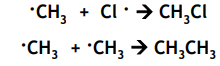Alkanes
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What are alkanes?
Saturated hydrocarbons
What is petroleum?
A mixture consisting mainly of alkane hydrocarbons which can be separated by fractional distillation.
Fractional distillation
Crude oil is pre-heated in a fractional distillation column which possesses a thermal gradient and then passed into column.
The fractions condense at different heights due to the thermal gradient as molecules condense when they reach temperature lower than their boiling.
Longer chain hydrocarbons have higher boiling points so they condense at higher temperatures than smaller chain hydrocarbons which condense at lower temperatures.
This is a physical process not chemical which involves splitting weak van der waals forces between molecules.
What is the vacuum distillation unit?
Heavy residues from the fractionating column are distilled again under a vacuum.
Lowering the pressure over a liquid will lower it’s boiling point which allows heavier fractions to be separated with high temperatures which could break them down.
What is cracking?
Breaking down larger hydrocarbons into smaller hydrocarbons.
This can be done via catalytic or thermal cracking.
Thermal Cracking Conditions
High pressure :(7000 kPa)
High temperature: (400°C to 900°C)
Produces mostly alkenes e.g. ethene used for making polymers and polymers.
Sometimes produces hydrogen used in the Haber Process and in margarine manufacture.
Bonds can be broken anywhere in the molecule by C-C bond fission and C-H bond fission.
C8H18 → C6H14 + C2H4
Catalytic Cracking conditions
Slight or moderate pressure
High temperature (450°C)
Zeolite catalyst
Produces branched and cyclic alkanes and aromatic hydrocarbons
Used for making motor fuels
Branched and cyclic hydrocarbons burn more cleanly and are used to give fuels a higher octane number.
Cheaper than thermal cracking because it saves energy as lower temperatures and pressures are used.
Complete combustion of alkanes formula
C8H18(g) + 12.5 O2 (g) → 8CO2 (g) + 9 H2O(l)
Incomplete Combustion
CH4 (g) + 3 /2 O2 (g) → CO(g) + 2 H2O(l)
CH4 (g) + O2 (g) → C(s) + 2 H2O(l)
Where are sulphur impurities found?
In petroleum fractions and they produce SO2 when burned.
Coal is high in sulphur content and large amounts of SO2 are emitted from power stations.
It will dissolve in atmospheric water and can produce acid rain.
What is flue gas desulphurisation?
Waste gases containing SO2 are passed through a scrubber containing a basic calcium oxide which reacts with the acidic sulphur dioxide in a neutralisation reaction.
SO2 + CaO → CaSO3 (calcium sulphite)
Calcium sulphite can be used to make calcium sulphate for plasterboard.
Nitrogen oxides
Form from the reaction between N2 and O2 inside car engines to due the high temperature and spark in the engine which provides sufficient energy to break the strong N2 bond.
NO is toxic and can form acidic gas NO2 NO2 is toxic and acidic and forms acid rain
Catalytic convertors
These remove CO, NOx and unburned hydrocarbons from the exhaust gases, turning them into CO2, N2 and H2O.
Converters have a ceramic honeycomb coated with a thin layer of catalyst metals, platinum, palladium and rhodium to give large surface area.
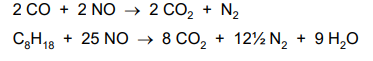
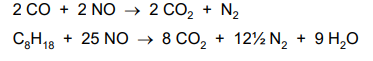
Pollutant and environmental consequence: Carbon monoxide
Formed during incomplete combustion.
Toxic
Pollutant and environmental consequence: Carbon dioxide
Produced during complete combustion
Contributes towards global warming as it’s a greenhouse gas.
Pollutant and Environmental consequence: Unburnt hydrocarbons
Not all fuels burn in the engine.
Contributes towards the formation of smog.
Pollutant and Environmental consequence: Soot/Carbon particulate
Formed during incomplete combustion
Global dimming and respiratory problems.
Mechanism of greenhouse effect
UV wavelength radiation passes through the atmosphere to the Earth’s surface and heats up Earth’s surface.
The Earth radiates out infrared long wavelength radiation.
The C=O bonds in CO2 absorb infrared radiation so the IR does not escape from the atmosphere.
Energy is transferred to other molecules in the atmosphere by collisions so the atmosphere is warmed.
Synthesis of Halogenoalkanes/ Reaction of alkanes with halogens in UV light
The overall reaction is
CH4 + Cl2 → CH3Cl + HCl (all gases)
Mechanism for this reaction is called free radical substitution.
Free radical substitution: Initiation
The UV light supplies the energy to break the Cl-Cl bond by homolytic fission. It is the weakest bond.
One electron from the covalent bond is given to each atom in the covalent bond forming 2 Cl radicals.
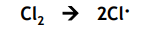
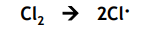
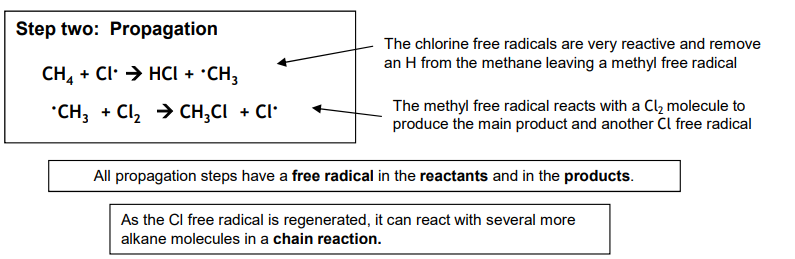
Free radical substitution: Propagation

Free radical substitution: Termination
Collision of two free radicals, producing a stable product.
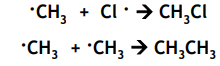
Cl. + Cl. → Cl2