Exam 1: Dairy Manufacturing II
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
135 Terms
Milk comp.
Water 86, fat 4, protein 3
factors impacting milk comp
Breed, environment, health, nutrition
Breed with high milk fat
Jersey
Hot and humid months
depress milk fat and protein concentration
mastitis
High somatic cell count and decreased fat
grazing vs mixed ration
Fat and protein change slightly
Definition of milk
-Lacteal secretion, practically free from colostrum
-Not less than 8.25% milk solids not fat
-Not less than 3.25% milkfat
-Milk may be homogenized
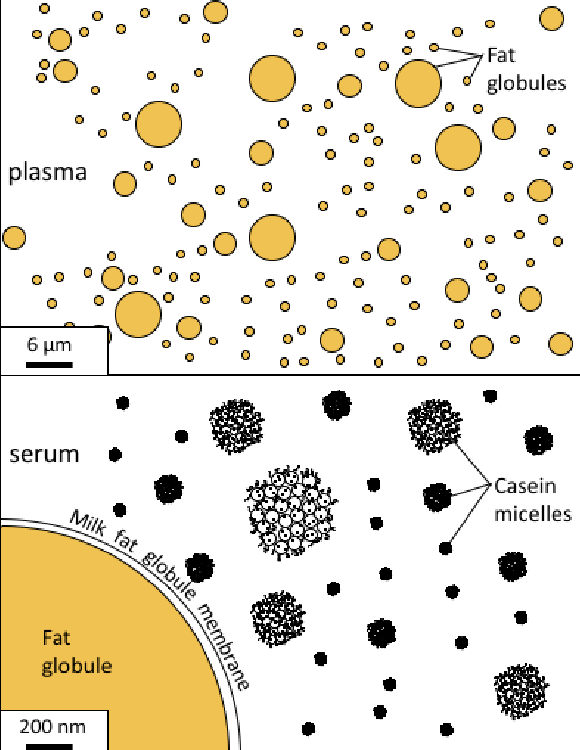
What is suspended in milk to make color
fat globules and Casin micelles
milk structure pic

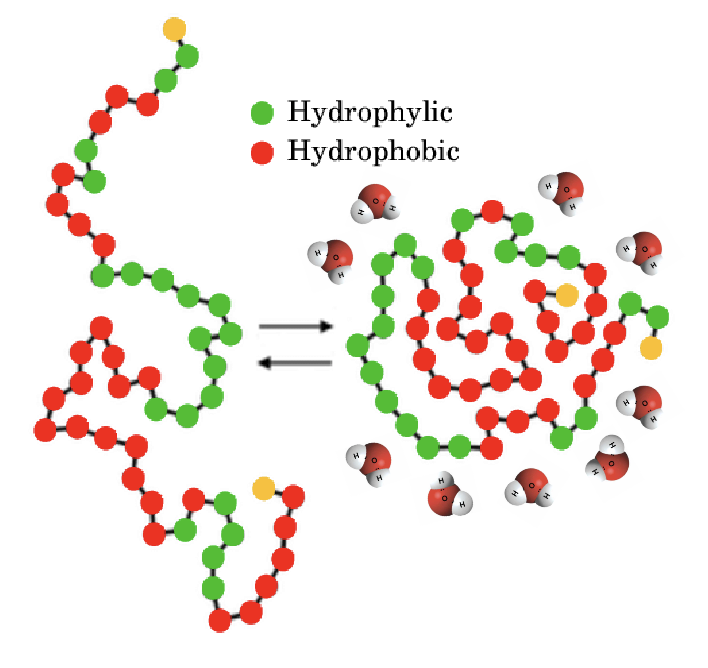
hydrophilic
Water loving
Proteins fold to expose primarily
hydrophilic groups to water
water activity
amount of water available to participate in
reactions
Removal of water from a dairy
product increases its shelf life by reducing water activity
true
Removal of water from dairy products is important for…
microbial safety
most important water activity
.85
no food poisoning below…
.85
moisture content of milk
87%
what hair product is most microbiologically stable
milk powder
In which dairy products can pathogens reasonably grow?
milk/cheese
In which dairy products can mold/yeasts reasonably grow?
cheese, milk, yogurt
lactose
major carbohydrate in milk
disaccharides of glucose and galactose
lactose forms
α-, and β-lactose (most soluble)
Lactose solubility
relatively low
lactose crystals
sandy defect
lactase
enzyme that breaks down lactose
maillard reaction
What component of milk is most susceptible to variation?
Fat
Prior to milk standardization, what is the approximate percentage of lactose in milk?
5%
A protein will fold to shield ____ amino acids from water
Hydrophobic
Milk fat
mainly composed of triglycerides
milk fat is contained in…
globules
variation of fatty acid is influenced by…
genetics, stage of lactation, feed, and season
emulsion
a fine dispersion of minute droplets of one liquid in another in which it is not soluble or miscible
milk fat microstructure
fat is low density and…
hydrophobic
milk fat globule membrane benefits
cognitive/in formula
lipolysis
hydrolysis of milk fat
_____ can hydrolyze milk fat
lipase
excessive levels of lipolysis are undesirable and result in ___
rancidity
homogenization
exposes fat to lipase
pasteurization
inactivates lipase
melting
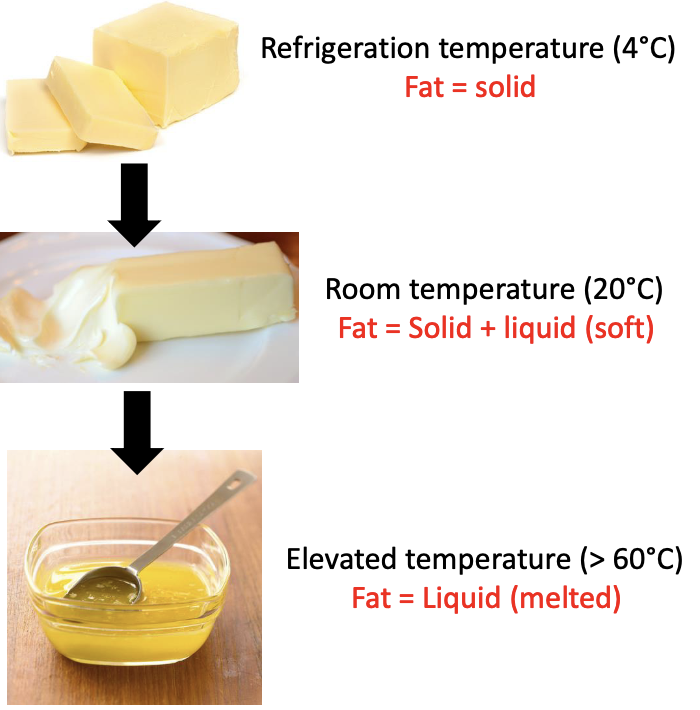
crystallization process
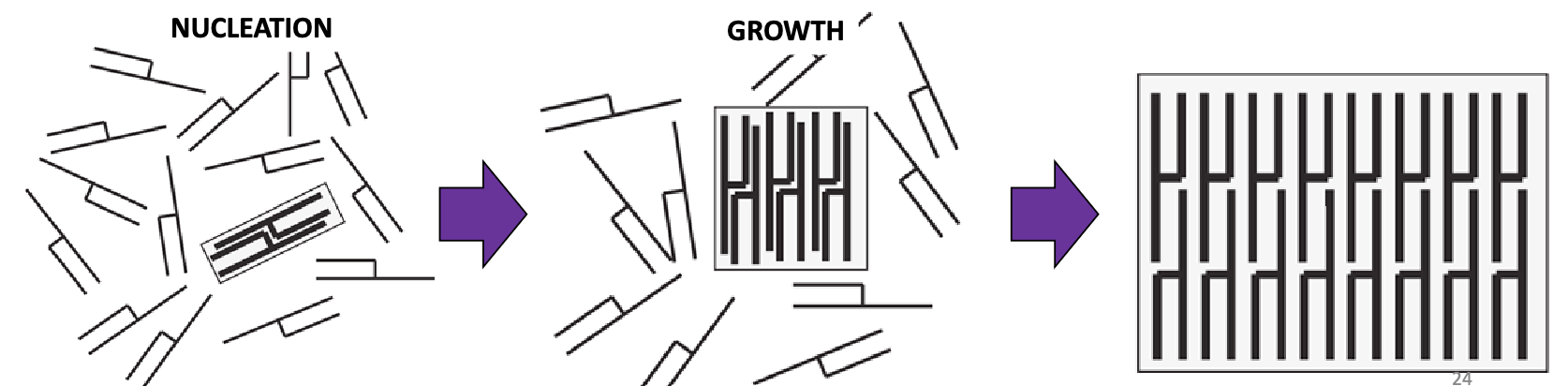
func. of caseins
delivery sys. for calcium and amino acids
milk proteins
Casein micelles: 80%
Whey Proteins: 20%
Isoelectric point
pH which molecule has no electric charge
______ is the major whey protein
β-lactoglobulin
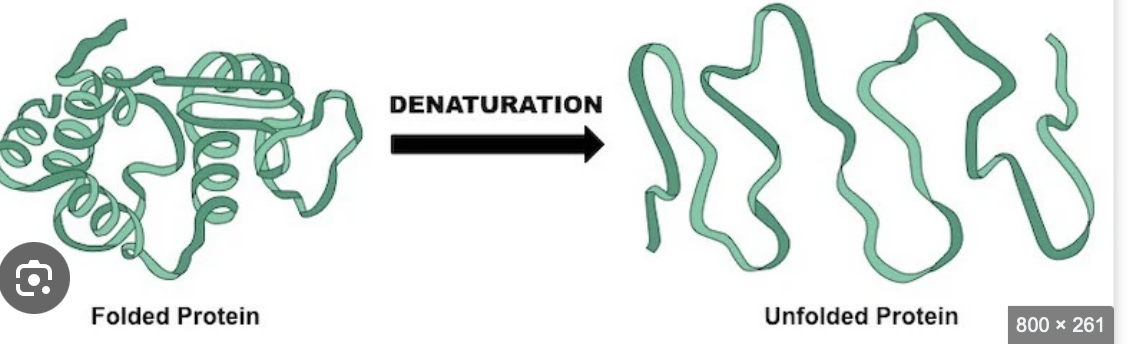
Denaturation
unfolding secondary and tertiary structure
β-lactoglobulin is not found in _____
human milk
α-lactalbumin is ___ heat stable than β-lactoglobulin
more
colostrum
richest source of bovine immunoglobulins
What percent milk is fat
4-5%
What contributes to the off flavors produced through the hydrolysis of fatty acids in milk fat?
The short chain fatty acids
Milk is __% protein
3.4
Which component of milk is most susceptible to variation?
Fat
Casein micelle
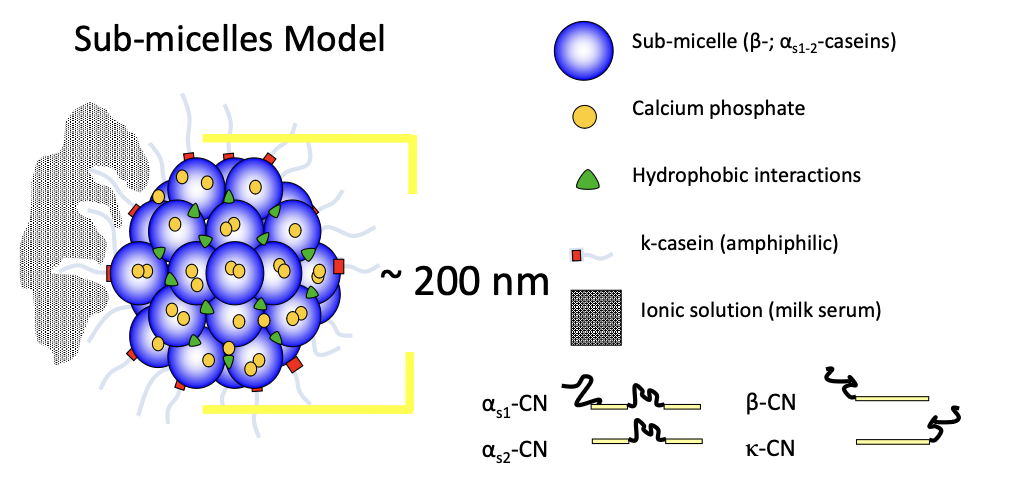
micelle
a loosely bound aggregation of several tens or hundreds of atoms, ions, or molecules, forming a colloidal particle
casein micelles carry ______ compounds
hydrophobic
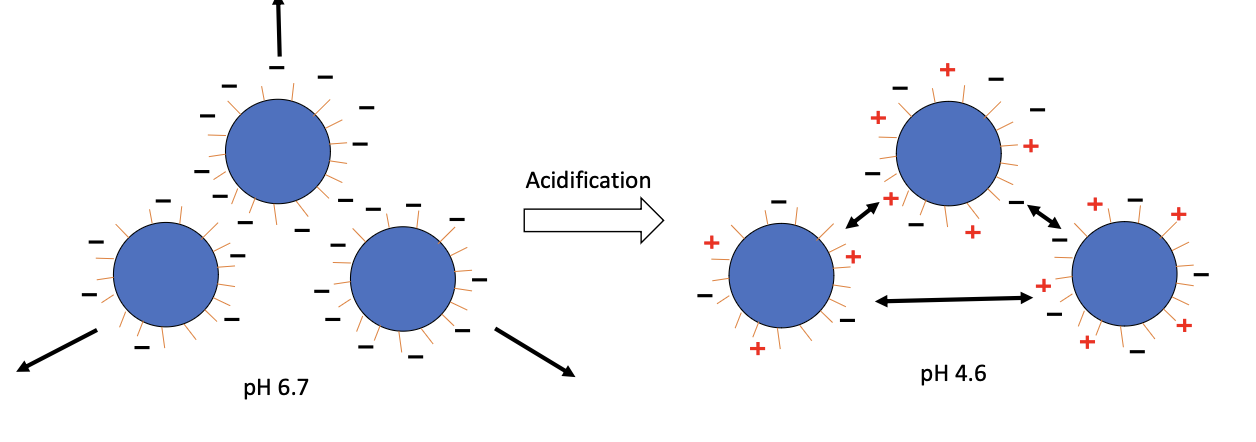
Isoelectric point of caseins
4.6
Acidification in CM
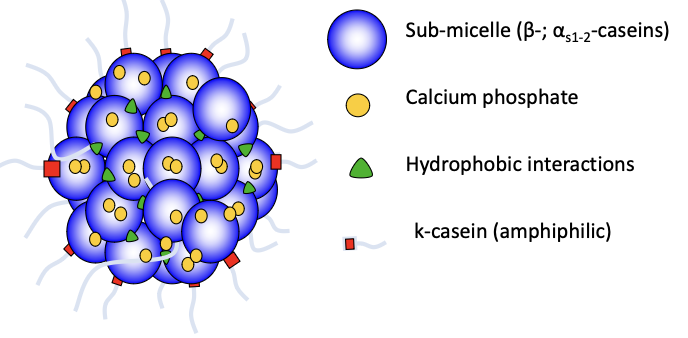
Casein Micelle structure
Acidification brings casein micelles closer to their ___________
Isoelectric point
Casein micelles are the _______ in many dairy products
building blocks
Casein proteins account for approximately what percent of milk proteins?
80%
Which casein(s) are located primarily in the hydrophobic core of casein micelles?
α-casein (alpha-casein)
β-casein (beta-casein)
True or False: High-temperature, short-time pasteurization denatures casein proteins?
False
Milk is high (> 50 mg minerals/100 g product) in which of the following minerals?
phosphorus
Fermented milks
are made from pasteurized milk using specific bacteria that lower the pH to 4.6, causing casein to coagulate.
Synersis
liquid (whey) is expelled from a gel or coagulated protein network, like in yogurt or curd, causing the gel to shrink and release moisture
Yogurt def
contains the lactic acid-producing bacteria (LB and ST)
yogurt contains not less than ___ percent milkfat and not less than___ percent milk-solids-not-fat
3.25, 8.25
yogurt has acidity of not less than ___ percent, expressed as lactic acid, or a pH of _____ or lower
0.7, 4.6
Yogurt processing diagram
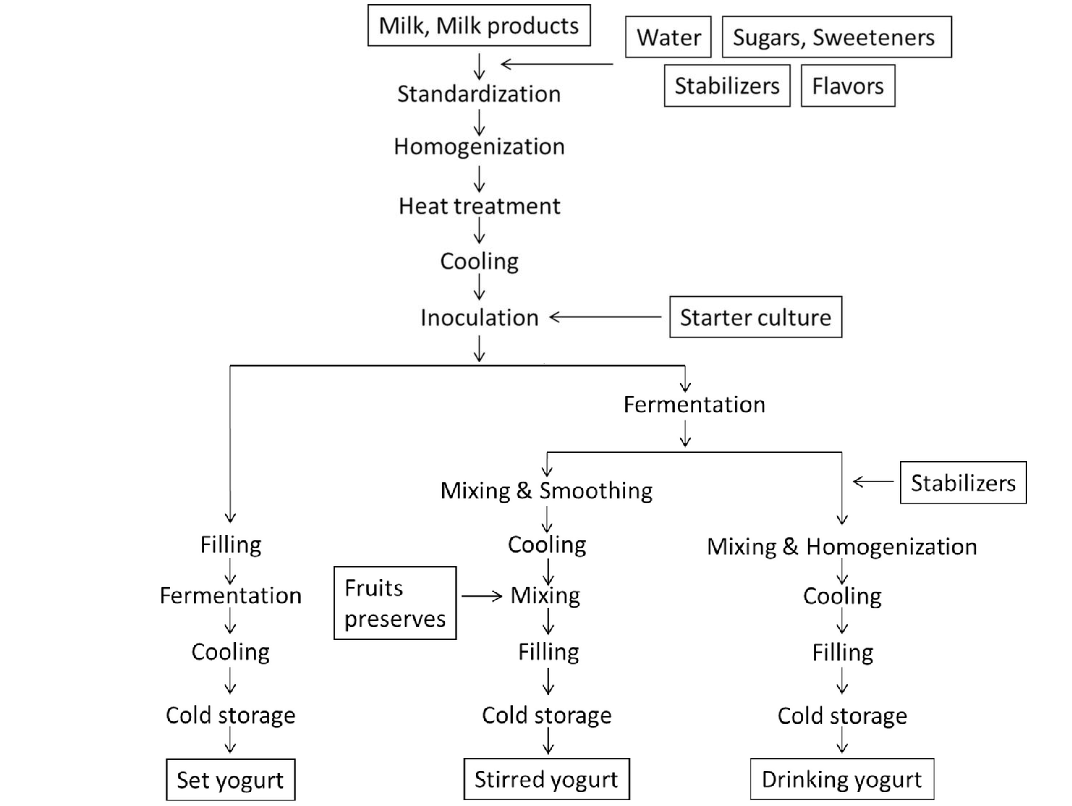
milk prior to high heat diagram
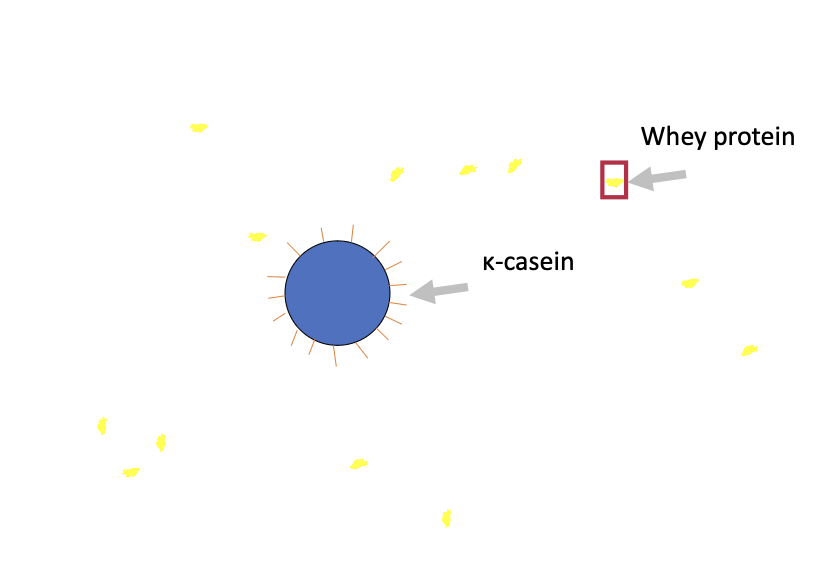
Whey denaturation
When milk is heated, whey proteins unfold and stick to casein. This changes milk’s texture and how it acts.
Yogurt steps simple:
Heat milk to kill germs (pasteurize).
Cool milk
Add starter culture
Fermentation
Coagulation: Acid makes milk thicken into yogurt.
Cool and store
Three production methods of greek yogurt
Centrifugal Separation, Ultrafiltration, milk proteins added
Centrifugal separation
Yogurt is run through a process until all solids are concentrated (whey removed)
Ultrafiltration
Whey is separated from the yogurt by specially designed filters, retaining more proteins
Milk proteins are added
No need for separation as milk proteins are added from the beginning
Can have gritty or chalky mouth-feel
by-product of greek yogurt
acid whey
What step in the yogurt manufacturing process causes the association between whey proteins with casein proteins?
Heat treatment
What is the main reason milk protein concentrate would be added to yogurt mix?
To increase the firmness of the yogurt coagulum
In contrast to regular yogurt, Greek yogurt is...
higher in protein
off flavors that can be caused by milk fat
hydrolytic rancidity
Oxidative rancidity
Lipase is inactivated by the _____ process.
Pasteurization
Which casein protein is located primarily on the surface of the casein micelle?
K-Casein
Glue of the casein micelle
Calcium Phosphate
Butter: Product with milk fat content not
less than ___ but less than ___
80%, 90%
• Butter has maximum water content of…
16%
Butter processing
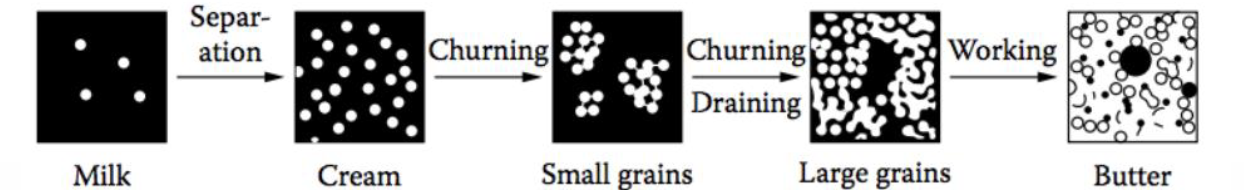
Solid fat content changes by…
changing temp. of storage
Aging
To promote crystallization of milk fat using
selected temperature regimes
churning
Phase inversion and emulsion destabilization from oil-in-water to water-in-oil by physical agitation
Butter manufacturing diagram
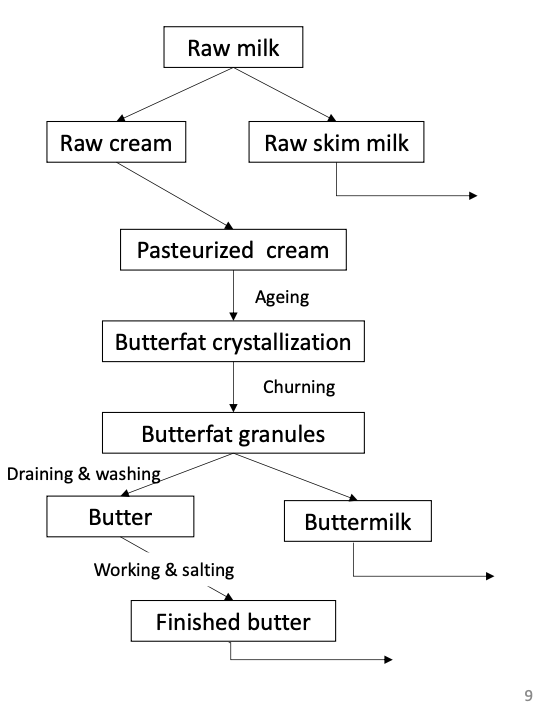
Traditional buttermilk
The liquid drained following fat coalescence
in butter manufacture
•High in phospholipids
Cultured buttermilk
lightly salted, fermented product
prepared usually from low-fat milk
• Uses mixed mesophilic starter
culture, which produced diacyetyl and acetic acid (in addition to lactic acid
Butteroil
not less than 99.6% mf