
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
What is pathology? Clinical pathology?
Branch of medicine that investigates the essential nature of disease – body tissues and organs that cause or are caused by disease
Clinical pathology: Pathology applied to the solution of clinical problems
Definitions for each
Activity limitations
Participation restrictions/Disability
Social implications
Friends, family, work
Activity limitation - What they cant do functionally
Participation restriction/disability - what they cant do in society due to their limitations Ex: cant walk so cant take dog out to the dog park
Social implication (friends family work) - Isolated, work disabled, etc.
Environmental factors: The physical, social and attitudinal environment in which people live and conduct their lives. These are either barriers to or facilitators of the person's functioning.
Personal factors: Gender, age, occupation, etc
What is health
A state of complete physical, mental and social well-being
HEALTH IS DYNAMIC in the sense that one point we are sick a few days later we are okay.
What do national health status look at?
Birth and death rates
Life expectancy
Quality of life (Functional quality of life) includes adapted equipment they need
Morbidity (how many disease you have, can have comorbidities. Ex: Diabetes leading to cardiovascular disease. Comorbidities are a huge issue for the sick population.
the flu is a sickness or deviation from a healthy state Perception and response of not being well and a reaction to the disease. this is typically considered an ________
illness EX flu
What is disease?
Biologic or psychologic alteration that results in a malfunction of a body organ or system
Uses objective data such as elevated temperature
Can occur in individuals that are unaware of illness
Ex Autoimmune disorder like lupus.
Number of new cases of a condition in a certain period of time in relation to the total number of people in the population who are at risk at the beginning of the period is called?
Incidence
All cases of the condition (new and old) among people at risk for developing the new condition (ALL TOTAL NUMBER OF PEOPLE AFFECTED, EVEN AFTER THEY ARE CURED) this is called?
Prevalence and its measured at one point in time (1 day)
an illness that is self limiting and has a rapid onset with short duration. Responds to self treatment. This illness would be considered being
acute
an illness that lasts longer than a few days (no definition of days but maybe 3 or 4 days) but less than several months is considered being
subacute
Most people move from acute to sub acute phase of illness then recovery. However if there are complications it can go from acute to what?
chronic
Chronic inflammatory conditions
what is a chronic illness
permanent impairment or disability, residual physical or cognitive disability. Need for special rehab and medical management, modifiable through lifestyle changes.
Fact: Chronic disease are now top of the list of causes of mobility and mortality in the US.
what are some examples of chronic illness (3)
-ALS (Nerve conduction stops peripherally, then centrally, then to the lungs)
-multiple sclerosis (plaque on spinal cord or in brain)
-spinal chord injury
What is natural history and how does it impact the plan of care?
How the disease is progressing overtime.
Used for cancer staging (IE how long before this and that or before death)
Based on predictive factors (Estimates for how long you might live, doesn’t necessarily mean that you will die on that exact time)
Not always clear
Knowing natural history can allow you to modify treatment for individuals with chronic illness
Long-term care implications for diseases and secondary impairments as a result of longevity. Why is this the case?
Living longer means more time for medical conditions to occur, usually by 70 or 80.
pre morbid compared to morbid personality implications and associations.
Negative thoughts affect neural wiring and firing may cause a progression of a psychologic disorder
Associated with:
depression
dependence
narcissism
stoicism
fear and anxiety
denial (natural part of healing process but can impact care)
What three things that encompasses all mental health illness?
Depression, alcoholism, schizophrenia
OFTEN UNDIAGNOSED, we cannot diagnose but identify signs and symptoms is important:
Behaviors: Motor behavior and social behavior IE anti social etc.
Brain lesions: right hemisphere, frontal lobe issues causing impulse control difficulty.
multiple sclerosis is an example of a chronic illness that is ______
residual cognitive and physical disability
how can chronic illness be modifiable
through changes in behavioral lifestyle
what is the #1 cause of morbidity and mortality in the U.S
chronic disease specifically heart disease
What are some implication for therapists when it comes to referral?
Is the referral necessary?
To what professional?
Is more than one needed?
NOTE: documentation is the most important thing you can do in your clinical practice.
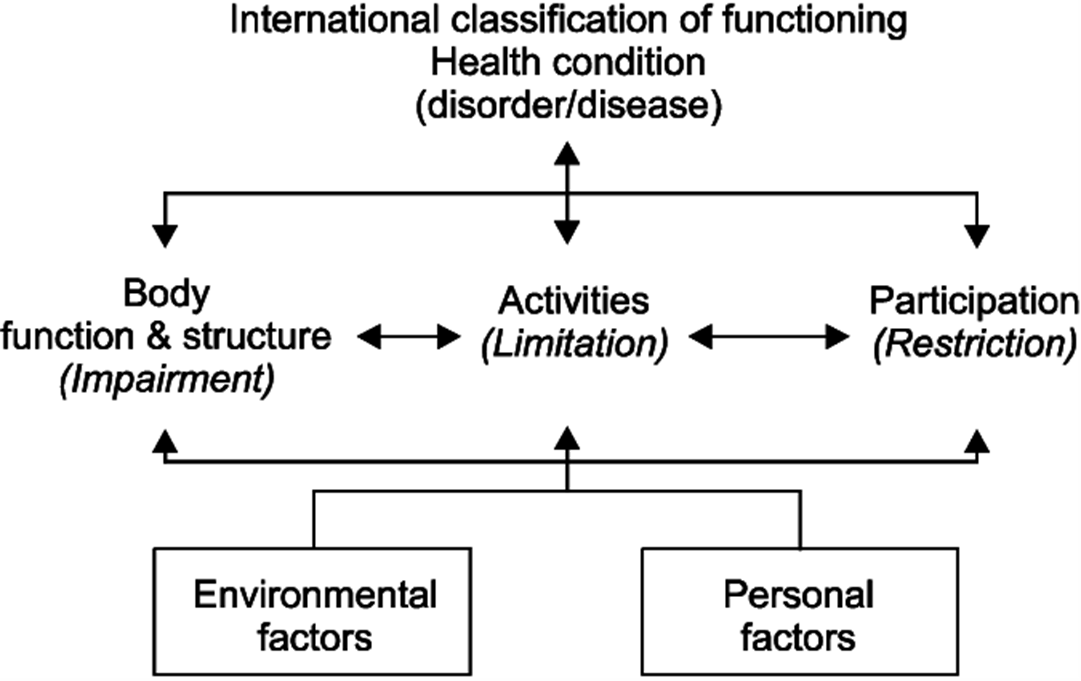
ICF model
Health condition: name of issue (ex rotator cuff tear)
Body structure and function: What is being impaired (Shoulder flexion ex)
Activities: What that impairment limits (ex can sit in the chair)
Participation: What that impairment limits in daily life (cant work or go to gym or drive)
what is the #1 risk factor for heart disease
smoking
Health promotion and disease prevention is all about ____.
Education and supplementing it with physical activity and exercise.
Hands on intervention? Most cost effective method and most effective method.
General health promotion, screening programs, risk factor assessment, and reducing or preventing the changes of progression of disease. What is this an example of?
primary prevention
what is secondary prevention
referral from a provider. the patient most likely already has the condition
ex: diabetes
what is tertiary prevention
specialized services that are more complex
ex: patient has. ALS or cancer. Much more specialized
When looking at genetics what is important to do?
Management of genetic factors that are associated with risk for conditions. Ex:
Stroke
Cardiovascular (cardiovascular disease is the #1 killer in the US)
Pulmonary
Arthritis?
Some call it the future of medicine, preventing disease by identifying predispositions to both visceral and musculoskeletal disease
what is epigenetics
study of biology (internal) and enviromental (external) signals that determine gene expression
Genes can be _____ or _____
upregulated (turned on) or downregulated (turned off)
What is DNA? What controls it?
•Its the Blueprint that directs the genes, this does not turn off or on
•The brain controls expression and expression of the DNA along with reading the gene can be changed (manipulated)
T/F genetic predisposition to a disease is not a single predictive factor of actually contracting the disease IE just because your family is prone to heart disease doesn’t mean you will get it too.
TRUE
attitudes, thoughts, emotions, beliefs and reaction responses to events that affect our physiologic function like fight or flight or getting mad and increasing BP are examples of what type of environment
internal. they directly affect physiologic function (how we think actually changes physiologic/biologic function). This is why we need the patient to be in a positive Mindspace during the healing process.
T/F How we think changes our physiologic AND biologic function
True,
what are examples of external enviroment
the air we breath, water, food, toxins in the environment.
social network, community, sense of purpose, and spiritual beliefs all seriously contribute to a sense of wellbeing
Recent causes of death and their associated lifestyle changes
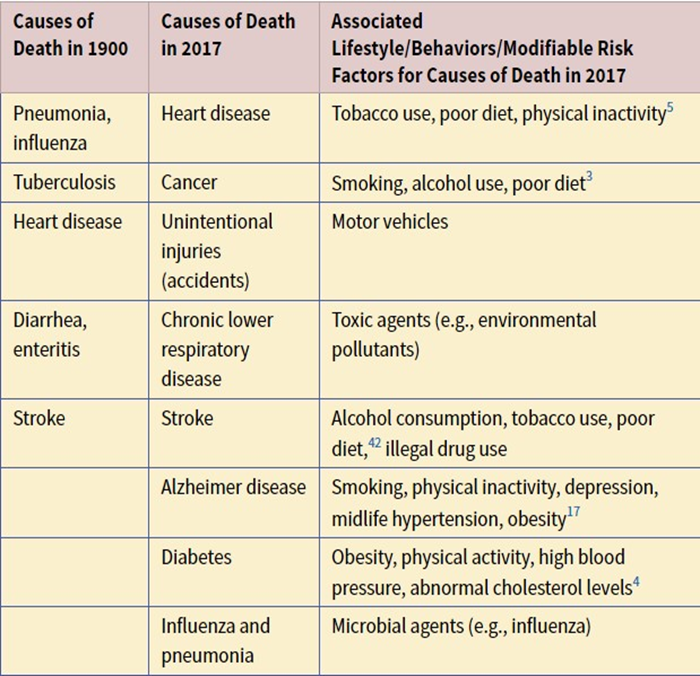
Changing behavior and lifestyle could help prevent death, enhance quality of life, and reduce the escalating costs of treating chronic illnesses
geographic variations, socioeconomic status and social support are other factors that affect wellbeing what are some examples
geographic:
-climate (air quality, water quality)
-stressful cities (Crime index, unemployment, commute time)
socioeconomic: Most adverse influence on health
-having access to healthcare, different attitudes about healthcare
social support:
-loss of telomeres due to chronic stress (social stress and aging)
-social support and social networks are connected to physical and mental health. IF one does not have a good support system, they will get worse compared to those who do
What are the 5 dimensions of health and well being?
Physical - Healthy diet, exercise, absence of illness, controlled ADD use
Mental (cognitive) - engaging meaningful work, up to date, lifelong learner
Emotional - positive thinking, emotion regulation and expression, coping strats, resilience
Social - support networks like maintain meaningful relations, sense of belonging, contribute to society
Spiritual - A sense of meaning, set of values/ethics, feeling connected to a higher power or nature, sense of peace or transcendence
Why is psychological considerations so important to talk about? How do we support our clients?
Helps us address underlying causes of psychologic phenomena to tackle symptoms:
Interdisciplinary care
Treat the whole person
We support our clients via:
Being familiar with techniques that help get information out the patient, motivational interviewing, cognitive behavioral therapy, etc.
Self aware of your own limitations and barriers (Ex knowing you are a touchy talking person and the client just wants to get in and get out)
Be aware of the clients perception with safety vs threat.
what nerve is responsible for mind and body connection?
vagus nerve (longest nerve in the body)
according to the polyvagal chart as arousal increases what stages do we go through (list them bottom to top)
social engagement (ventral vagal feeling safe) calm, mindful, compassionate
Parasympathetic system increases things like digestion, resistance to infection, breath, immune response, etc. decreases defense
fight or flight (sympathetic system feeling danger, hyperarousal)
Fight: Anger rage frustration irritation
Flight: Panic fear anxiety worry
Sympathetic nervous system increases blood pressure, adrenaline, blood clotting, pupil size, defense, etc. decreases digestion, salivation, immune response, insulin activity etc.
freeze (dorsal vagal life threatening, hypo arousal, spent too long in fight or flight mode) helplessness, depression, numbness, shutdown, zoned out, disassociated
parasympathetic nervous system increases fuel storage, insulin activity, immobilization with fear, endorphins that help numb and increase pain threshold, etc. Decreases heart rate, temp, muscle tone, facial expressions, sexual responses, immune response, etc.
what is physiologic healing?
higher brain perceives safety in surroundings allowing brainstem to regulate ANS that promotes heath, growth, and restoration
in physiologic healing messages are received and confirmed by what parts of the brain
cognitive (left hemisphere) and emotional (right hemisphere)
what are the 3 phases of trauma healing
phase 1 safety and stabilization:
feelings of being unsafe in environment/relations. PT should orient to the present using senses, encourage affirmations
phase 2 remembrance/mourning:
processing trauma, putting words emotions meaning to the experience. PT should encourage calmness and breathing while they tell their story
phase 3 reconnection/integration:
developing an sense of self and creating a new future, trauma doesn’t define them. PT should focus on meaningful goals.
what is pain perception? How can clinicians play a role in pain reduction?
response to perceived threat, 2 different people will have two different experiences based on same stimuli.
We can play a role in pain reduction by simply changing the vocabulary we use when educating patients.
Pain is an output by the?
Pain is an output by the central nervous system
Common pain conditions

Persistent/chronic pain
Occurs at any age
Unlike acute, doesn’t follow any typical or predictable timelines for healing
It does not serve a biological function or purpose
Must manage expectations and set realistic outcomes.
how long do most nonsurgical tissue take to heal
8-16 weeks if longer it can be considered chronic pain
Pain mechanism classification systems
Identification or diagnosis of the primary disease/etiologic factors considered responsible for producing/initiating the pain
Placing the individual within a pain mechanism category
Identifying the anatomic distribution, quality, and intensity of pain
Explain the three components of nociceptive pain
Inflammatory component: Swelling
Mechanical component: Anything wrong with the muscle tissue or joint
Ischemic component: Blood flow reduction or reduction of ability of muscle to contract
Compressed means no signal below, causes numbness.
a patient had an injury that stimulated pain receptors (Nociceptor) resulting in localized pain. this is an example of what type of pain
nociceptive
Are there such thing as pain receptors?
NO they’re not.
We have nociceptors, they send danger messages for interpretation to the nervous system. The CNS then OUTPUTS the pain response.
excessive fluid activates nocipceptors that are thermal mechanical and chemical. this is known as
nociceptive inflammation, in response to specific irritation from inflammation and occurs in connective tissue in periphery (muscles, ligaments, bone, tendon, fascia, cartilage.
one of your patient injured their knee. the tissue is swollen due to cells that go into it to repair therefore it also gets inflamed. this is an example of
nociceptive inflammation (needed to heal)
Insufficient blood flow and oxygen. A tissue becomes more acidic, hypoxic and rich in chemicals like bradykinin, potassium ions, prostaglandins. Essential circulation is deprived as a result of continuous stretching, compression, sustained positioning, or poor repair and remodeling phases of connective tissue healing. What is this?
nociceptive ischemic
strains, tears and trigger points are examples of what
nociceptive ischemic
what is neuropathic pain
Neuropathic and neurogenic pain result from alterations in nerve structure, function, and dynamics that cause neural dysfunction.
Compression of a nerve means no feeling under and weakness, pushing up against/irritating a nerve (like a muscle) is what causes the tingling and the burning sensation.
neuropathic pathologies can be either
interneural - Problem with the nerve itself
Extra neural - Problem with another muscle or part of the body bothering the nerve.
what happens if a nerve doesnt fire due to being shortened or compressed (leads to inflammation)
no muscle activity
you push your finger into a table for as long as possible until it becomes uncomfortable. this is known as
irritation
you squeeze your finger hard enough to reduce bloodflow. you just _____________ your finger
compressed
what is nociplastic pain
Altered nociception despite no clear evidence of actual or threatened tissue damage causing the activation of peripheral nociceptors or evidence for disease or lesion of the somatosensory system causing the pain
Alterations of nociceptive processing within the CNS are suspected such as enhanced central excitability or diminished central inhibition
nervous system thinks "i’m doing harm" despite no actual threat. mainly dominated by patients thoughts, worries or beliefs or concerns in relation to the pain experience and potential threat of injury un healed tissue or pathology. (hypersensitivity)
Ex: fiber myalgia
what is an affective reaction
physical reaction to emotional turmoil pain manifests as a result of emotional turmoil or unresolved emotional or social conflict (psychosomatic reactions Mind - body)
ex: when angry heart rate goes up
general malaise, lymphedema, hypersensitivity involve involuntary sympathetic/parasympathetic systems. Heavily influenced by the somatic, motor and autonomic nervous systems and neuroendocrine and immune system symptoms. This is an example
motor/autonomic reactions
what is fear avoidance behavior
fear of pain leads to avoiding physical or social activities
Should include education that addresses the client’s fear and avoidance behavior while considering a graded approach to therapeutic exercise
ex: persons fear (not physical impairment) is the most important in how they respond to low back pain.
what are examples of trauma
physical, sexual or emotional abuse, injuries during combat, assault, medical interventions etc
a veteran with a history of trauma perceived a threat that resulted in psychologic stress. He then froze and did nothing. what happened?
he was in a sympathetic state too long (dangerous can lead to stroke for example) so his nervous system activated his parasympathetic state to help him dissociate (polyvagal chart)
What are the most important things you can do when trying to treat patients with persistent or chronic pain disorders?
Education is key
Get all providers to speak the same language (be more encouraging and hopeful)
Find the patients WHY via extensive history both of initial injury and social history
Ex: loss of job, lack of sleep, relationships (familial or friendships)
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT): Change the thoughts and perceptions.
For chronic pain the pain doesn’t really change, so asking what is your pain level today every time they come in, they will start to wonder if they’re even getting better. Instead ask if they did more today then last week, or did you take more or less medication than last week.
What is trauma?
Can include physical, sexual, or emotional abuse.
Usually a violent injury such as a motor vehicle accident MVA, injuries sustained in combat, assault, and medical interventions and surgeries.
Unexpected events that are perceived as threats (EX dog bite) can result in acute psychologic stress, symptoms such as anxiety, dissociation, intense fear, helplessness or horror when reexperiencing event. Increased arousal.
what is physical abuse
non accidental physical injury, ranging from superficial bruises and welts to broken bones burns serious internal injury and even death
what population require consent before you can report them as experiencing physical abuse
adults (A sign that there is abuse is if that person cannot be left alone by their partner and that the partner answer and talks for them.
what population needs to be reported immediately if you suspect physical abuse or you could be held liable
elderly
child
person w/ cognitive deffects
ivan got bullied in school being called all form of names that led him to develop a mental disorder. what type of trauma did ivan experienced?
psychological,emotional abuse
Result from acts or omissions that cause or could cause serious behavioral, cognitive, emotional, or mental disorders as a result of actions such as confinement or the constant use of verbally abusive language and criticism
Can seem very benign, does not necessarily have to be with foul language, aggressive, or loud (Ex: Oh this is not for you, you really cant do that because you’re not smart enough)
what are examples of sexual abuse (6)
non-touching offenses, exhibitionism (Flashing people), fondling, rape, molestation, or forced use of a child or adult in the production of porno materials
(same rules as physical abuse apply for reporting)
what is neglect with examples? (3)
Can involve the withholding of or failure to provide adequate food, shelter, clothing, hygiene, emotional support, medical care, or supervision needed for optimal health and well-being
refusal or delay of healthcare, abandonment, expulsion from home, inadequate supervision
Usually happens to older and younger populations.
what is stalking and what are some examples (3)
Repeated visual or physical proximity, nonconsensual communication, or verbal, written, or implied threats, or a combination thereof, that would cause a reasonable person fear.
what are some stats of reported incidence of child abuse, adult/elder abuse, and rape?
Child abuse: 12.7% population reported, 740000 treated each year
Adult elder abuse: 1-2 million anually, 51000 deaths annually.
Rape: 10.6% - 17.6% females, 2.1% - 3% males.
what population is more at risk for ptsd
can occur at any age, including childhood
What is PTSD and how does it occur.
Traumatic stress disorder that occurs at any age.
can result from emotional, mental, spiritual, physical or sexual trauma
your treating a patient with ptsd and he suffers an acute stage mid session. what are some triggers that he might be experiencing (4)
reminders of event
flashbacks
intrusive thoughts/ images
nightmares
hyperarousal
sleep disturbance
agitation
irritability
anger
impulsiveness
etc
could be caused by loud noise flashing light etc
what is the most common cause of ptsd for women and man and healthcare workers
women: sexual assault
men: combat deployment
healthcare workers: dealing with the aftermath of violence or natural disasters
What are some clinical manifestations of PTSD?
Anxiety, unwanted and distressing thoughts and nightmares, increased arousal, or hypervigilance not present before the trauma
Difficulty falling or staying asleep, exaggerated startle response, or difficulty concentrating on or completing tasks
Difficulty with relationships, insomnia, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and being easily startled are hallmark symptoms of PTSD
what are the 3 types of anger and whats the most dangerous
-expressive (actually expressing your anger)
-internalized (Bottling up)
-physical violence (you actually get assaulted)
what is intrusion in terms of ptsd
re-experiencing trauma in nightmares, daytime flashbacks, unwanted memories etc
what is avoidance in terms of ptsd
social withdrawal, becoming numb to feelings of any kind (Positive or negative) , avoid stimulant that may be a trigger memories or experiences similar to trauma
Acting bored, cold, or preoccupied. Isolates themselves.
what are arousal symptoms of ptsd and how can you calm them down
-psychosomatic responses
-person is on guard and may lead to panic attack
-exaggerated startle response
-sweaty
-trouble breathing
-increased hr
-dizzy/nauseous
box breathing "4 second" is a technique to calm down since it activates the vagus nerve
what is an anxiety disorder? Why is it important to know the signs and symptoms?
excessive emotional state of fear and apprehension associated w/ increased physiologic arousal
Important to be aware of the symptoms associated with anxiety disorders in order to modify treatment
what are the most common anxiety disorders
-general anxiety
-panic disorder
-specific phobias (Ex arachnophobia or agoraphobia)
what are the most common physical signs of an anxiety disorder (3)
-Increases signing respiration
-increased bp
-tachycardia
-shortness of breath
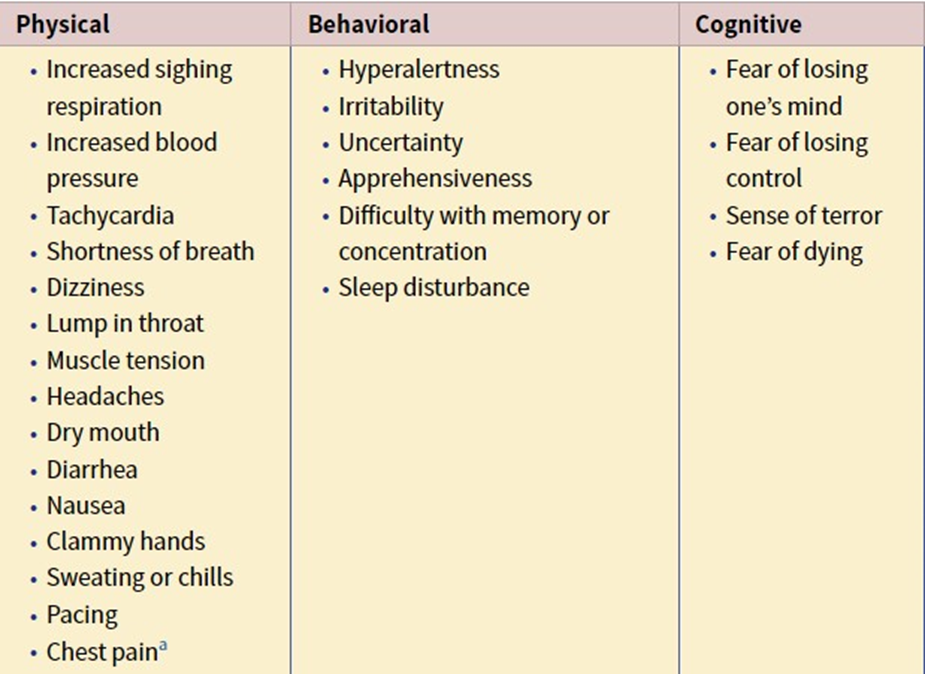
what are the most common behavioral signs of an anxiety disorder (2)
-irritability
-apprehensiveness
what are the most common cognitive signs of an anxiety disorder
sense of terror, fear of losing mind, control and finally fear of dying.
what is a panic attack
acute onset of intense excessive fear, anxiety, or disorder that include 4 or more symptoms
what are some symptoms of a panic attack and how can you diagnose it
minimum of 4 have to happen to be considered a panic attack
Palpations, pounding heart, tachycardia, sweating, trembling shortness of breath, heat or chills, cold and clammy feeling, chest tightness, dizziness, light headed, unsteadiness, numbness, dethatched, nausea, diarrhea, fear of losing control or going crazy, fear of dying.
what are other conditions that can present like anxiety but therye not (3)
-hypoglycemia
-panic attack'
-cardiac event (will have referral pain up the left shoulder, down the arm on the ulnar distribution, to the fingers and jaw and neck on left side. During a panic attack the pain is not there)
REFER OUT TO APPROPRIATE MEDIAL PROFESSIONAL
what population expreiences the most depressive disorders
MOST SEEN MOOD DISORDER in therapy practice
2x more prevalent in young woman than men ages 14-25
why do depressive disorders occur/pathophysiology
Genetic predisposition + psychosocial stressors = exacerbated symptoms
ex: history of trauma, sexual abuse, significant life events
wha are signs/chinical manifestations of depressive disorders (3)
-decreased energy
-difficulty concentrating and memory
-GI disturbance, headache, unexplained pain (somatic complains)
how do you diagnose a depressive disorder
depressed mood or loss of interest/pleasure + more than 5 symptoms during a 2wk period
how long can medication take to have an effect and what side effect may it have on a depresive person
it can take 4-6 weels (different for everyone) and increases the risk of suicide due to the way chemicals interact in the brain