2.4 Immune system
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is an antigen?
A foreign molecule that stimulates an immune response, leading to the production on an antibody
How are cells identified by the immune system?
Each type of cell has specific molecules on its surface that identify it
What type of cells can the immune system identify?
Pathogens (viruses,bacteria)
Cells from other organisms (organ transplants)
Abnormal body cells (tumour, cancer)
Toxins (poisons released by some bacteria)
What is the non-specific immune response?
Phagocytosis
What is the cellular response?
T lymphocytes forming clones which stimulate cytotoxic t cells, specific B cells and phagocytes
What is the humoral response?
B lymphocytes forming clones which differentiate into B plasma cells or B memory cells
Describe the process of phagocytosis/non-specific immune response
Phagocyte recognises foreign antigens on pathogen
Phagocyte engulfs pathogen by moving around it
Pathogen is contained in phagosome in cytoplasm of phagocyte
Lysosome fuses with phagosome and releases lysozymes
Lysozymes digest pathogen
Antigens presented on surface of phagocyte to stimulate an immune response
Describe the process of the cellular response
T lymphocytes recognise antigens on surface of antugen presenting cells (infected cells, phagocytes, tumour cells, transplanted cells)
Specific T helper cells with complimentary receptors on the surface bind to antigens on antigen-presenting cell
This activates the T cell and causes it to divide by mitosis to form clones which stimulate cytotoxic T cells, specific B cells, phagocytes
What do cytotoxic T cells do?
Kill infected cells/tumour cells
Describe the process of the humoral response
Clonal selection -
Specific B lymphocyte with complimentary receptors on cell surface bind to antigen
This is stimulated by helper T cells
B lymphocyte divides rapidly by mitosis to form clones which differentiate into B plasma cells or B memory cells
What do B plasma cells do?
Secrete large amounts of antibodies
What do B memory cells do?
Remain in the blood for secondary immune response
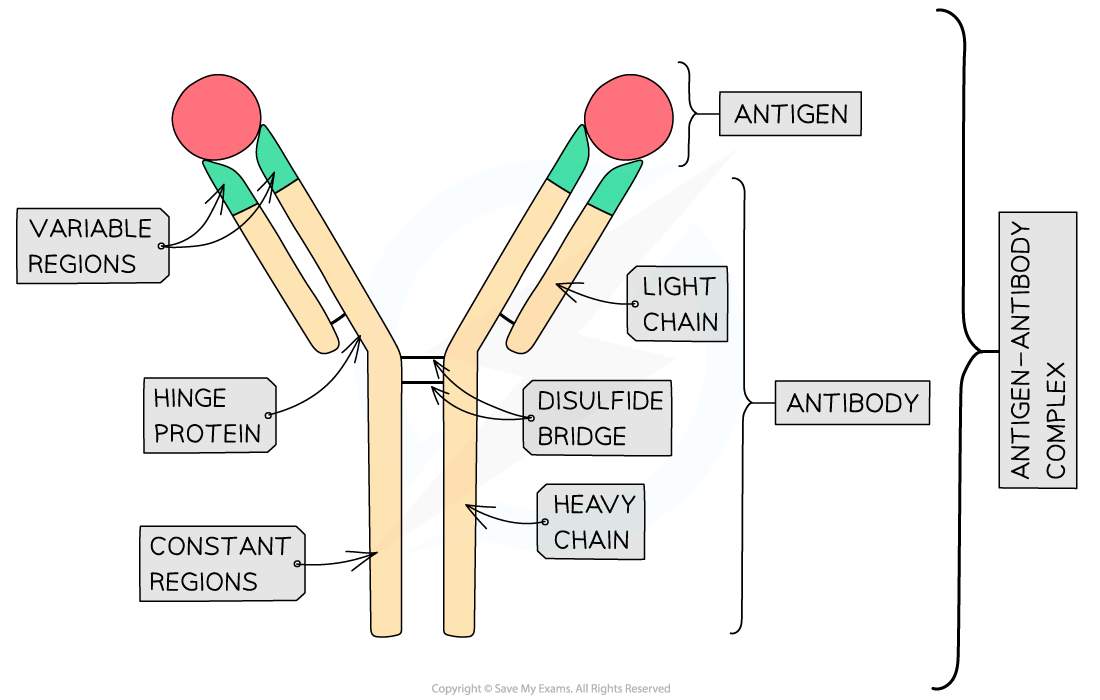
What are antibodies?
Quaternary structure proteins secreted by B lymphocytes (eg plasma cells) in response to specific antigens
What do antibodies bind to and what does this form?
Antibodies bind to specific antigens, forming antigen-antibody complexes
Label the structure of an antibody
What is agglutination?
Antibodies bind to 2 pathogens at once causing them to clump together
How do antibodies lead to the destruction of pathogens?
Antibodies bind to antigens on pathogens, forming an antigen-antibody complex (specific tertiary structure so binding site/variable region binds to complementary antigen)
Each antibody binds to 2 pathogens at a time, causing agglutination (clumping) of pathogens
Antibodies attract phagocytes
Phagocytes bind to the antibodies and phagocytosis many pathogens are once
Explain the primary immune response
Happens during first exposure to antigen
Antibodies are produced slowly and at a lower concentration
Takes time for specific B plasma cells to be stimulated to produce specific antibodies
Memory cells are produced
Explain the secondary immune response
Happens during second exposure to antigen
Antibodies are produced faster and at a higher concentration
B memory cells rapidly undergo mitosis to produce many plasma cells which produce specific antibodies
What is a vaccine?
Injection of antigens from dead or inactive pathogens, stimulating the formation of memory cells
Explain how vaccines protect individuals from disease
Specific B lymphocyte with complimentary receptor binds to antigen
Specific T helper cell binds to antigen-presenting cell and stimulates B cell
B lymphocyte divides by mitosis to form clones which differentiate into B plasma cells which release antibodies or B memory cells
On secondary exposure to antigen, B plasma cells rapidly divide by mitosis to produce B plasma cells. These release antibodies faster and at a higher concentration
Explain how vaccines protect populations against disease
Herd immunity - large proportion of populations against vaccinated, reducing spread of pathogen
Large proportion of population immune so do not become ill from infection
Fewer infected people to pass pathogen on/unvaccinated people less likely to come in contact with someone with disease
Describe the differences between active and passive immunity
Active - Initial exposure to antigen (eg vaccine or primary infection)
Passive - No exposure to antigen
Active - Memory cells involved
Passive - No memory cells involved
Active - Antibodies produced and secreted by B plasma cells
Passive - Antibodies introduced from another organism (eg through breast milk)
Active - Slow so takes longer to develop
Passive - Faster acting
Active - Long term immunity as antibody can be produced in response to a specific antigen again
Passive - Short term immunity as antibody hydrolysed
Explain the effect of antigen variability on disease and disease prevention
Antigens on pathogens change shape/tertiarystructure due to gene mutations
No longer immune (from vaccines or prior infection) as B memory cells receptors can’t bind to changed antigen on secondary exposure and specific antibodies aren’t complimentary/can’t bind to changed antigen
Examples - yearly new flu vaccines
Label the structure of a HIV particle
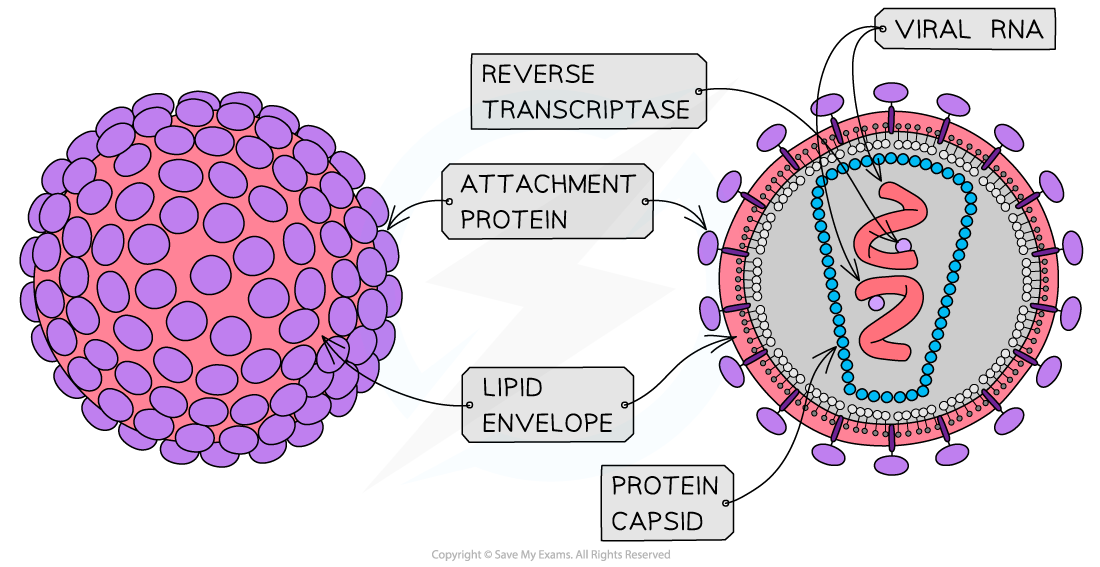
Describe the replication of HIV in T-helper cells
HIV attachment proteins attach to receptors on helper T cell
Lipid envelope fuses with cell-surface membrane, releasing capsid into cell
Capsid uncoats, releasing RNA and reverse transcriptase
Reverse transcriptase converts viral RNA to DNA
Viral DNA inserted into helper T cell DNA
Viral proteins are produced
Virus particles assembled and released from cell
What does AIDS stand for?
Acquired immune deficiency syndrome
Explain how HIV causes the symptoms of AIDS