Urinalysis
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Physical Exam of Urine Includes
Volume, color, odor, transparency, specific gravity
Pollakuria
Frequent urination
Polyuria
increased production of urine
Factors involved in urine volume
fluid intake, external losses, temp, humidity, amount/type of food, activity level, size of animal, species
Polyuria often accompanied by ____________
polydipsia
Oliguria
decreased urine output
Anuria
absence of urine production
Normal color of urine
light yellow to amber
Dark yellow urine
more concentrated- higher USG
Lighter colored urine
Less concentrated- lower USG
Yellow-brown or green urine
Contain bile pigments
Red or Brownish Urine
presence of RBCs or hemoglobin
Hematuria
presence of blood in the urine
Hemoglobinuria
hemoglobin in the urine
Normal clarity/transparency of urine in most species
Clear or transparent
Normal equine urine clarity
cloudy
Normal rabbit urine clarity
milky
Classifications of clarity/transparency of urine
clear, slightly cloudy, cloudy, or turbid
A sweet or fruity odor to urine may indicate what?
Presence of ketones
Normal urine specific gravity of dogs
1
Normal urine specific gravity of cats
1
Isosthenuria
When USG approaches that of glomerular filtrate; occurs with chronic renal disease; the closer to the isosthenuria, the more kidney function is lsot
SG of glomerular filtration
1.008-1.012
Storage of chemical reagent strips
Stored at room temp, lid tightly closed
Urine pH
measures the degree of acidity or alkalinity of urine
What can cause decreased urine pH?
Fever, starvation, excessive muscular activity, or certain drugs
What can cause increased urine pH
UTI with urease bacteria, certain drugs, urine retention
Normal urine protein concentration
usually absent or in trace amounts; trace amounts can be found due to collection techniques
Sulfosalicylic Acid Turbidity Test
determine urine protein levels by acid precipitation
Protein/Creatinin ratio
Confirms signifcant amounts of protein and compares to levels of creatinine; aids in accurate measurement of protein loss with low SG
Glucosuria/glycosuria
glucose in the urine
Ketonuria
presence of ketones in the urine
What species is bilirubinuria normal in?
Dogs
In what species is any amount of bilirubin in the urine considered abnormal?
Cats
Ictotest
detects bilirubinuria
Urobilinogen
breakdown product of bilirubin formed by the action of intestinal bacteria; considered normal in urine sample
Myoglobinuria
presence of myoglobin in urine
What is a red color to the supernatant after centrifugation indicative of?
Hemoglobinuria
What causes myoglobinuria?
Severe muscle damage
What centrifuge settings should urine be centrifuged at?
3-5 minutes at 1000-2000 rpm
How should you start evaluating urine sediment on the microscope?
Start under low power to evaluate larger elements, then move to 40x to detect bacteria and differentiate cell types
How are epithelial cells, RBCs, and WBCs reported in urinalysis?
Reported per high power field
How are bacteria reported in urinalysis?
Reported as few, moderate, or many and morphology
Sediment dry mount
Prepared when abnormal cells present; prep similar to blood smear, air dried, stained with diff quick, viewed at 100x
Normal constinuents of urine sedmient
Few casts, crystals, epithelial cells, RBCs and WBCs, mucus threads and sperm, fat droplets
Abnormal constituents of urine sediment
More than a few RBCs and WBCs, hyperplastic or neoplastic epithelial cells, casts, crystals, parasite ova, bacteria, and yeast
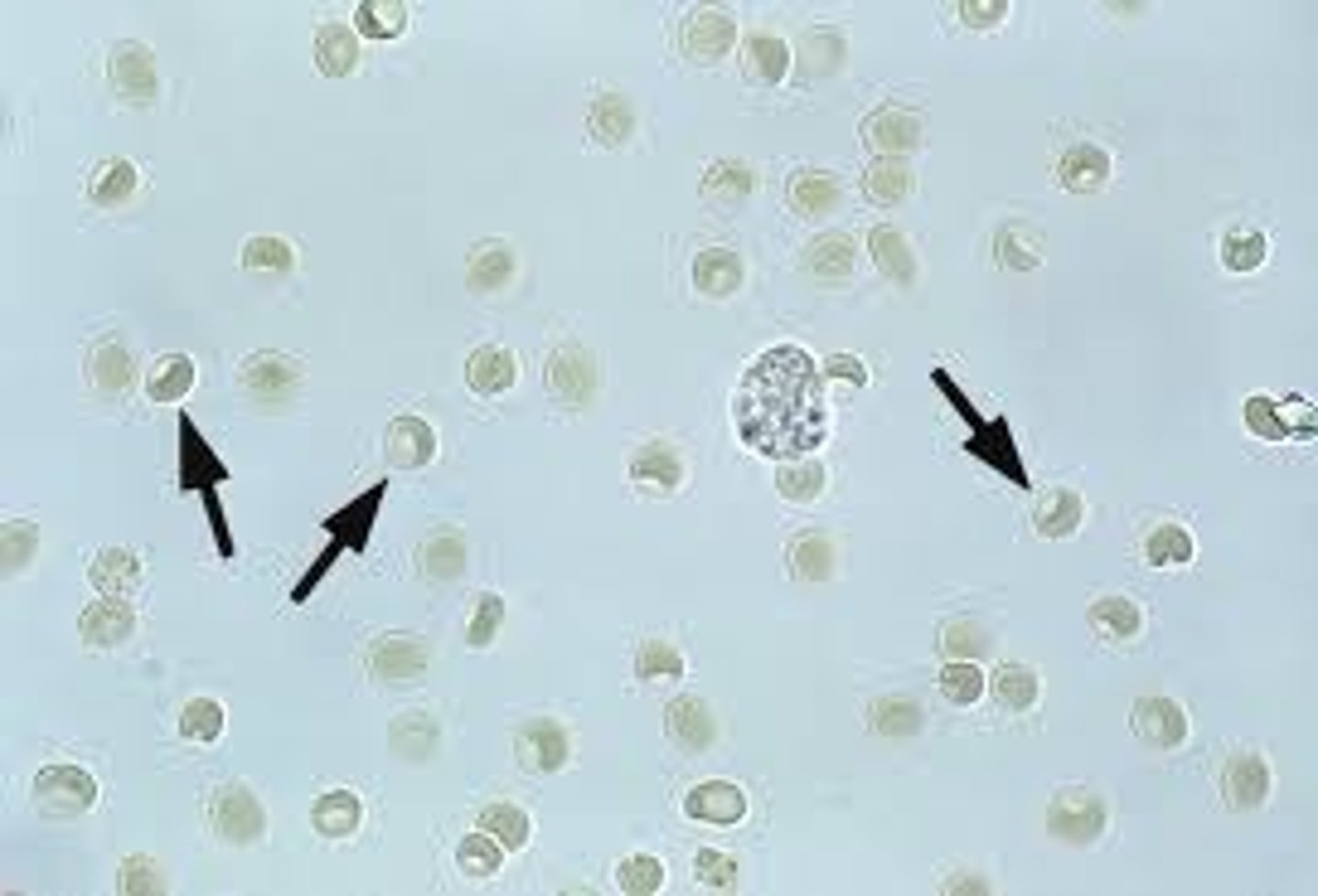
Erythrocytes in fresh urine
small, round, smooth edges
Erythrocytes in older concentrated urine
shrunken and crenate
Erythrocytes in dilute urine
Swollen and lyses
Normal amount of erythrocytes in urine
2-3 RBCs/hpf
Urine erythrocytes
Leukocytes in urine
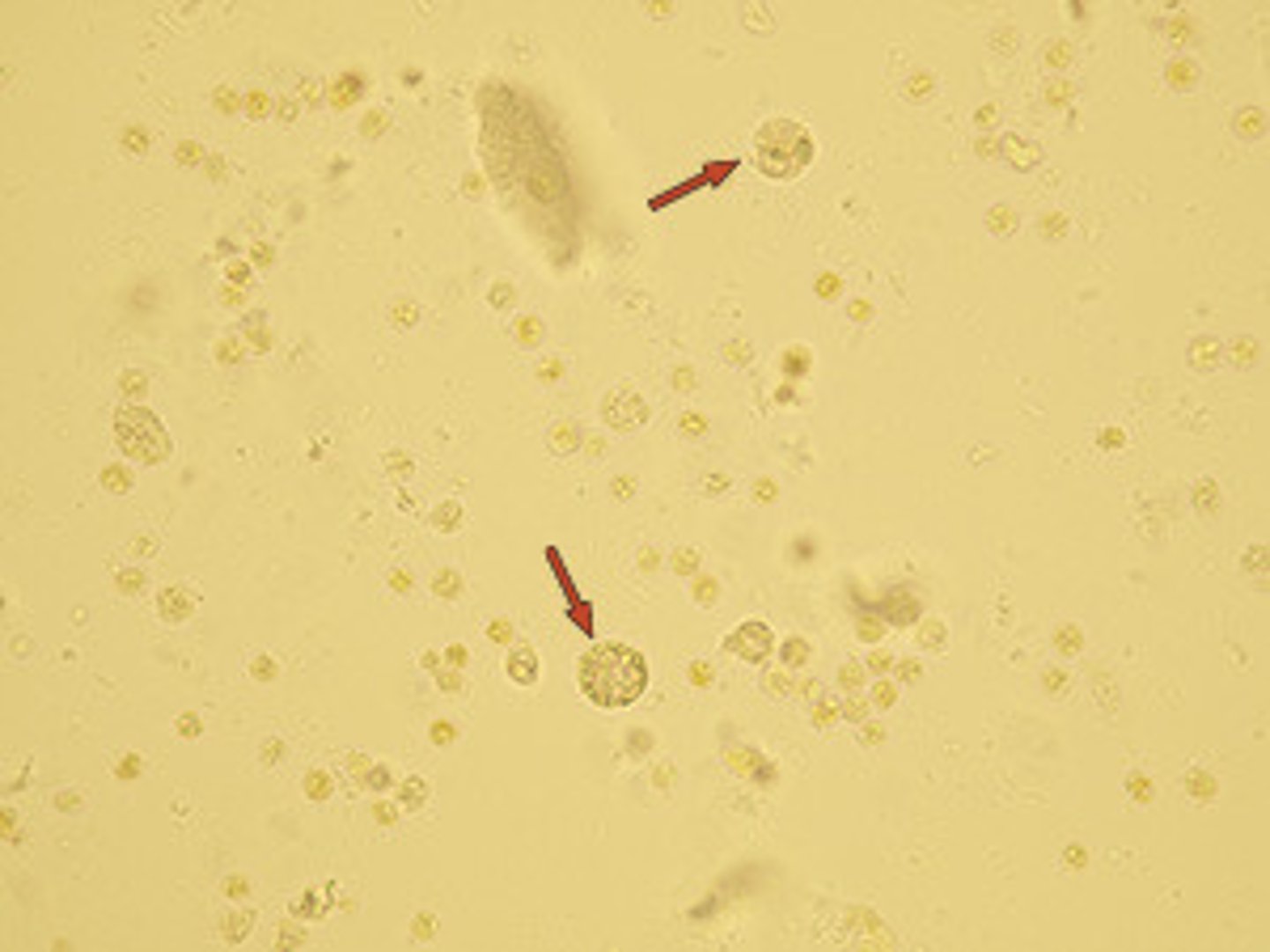
spherical, dull gray or greenish yellow; identified by granules or lobes of nucleus
Pyuria
excessive WBCs in the urine
Urine leukocytes
Increased epithelial cells in urine indicate what?
Inflammation
True or false: A few epithelial cells in urine is considered normal
True
Squamous epithelial cells in urine
Derived from the distal urethra, vagina, vulva, or prepuce; not significant; flat, thin cells with homogenous appearance
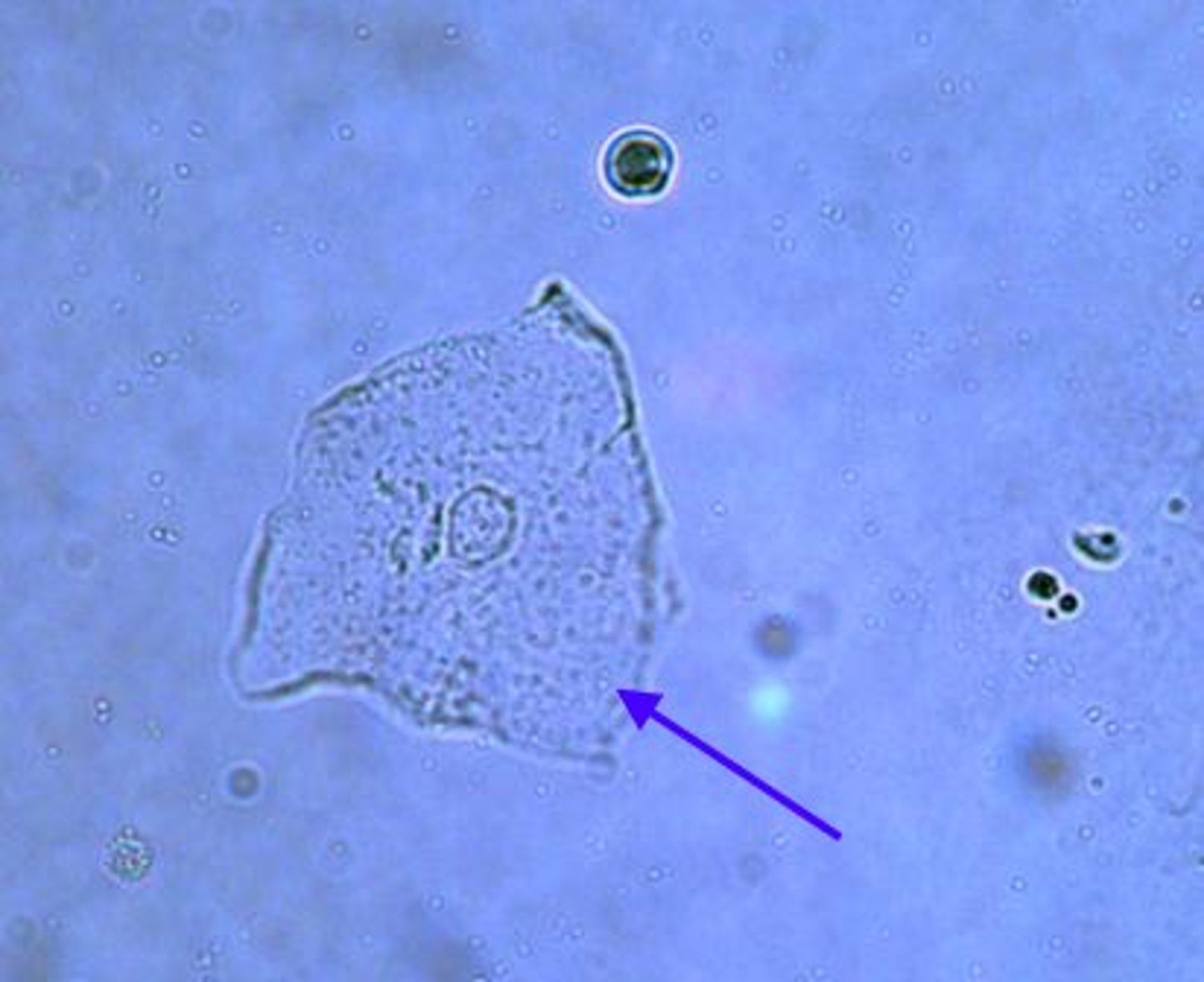
Squamous epithelial cell
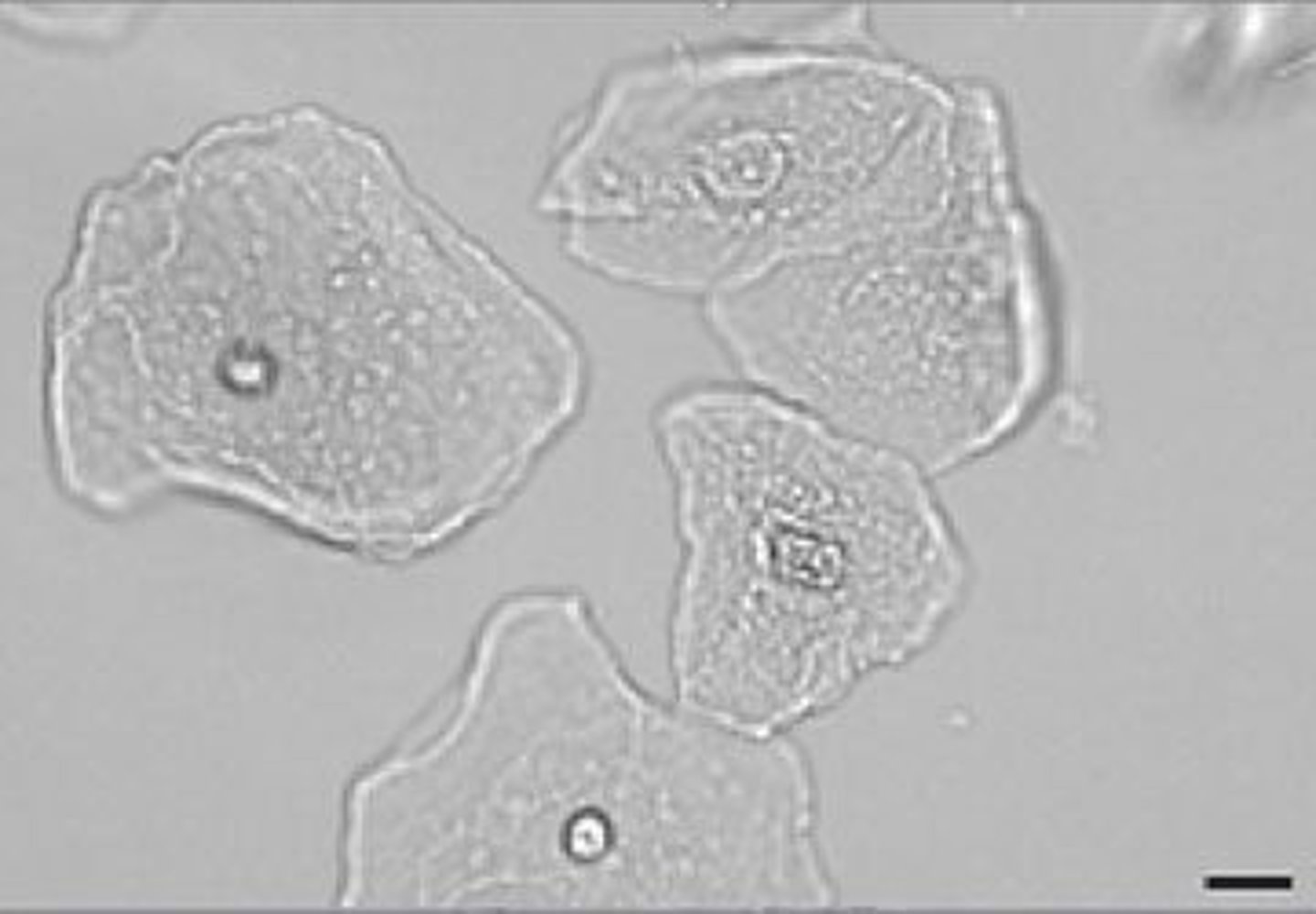
Transitional epithelial cells in urine
From bladder, ureters, renal pelvis, and proximal urethra; round but occasionalyl pear shaped; small, granular nucleus; low numbers normal;
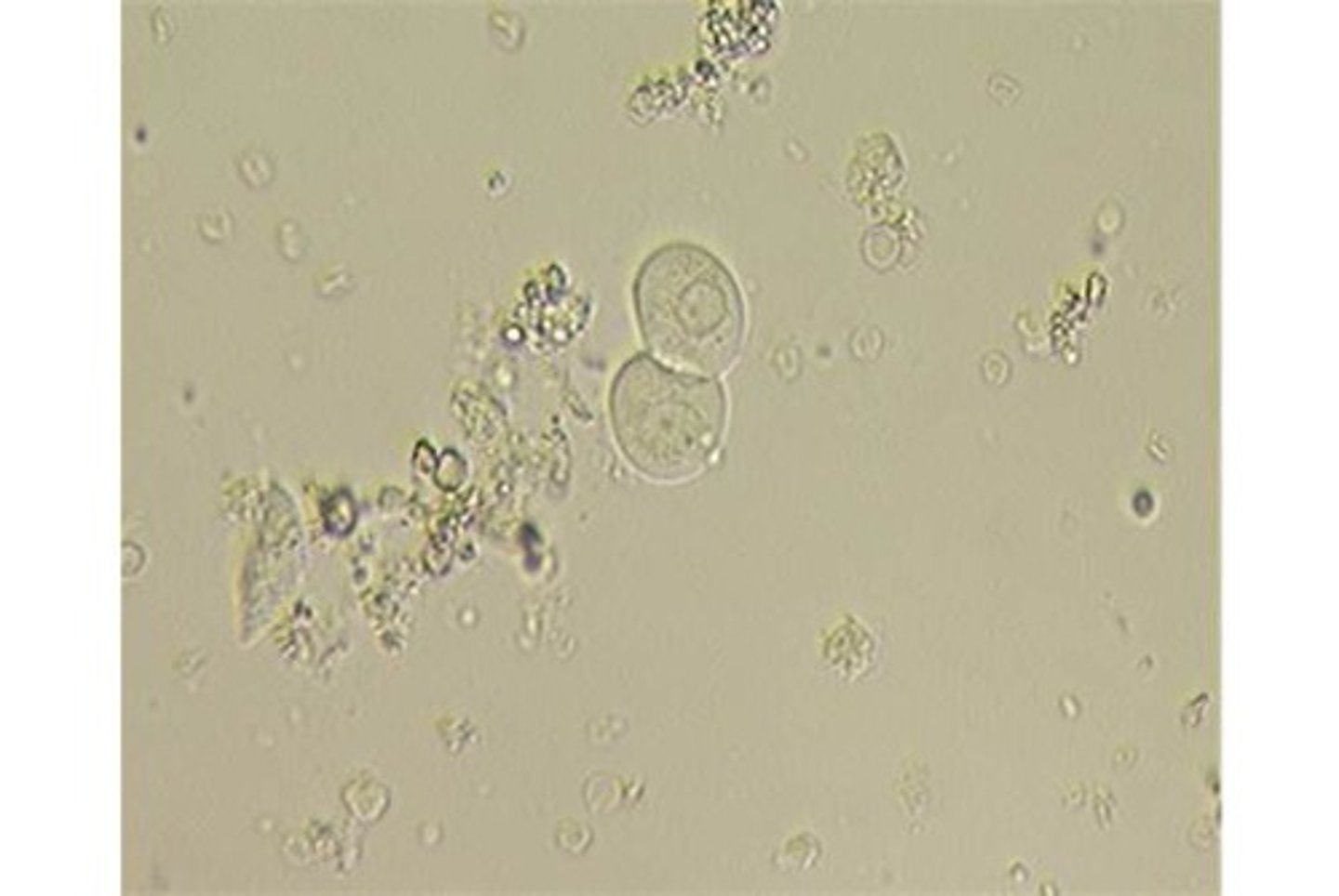
What do high numbers of transitional epithelial cells in urine indicate?
Cystitis or pyelonephritis; also seen with catheterization
Transitional Epithelial cells
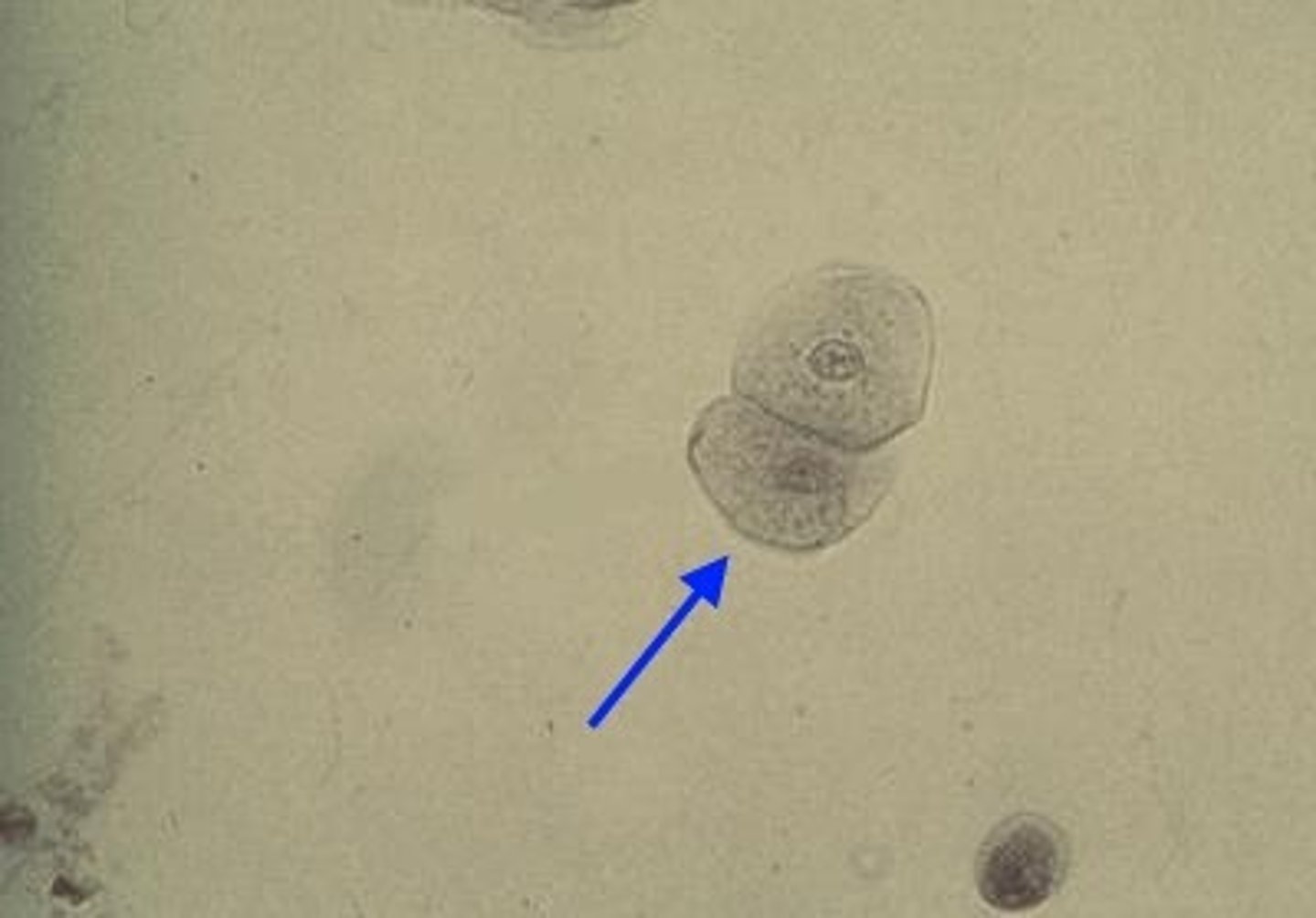
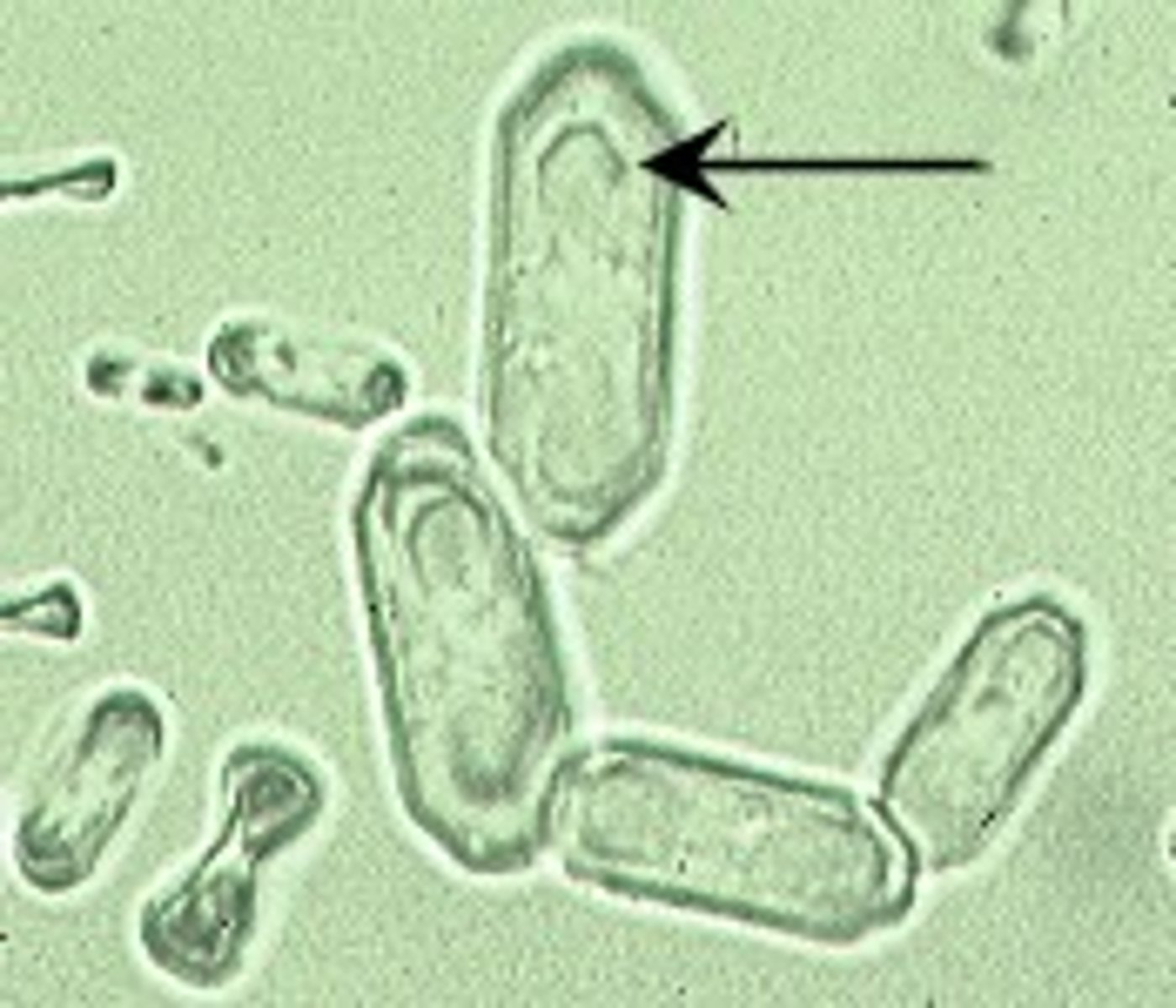
Renal epithelial cells in urine
Smallest epithelial cell; originate in renal tubules; often confused with RBCs; generally round and contain a large nucleus with nongranular cytoplasm; rarely found
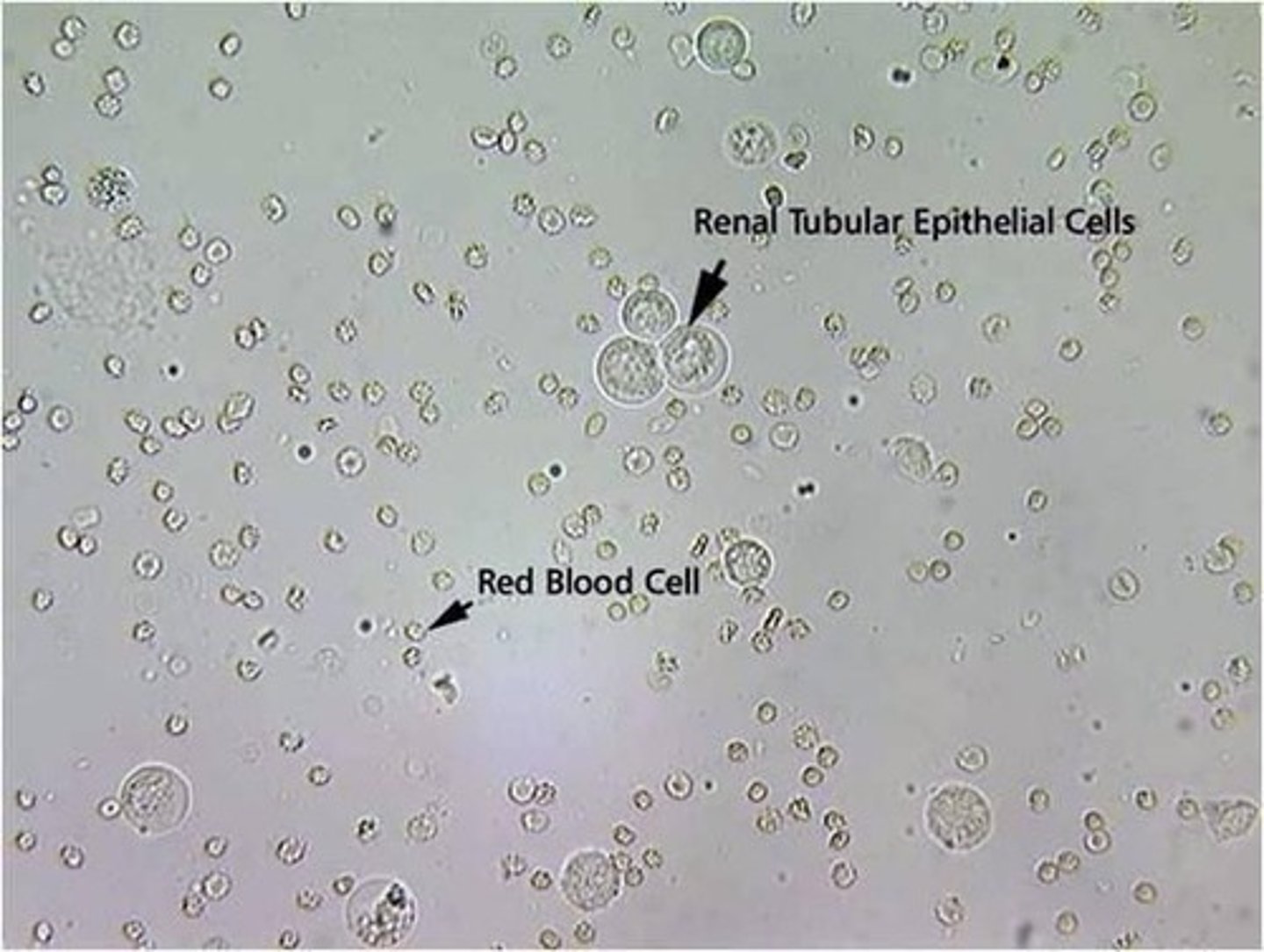
What do increased numbers of renal epithelial cells indicate?
Kidney parenchyma
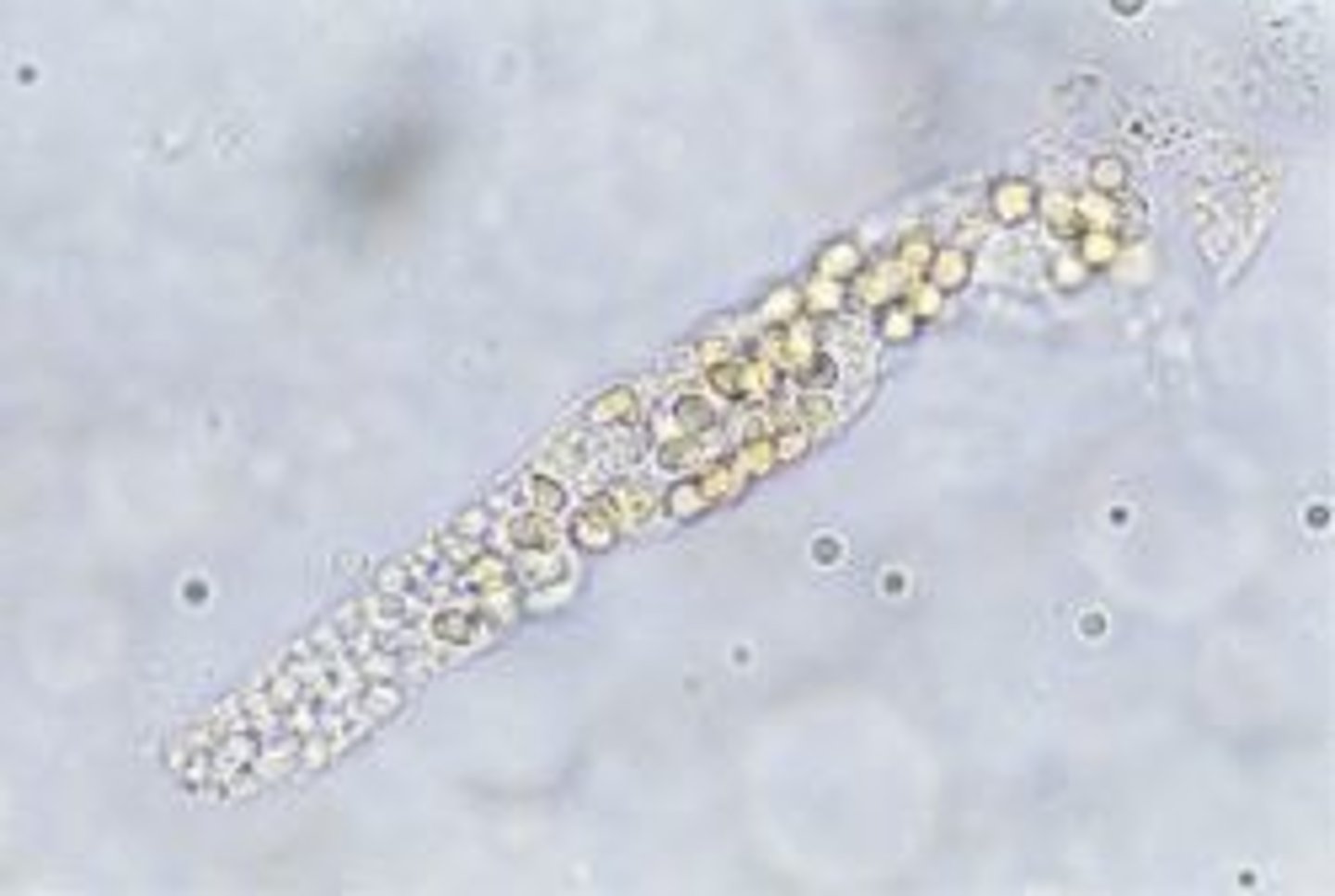
Casts
Formed in the lumen of the distal and collecting tubules of the kidney; classified based on appearance
Hyaline casts
clear and colorless; composed mostly of protein; cylindrical with parallel sides and rounded ends
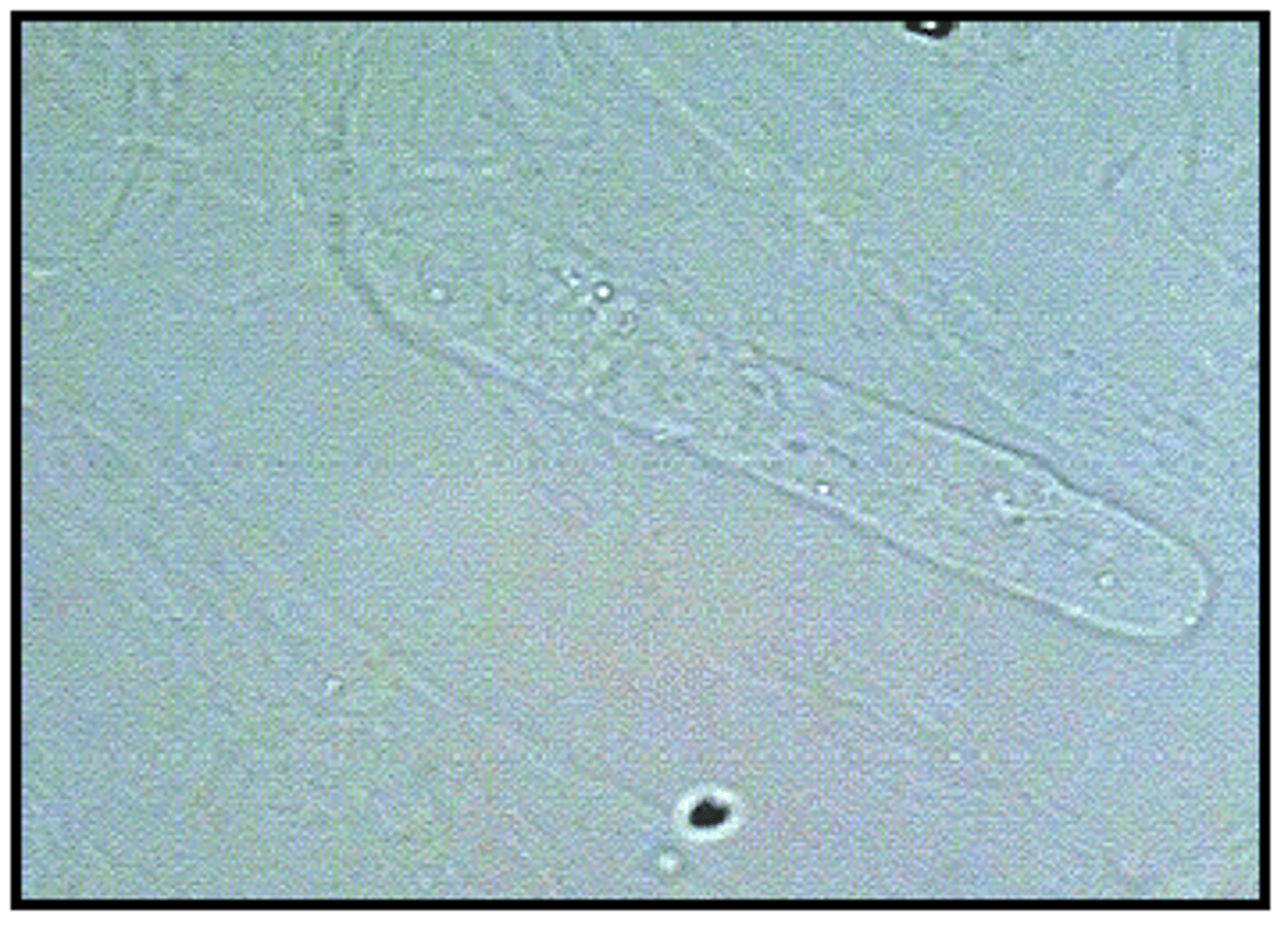
Granular casts
Hyaline casts with granules; most common type seen
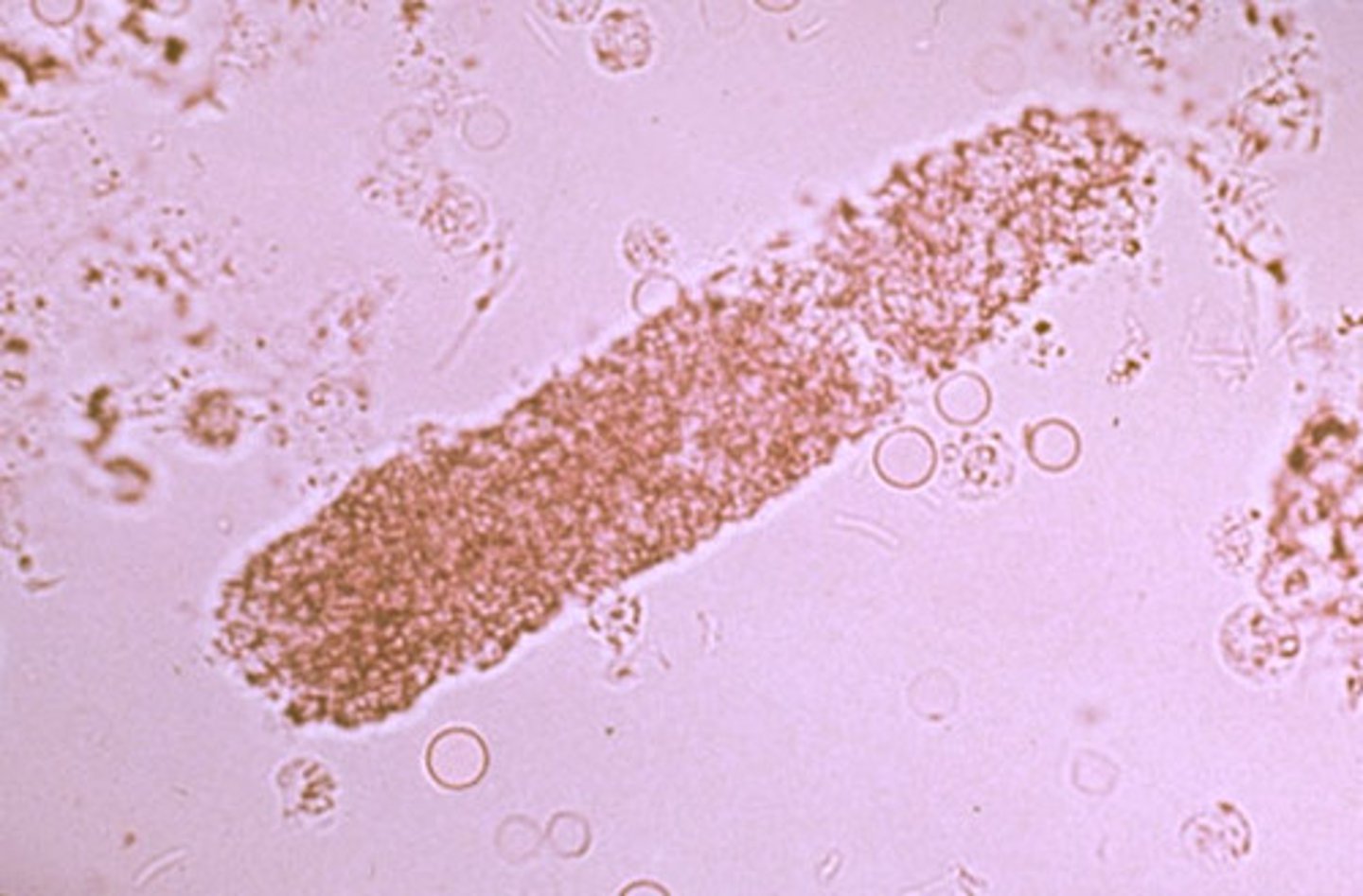
Epithelial casts
consist of epithelial cells from renal tubules embedded in the hyaline matrix
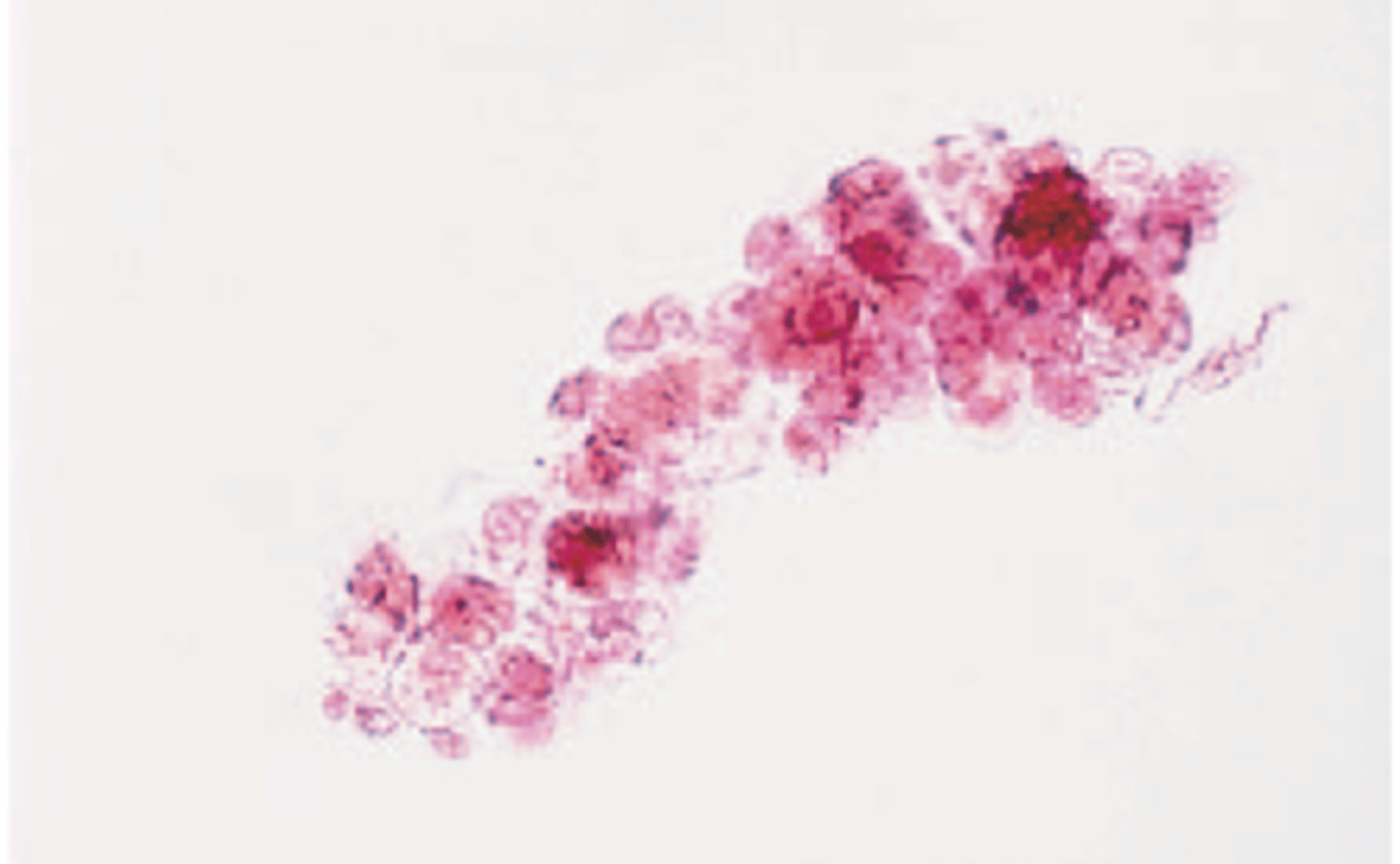
Leukocyte casts
Contain WBCs, mostly neutrophils
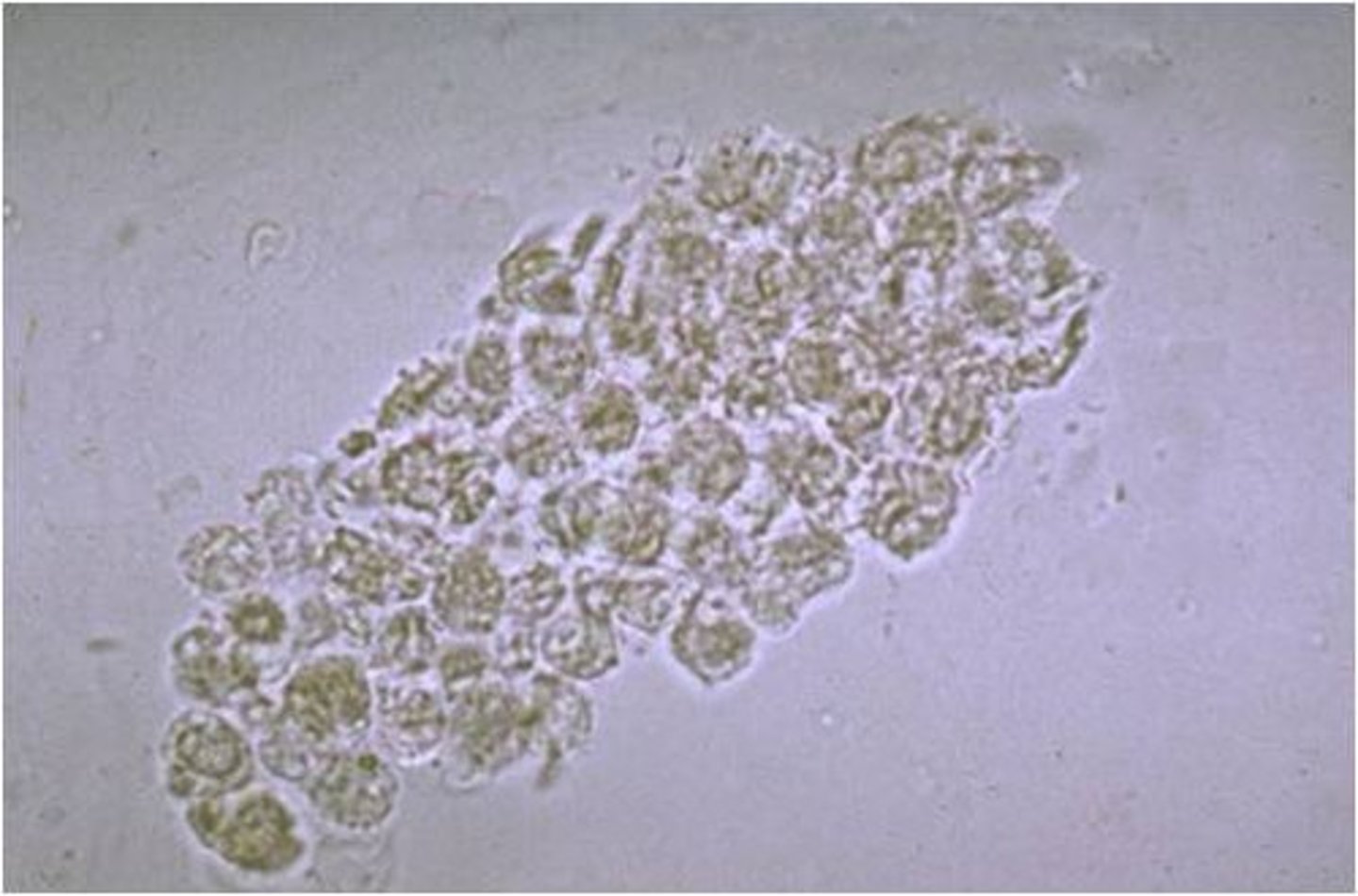
Erythrocyte cast
Deep yellow to orange; contain RBCs
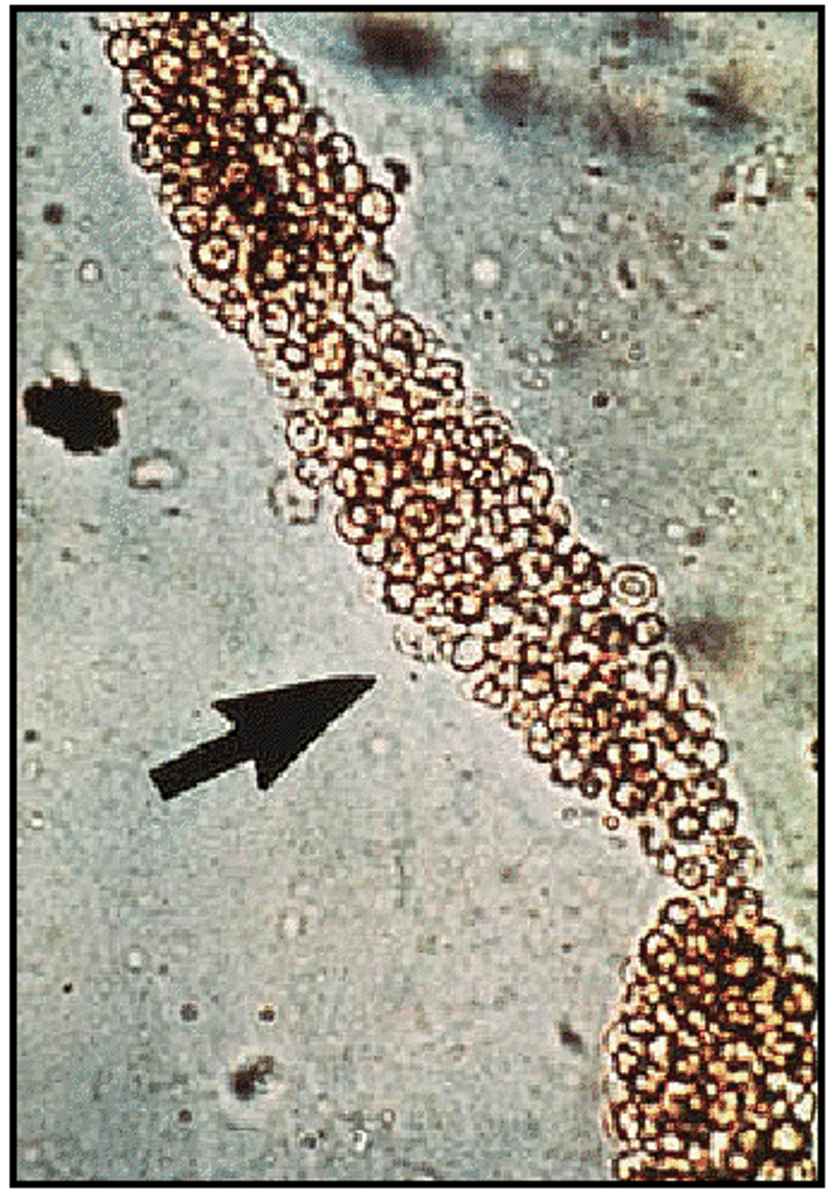
Waxy casts
Wider with square ends, dull, homogenous, waxy appearance
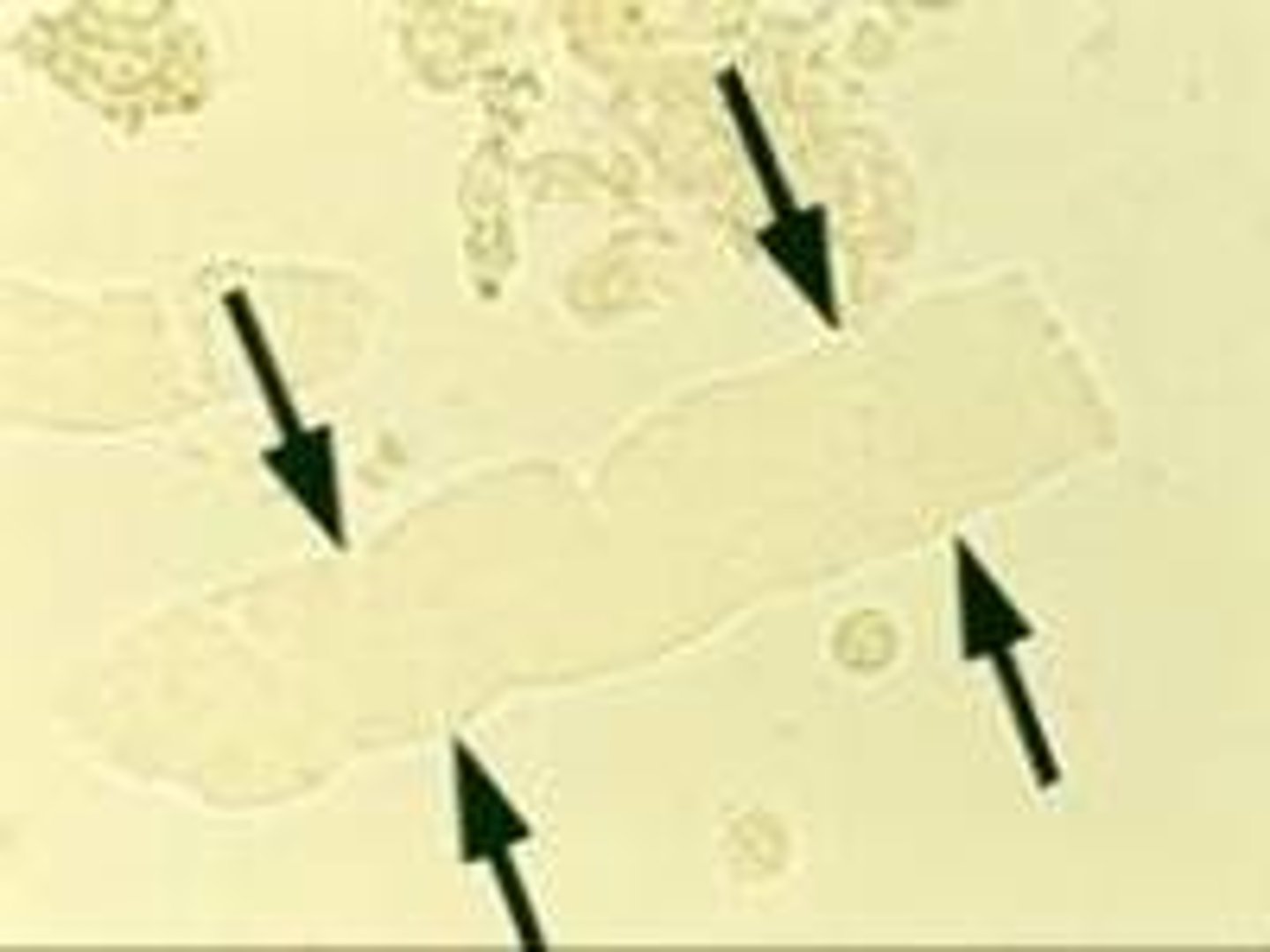
Fatty casts
contain small droplets of fat
Cystalluria
presence of crystals
How are crystals reported?
Type and quantity; occasional, moderate, many or 1+-4+
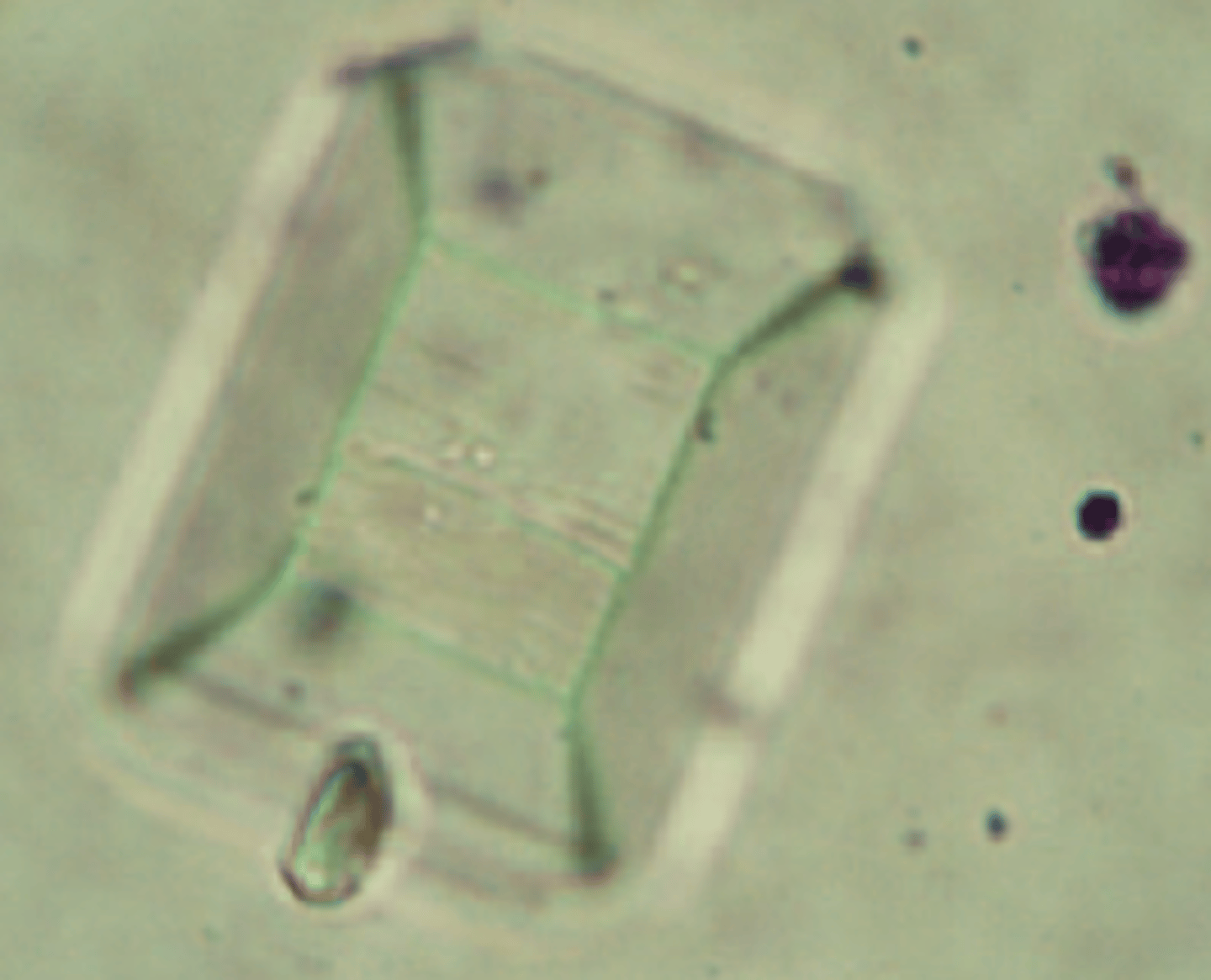
What are struvite crystals also known as?
triple phosphate crystals or magnesium ammonium phosphate crystals
What type of urine are struvite crystals found in?
Alkaline to slightly acidic urine
Struvite crystal
Eight-sided prism with tapered ends; referred to as coffin lids but can take other shapes

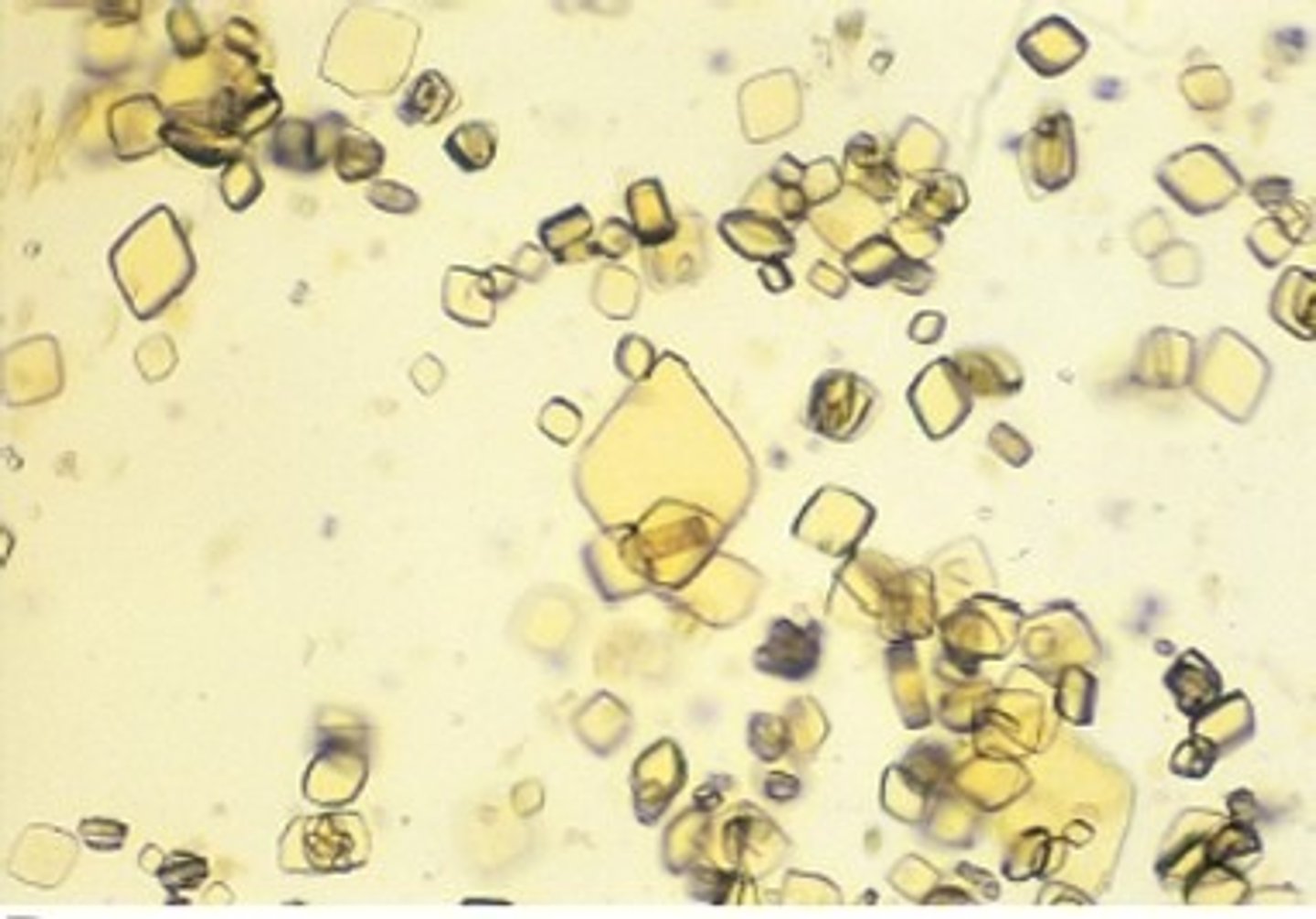
Calcium Oxalate Dihydrate Crystals
Small squares with an X across the crystal resembling the back of an envelope; commonly seen in small dogs and horses
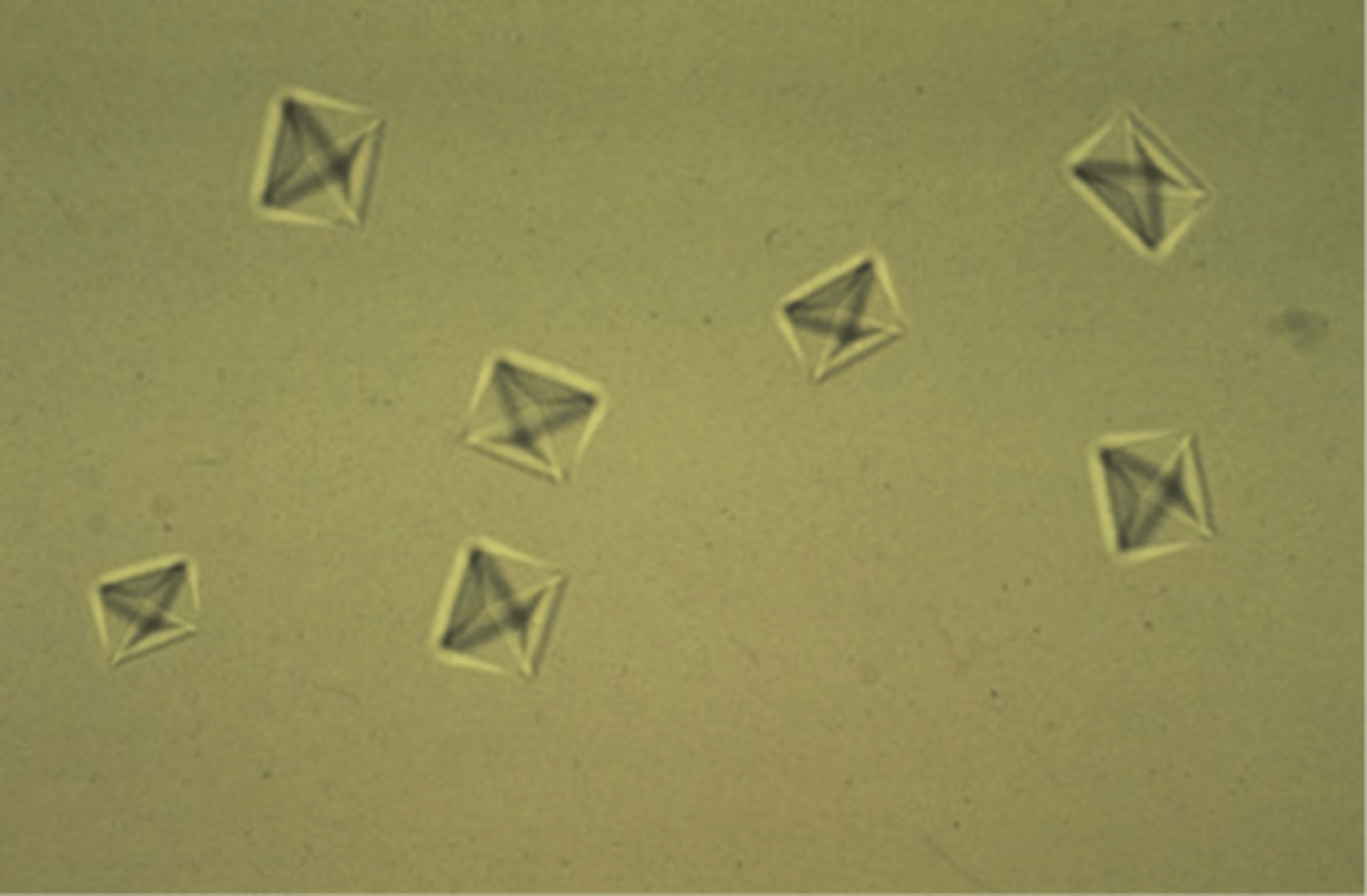
What type of urine are Calcium Oxalate Dihydrate crystals found in?
Acidic to neutral urine
Calcium Oxalate Monohydrate Crystals
small dumbbell-shaped or elongated and pointed at each end (picket fence); ethylene glycol poisoning
Urice acid crystals
variety of shapes, yellow or brown; not common except in dalmations
Amorphous Crystalline Material
granular preciptate appearance
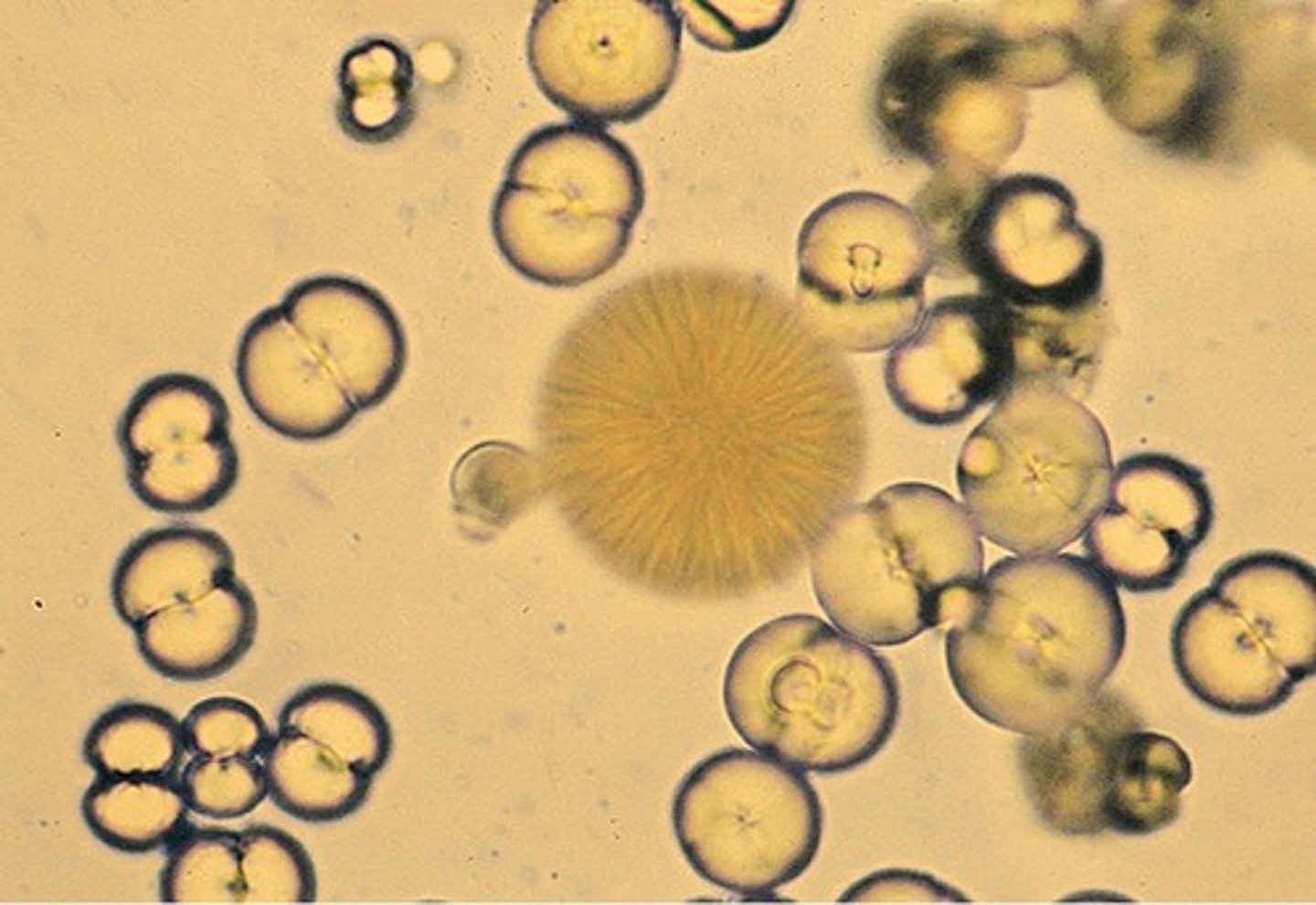
Amorphous urates
found in acidic urine
Amorphous phosphates
found in alkaline urine
Calcium Carbonate Crystals
Common in horses and rabbits; round with lines radiating from center or large granular masses or dumbbell shaped
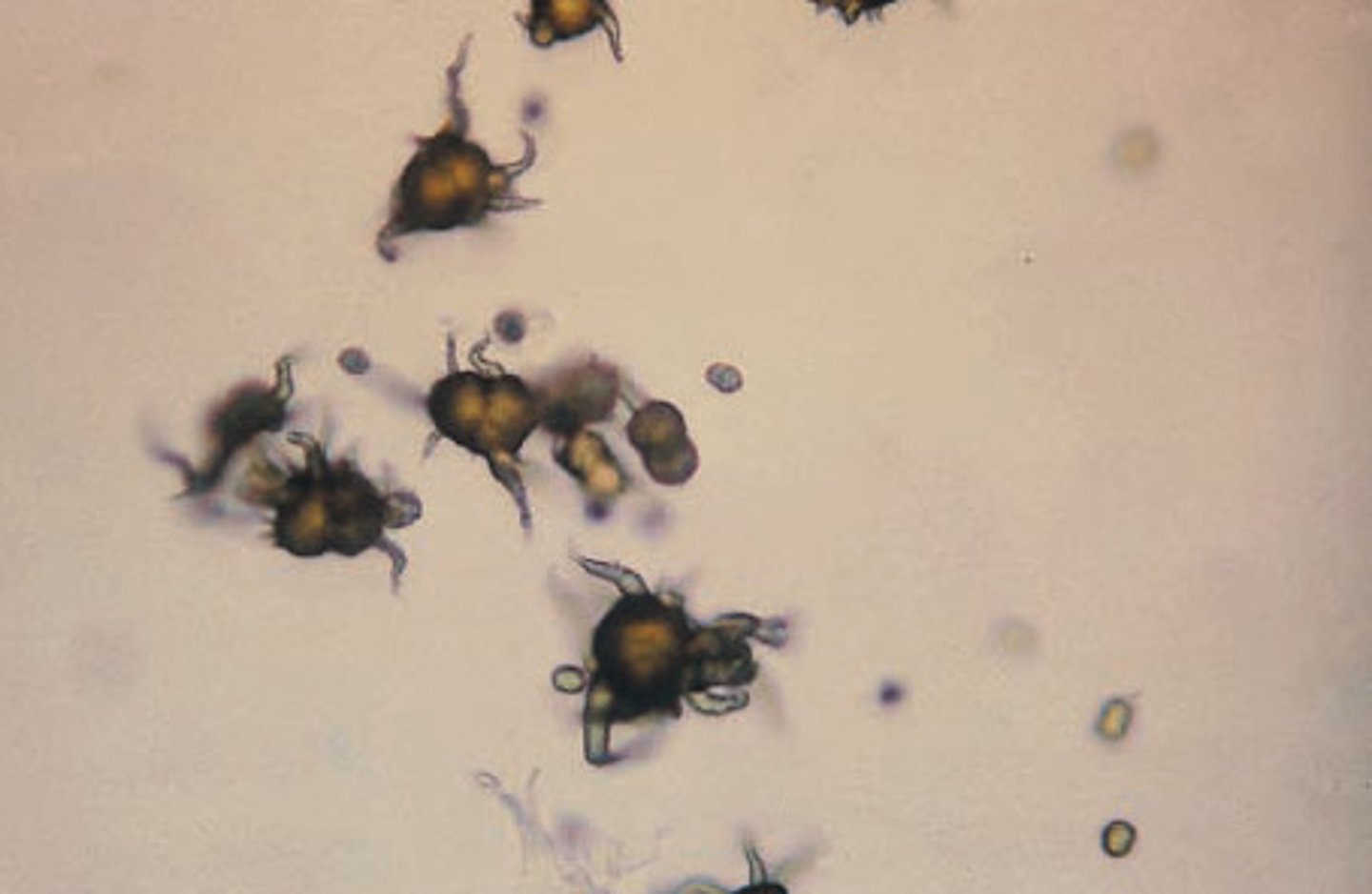
Ammonium Biurate Crystals
brown in color with long, irregular spicules
Sulfonamide Crystals
round, dark with a radiating center
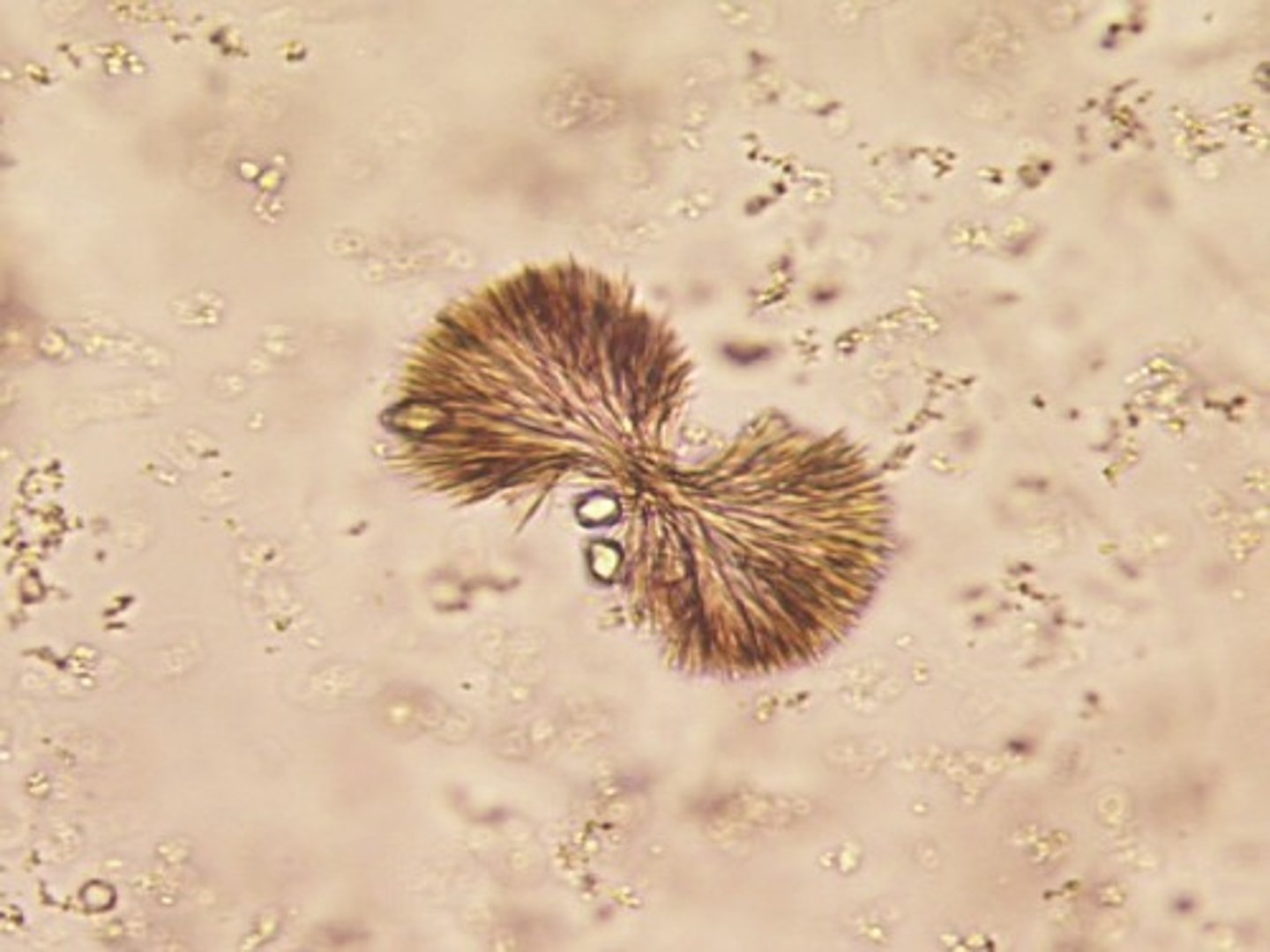
Leucine crystals
Wheel or pincushion, yellow to brown in color
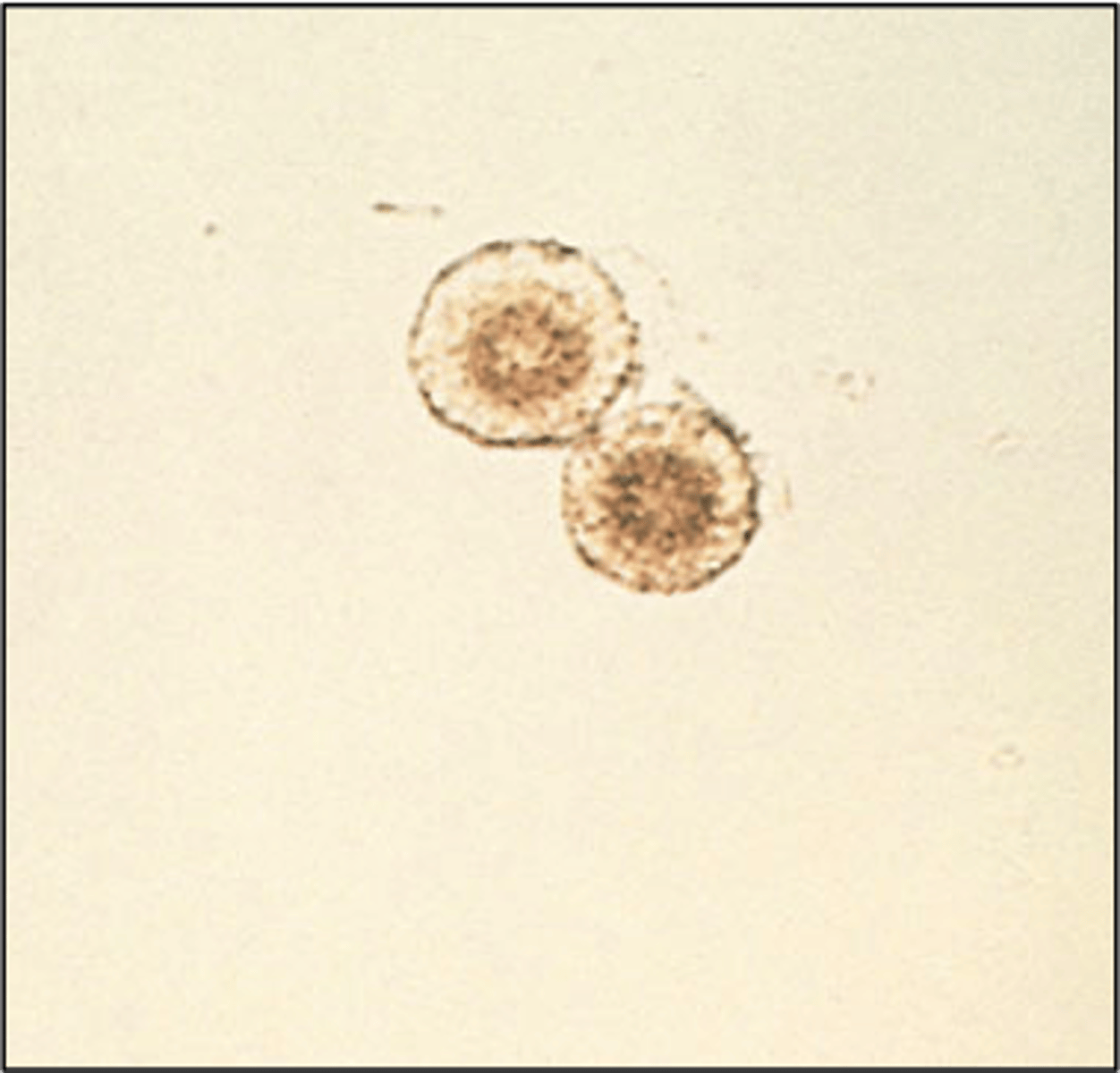
Tyrosine crystals
dark, needlelike projections
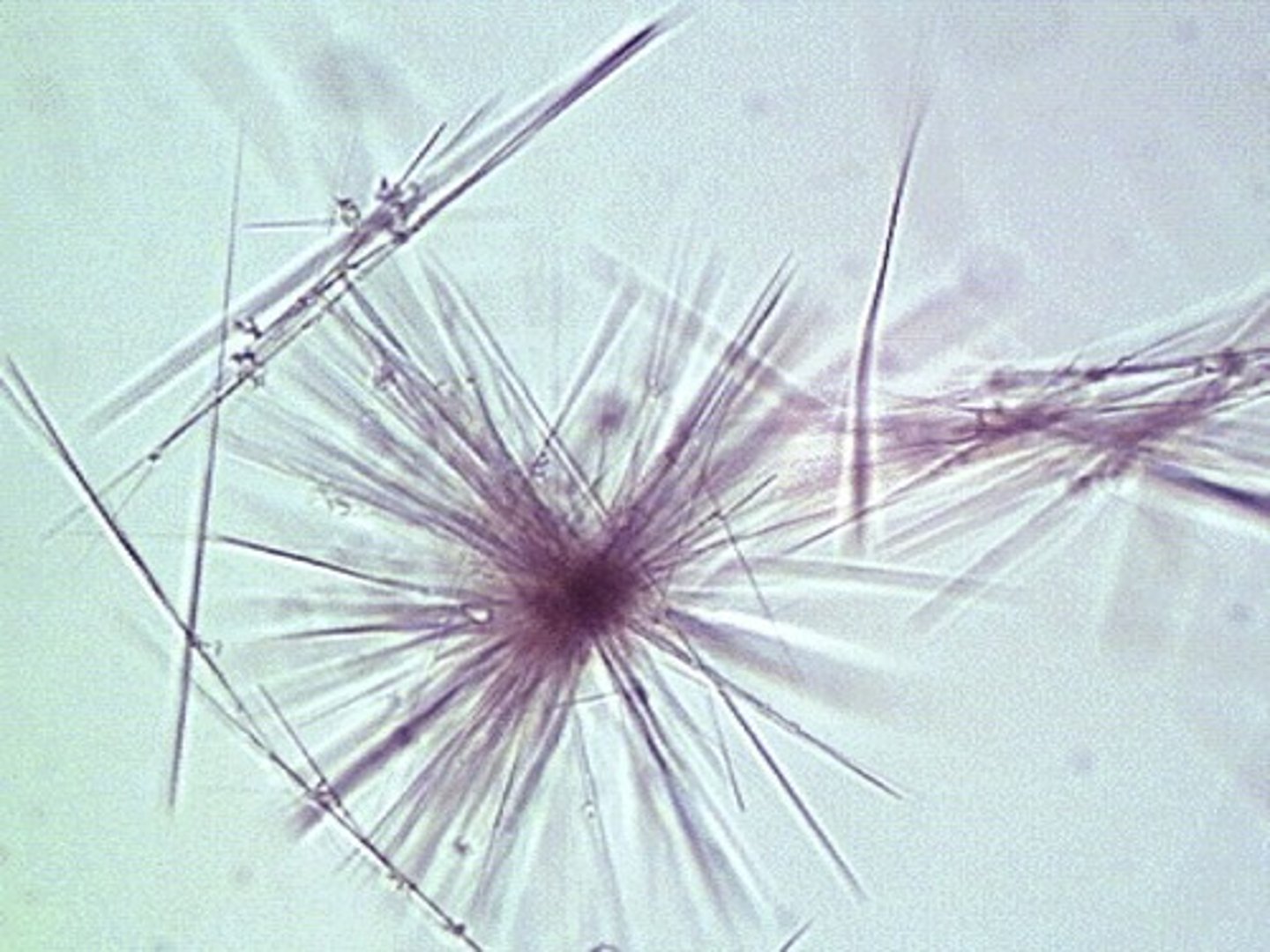
Cystine crystals
flat, six-sided, colorless and thin
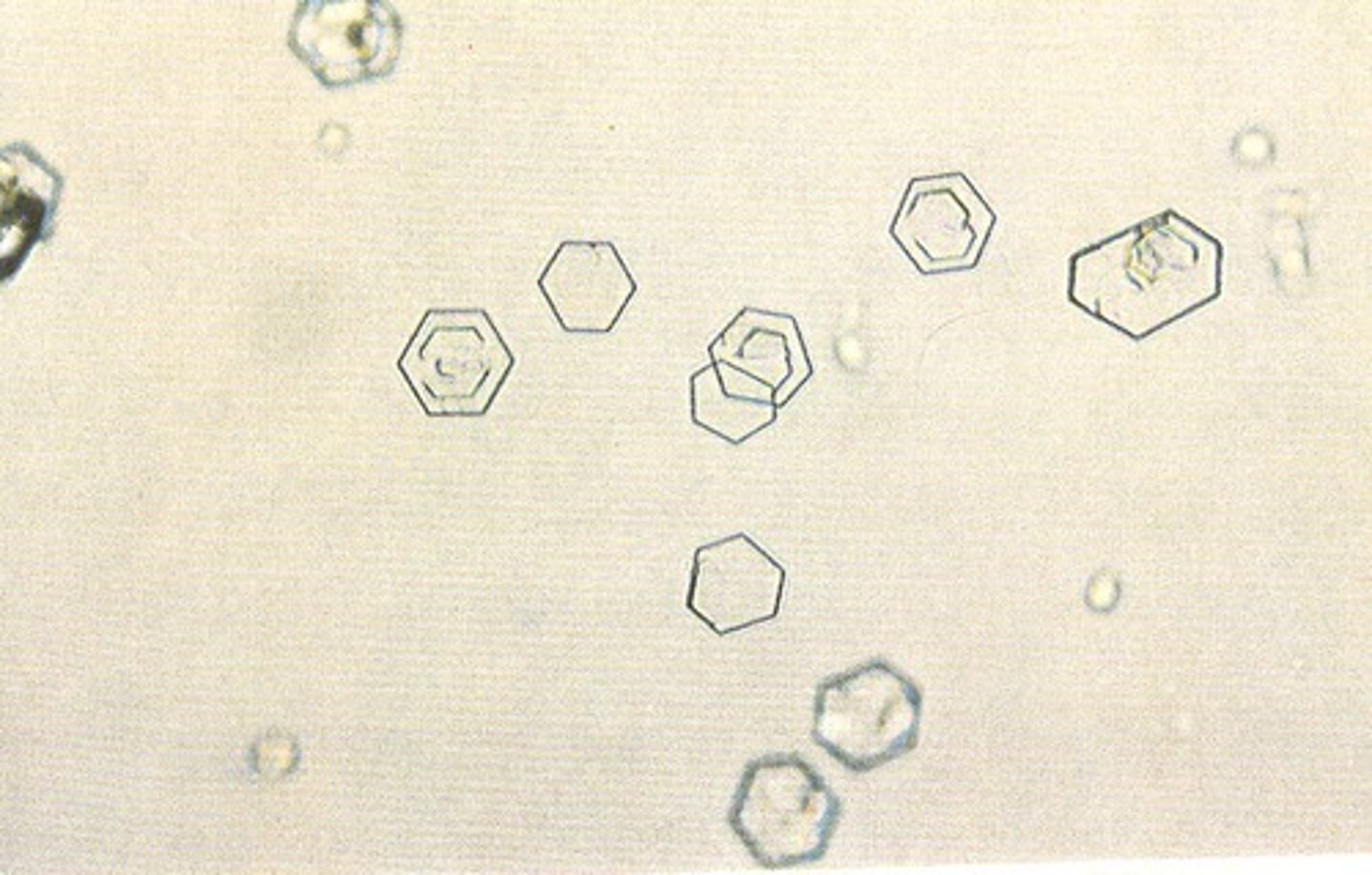
Pearsonema plica
bladder worm

Dictophyma renale
kidney worm of dogs
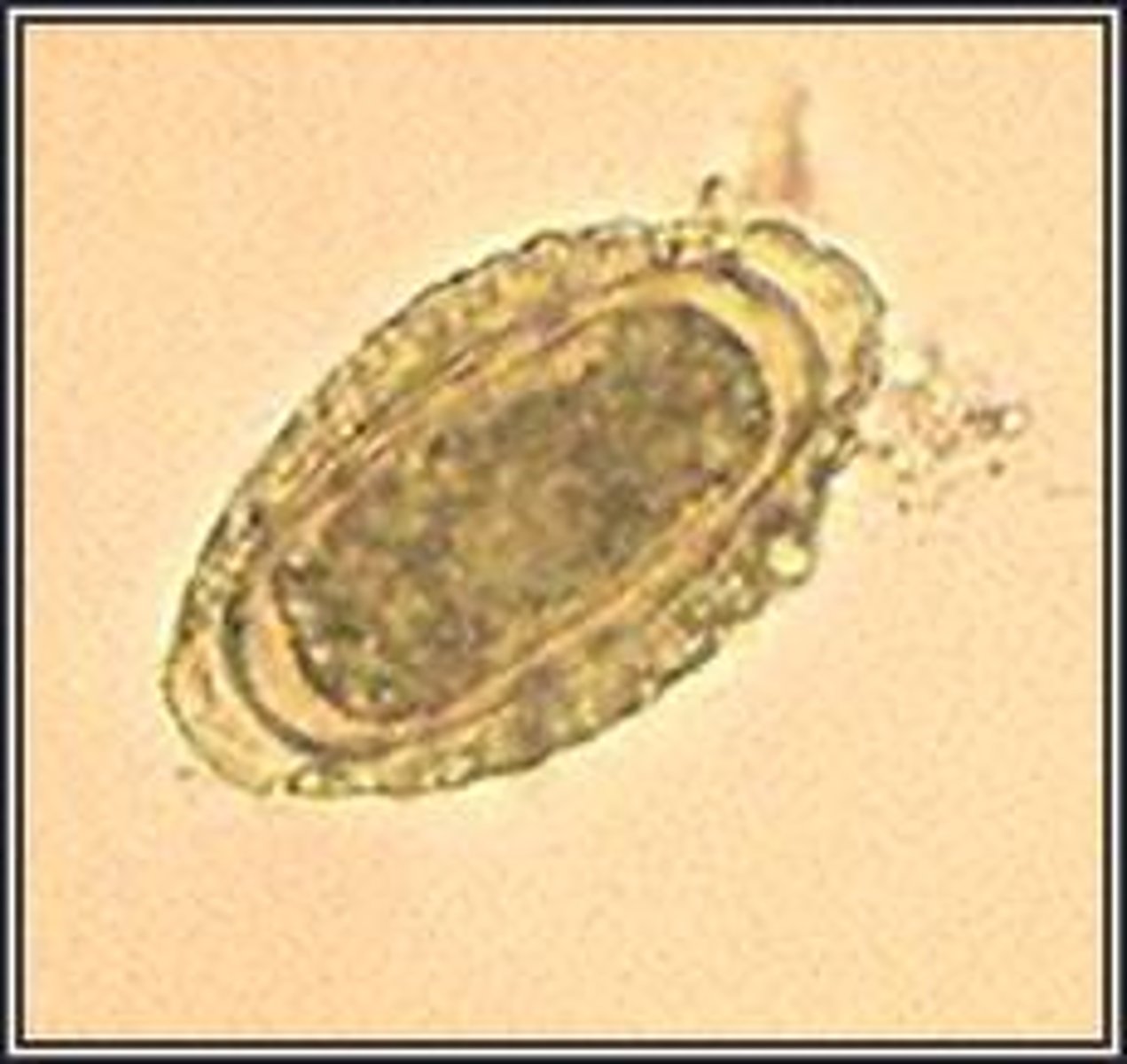
Microfilaria immitis
Heartworm
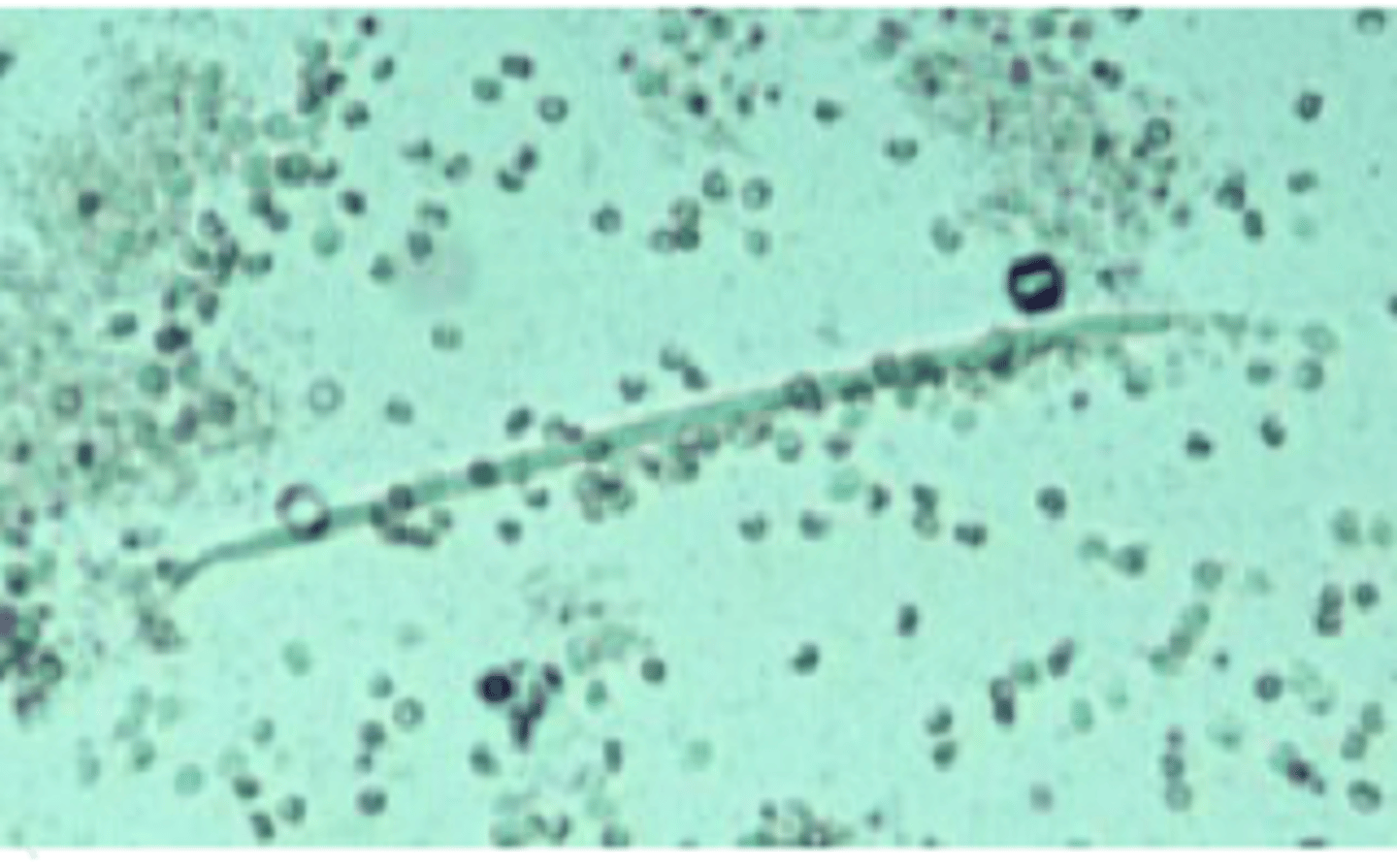
Mucus threads
Resemble a twisted ribbon; often confused with casts; large number in horses
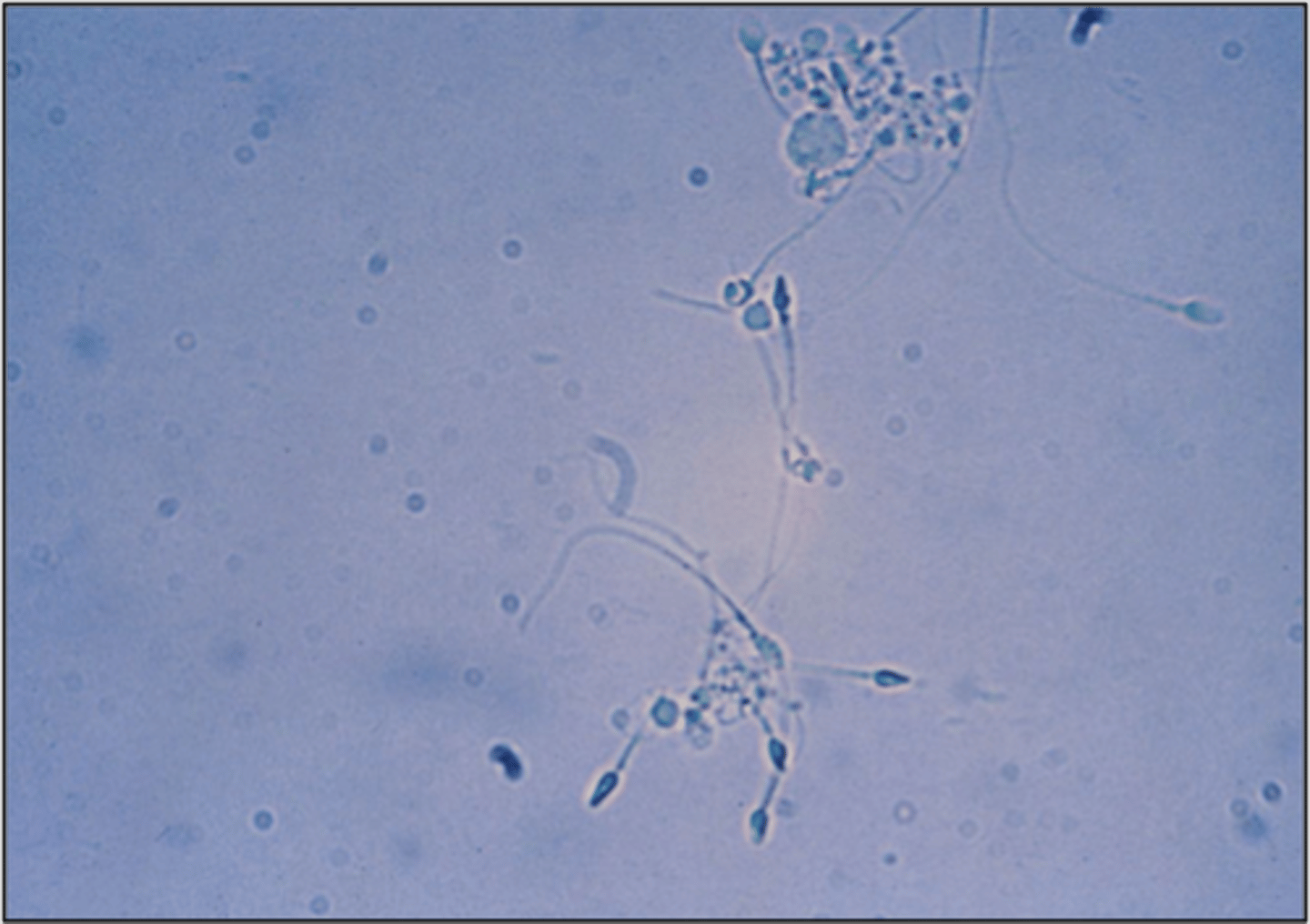
Spermatozoa
sperm cells; often seen with intact males; large numbers can give false-positives for proteins
Fat Droplets in Urine
Lightly green tinged, highly refractile spheres; will rise to surface if set for few moments
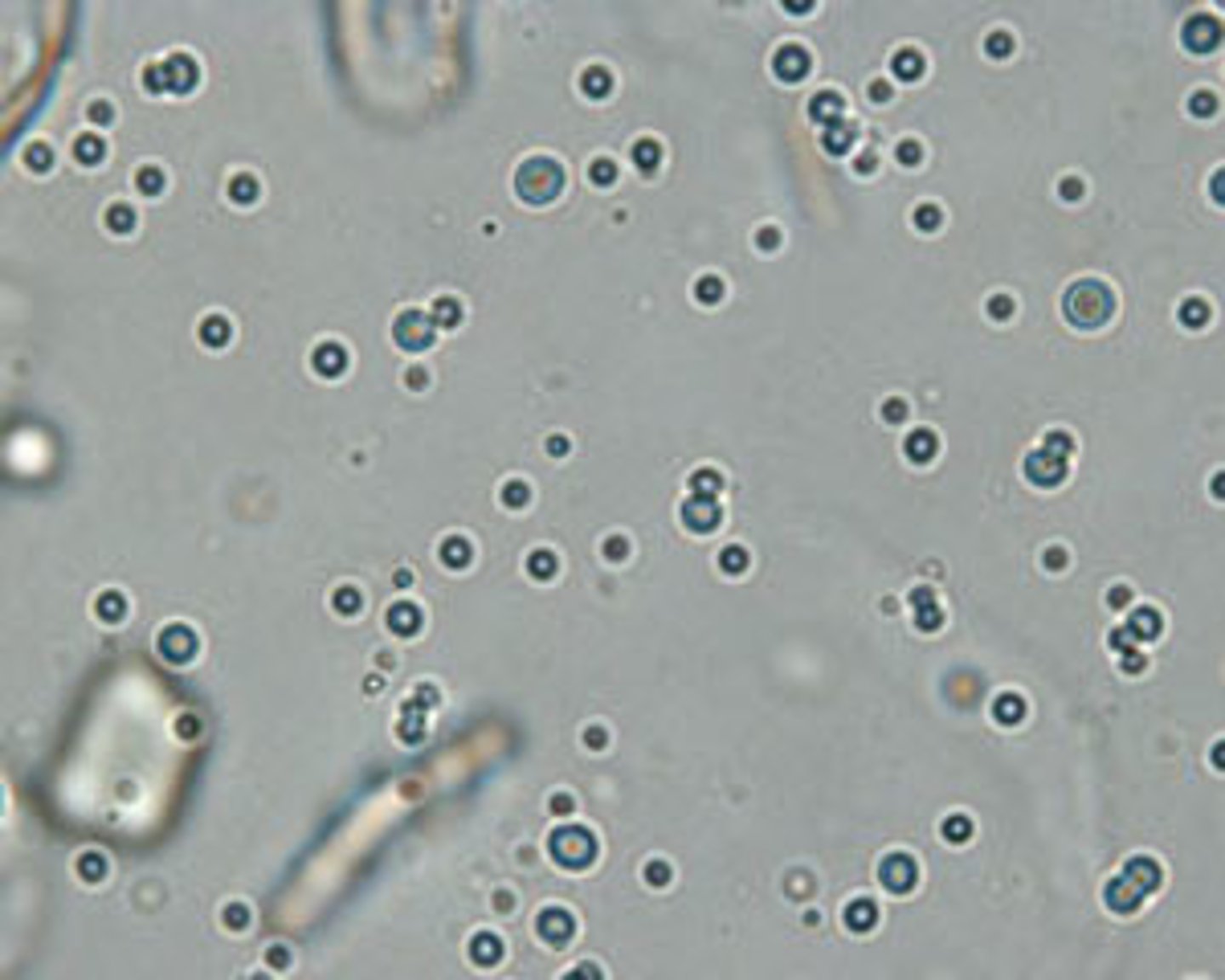
Lipuria
fat in urine
Urolithiasis
Formation of stones in the urinary tract.
Most common urinary crystals in dogs and cats
Struvites and calcium oxalate
Most common urolithiasis in dogs and cats
struvite
Caliculi
stones