PHRM 3900: Patient-Centered Communication in Pharmacy Practice
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
What is the purpose of learning about patient-centered communication in Pharmacy practice?
to optimize patient outcomes by becoming an effective team member who effectively provides patient centered care
Patient-Centered Care is...
the practice of caring for patients in ways that are meaningful and valuable to the individual patient
Practicing patient-centered care involves
- listening to patients
- informing patients
- involving patients in their care
An example of patient-centered care is a
Patient-Centered Medical Home (PCMH)
Characteristics of a Patient-Centered Medical Home (PCMH)
- Physician-led practice
- Whole-person orientation
- Integrated and coordinated care
- Focus on quality and safety
- Access to care
To provide patient-centered care, the pharmacist must be able to
- understand all aspects of the patient's illness experience (the social, psychological, and biomedical factors)
- perceive each patient as a person; understand the patients unique experience of illness and the "personal meaning" it entails
- foster a more egalitarian relationship with patients; allow patients to be actively involved in dialogue and the decision-making surrounding treatment
- build a "therapeutic alliance" with patients by incorporating patient perceptions of the accessibility of interventions in treatment plans, defining mutually agreed-upon goals for treatment, and establishing a trusting, caring relationship with the patient
- develop self awareness of his or her personal effects on patients and how his or her own responses to patients may affect patient behavior
Pharmacist responsibilities in the Patient Care and Pharmacists Patient Care Process: Traditional Health Care Model
- identify and treat the most common health care in a population
- reactive
- healthcare provided by narrowly defined professional models due to lack of collaboration
Pharmacist responsibilities in the Patient Care and Pharmacists Patient Care Process: Preventative Health Care
- identify and prevent the most likely health care problems in a population
- prospective
- healthcare is inter-professional with patient as an active participant
Treatments for diagnosed diseases include:
- drugs
- surgery
- therapy
Quote by C. Everett Koop
"Drugs don't work if patients don't take them."
_____________________________ is a worldwide problem with reported rates between 25-50%.
Non-adherence
Why does non-adherence occur?
- lack of motivation
- patient health beliefs
- patient belief regarding medication (therapy)
The Institutes of Medication Safety reported that ____________________________ were common and preventable causes of harm.
medication errors
When dealing with patient non-adherence, what is important ?
- patient participation in self-care
- patient education regarding the risks and benefits of therapy
Pharmacists are _________________________________ for patients in the healthcare system.
frequent contact points
Helper and Strand in 1990 and 2001 provided:
- background rationale for "pharmaceutical care"
- a definition of "Drug Therapy Problems" pharmacists should target for intervention
The roles of pharmacists are outlines in:
- the Scope of Contemporary Pharmacy Practice: roles, responsibilities, and functions of pharmacists and pharmacy technicians
- Future vision of Pharmacy Practice
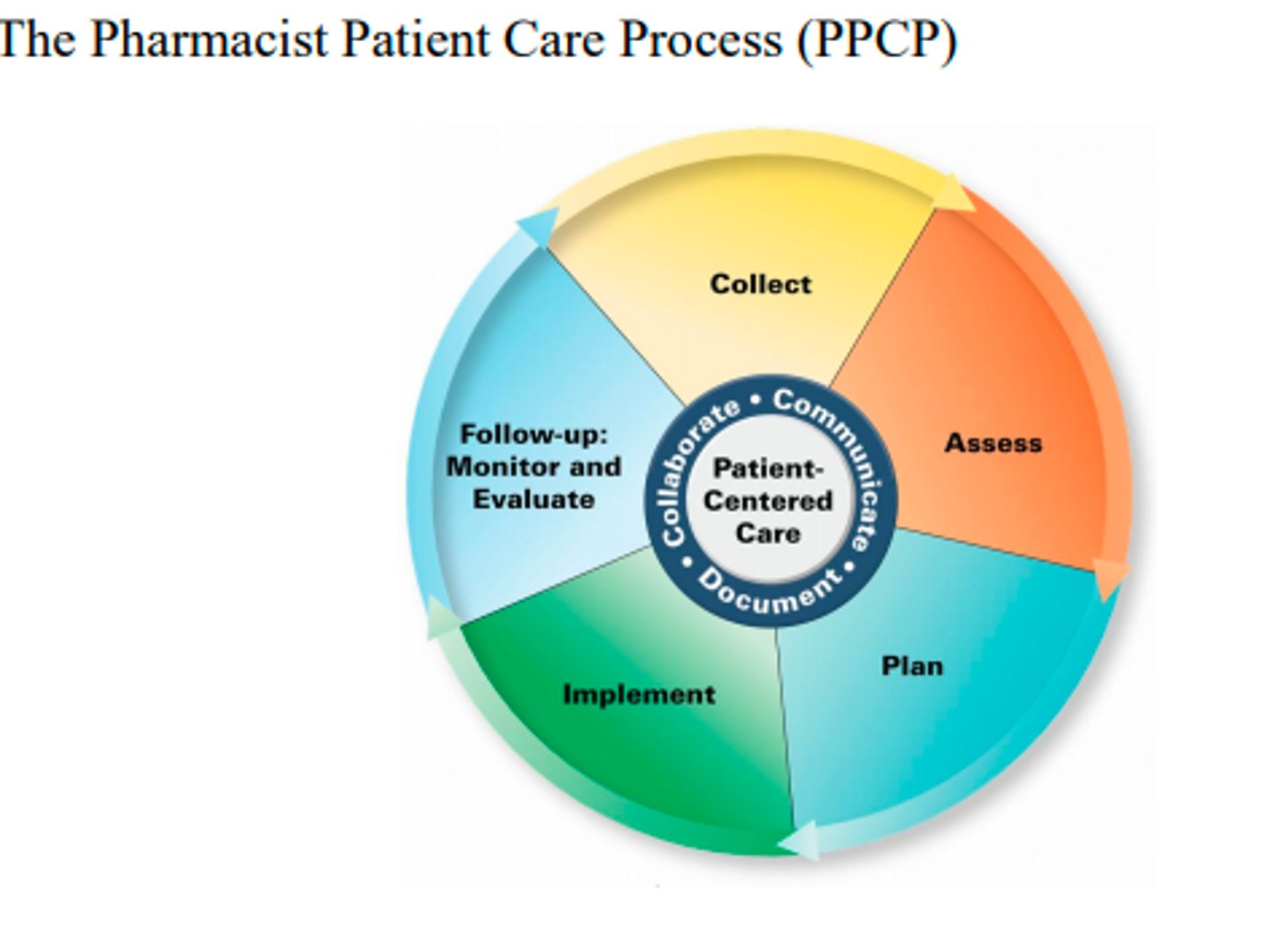
The Pharmacist Patient Care Process was released by
the Joint Commission of Pharmacy Practitioners (JCPP)
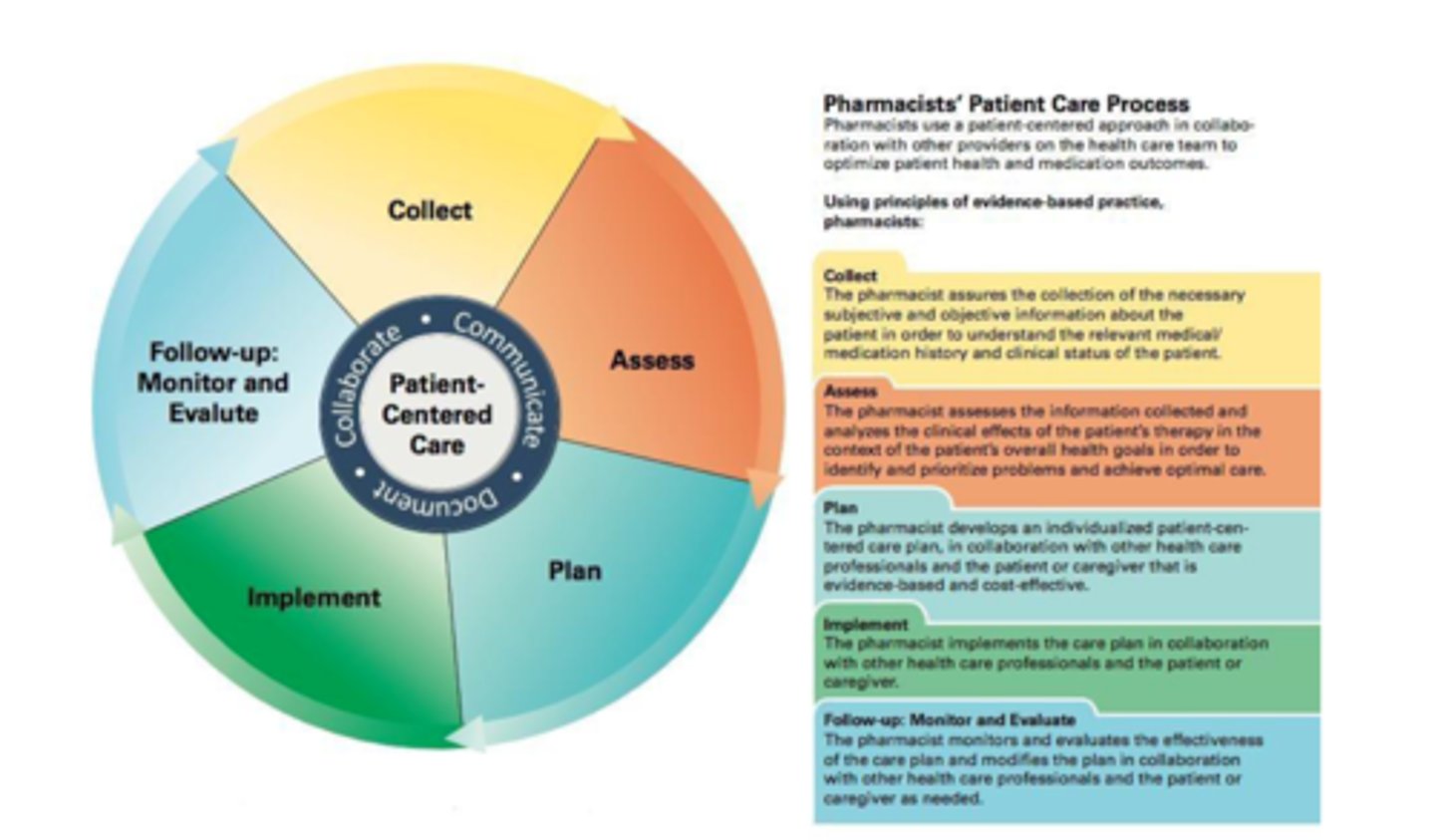
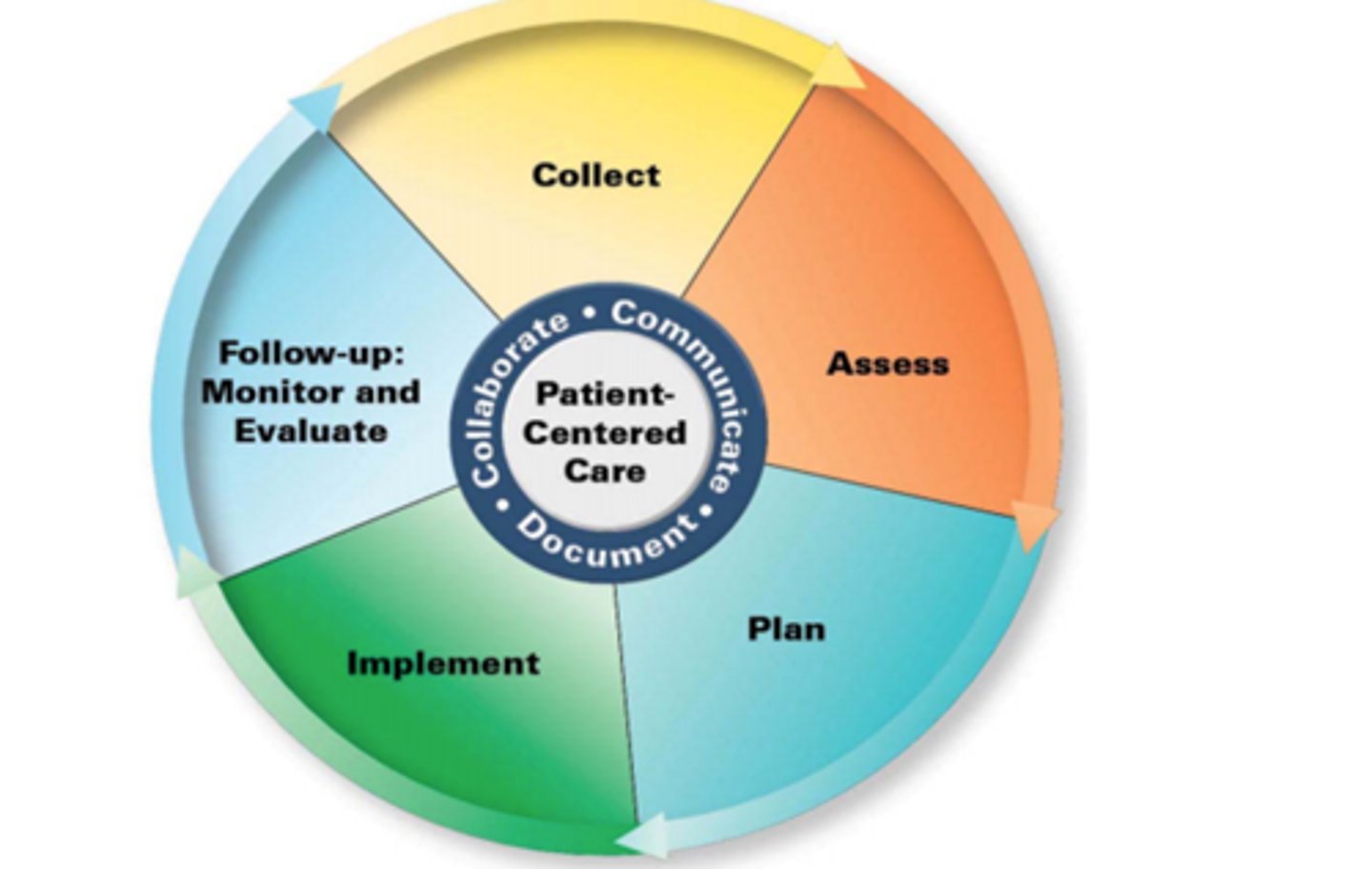
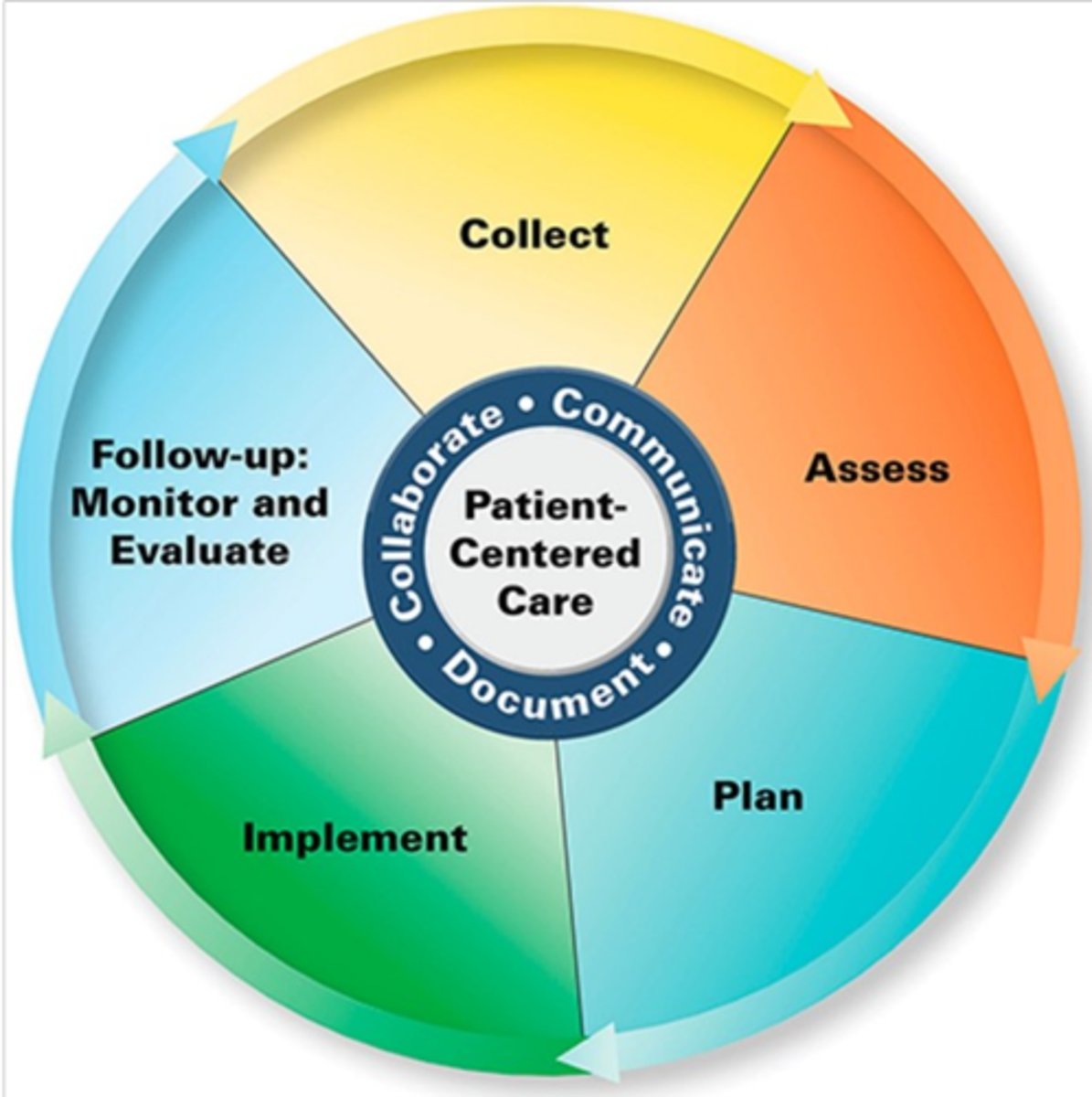
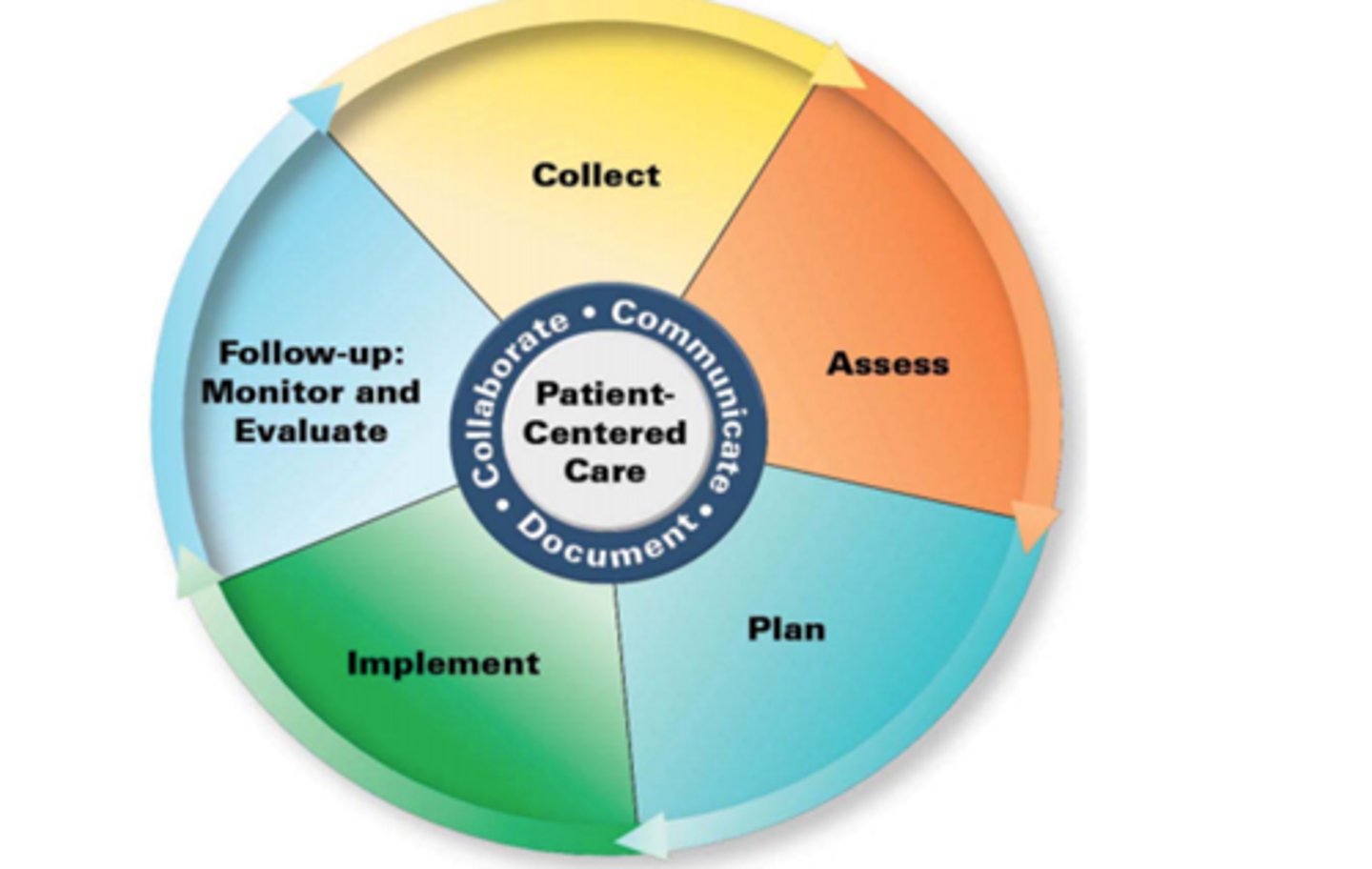
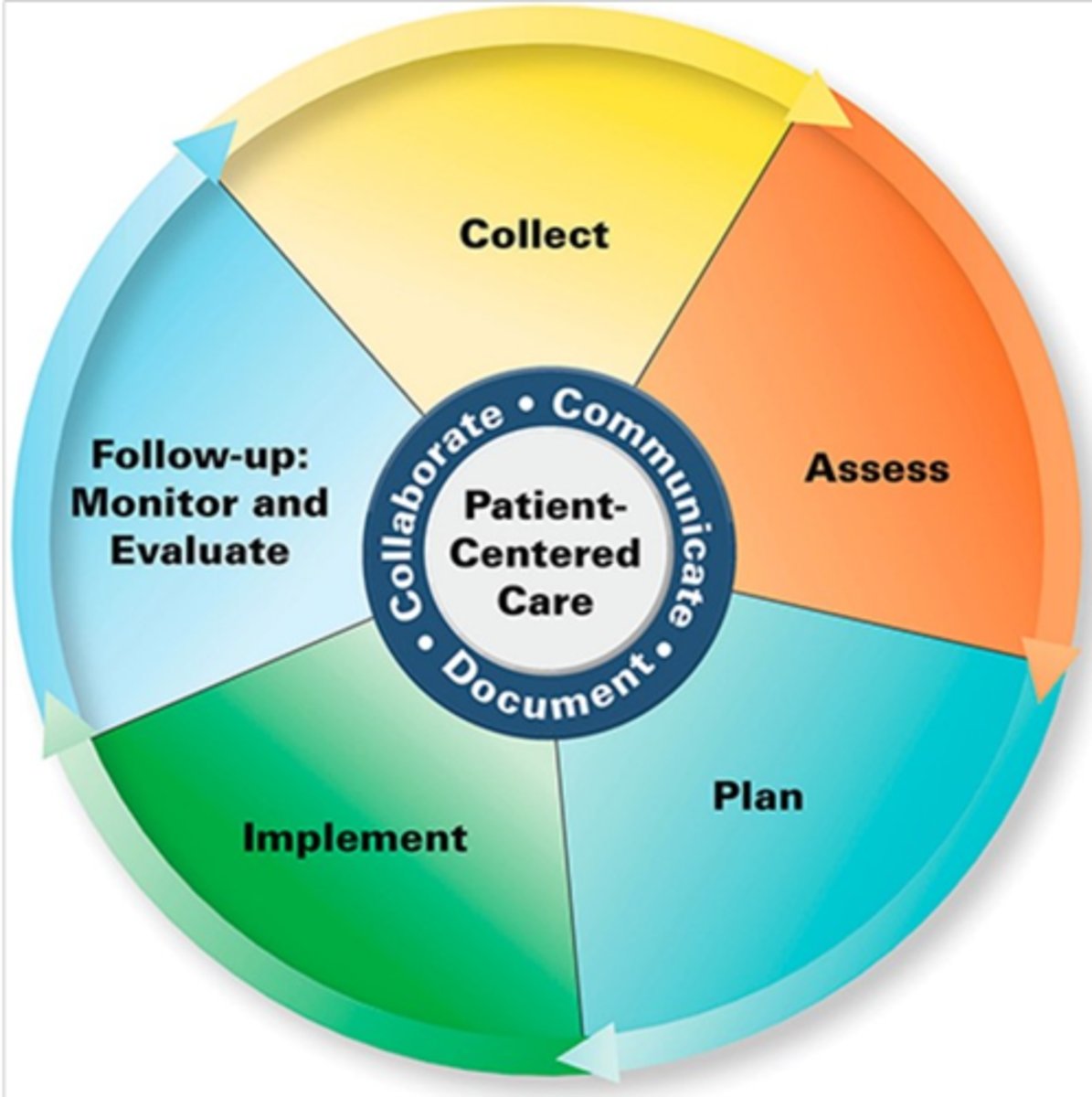
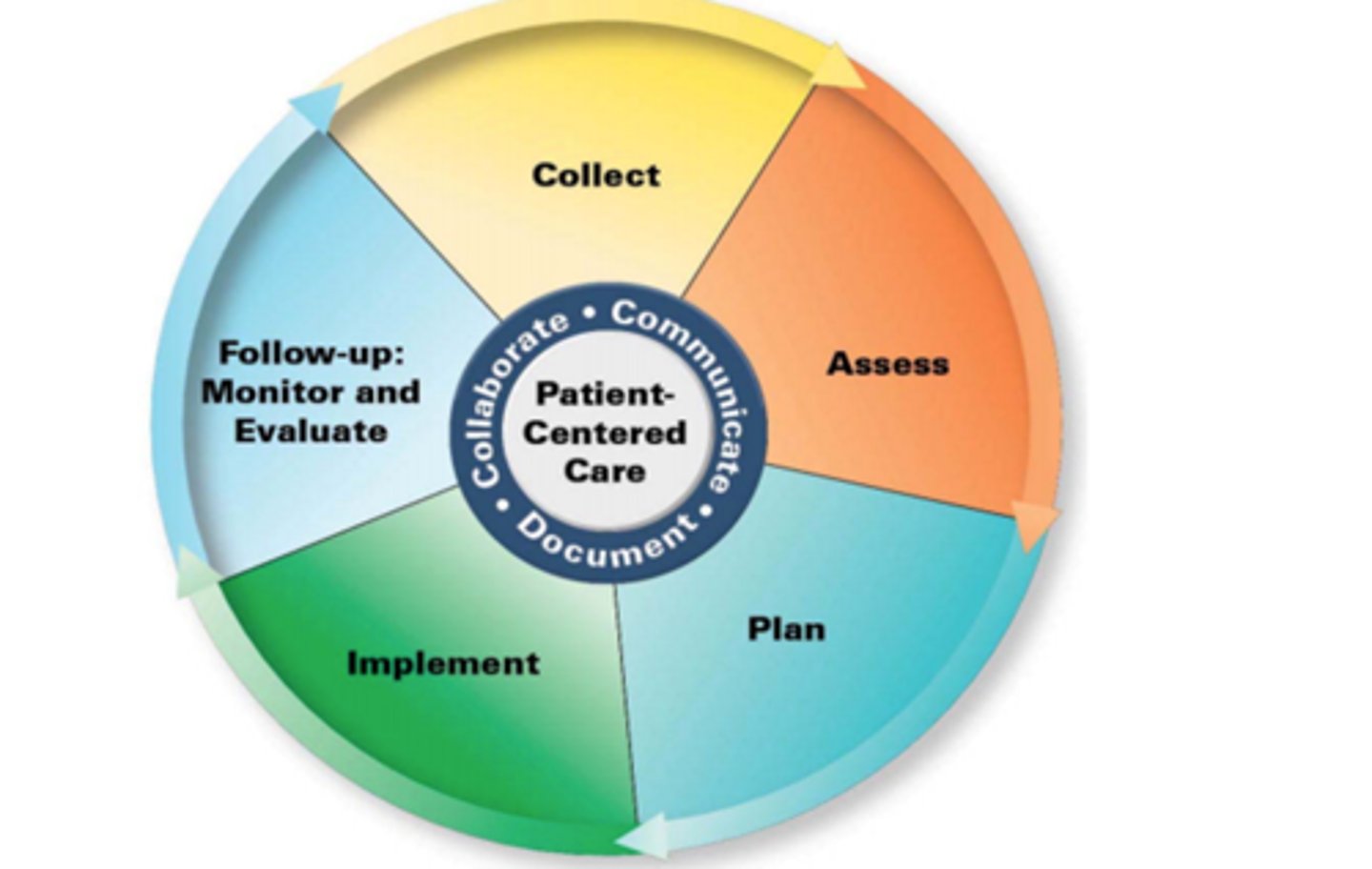
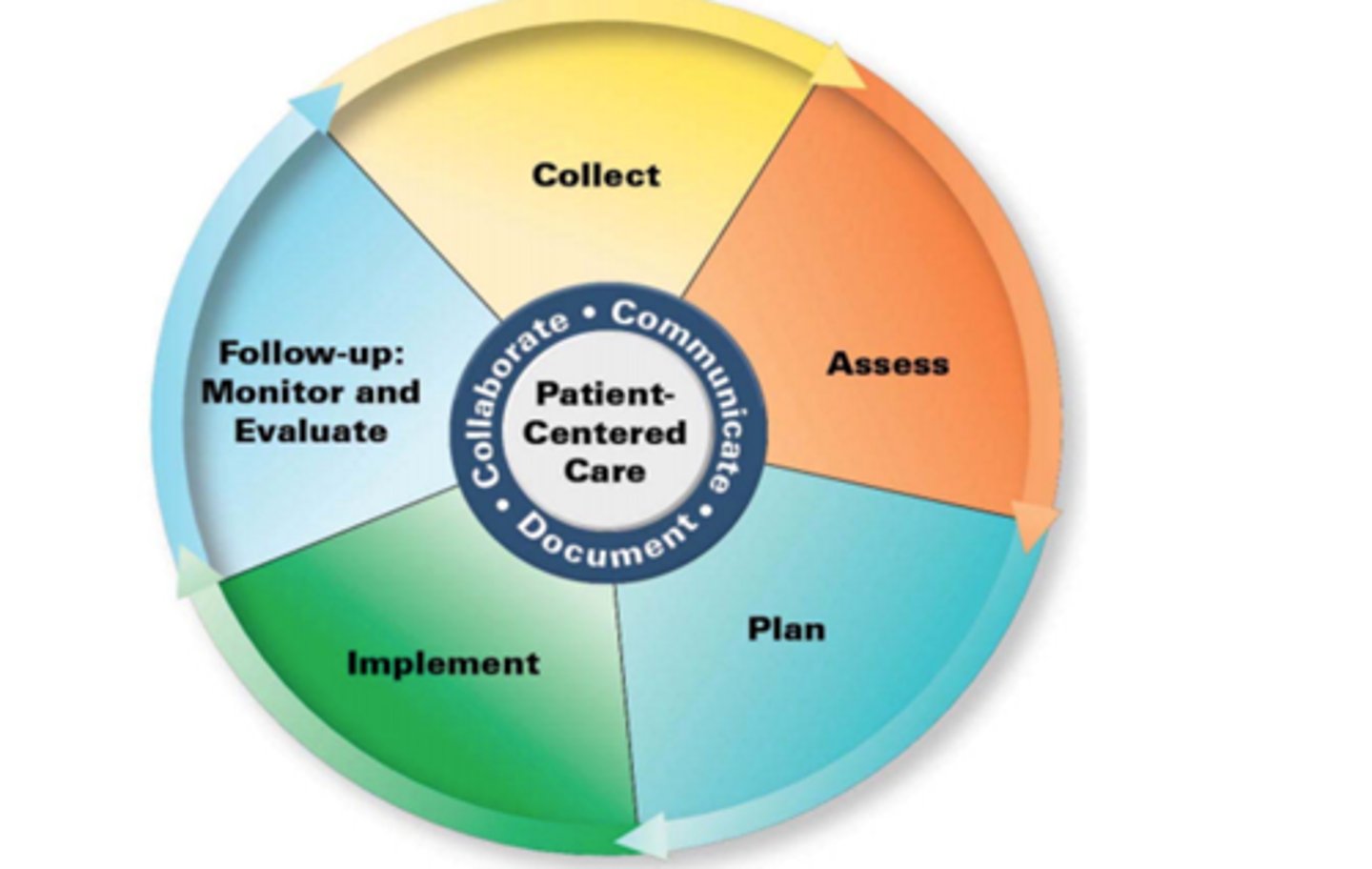
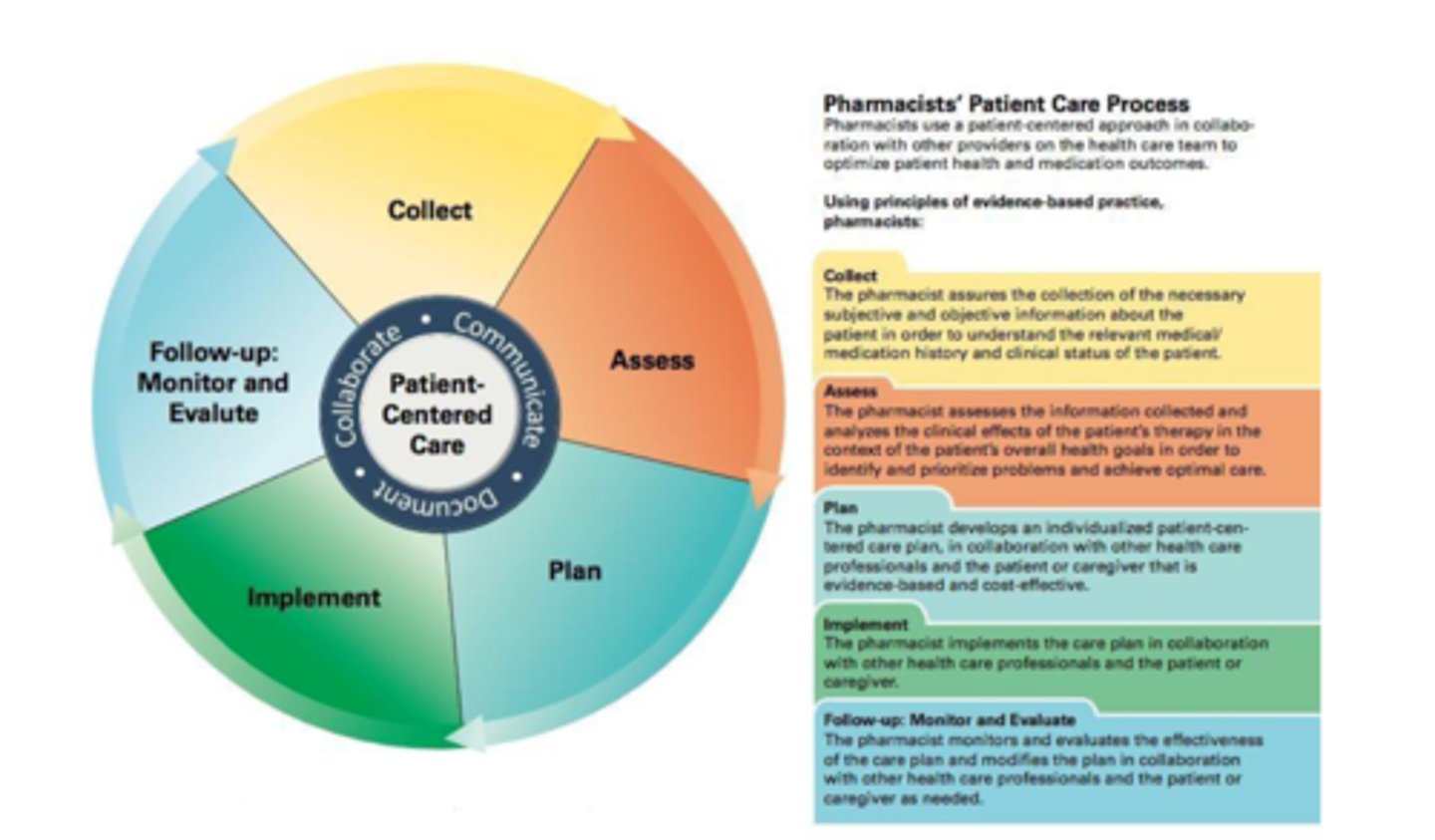
Steps in the Pharmacist Patient Care Process:
- Collect
- Access
- Plan
- Implement
- Follow ups (Monitor and Evaluate)
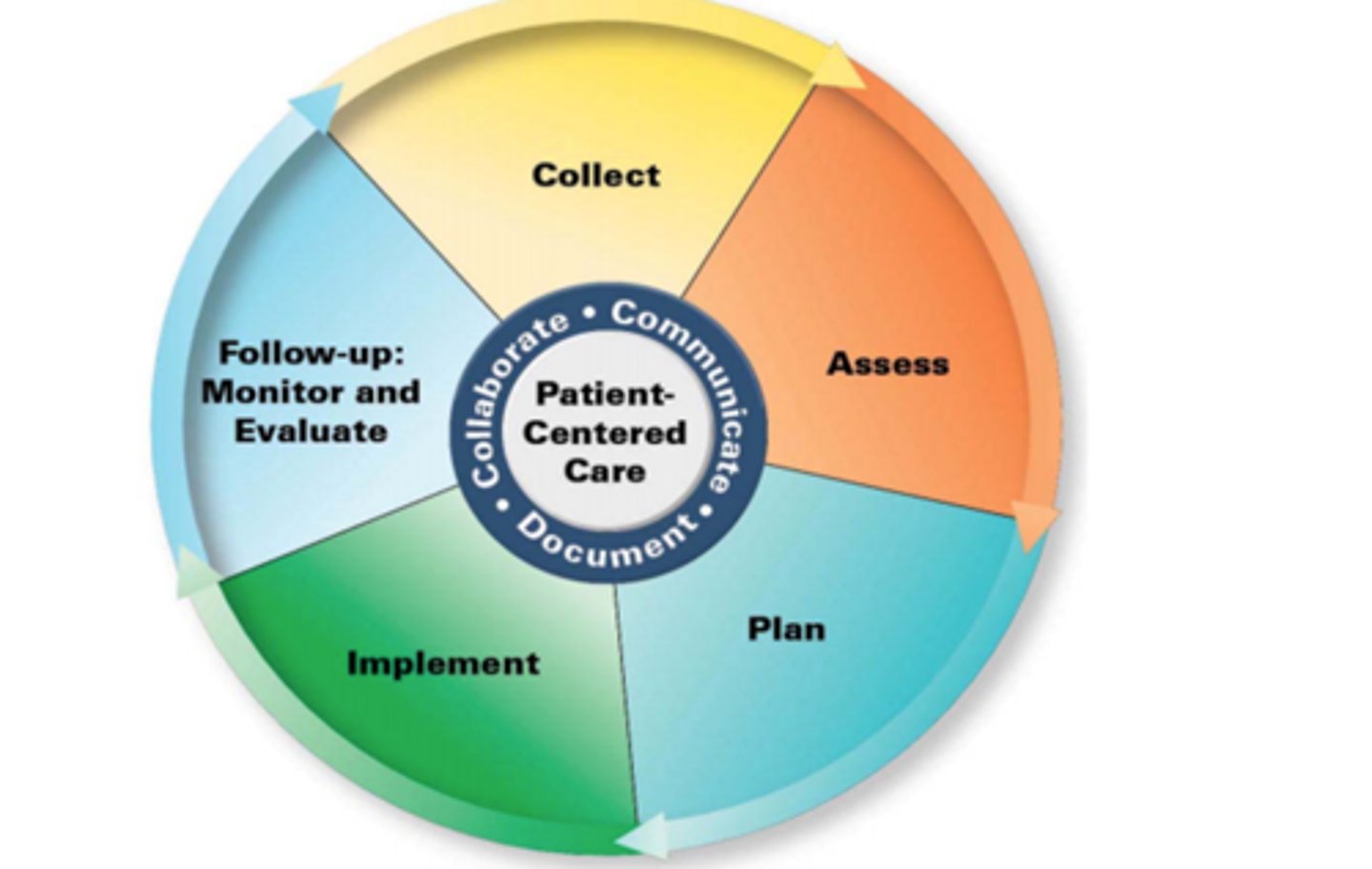
Pharmacist Patient Care Process: Collect
involves collecting information to understand the relevant medical/medication history and clinical status of the patient
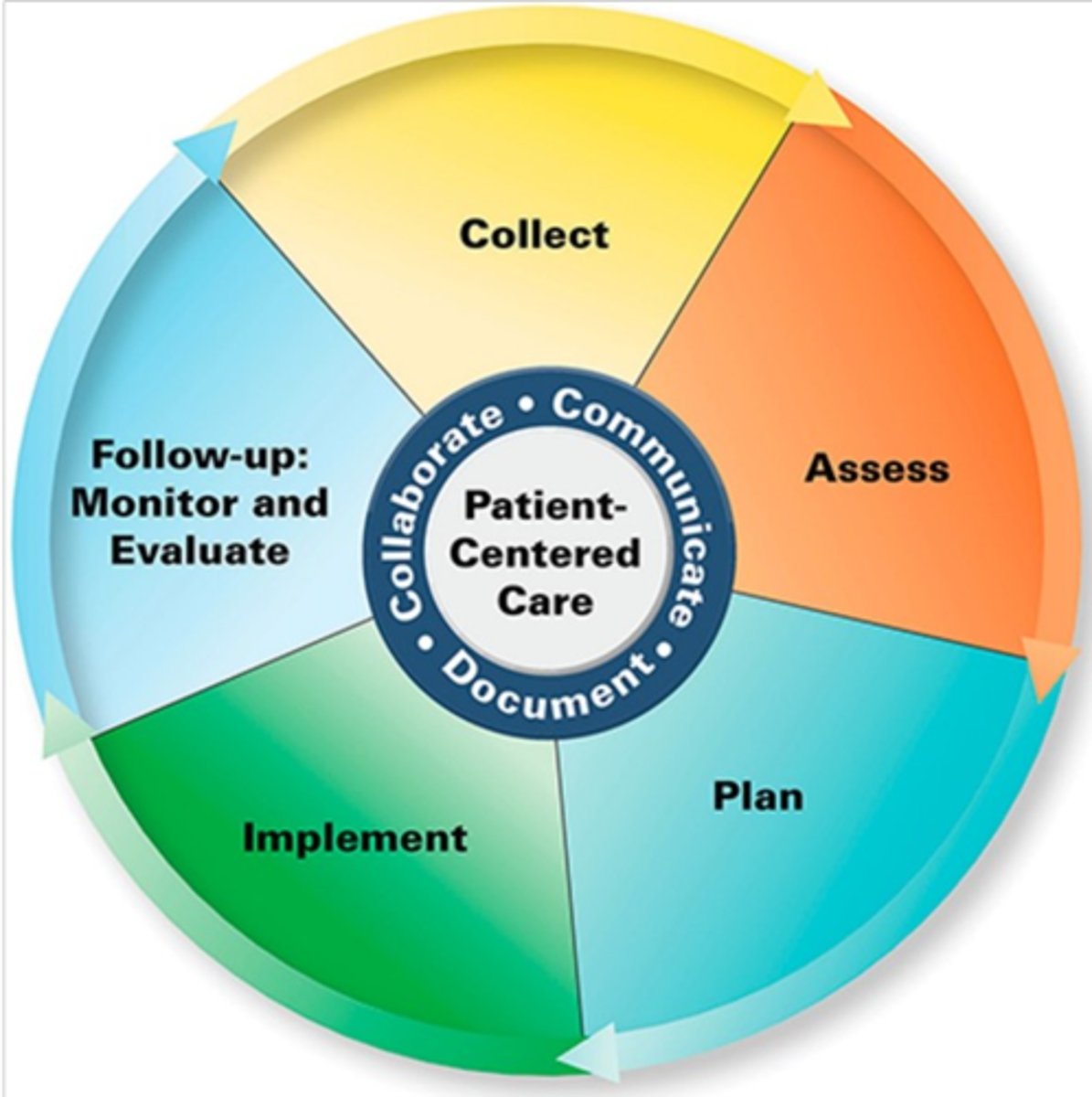
Information commonly collected during the Pharmacist Patient Care Process includes:
- a current medication list and medication use history
- relevant health data (past and current medical history, labs, etc.)
- patient lifestyle habits, preference and beliefs, health and functional goals, socioeconomic factors
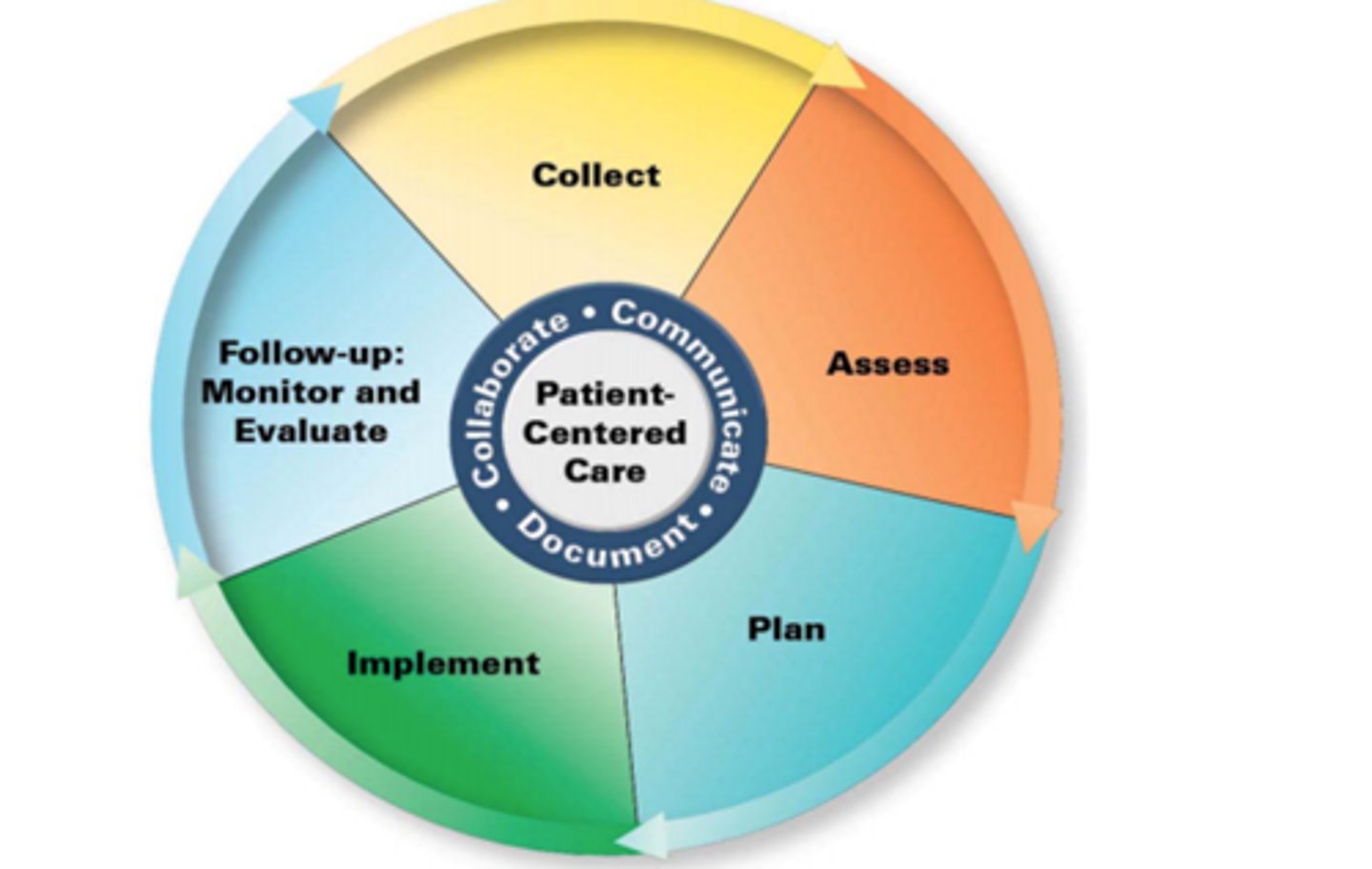
Types/Sources of information collected during the Pharmacist Patient Care Process:
- subjective information (comes from patient or caregiver's perspective)
- objective information (is observable and measurable data)
GA Patient Record Systems include what information?
- patient's full name
- address and phone number
- date of birth/ age
- gender
- drug list (profile) including all Rx, OTC, herbal supplements, devices, etc.
- medication allergies and/or drug reactions
- chronic medical conditions (diagnoses)
- pharmacist comments
GA Patient Record Systems must be kept around for at least _______________.
2 years
Pharmacist Patient Care Process: Assess
involves assessing information collected and analyzing the effects of the patient's therapy
Assessments made during the Pharmacist Patient Care Process include:
- disease risk, immunization status, and need for preventative care
- disease state control
- patient adherence
- factors related to current health status
- appropriateness, effectiveness, and safety of therapy
Drug Therapy Problems (DTP) lists are categorized into seven major classes according to the Cipolle-Strrand-Morley (2012) criteria. These classes include:
- unnecessary drug therapy
- need additional drug therapy
- ineffective drug therapy
- dosage too low
- dosage too high
- adverse drug reaction (ADR)
- non-compliance
In Georgia, the assessment phase of the Pharmacist Patient Care Process is ensured by
the GA PRO-DUR (prospective) program
Pharmacist Patient Care Process: Plan
involves developing a patient-centered care plan
A plan created during the Pharmacist Patient Care Process should:
- assess medication-related problems and optimize medication therapy (including specific recommendations to initiate or adjust therapy to meet outcome goals)
- set goals of therapy for achieving clinical outcomes
- monitor for safety and efficacy of therapies
- support continuity of care and plan for follow up
- be completed in collaboration with other health care professionals and the patient
Pharmacist Patient Care Process: Implement
involves implementing a plan in collaboration with other health care providers and the patient
When implementing a plan during the Pharmacist Patient Care Process, the pharmacist should:
- address medication/health-related problems
- initiate, modify, discontinue, or administer medication therapy as authorized
- engage in preventative care strategies (i.e. immunizations)
- provide patient education and self management training
- coordinate referrals and follow up appointments
In Georgia, the plan and implement phases of the Pharmacist Patient Care Process are ensured by...
the GA Patient Counseling Law
Pharmacist Patient Care Process: Follow Up
involves monitoring and evaluating effectiveness of care plan
Following up during the Pharmacist Patient Care Process involves:
- evaluating progress towards meeting goals and outcomes of therapy (cure disease, reduce or eliminate symptoms, arrest or slow disease, and disease prevention)
- modifying plan in collaboration with other health care professionals and the patient
- repeating steps 1-4 and updating the care plan as needed
____________________________ should be done at the end of the Pharmacist Patient Care Process.
Documemntation
Documentation of the Pharmacist Patient Care Process serves as:
- a communication tool with other healthcare providers which improves patient care and outcomes and enhances continuity of care
- a legal permanent health record
- a means to ensure compliance with the laws and regulations
- protection against professional liability
- a justification for reimbursements
- quality assurance tool
Documentation of Pharmacist Patient Care Process can be carried out as:
- notation formats (SOAP note and E-care plan)
- verbal communication via SBAR
Who is at the center of the Pharmacist Patient Care Process?
the patient
What is the importance of communication in meeting your patient care responsibilities as a pharmacist?
- it establishes an ongoing trusting relationship between you and your patients
- it allows for the exchange of important information
Communication is vital in meeting your patients care responsibilities because it provides the exchange of information necessary to:
- access you patients health conditions
- reach decisions on treatment plans
- implement the plans, evaluate the effects of treatment on your patient's quality of life
- enhance patient safety
Therapy monitoring outcomes consist of:
- objective facts (lab tests)
- subjective facts (reported by patients)
Subjective reported facts are
relayed by patients and can yield key information in treatment decision making process
Sites with resources that advice on encouraging a more active role in therapeutic monitoring:
- the Joint Commission (2016): "speak up"
- the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ)(AHRQ 2017b)
- the National Council on Patient Information and Education (NCPIE)(2017)
We don't use drugs because patients have a drug deficit, we use drugs to
treat an illness
A patient-centered view of the medication use process:
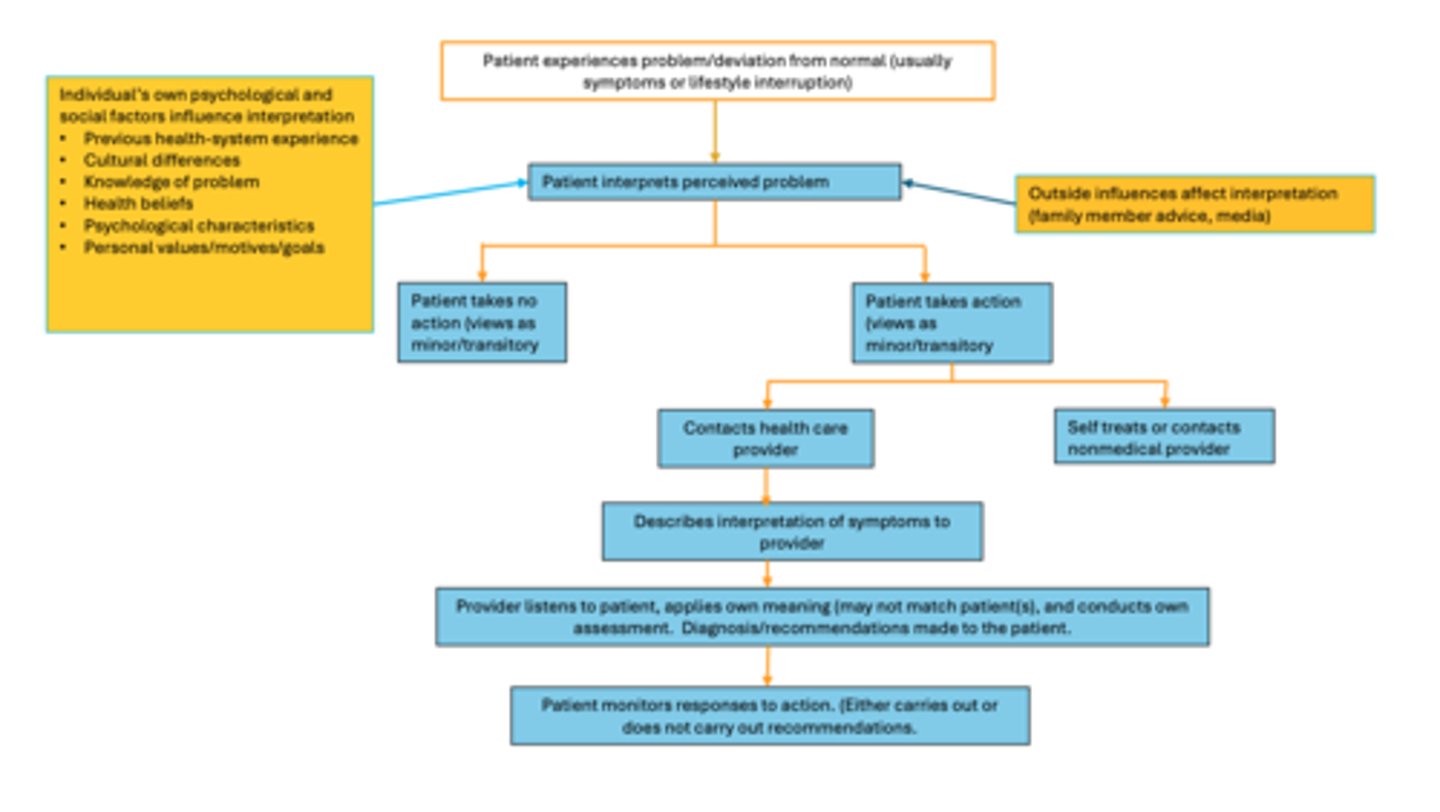
A patient-centered view of medication use process: Problem
many prescriptions are never filled or picked up
Why are many prescriptions never filled or picked up?
- economic concerns
- external barriers
- concerns regarding diagnosis
- concerns over therapy
Approximately 20% of people report that...
they take less medication than prescribed due to cost
Targeted Intervention Pyramid
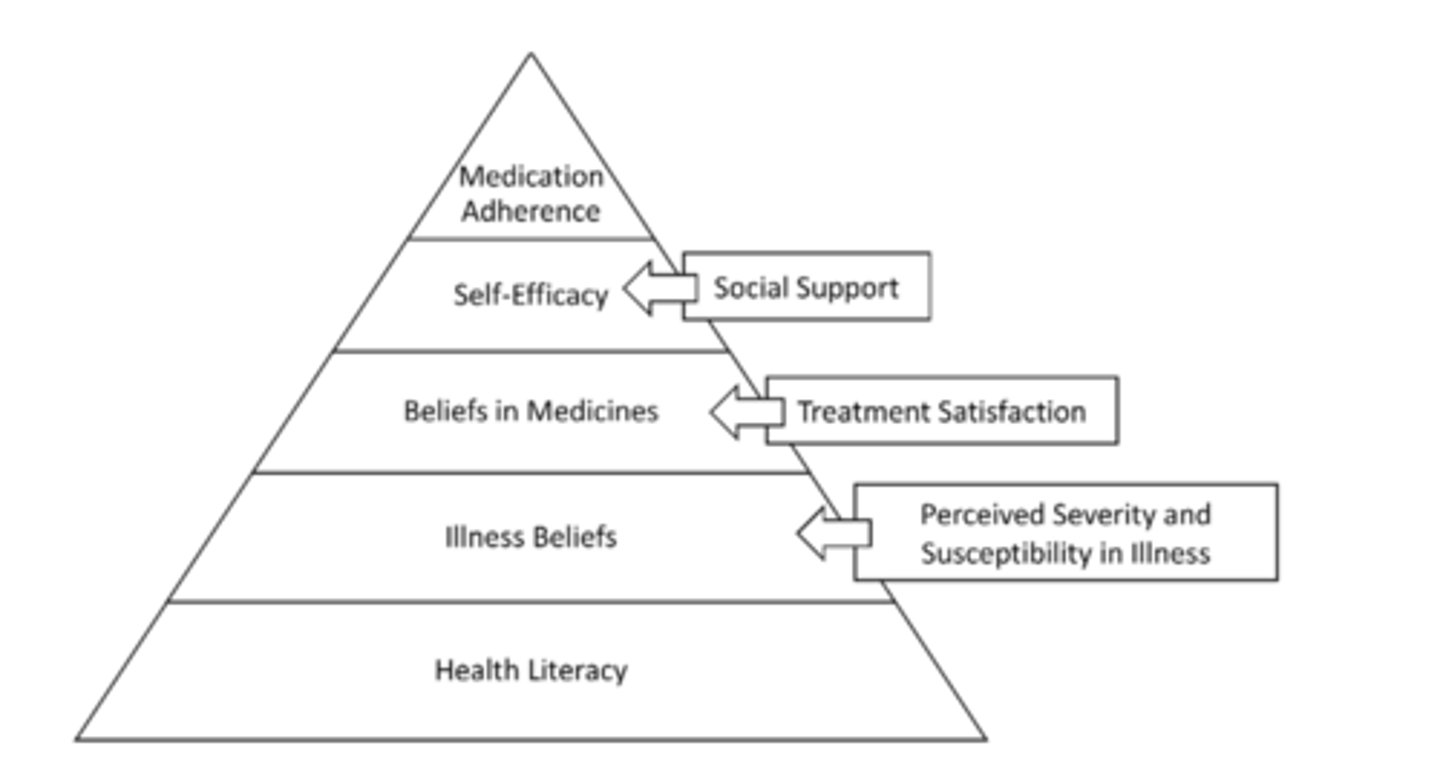
Pharmacists should encourage patients to share their experiences with therapy because:
- patients may have unanswered questions
- patients may have misunderstanding or misperceptions
- patients may experience problems related to therapy and not tell you
- patient may "monitor" their own response to treatment without involving you
- patients may make their own decisions regarding therapy
- patients may not reveal key information to you unless you initiate a dialogue
Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act (OBRA) of 1990
landmark legislation that requires drug therapy review before filing prescriptions and mandates that states establish standards for patient counseling
Three parts of the Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act (OBRA) of 1990:
- Maintaining Patient Records
- Prospective Drug Utilization Review (Pro-DUR)
- Patient Counseling Standards
Why is the Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act (OBRA) of 1990 important?
- it assures information is available
- it is proactive, not reactive
- it defines responsibility
States must comply with Drug Utilization Review (DUR) requirements/guidelines including:
- providing patient counseling information to pharmacists
- maintaining detailed patient profiles to document prospective drug reviews
The state of Georgia has set its own standards for patient counseling. These standards help ensure pharmacists provide...
consistent and comprehensive patient counseling
The GA Patient Counseling Law states that
upon receipt of a prescription drug order and following a review of the patient's records, the pharmacists or the pharmacy intern operating under the direct supervision of the pharmacists shall personally offer to discuss matters which will enhance or optimize drug therapy with each patient or caregiver of such patient
Patient counseling involves discussing the following information with the patient:
- name of drug (generic)
- intended use and expected action
- route, dosage form, and dosage and administration schedule
- special directions for preparation, storage, or administration
- precautions to be observed while taking
- common side effects and how to avoid them or actions required if they occur
- techniques for self monitoring of drug therapy
- potential interactions or therapeutic contraindications
- refill information
- what to do if you miss a dose
- any other information that particular patient may need to ensure safe use
GA PRO-DUR prospective program involves looking at
- over/ underutilization
- therapeutic duplications
- drug-disease interactions
- drug-drug interactions (including OTC)
- incorrect dosage or duration of treatment
- drug allergy interactions
- clinical abuse (misuse)
Georgia Pharmacy Practice Act
- AKA Title 26 - Food, Drugs, and Cosmetics
- chapter 4 is specific for pharmacists and pharmacies
- article 5 of chapter 4 specific rules for prescription drugs

Pharmacies must make the state-mandated counseling information available to their pharmacists to ensure
patients receive comprehensive guidance on their medications
Pharmacists are required to offer counseling to each patient or caregiver who presents a prescription. This can be done:
- in person
- via toll-free telephone (if the patient is located at a distance)
Pharmacists must document
any refusal of counseling by the patient
Pharmacists are especially responsible for counseling patients on any matters the pharmacist considers ________________________, so patients have the information they need to use their medications safely and effectively.
significant