over 3500 anti-dumping measures (e.g. duties) in force globally. They are most common for protecting base metals, chemicals plastic rubber.
35
New cards
What plays more of a role in job loss? Technology and Automation or Trade?
Technology and Automation
36
New cards
What is the long-run impact of protecting domestic employment?
Will lead to higher levels of unemployment and lower growth rates. The net result would be that a country would maintain employment in less efficient protected industries but lose employment in more efficient export industries.
37
New cards
Why would export policies be emplaced?
e.g. Australia restricting amount of uranium exported due to fears of nuclear weapons being produced, also e.g. Live Sheep Exports being reduced due to poor conditions and public outcry
38
New cards
Define Tariff
Taxes on imported goods imposed for the purpose of protecting Australian industries.
39
New cards
Briefly outline the trends in protectionist policies
There has been a shift from traditional protectionist measures such as tariffs and subsidies towards less visible measures such as Administrative Barriers and Industry Assistance Plans.
40
New cards
Outline the economic effects of a tariff

41
New cards
What are Quotas?
Refer to restrictions on the amounts or values of various kinds of goods that may be imported. Restriction on volume of good. Guarantees domestic produces a share of the market.
42
New cards
What are Tariff Quotas?
A protectionist method where goods import up to the quota pay the standard tariff rate, whereas goods imported above the quota pay a higher rate. In the past Australia protected textiles, clothing and cars this way.
43
New cards
What are the economic effects of a quota?
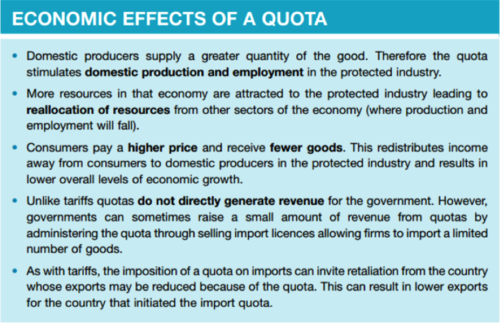
44
New cards
What are subsidies?
Cash payments from the government to businesses to encourage production of a good or service and influence the allocation of resources in an economy. Subsidies are often granted to businesses to help them compete with overseas produced goods and services.
45
New cards
What are the economic effects of a subsidy?

46
New cards
What are Local Content Rules?
Specify that goods must contain a minimum percentage of locally made parts. In return the imported components may not attract a tariff.
47
New cards
What are Export Incentive Programs?
Give domestic producers assistance such as grants, loans or technical advice (marketing or legal information) and encourage businesses to penetrate global markets or expand their foreign market share. They are still considered an artificial barrier to free trade even though not technically protectionist.
48
New cards
What is an Export Market Development Grant (EMDG)?
Provides direct funding and general assistance to local manufacturers looking to break into international markets.
49
New cards
What are the overall economic effects of protectionism?

50
New cards
What is a Trade Bloc?
When a number of countries join together in a formal preferential trading agreement to the exclusion of other countries. E.g. EU and North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA).
51
New cards
What are Free Trade Agreements (FTAs)?
Formal agreements that may be bilateral, multilateral (or regional) or global. More accurate term is Preferential Trade Agreements because in effect they give more favourable access to goods and services from some nationals compared to another.
52
New cards
List some global trade agreements
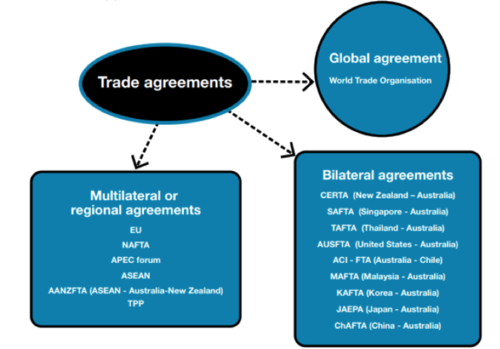
53
New cards
Name a Trump Quote against trade liberalisation
"When a country (USA) is losing many billions of dollars on trade with virtually every country it does business with, trade wars are good and easy to win"
54
New cards
What did Donald Trump do in 2018 in regards to protectionist policies?
Trump put 25% tariff on $50 billion worth of Chinese steel and aluminium imports. Threatening to extend this to half of America's $505 billion worth of imports with China. Sparked retaliation.
55
New cards
State the trend in regionalisation
The number of regional trade agreements increasing from 27 in 1990 to 459 in 2018.
56
New cards
What % of European trade occurs within the EU?
2/3
57
New cards
What were the findings of the 2018 study into Free Trade Agreement Utilisation?
78% of Australian businesses surveyed used at least one FTA arrangement to source their products from overseas. 62% of Australian exporting businesses used at least one FTA to sell their product to foreign markets.
There was 97% use of the FTA with Japan for vehicles compared to only 82% for China and 70% for the USA.
There was 97% use of the FTA with Japan for vehicles compared to only 82% for China and 70% for the USA.
58
New cards
What is the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) forum?
Established in 1990s, 21 members. Accounts for 40% of the world's population (2.9 billion), 60% of world GDP (45 trillion) and 47% of world trade in 2017. Average tariff levels in the region since 1994 have fallen from 19.6% to 13.4% in 2016.
59
New cards
What are the Bogor Goals?
Made in 1994 APEC forum, a target of free trade to be achieved by 2020. Also agreed not to become a protectionist trading bloc like EU but to reduce barriers to non-member economies as well. However, it never delivered on this ambitious goal. No longer is it used as a forum for just trade by relevant issues such as Climate Change and Terrorism.
60
New cards
State a quote by Peter Harris of the Productivity Commission on bilateral and multilateral trade agreements
"Proponents of preferential bilateral and regional trade agreements do not systematically quantify the costs and benefits of agreement provisions, fail to consider the opportunity costs of pursuing preferential arrangements compared to unilateral reform, ignore the extent to which agreements actually liberalise existing markets and are silent on the need for post-agreement evaluations of actual impacts"
61
New cards
What is the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP-11)?
A multilateral trade agreement among 11 pacific rim countries that was formally signed and ratified as of March 2018 in an effort to lower 18,000 tariffs. Represents 13% of global economic output and around 15% of global trade, even though they make up 6.8% of global population. Australia's exports to TPP-11 members in 2018 were worth $164 billion, 22% of Australia's trade. WTO estimates that TPP members could increase trade by 11% by 2030, GDP in member countries by 1.1%.
62
New cards
What is ASEAN?
Covers emerging and developing economies, and acts as a counter weight to the APEC forum which is dominated by large developed countries such as America, Japan South, Korea.
63
New cards
What is the ASEAN-Australia-New Zealand Free Trade Area (AANZFTA)?
Came into effect 2010. ASEAN committing to lowering and eliminating tariffs on 96% of Australian exports to the region. Largest preferential trade agreement with Australia, representing 20% of Australia's trade.
64
New cards
What is the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP)?
Potentially major regional agreement expected to come into effect 2019, spearheaded by China as an alternative to TPP-11.
65
New cards
What is the European Union (EU)?
17% of world market for exports, 28 members countries. Often accused as a closed trading bloc with tariff barriers against non-member countries. The high rates of protection applied to agricultural products in the EU and the oversupply of agricultural commodities that this generated has prompted the US to retaliate with similar protectionist policies.
66
New cards
What is the Eurozone?
A monetary union introduced in 1999 that brought 19 countries currencies into line under the euro, however it has failed to require common fiscal policies across the Eurozone and failed to account for different economic conditions across the region.
67
New cards
What is the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA)?
Established 1994 with USA, Canada and Mexico, focussed on phasing out agricultural protection. It has caused a tripling of trade between the economies in the last 2 decades. 13% of global merchandise trade.
68
New cards
What happened to the proposed Free Trade Area of the Americas (FTAA)?
Was meant as a counterbalance to the EU, however due to differences between advanced and developing economies it never came to fruition.
69
New cards
What is the Closer Economic Relations Trade Agreement (CERTA)?
Led to the elimination of trade restriction between Australia and New Zealand. It began in 1983, since then it has contributed to an average annual increase in trade between Australia and New Zealand of around 8%.
70
New cards
Briefly outline the trend in global bilateral trade agreements in recent years and their impact
Bilateral trade agreements have surged in recent years. However, bilateral agreements can contribute to greater "trade diversion" - not adding to overall world trade, but simply diverting it to nations that are party to an agreement.
71
New cards
Are bilateral negotiations more efficient than multilateral negotiations?
Not always, in some cases bilateral negotiations can be just as slow as multilateral ones, with Australia-China FTA taking 10 years.
72
New cards
Where were the IMF and World Bank established?
Bretton Woods conference 1944.
73
New cards
What is the Role of the WTO?
-Implement and Advance global trade agreements
-Resolve trade disputes between economies
-Resolve trade disputes between economies
74
New cards
What is the WTO?
Established 1995, extends beyond the trade of goods to the trade of services and intellectual property. If a country does not comply with the WTO's directive following a trade dispute, other countries may impose trade sanctions. It is effective for disputes between small countries, but ineffective against EU vs. USA disputes. It has 164 members and 23 negotiating to join.
75
New cards
What is the Trade Facilitation Agreement?
Formed by the WTO in 2014 with the aim of reducing the cost of trade by 10-15% by making customs procedures simpler and more efficient.
76
New cards
What was the Doha Round?
Aimed to be a comprehensive global trade agreement since 2001. Claimed to lift 140 million people out of poverty but nothing came to fruition. However discussions did produce the Nairobi Package, a voluntary agreement in 2015 to reduce export subsidies for farm exports.
77
New cards
What is the International Monetary Fund (IMF)?
189 members, its role is to maintain international financial stability particularly in relation to foreign exchange markets. When a crisis occurs in an economy, the IMF will develop a "rescue package" to help stabilise the economy (e.g. $17 billion urgent loan to Ukraine in 2014). In response to the GFC it injected $250 billion into the global economy to promote liquidity in the global financial system, during this time it also suspended interest payments on some loans.
78
New cards
What are the policies of the IMF?
The policies the IMF requires countries to adopt are generally known as "structural adjustment policies" or the "Washington Consensus" policies. Many international banks or private lenders also require these policies before lending.
79
New cards
Outline the criticisms of the IMF
The IMF is sometimes criticised such as when it demanded governments adopt contractionary macroeconomic policies during the Asian Financial Crisis of the 1990s (should have been expansionary). They also responded incorrectly to the Sovereign Debt Crisis and lent 80% of its funding from 2011-2014 to just 3 countries (Greece, Portugal and Ireland).
The IMF's statistics are often wrong as well, after a bailout package for Greece, expected unemployment to rise to 15%, but went to 25%.
The IMF's statistics are often wrong as well, after a bailout package for Greece, expected unemployment to rise to 15%, but went to 25%.
80
New cards
What is the World Bank?
Primarily for helping poorer countries with their economic development. Also funds investment in infrastructure, reduces poverty, and helps countries adjust to the demands of globalisation.
81
New cards
List some organisations that fall under the World Bank
1. International Development Association (provides soft loans)
2. International Finance Corporation (attracts private sector investment into bank's projects)
3. Multilateral Insurance Guarantee Agency (provides risk insurance to investors)
4. International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes
2. International Finance Corporation (attracts private sector investment into bank's projects)
3. Multilateral Insurance Guarantee Agency (provides risk insurance to investors)
4. International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes
82
New cards
How much did the World Bank lend in 2017?
The World Bank provided $60 billion in loans, grants, equity investments and guarantees in 2017. However as private lending markets have expanded, its importance as a lender has declined.
83
New cards
What is the value of the World Bank's portfolio?
US $200 billion
84
New cards
What are the main goals of the World Bank?
1. Reduce rate of extreme poverty to less than 3% of the world's population by 2030 (in contrast to current forecasts of 6-9%)
2. Reducing inequality by fostering income growth for the world's bottom 40%.
2. Reducing inequality by fostering income growth for the world's bottom 40%.
85
New cards
What is the UN?
193 members, broadest goal, including the; global economy, international security, the environment, poverty and development and global health issues. Established the Millennium Development Goals and now the Sustainable Development Goals (The Global Goals) (17 goals and 169 targets, world hunger, equal pay, education, clean water, clean energy etc.)
86
New cards
List some key UN agencies
-UN Development Programme
-UN Children's Fund
-UN Refugee Agency
-World Food Programme
-UN Children's Fund
-UN Refugee Agency
-World Food Programme
87
New cards
What is the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)?
36 countries, sustainable growth, raise living standards, fiscal stability. Publishes research on a range of economic issues, helps countries cooperate. Their research is regarded as the most reliable.
88
New cards
What is the Group of 7 Nations (G7)?
The most important government economic forum includes 7 largest industrialised economies, US, UK, France, Germany, Canada, Japan and Italy. Russia was suspended in 2014 for its military seizure of Ukraine. However the significance of G7 is in decline (emerging economies rising). Their share of global GDP shrunk from 68% in 1992 to 39% in 2018.
89
New cards
What is the Outreach 5 (O5)?
5 developing countries including brazil, China, India, Mexico and South Africa.
90
New cards
What is the Group of Nations 20 (G20)?
19 of the world's largest economies plus the EU, covering 80% of world GDP, 2/3 world population. Has an annual summit.
91
New cards
What has happened to the population of people living in extreme poverty?
It has declined significantly, with less than 11% of the global population living below US$1.90 per day in 2013 compared to 42% in 1981.
92
New cards
What has happened to the under-5 mortality rate in recent decades?
It has been reduced by more than 1/2 between 1990 and 2016.
93
New cards
What has happened to the global primary school net enrolment rate in past decades?
Increased from 81% to 89% between 1996 and 2016.
94
New cards
How many people live in extreme poverty and where are they from?
Estimated 767 million live in extreme poverty as of 2013. Half of this population lives in sub-saharan Africa.
95
New cards
How many people live without access to sanitation or electricity?
2.3 billion live without access to basic sanitation and 1 billion live without access to electricity
96
New cards
How many children under 5 died in 2016?
An estimated 5.6 million
97
New cards
What is Gross National Income (GNI)?
The sum of value added by all resident producers in an economy plys receipts of primary income from foreign sources
98
New cards
What are the largest economies in the world by GNI?
USA has the largest economy in the world by GNI, 1.5 times that of second which is China and almost 4 times the size of Japan which is 3rd.
99
New cards
What is Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)?
A theory that states that exchange rates should adjust to equalise the price of identical goods and services in different economies throughout the world when using GNI to compared them. It provides a standard comparison of real income levels between countries.
100
New cards
How much of the world's income do advanced economies receive?
Advanced economies receive around 2/3 of the world's income using raw GNI figures, and ½ when using PPP-adjusted GNI.