integumentary system part 2
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
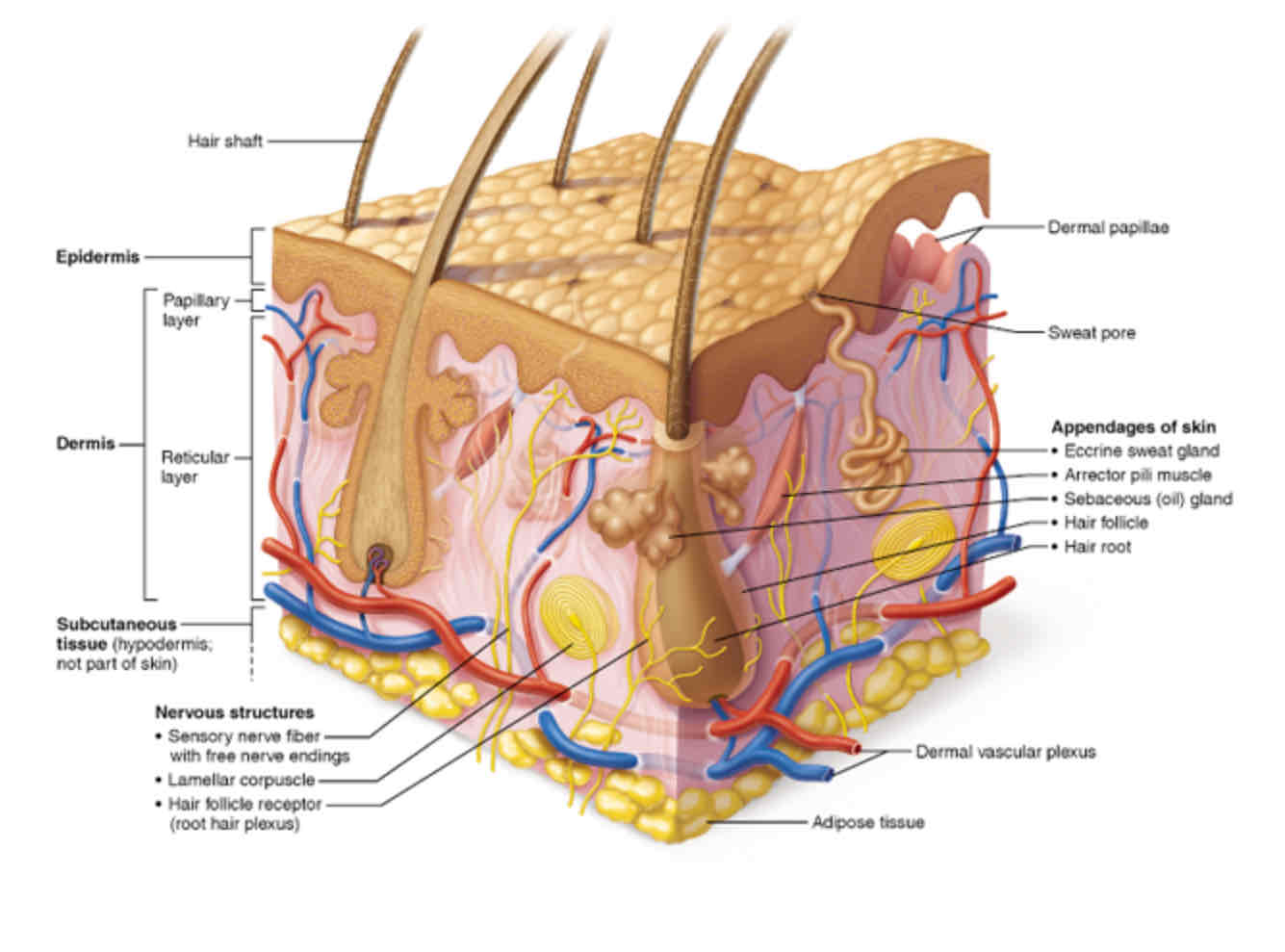
hair
consists of dead keratinized cells
none located on palms , soles , lips , nipples , and portion of external genitalia
functions
warn of insects on skin
hair on head guards against physical trauma
protect from heat loss
shield from sunlight
structure of hair
also called pili- flexible strands of dead kerantized cells
produce by hair follicles
contains hard keratin
together and more durable
cells do not flake off
2 regions of hair
shaft - area that extends above scalp , where keratinization is complete.
root- area within scale , where keratinization is still going on
3 parts of the shaft
medulla (inner or middle)- central core of large cellls and air spaces
cortex(outer) several layers of flattened cells surrounding medulla
cuticle (outer ) consist of overlapping layers of single cells
hair pigment is made by
melanocytes
combinations of different melanin (yellow, rust, brown, black) create al the hair colors
red hair has additional phenomena in pigment
gray and white hair is a result of air bubbles in melanin in shaft
structure of hair follicle
extends from epidermal surface to dermis
hair bulb- deep end of follicle
hair follicle receptor(root hair plexus) - sensory nerve ending thats wrap around bulb
hair matrix - actively dividing area of bulb that produces hairs cells, makes new cells pushes old cells upward
arrector pili- smooth muscle attached to follicle, responsible for goosebumps - involuntary
hair papilla - dermal tissue containing knot of capillaries that supplies nutrients to growing hair
types of growth of hair
vellus hair - pale fine bod hair of children and adult females
terminal hair - coarse , long hair
scalp and eyebrows
puberty - appear in axillary (armpit) and pubic regions of both sexes
______ and ______ affect hair grow
nutrition and horomones
true (frank) baldness
genetically determines and sex influenced condition
male patter baldness cause by follicular response to DHT
growth cycles are shortened - follicles shed before reaching the surface
nails
contain hard keratin
protective cover for distal, dorsal surface of fingers
nail bed is epidermis underneath keratinized nail plate
matrix - thickened portion of bed responsible for nail growth
nail folds - skin that overlaps border of nail
epinychium (in nail)
nail folds that projects onto surface of nail body
also called cuticle
nils normally appear pin because of underlying capillaries
lunule- thickened nail matrix appears white
hyponchium (in nail)
area of under free edges of plate that accumulates dirt
abnormal color or shape can be an indicator of disease
clinical homeostatic imbalance 5.6
nails appearance can help diagnosing some diseases
yellow - tinged
may indicate respiratory or thyroid gland disorder
thickened yellow nails can be due to fungle infection of nail
koilonchya
spoon nail - outward concavity of nail
may single iron deficiency
beau’s line
horizontal line across nails may indicate severe illnesses such as uncontrolled diabetes, heart attach or cancer chemotherapy
sweat glands (sudoriferous glands)
all skin except nipples part of. external genitalia contains sweat glands
3 million per person
two types of sweat glands
eccrine (merocrine ) sweat glands
apocrine sweat glands
eccrine (merocrine ) sweat glands
most number type
abundant on plasm , soles , and forehead
ducts connect pores
function in thermoregulation - allow for vapor action
regulated by sympathetic nervous system
their secretion is sweat
99% water
salts
vitamin c
dermcidin (microbe - killing peptide )
Matoblic waste
apocrine sweat glands
confined to axillary and anegential areas
secrete vicious milky or yellowish sweat that contains fatty substances and proteins
bacteria breaks down sweat leading to body odor
larger then eccrine sweat glands with ducts into hair follicles
begin at puberty
function unknown but may act as sexual scent gland
sebaceous (oil ) glands
widely distributed, except for thick skin of palms and soles
most devolve from hair follicles and secrete into hair follicles
relatively inactive until puberty
stimulated by hormones, especially androgens
secrete sebum
oily HOLOCRINE secretion
glands accumulate products then rupture
bactericidal ( bacteria - killing ) properties
soft skin and hair
Know Table 5.1 Summary of Cutaneous Glands
clinical homeostatic imbalance 5.7
acne is usually infectious inflammation of sebaceous glands, resulting in pimples (pustules or cysts)
associated with propionibacterium acne infection
white heads are blocked sebaceous glands
if secretion is oxidized , whitehead become a black head
overreactive sebaceous glands in infants can lead to seborrhea , aka “”crackle cap”
begins as pink , raised lesions on scalp that turns yellow / brown and flake off
functions of skin
protection
body temp regulation
cataneous sensation
blood reservoir
excretion of waste
protection has 3 barriers
1. Chemical barrier
2. Physical barrier
3. Biological barrier
Chemical barrier
• Skin secretes many chemicals, such as:
o Sweat, which contains antimicrobial proteins
o Sebum and defensins, which kill bacteria
o Cells also secrete antimicrobial defensin
• Acid mantle: low ph of skin retards bacterial multiplication
• Melanin provides a chemical barrier against UV radiation damage
Physical barrier
Flat, dead, keratinized cells of stratum corneum, surrounded by glycolipids, block most water and water-soluble substances
• Some chemicals have limited penetration of skin
o Plant oleoresins (e.g., poison ivy)
o Organic solvents (acetone, paint thinner)
o Salts of heavy metals (lead, mercury)
o Some drugs (nitroglycerin)
o Drug agents (enhancers that help carry other drugs across skin)
Biological barriers
Epidermis contains phagocytic cells
o Dendritic cells of epidermis engulf foreign antigens (invaders) and present to white blood cells, activating the immune response
• Dermis contains macrophages
o Macrophages also activate immune system by presenting foreign antigens to white blood cells
• DNA can absorb harmful UV radiation, converting it to harmless heat
Body Temperature Regulation
• Under normal, resting body temperature, sweat glands produce about 500 ml/day of unnoticeable sweat
o Called insensible perspiration
If body temperature rises, dilation of dermal vessels can increase sweat gland activity to produce 12 L (3 gallons) of noticeable sweat
Called sensible perspiration (WHEN YOU WORK OUT)
▪ - designed to COOL BODY
Cold external environment
Dermal blood vessels constrict
Skin temperature drops to slow passive heat loss
Cutaneous Sensations
sensory receptors are part of the nervous system
o Exteroreceptors respond to stimuli outside body, such as temperature and touch
o Free nerve endings sense painful stimuli
Metabolic Functions
• Skin can synthesize vitamin d needed for calcium absorption in intestine
• Chemicals from keratinocytes can disarm some carcinogens
• Keratinocytes can activate some hormones
Example: convert cortisone into hydrocortisone
• Skin makes collagenase, which aids in natural turnover of collagen to prevent wrinkles
Blood Reservoir
****Skin can hold up to 5% of the body’s total blood volume(in dermis) *****
• Skin vessels can be constricted to shunt blood to other organs, such as an exercising muscle
Excretion
• Skin can secrete limited amounts of nitrogenous wastes, such as ammonia, urea, and uric acid
• Sweating can cause salt and water loss
Developmental Aspects of the Integumentary System
Fetal: by end of 4th month, skin of fetus is developed
• Lanugo coat: delicate hairs in 5th and 6th month
• Vernix caseosa: sebaceous gland secretion that protects skin of fetus while in watery amniotic fluid
Infancy to adulthood
skin thickens and accumulates more subcutaneous fat; sweat and sebaceous gland activity increases, leading to acne
• Optimal appearance during 20s and 30s
• After age 30, effects of cumulative environmental assaults start to show
• Scaling and dermatitis become more common
Aging skin
• Epidermal replacement slows; skin becomes thin, dry, and itchy
• Decreased sebaceous gland activity
• Subcutaneous fat and elasticity decrease = winkles and being cold
• Increased risk of cancer due to decreased numbers of melanocytes and dendritic cells
• Hair thinning
Ways to delay aging
1.uv protection
2.good nutrition
3.lots of fluid
4.good hydride
review