chapter 5 - dna and chromosomes
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
chemical basis of genes
building blocks of dna
double stranded
double helix
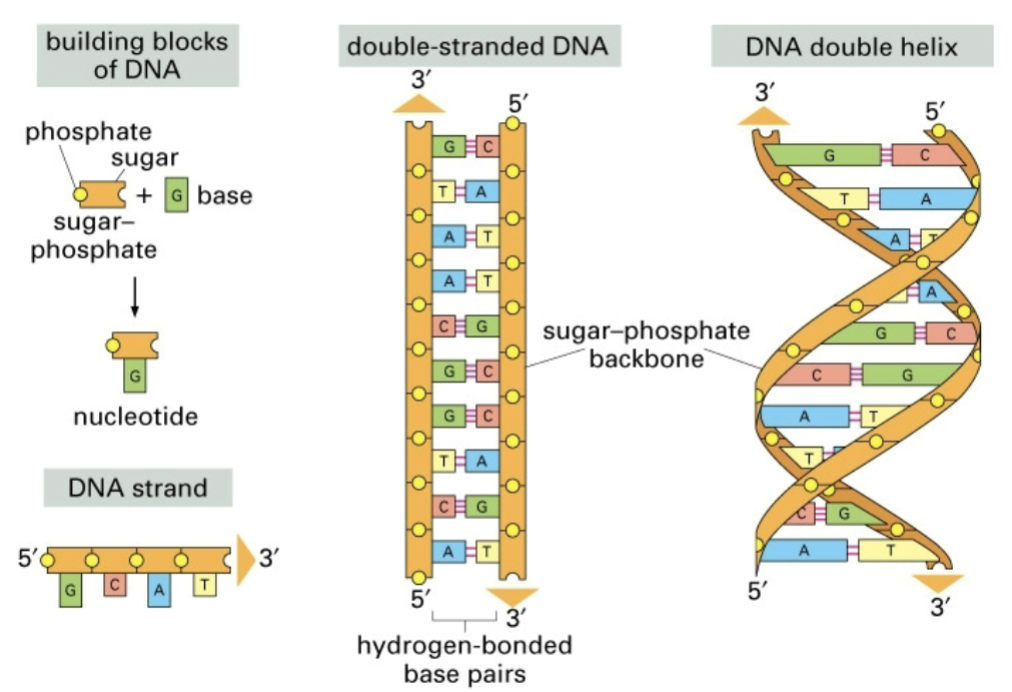
building blocks of dna
phosphate backbone + base → nucleotide
sugar phosphate backbone + hydrogen bonded base pairs → double stranded helix
5’ → 3’
first key experiment leading to identification of dna as genetic material
frederick griffith - studied streptococcus pneumococcus pathogenicity, showing that material could be transferred from a heat killed virulent strain to a non virulent strain making the non virulent strain virulent
the process of transformation
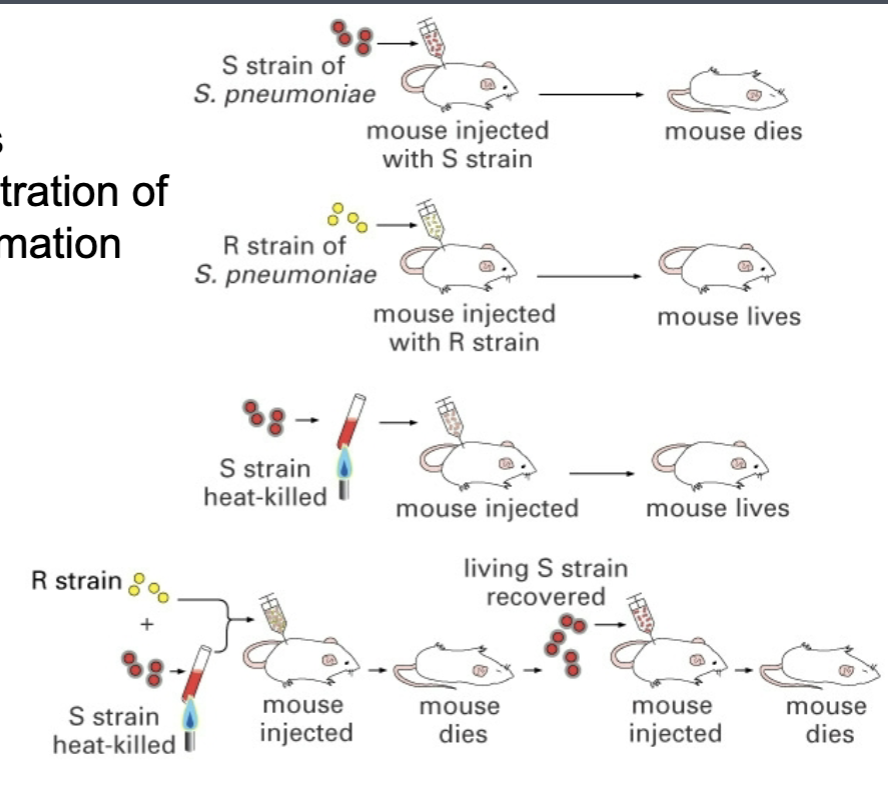
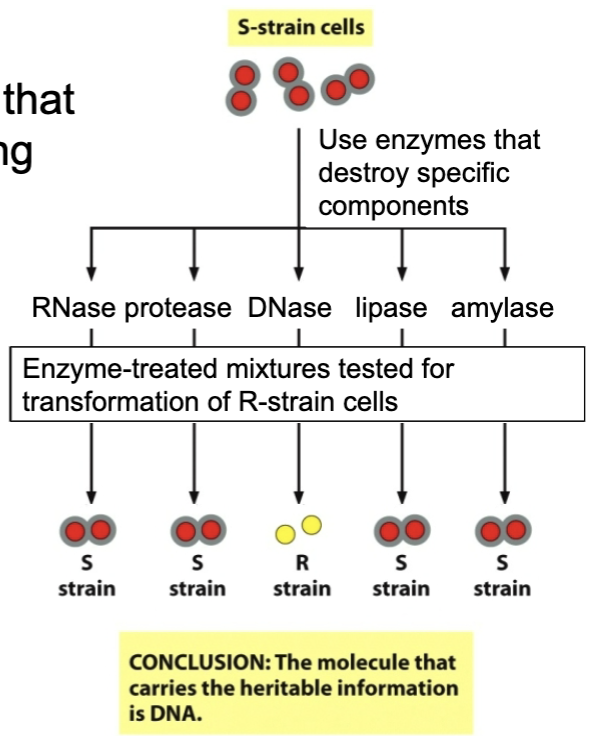
key idea 1 - demonstrating that dna is transforming principle
a mixture of things has an effect on something
separate the components, see which one has the effect
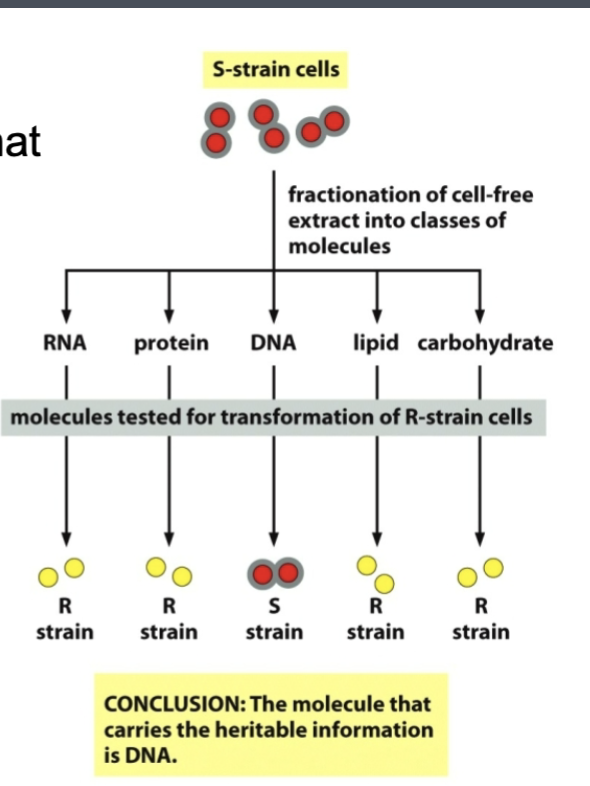
key idea 2 - demonstrating that dna is transforming principle
a mixture of things has an effect on something
delete components one by one, see which deletion cause the effect to disappear
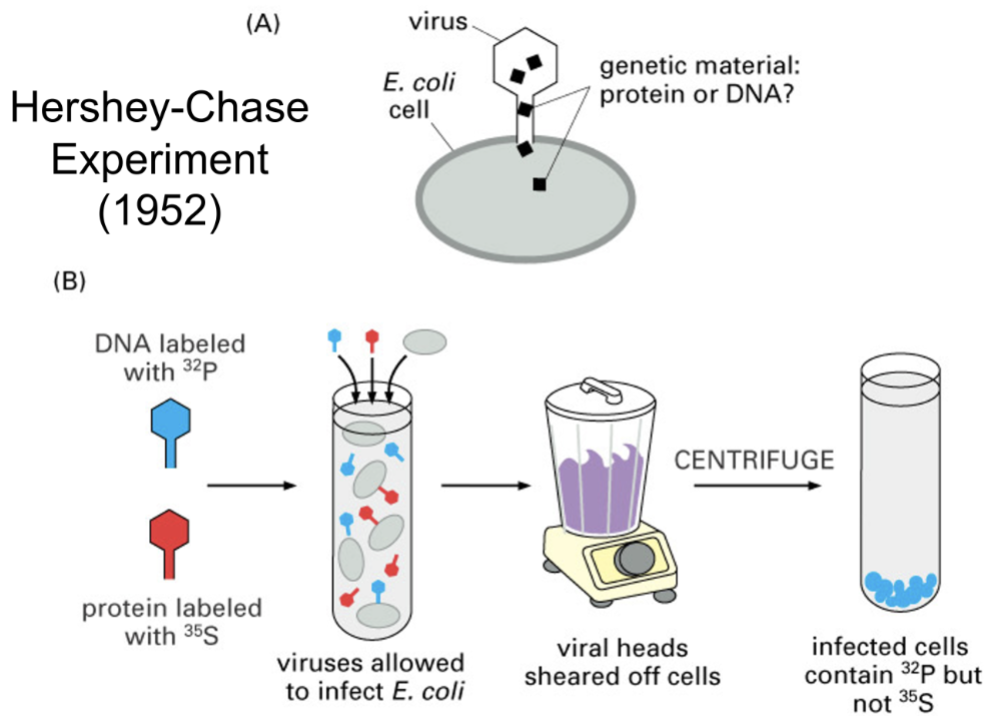
hershey chase experiment
some phage viruses contain dna and protein, when they infect bacteria, the bacteria make more viruses, so something in the virus has genetic information
electron microscopy showed that the virus attaches to the bacteria, and injects something into it
label phage dna with P³² and phage proteins with S35 then infect bacteria, let the injection occur, then tear off the virus and see what got injected into the bacteria
chargaffs rule
complementary base pairing
base composition varies significantly between species
it did not matter from which tissue or organ the dna came from, base composition was constant within the species
A=T and C=G - present in equimolar amounts
A=T does not equal to C=G
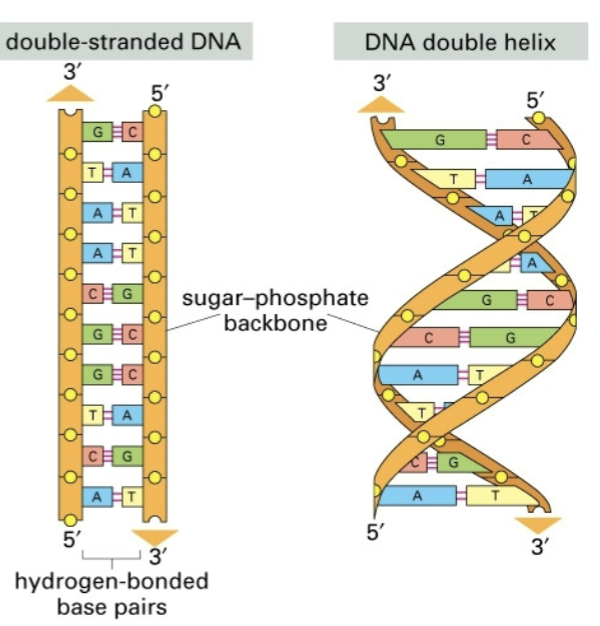
structure of dna
1953 watson and crick used molecular models based on x ray diffraction data from franklin and wilkins to propose a double helical structure for dna where the helix was held together by A-T and C-G base pairs
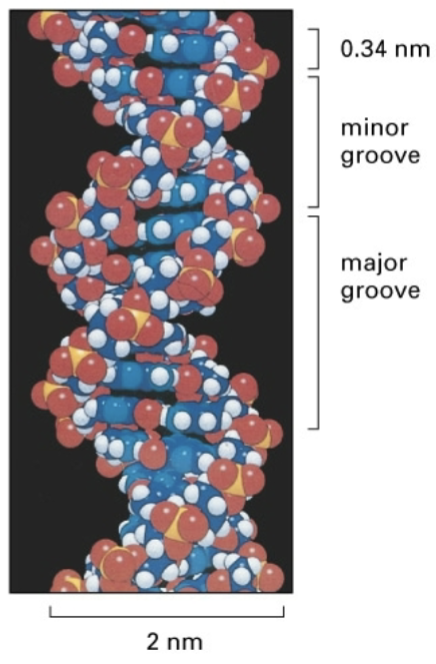
properties of dna double helix
two dns strands wrapped in a right handed helix
two chains are antiparallel
sugar phosphate backbone on the outside, bases project toward the center
the bases are stacked one on top of the other
hydrophobic interactions and van der waals forces stabilize the helix
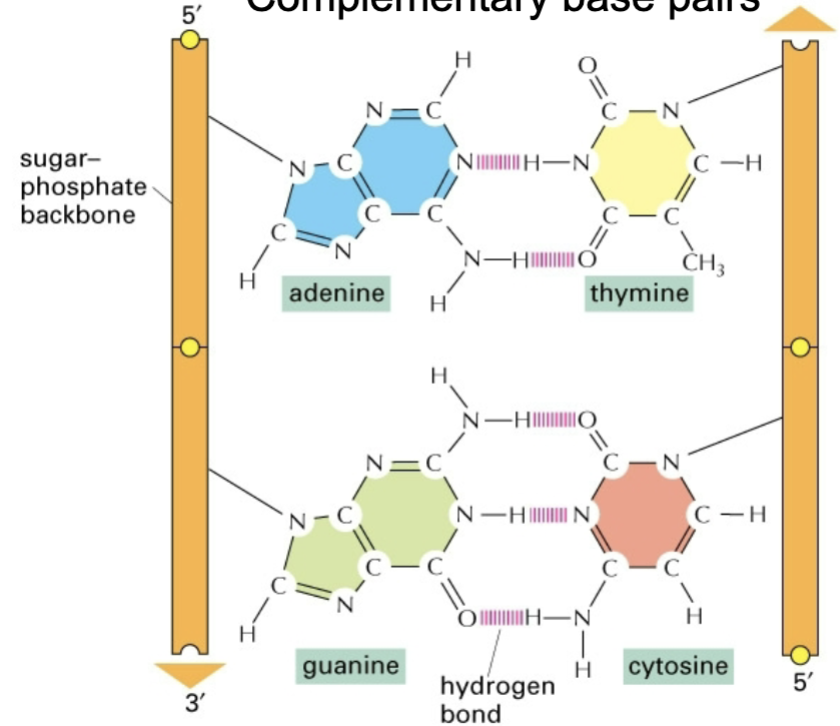
complementary base pairing
purine/pyrimidine base pairs
A - T
2 H bonds
less stable than g-c
G-C
3 H bonds
more stable than a-t
properties of dna double helix - nucleotide
h bonds between the bases contribute to helical stability
helix diameter is uniform because pase pairs have identical widths
10 bases per helical turn
spaces between the turns of the helix forms major and minor grooves
important sites for dna/protein interactions
complementarity - nucleotides on one chain are complementary to nucleotides on the other strand
implications of watson crick model
linear arrangement of nucleotides could store the genetic information
complementarity provided a mechanism for replication of genetic information
how genetic info was expressed was still unknown
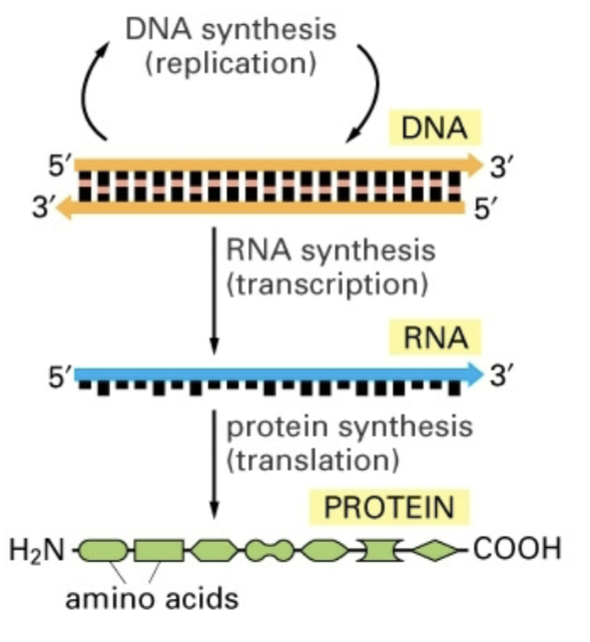
central dogma of molecular biology
replication makes dna → transcription makes rna → translation makes protein
genome
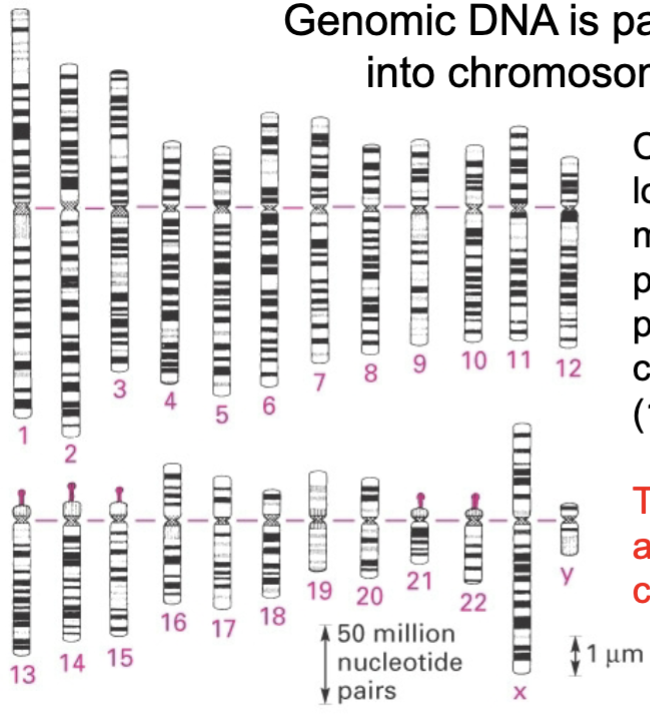
the total dna complement of an organism
the more complex an organism, the larger its genome
the complete genomes of many organisms, including humans, have been sequenced
bioinformatics tools are now used to identify and count genes in sequences genomes
genome can be haploid, diploid, or polyploid
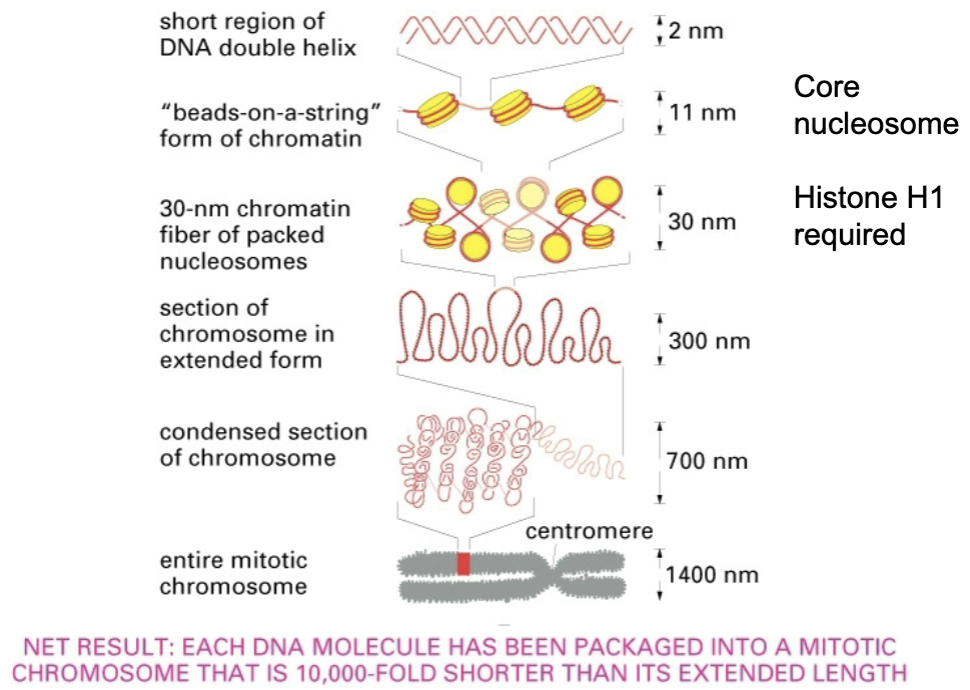
genomic dna is packaged into chromosomes
chromosomes - long, single dna molecules associated with proteins that fold and pack the dna into a compact structure
10,000 fold compaction
chromatin
a complex of dna and associated proteins
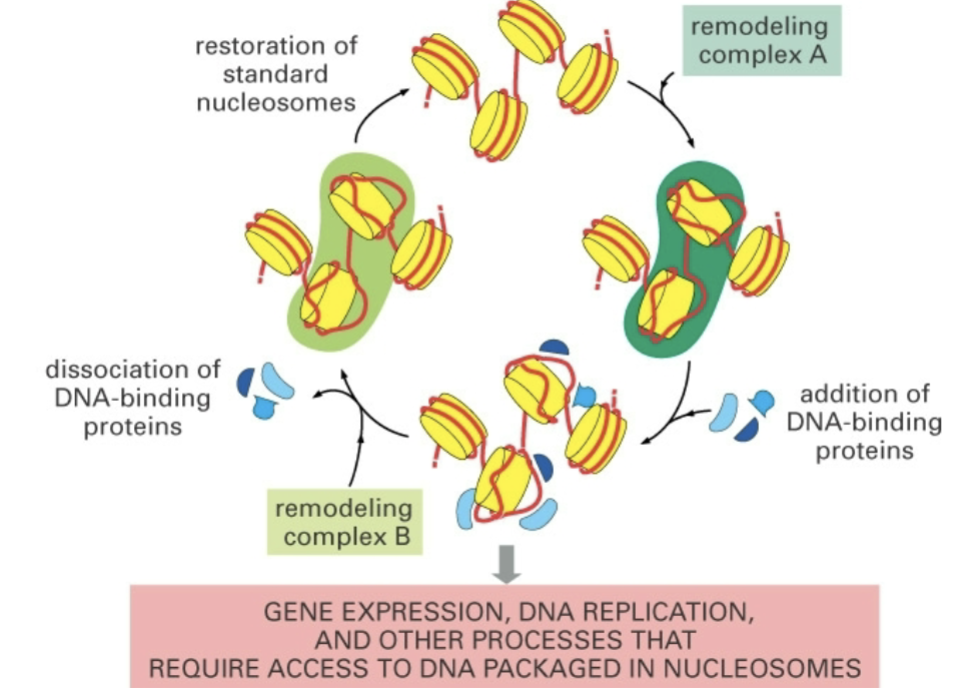
the organization of dna in chromosomes must be _
dynamic
cell cycle
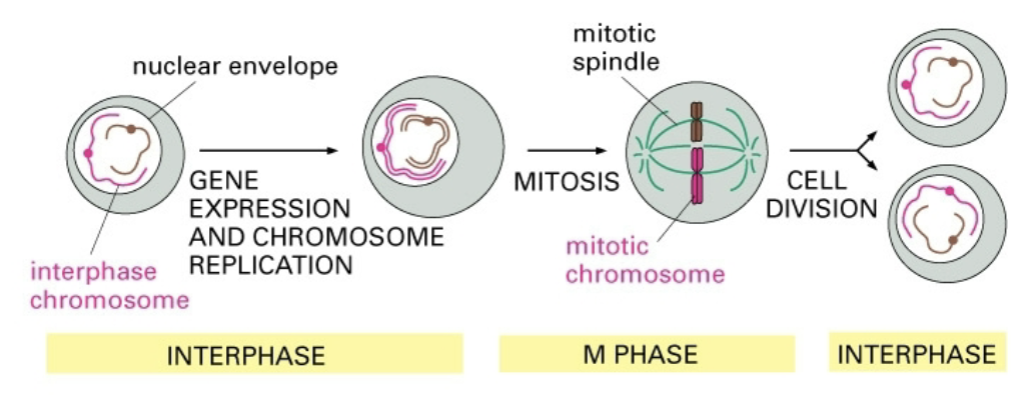
interphase = G1 + S + G2
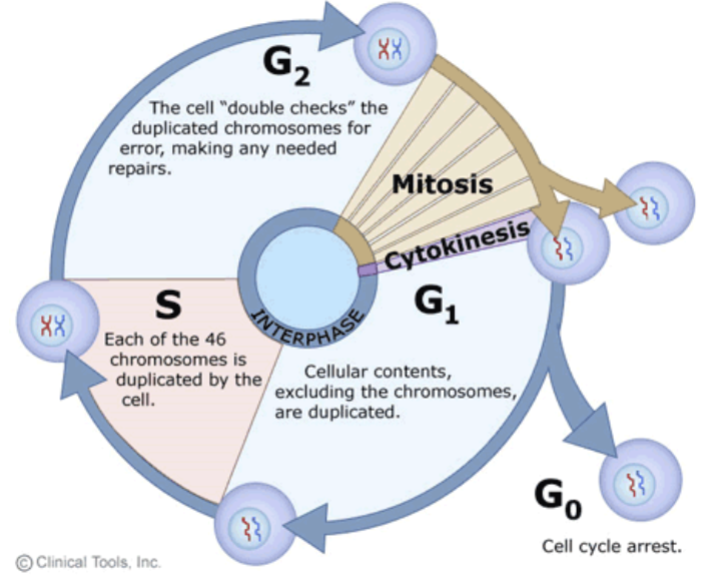
chromosomes during interphase and mitosis
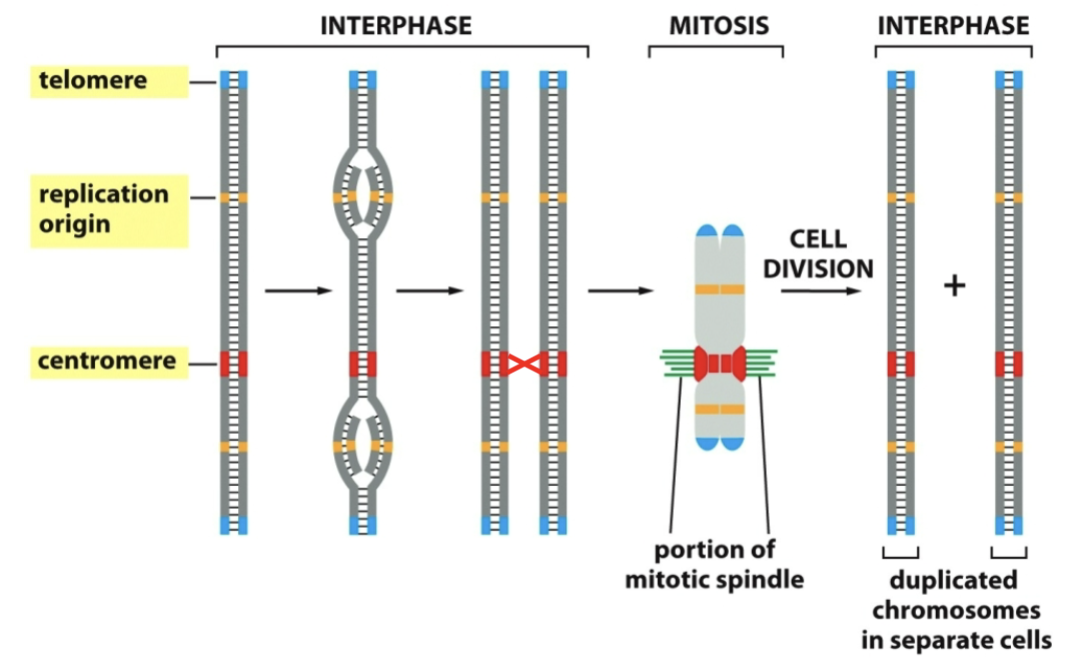
interphase chromosomes are organized within the _
nucleus
is 1000 fold less compact than metaphase chromosomes
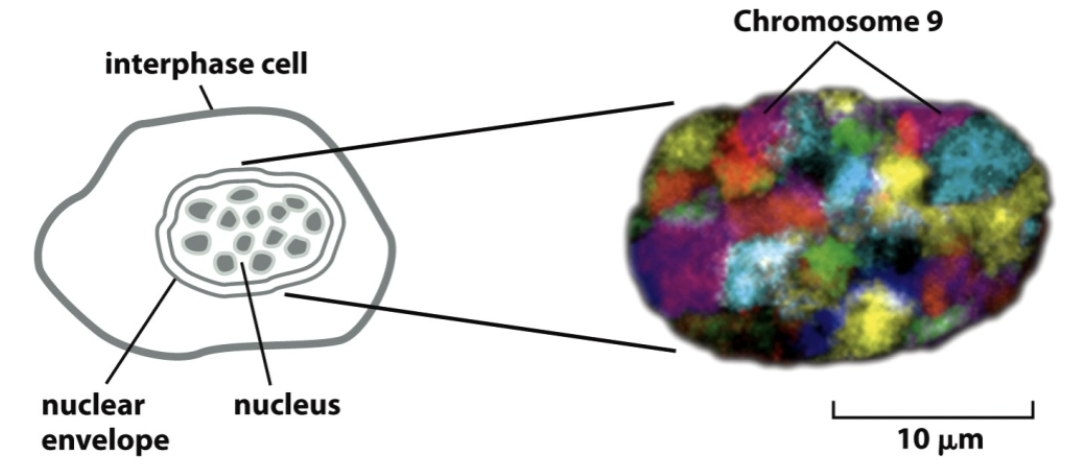
_ are the basic units of eukaryotic chromatin structure
nucleosomes
bacteria dont have nucleosomes - they have a big piece of circular dna that is compacted by various proteins
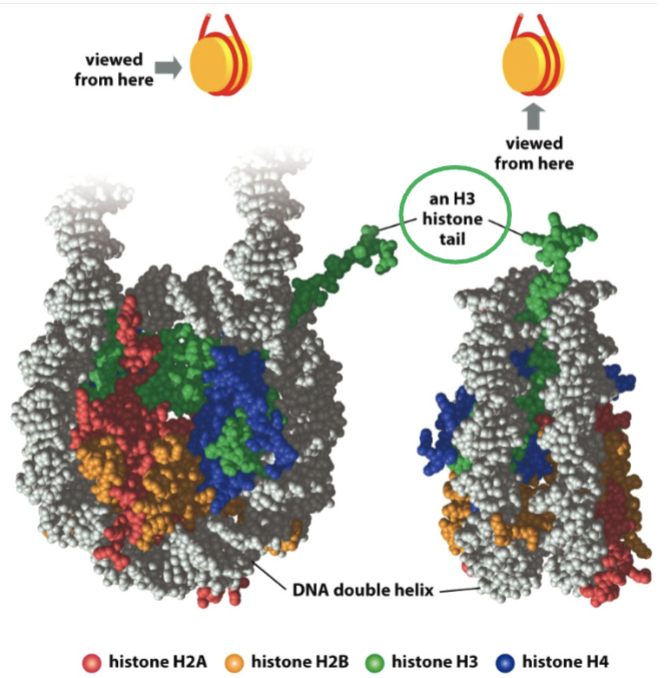
_ form the nucleosomal core
histone octamers
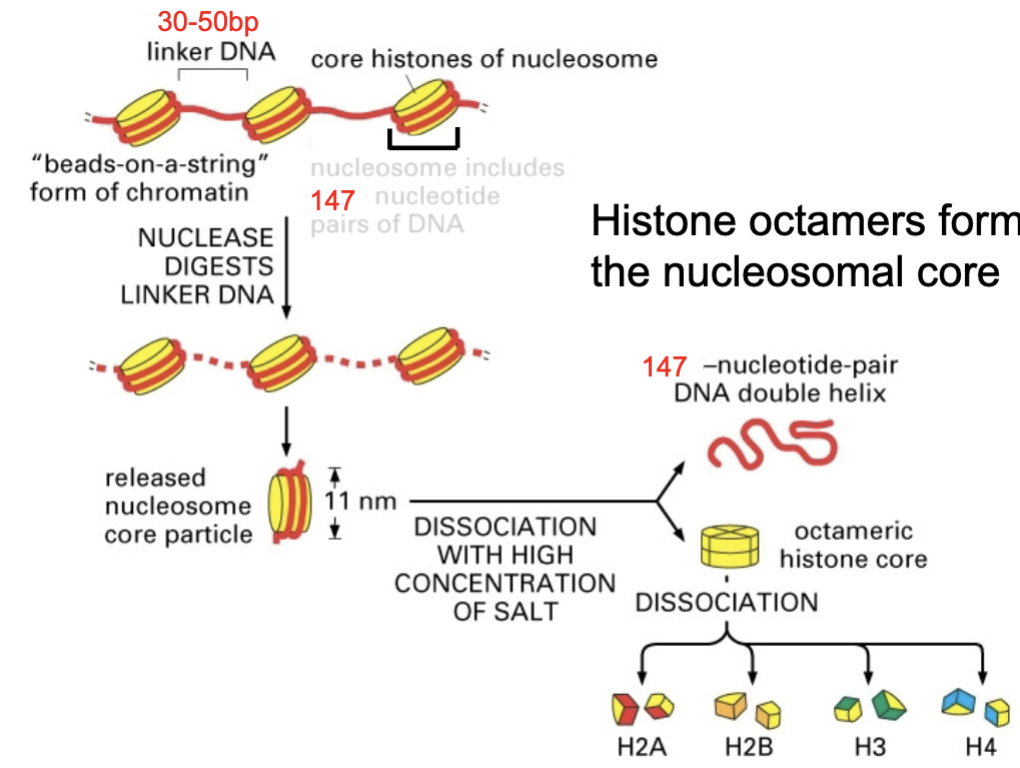
properties of histones
5 histones
positively charged
evolutionary conserved
one nucleosome
properties of histones - 5 histones
nucleosome core
H2A
H2B
H3
H4
required for 30 nm fiber packing level
H1
properties of histones - positively chraged
rich in lysine and arginine
properties of histones - evolutionary conserved
bovine and pea H4 differ by only 2 aa
properties of histones - one nucleosome
146 bp DNA fragment + 2 H2A, 2 H2B, 2 H3, and 2 H4 (histone octamer)
dna vs protein in nucleosome
levels of chromosomal prganization
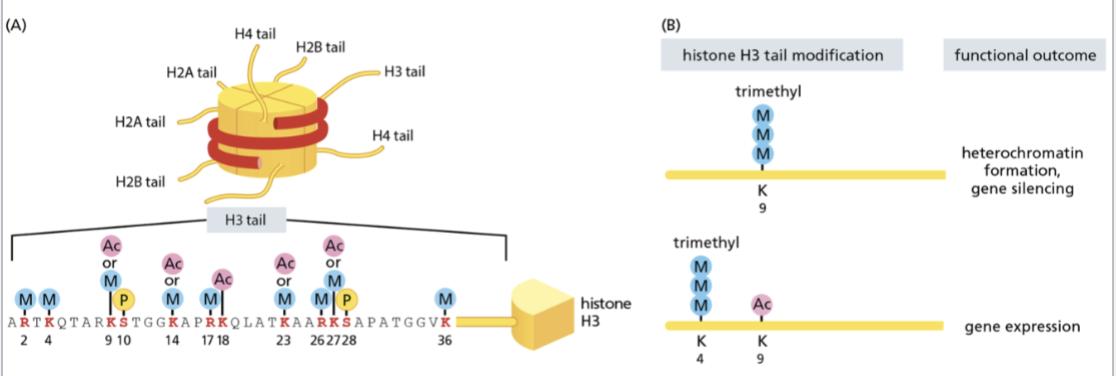
chromatin remodeling complexes alter chromatin structure
modification of _ tails also alters chromatin structure
modification of histone n-terminal tails