A-Level Chemistry - Isomerism
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Isomer
A molecule that has the same molecular formula but where they are arranged differently
Types of Isomerism
Structural Isomerism and Stereoisomerism
Sub-Divisions of Structural Isomerism
Positional isomerism, functional group isomerism and chain isomerism
Sub-Divisions of Stereoisomerism
E-Z isomerism and optical isomerism (covered in 25.2)
Structural Isomerism
Isomers that have the same molecule formula but different structural formulae
Stereoisomerism
Where two or more compounds have the same structural formula. They differ in the arrangements of the bonds in space
Positional Isomerism (Structural)
The functional group is attached to the main chain at different points
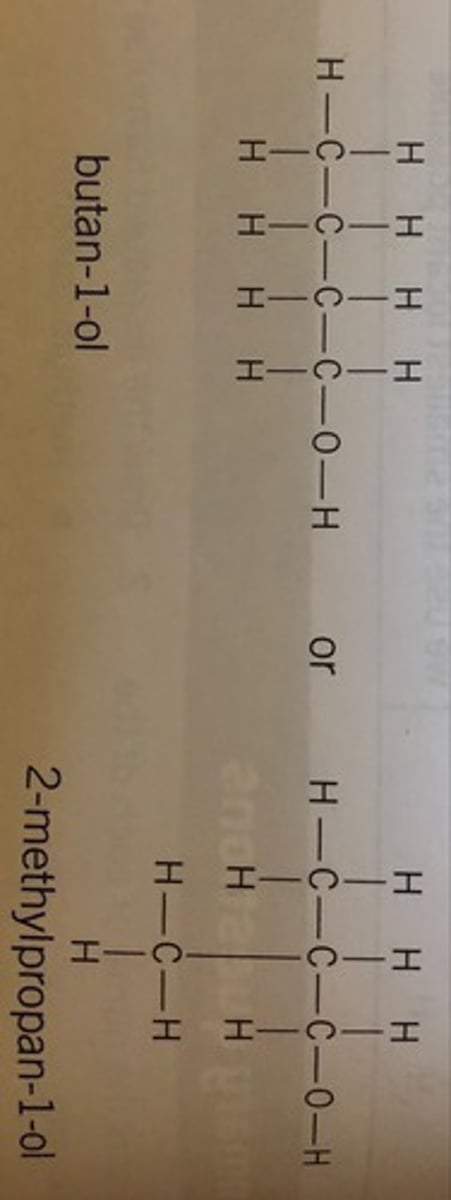
Functional Group Isomerism (Structural)
There are different functional groups
Functional Group Isomerism (Diagram)

Chain Isomerism (Structural)
The hydrocarbon is arranged in a different way
Chain Isomerism (Diagram)
E-Z Isomerism (Stereo)
Tells us about the position of the substituents at either side of the carbon-carbon double bond. They may be on the same side of the bond (Z) or on opposite sides (E)
E-Z Isomerism (Diagram)
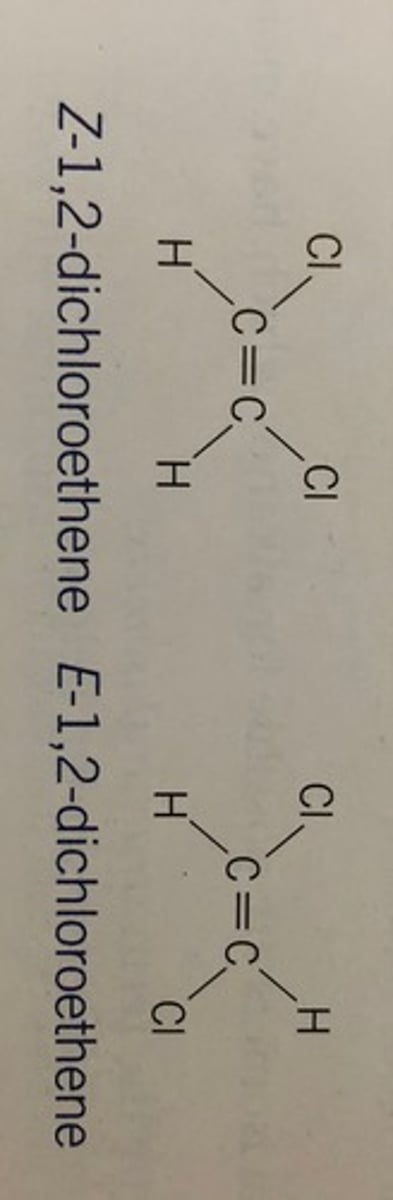
Cis-Trans Isomerism
E-Z isomerism for less complex molecules. Z corresponds with cis and E with trans