A&P CH.7 PT A. The Skeleton
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
what is the skeleton composed of
bones, cartilage, joints, and ligaments
what do ligaments do
connect bone to bone and reinforce joints
what are the two major divisions of the skeleton
axial and appendicular skeleton
axial skeleton explained
•80 bones
• three regions- skull, vertebral column, and thoracic cage
•three functions: form longitudinal axis of body, support head neck and tunk, and protect brain spinal cord and thoracic organs
bone markings such as projections, depression, and openings form what
attachment sites for muscles, ligaments, and tendons
articular surfaces (joints)
channels for blood vessels and nerves
Bone markings;projections that are sites of muscle and ligament attatchment
tuberosity, crest, trochanter, line, tubercle, epicondyle, spine, and process
tuberosity
large rounded projection that may be roughened
crest
narrow ridge of bone; usually prominent
trochanter
very large irregularly shaped process
line
narrow ridge of bone, less prominent
tubercle
small rounded projection or process
epicondyle
raised area on or above a condyle
spine
sharp slended and often pointed projection
process
any bony prominence
projections that help form joints
head, facet, condyle
head
bony expansion carried on a narrow”neck”
facet
smooth and nearly flat articular (joint) surface
condyle
rounded articular projection; often articulated with corresponding fossa
projections for passage of vessels and nerves
groove, fissure, foramen, notch, meatus, sinus, fossa
groove
furrow
fissure
narrow, slit like opening
foramen
round or oval opening through a bone
notch
indentation at the edge of a structure
meatus
canal like passageway
sinus
cavity within bones filled w air and line with mucous membrane within skull
fossa
shallow, depression in bone which often serves as an articular surface
the skull is formed by two sets fo bones
8 cranial bones
name the 8 cranial bones (PEST OF 6)
parietals(2), ethmoid, sphenoid, temporal (2), occipital, and frontal
what does the temporal bone do
houses organs of hearing and equilibrium
frontal bone
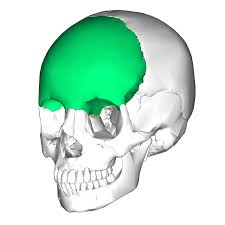
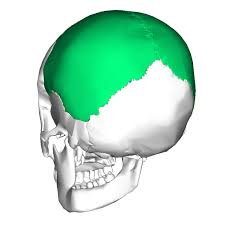
parietal bone
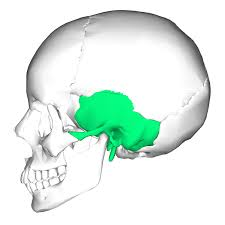
temporal bone
sphenoid bone (butterfly bone)
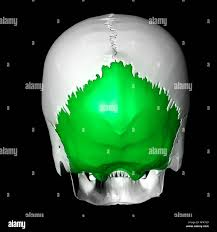
what is included in the sphenoid
optical canal and various other foramina for passage of blood vessels and nerves
ethmoid bone is the
deepest skull bone
what do the cribriform plates do
form roof of nasal cavity and floor of anterior cranial fossa
crista galli is
point of attachment for brain’s dura mater covering
what are the three major regions of temporal bone
squamous, tympanic, and petrous region
squamous region for temporal bone
zygomatic processes articulate with zygomatic bone to form zygomatic arch and mandibular fossa makes up part of temporomandibular joint
tympanic region for temporal bone
surround external acoustic meatus (external ear canal)
what is the mastoid and styloid processes
areas for attachment of several neck and tongue muscles
petrous region for temporal bone
houses middle and internal ear cavities, makes up part of middle cranial fossa
what are the major sutures of the bone
coronal suture, sagittal suture, lambdoid suture, and squamous suture
coronal suture
between parietal bones and frontal bones
sagittal suture
between right and left parietal bones
lambdoid suture
between parietal and occipital sutures
squamous sutures
between parietal and temporal bone
what is a sutural bone?
tiny, irregularly shaped bones that appear within sutures (unknown of what they do)
what does the occipital bone articulate with
C1 vertebrae aka atlas at occipital condyles (looks like little nubs)
ligamentum nuchae
site of attachment for many neck and back muscles
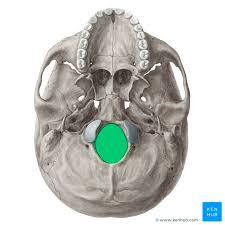
what does foramen magnum do?
allows passage of spinal cord and vertebral artery and vein (Big Whole); spinal cord exits brain cavity in this area
vultures can Not make my Pet Zebra laugh (in caps= 2 of them)
vomer, inferior nasal conchae, nasals (2), maxillae, mandible, palatines (2), zygomatics (2), and lacrimals
maxilla
upper jaw, larger bone
lacrimal bones
think tear ducts
what is the largest, strongest bone of face
mandible
************does the mandibular articulate with the temporal bone
YES
alveolar process
sockets for teeth held into mandible
what does the mandibular notch do
separates processes
coronoid process
superior end of rami serves as insertion point for large temporalis muscle
orbits are formed by
7 BONES; frontal, sphenoid, zygomatic, maxilla, palatine, lacrimal, and ethmoid
nasal cavity
formed by several bones
how is the roof, lateral walls, and floor of nasal cavity formed
ethmoid bone, palatine bones, maxillary bones, and inferior nasal conchae
paranasal sinuses
•formed from five skull bones: frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid, and paired maxillary bones
•all contain mucosa-lined, air filled spaces
•function: warm+humidify air, help to lighten skull, enhances resonance of voice
hyoid bone
does not articulate with any other bones directly. held in place by ligaments. acts as movable base for tongue and site of attachment for muscles of swallowing and speech
vertebral column
spine or spinal column
cervical
consists of 7 vertebrae of the neck (c1-c7)
Thoracic
12 vertebrae of thoracic cage (T1-T12)
Lumbar
5 vertebrae of lower back (L1-L5)
sacrum
5 fused vertebrae of the pelvis
Coccyx
3-5 (usually 4) fused vertebrae of the tailbone
name the four main curves in the column
•Thoracic and sacral curvatures- convex posteriorly
•Cervical and Lumbar curvatures- concave posteriorly
ligaments attach
bone to bone
Anterior and posterior longitudinal ligaments
Help support to avoid hyperextension (backward) or hyper flexion (forward)
Ligamentum Flavum
connects adjacent vertebrae
short ligaments
connect each vertebra to those above and below
intervertebral discs
cushion like pad between vertebrae that act as shock absorbers
what are the two parts of the in vertebral disks
• Nucleus Pulposus- gives disc its elasticity and compressibility
• Annulus Fibrosus- outer collar composed of collagen and fibrocartilage/limits expansion of nucleus when compressed
Abnormal spinal curvatures+explain
• scoliosis:abnormal lateral rotation of spine most often in thoracic; can lead to breathing difficulties
•Kyphosis (hunchback): abnormal dorsal thoracic curvature and common in older women.
• Lordosis (swayback): accentuated lumbar curvature that can result from disease but also seen in men w pot bellies & pregnant women
body (centrum)
anterior weight-bearing) region
vertebral arch composed of
•two pedicles-short pillars form sides of arch
•two laminae-fused, flattened plates from posterior arch
vertebral foramen
enclosure formed by body and vertebral arch coming together; make up the vertebral canal
intervertebral foramina
lateral openings between vertebrae for passage of spinal nerves
how many processes does the vertebrae have
7
spinous process-project posteriorly
transverse processes (2)- project laterally
superior articular processes(2)-protrude superiorly
inferior articular processes (2)-protrude inferiorly
what is c7
vertebra prominens- large, triangular vertebral foramen
what is the transverse foramen (only in cervical vertebrae)
found in each transverse process for artery passage ways
C1 is the
Atlas
-no body or spinous process
-consists of anterior and posterior arches, and two lateral masses
-occipital condyles (slide 20) “carry” the skull
-movement for nodding head “yes”
C2 is the
Axis
-has body and processes like other vertebrae
-has a knoblike dens that projects superiorly (up) in the anterior arch of atlas
-movement allows side to side rotation for saying “no”
-pivot for rotation of atlas
T1-T12
-increase in size and articulate w ribs
-have only single facet not two
-foramen is circular
-transverse processes have transverse costal facets that articulate w the ribs (except T11 & T12)
articular facets allow what
rotation of this area of the spine (T1-T12)
L1-L5
-small of back; receives most stress so bodies are massive
-short thick pedicles and laminae
-flat, hatchet-shaped spinous processes point posteriorly
-vertebral foramen is triangular
S1-S5
-fused bones
-articulate superiorly w L5, articulates inferiorly w coccyx, and articulates laterally w hip bones
coccyx
-tailbone
-3-5 fused vertebrae
-articulates superiorly w sacrum
Thoracic cage is composed of
-thoracic vertebrae
-sternum
-ribs and costal cartilages
what are the functions of the thoracic cage
-protects vital organs of thoracic cavity
-supports shoulder (pectoral) girdles and upper limbs
-supports shoulder girdles and upper limbs
-provides attachment sites for muscle of neck, back, chest, and shoulders
bone marking in sternum to know
jugular notch
the sternum aka the breast bone consists of three fused bones that include
mandubrium-superior portion, articulates w clavicle and ribs 1+2
body-midportion that articulates w costal cartilages of ribs 2-7
Xiphoid process- inferior end that is site of muscle attachment
what are the three important landmarks of sternum
jugular notch, sternal angle, and xiphisternal joint
ribs
-12 pairs from sides of thoracic cage
-all attatch posteriorly to bodies
true ribs are
-pairs 1-7= true; attatch directly to sternum by individual costal cartilages
-false ribs 8-10; attatch indirectly to sternum by joining costal cartilage of rib above
-vertebral (floating) ribs 11-12; no attachment to sternum
name the main parts of the rib
-shaft-flat bone that makes up most of rib
-head (posterior end)-articulates w facets on two adjacent vertebrae
-neck-constricted portion beyond head
-tubercle: knoblike structure lateral to neck (articulates posteriorly w transverse costal facet fo same numbered thoracic vertebra