Lecture 1: Terms, Planes, Language of anatomy, Histology of tissues – Vocabulary Flashcards
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key terms from Lecture 1 notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Anatomy
The study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another.
Physiology
The study of the function of the body's structural machinery.
Gross anatomy
The study of large structures visible to the naked eye.
Regional anatomy
Gross anatomy studied by specific region of the body (e.g., abdomen, leg). (Type of gross anatomy)
Systemic anatomy
Gross anatomy studied by body system. (Type of gross anatomy)
Surface anatomy
Study of internal structures as they relate to the overlying skin. (Type of gross anatomy)
Microscopic anatomy
Study of structures that require magnification to be seen.
Cytology
Study of the cell. (Type of microscopic anatomy)
Histology
Study of tissues. (Type of microscopic anatomy)
Developmental anatomy
Traces structural changes throughout life.
Embryology
Developmental changes before birth. (Type of developmental anatomy)
Pathological anatomy
Study of structural changes caused by disease. (Specialized branch of anatomy)
Radiographic anatomy
Study of internal structures visualized by X-ray. (Specialized branch of anatomy)
Molecular biology
Study of anatomical structures at a subcellular level. (Specialized branch of anatomy)
Principle of Complementarity
Function reflects structure; form and function are interdependent.
Chemical/Physical level
Atoms form molecules; molecules form macromolecules.
Cellular level
made of molecules and organelles.;The basic units of life
Tissue level
consist of similar types of cells that perform a common function
Organ level
made up of different tissue types that perform specific functions.
Organ system level
consist of different organs that work together to perform a common set of tasks.
Organismal level
made up of many organ systems.
Atoms
The basic units of matter that form molecules.
Molecules
Two or more atoms bonded together.
Macromolecules
Large, complex molecules (e.g., proteins, nucleic acids).
Standard Anatomical Position
Body is upright, feet together, arms at sides, palms facing forward, thumbs away from the body.
Superior
Toward the head end or upper part of a structure or the body; above.
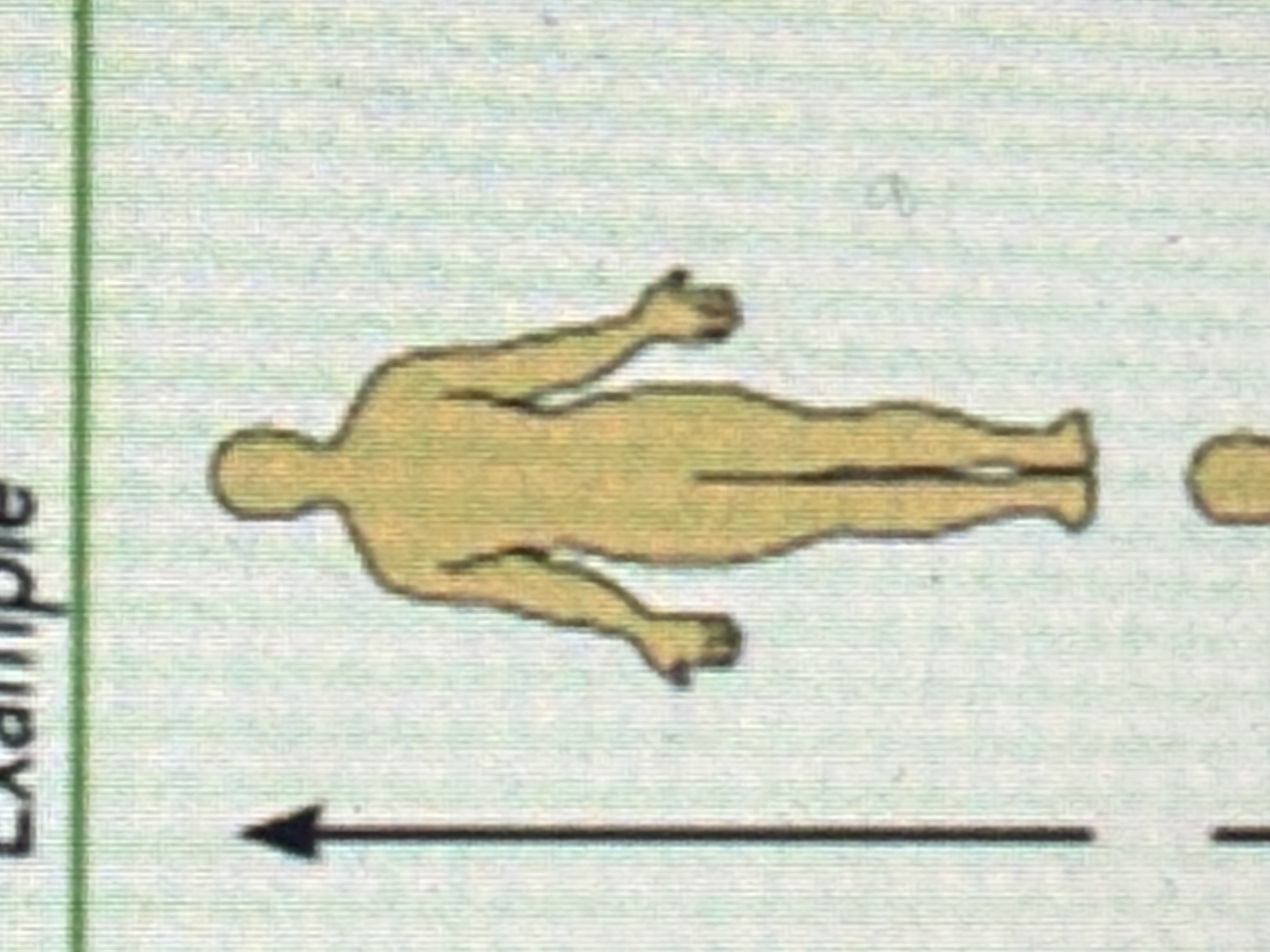
Inferior
Toward the lower part of a structure or the body; below.
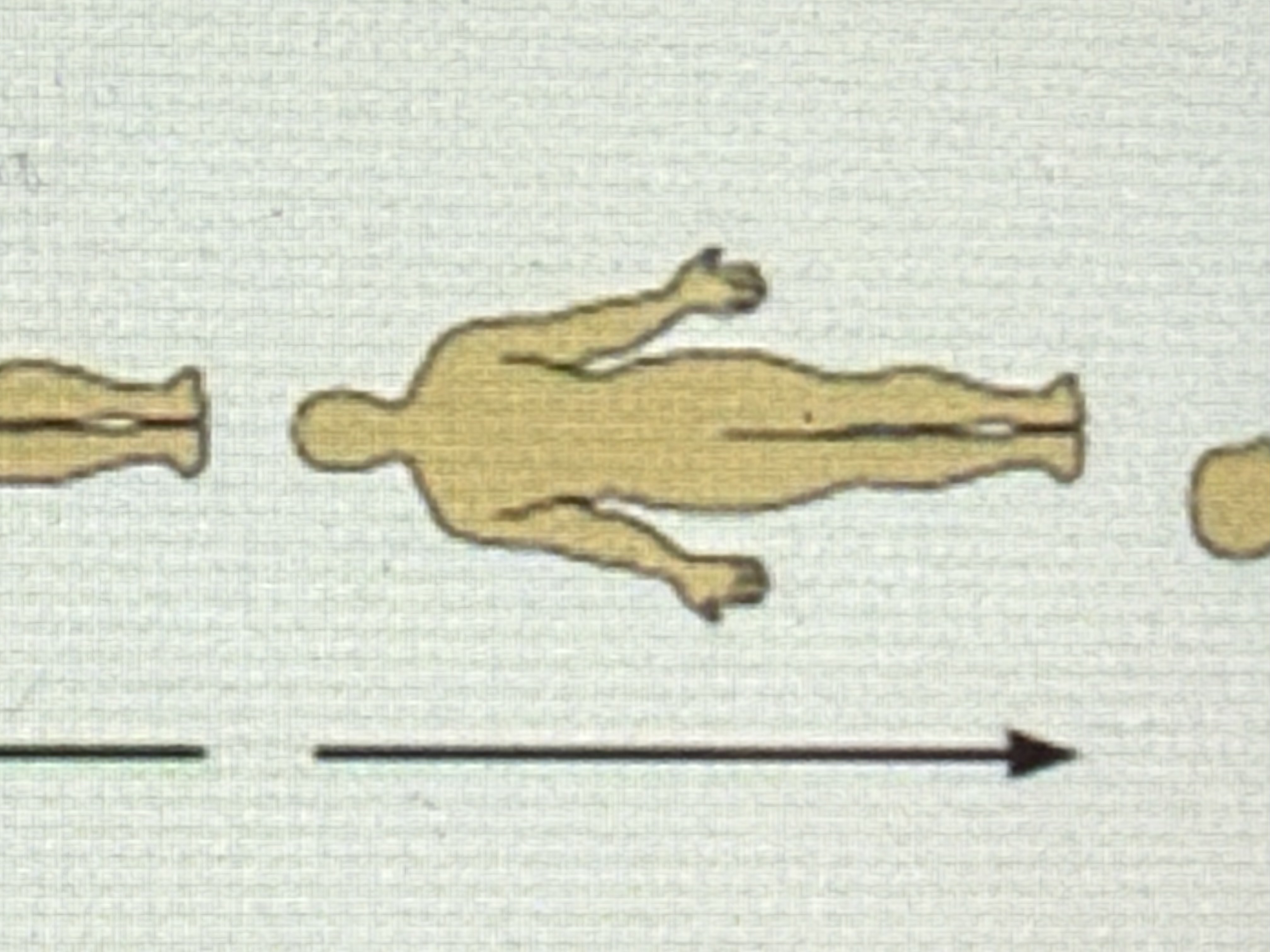
Anterior
Toward the front of the body; in front of.
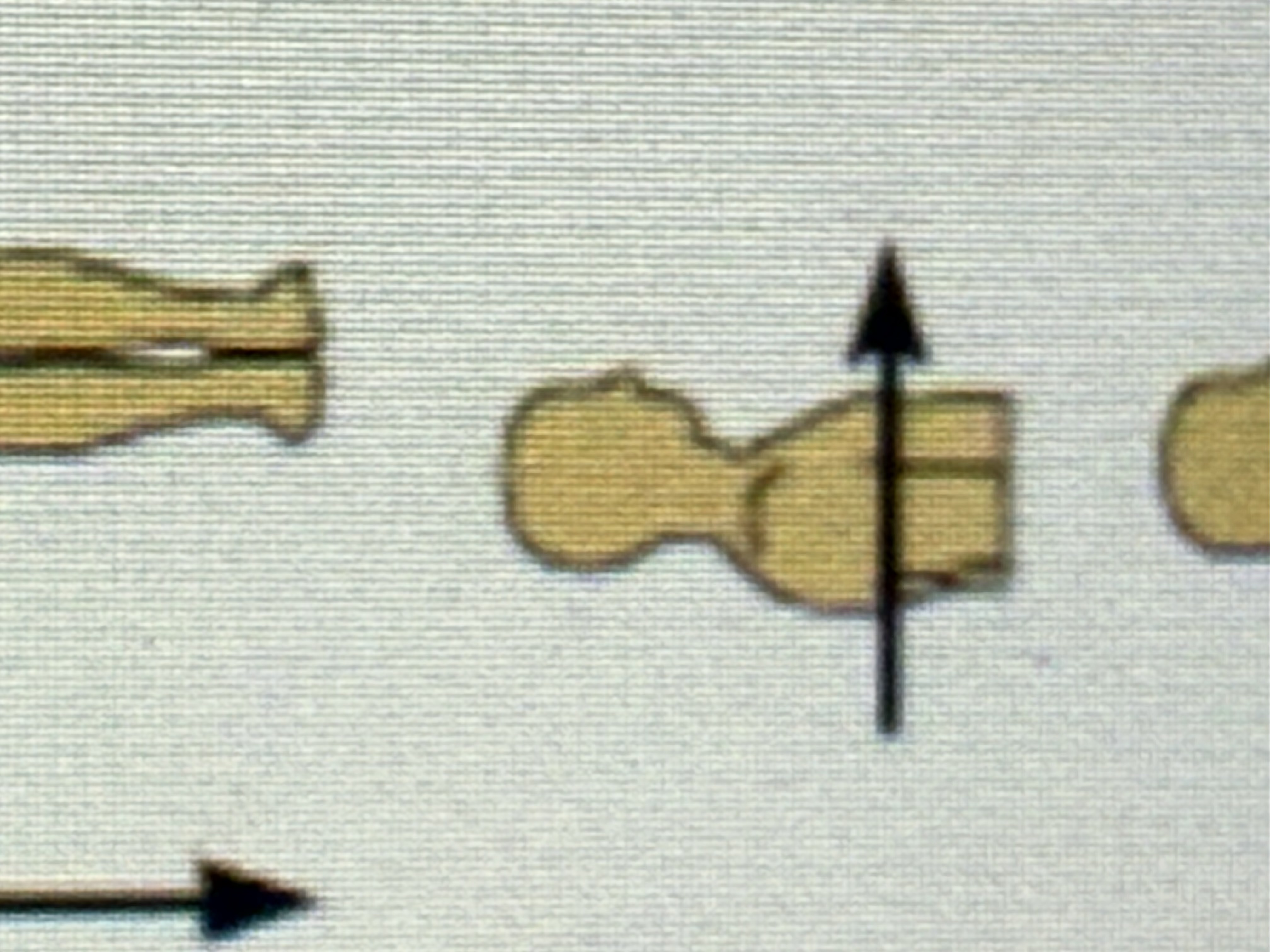
Posterior
Toward the back of the body; behind.
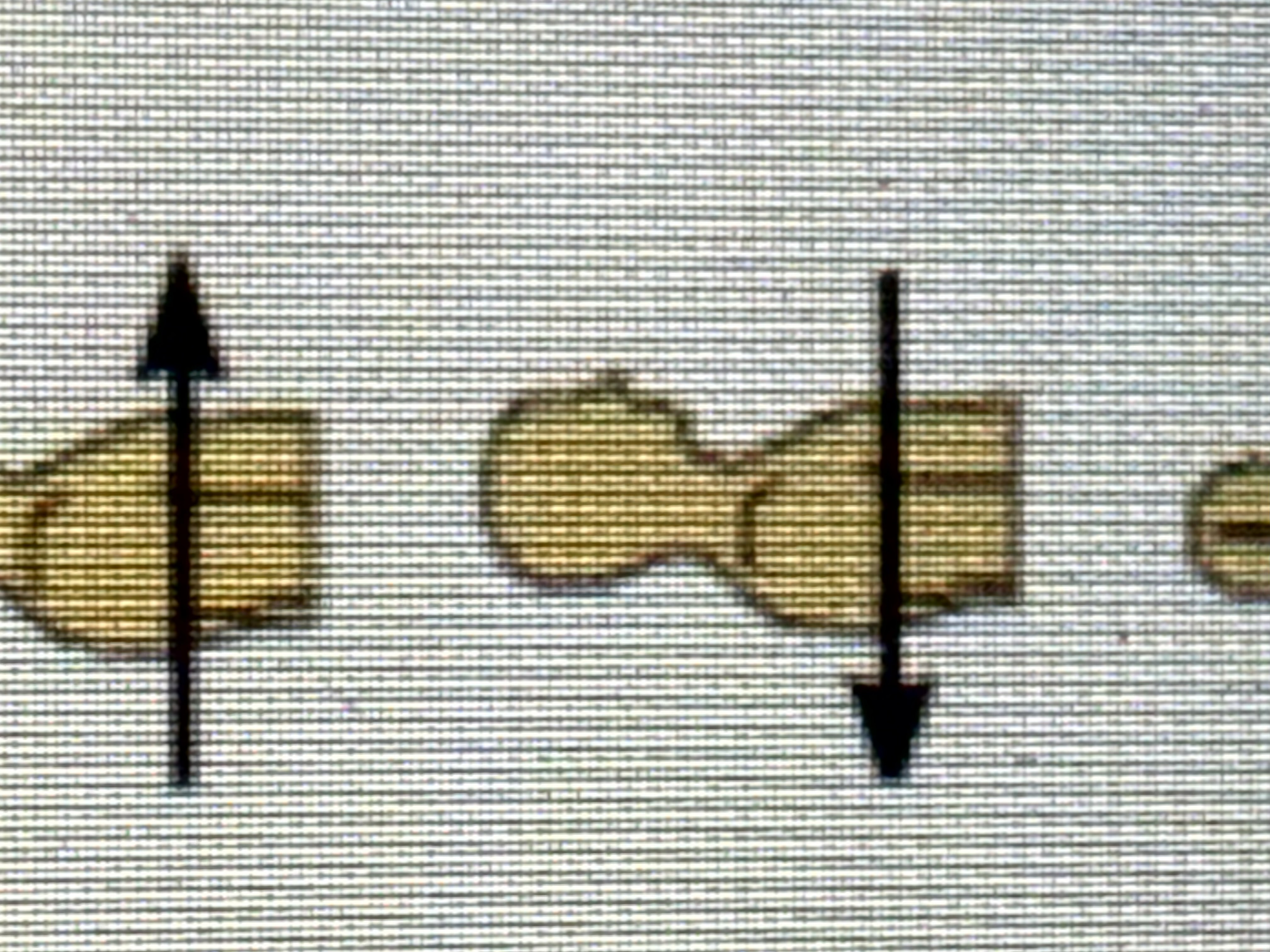
Medial
Toward the midline of the body.
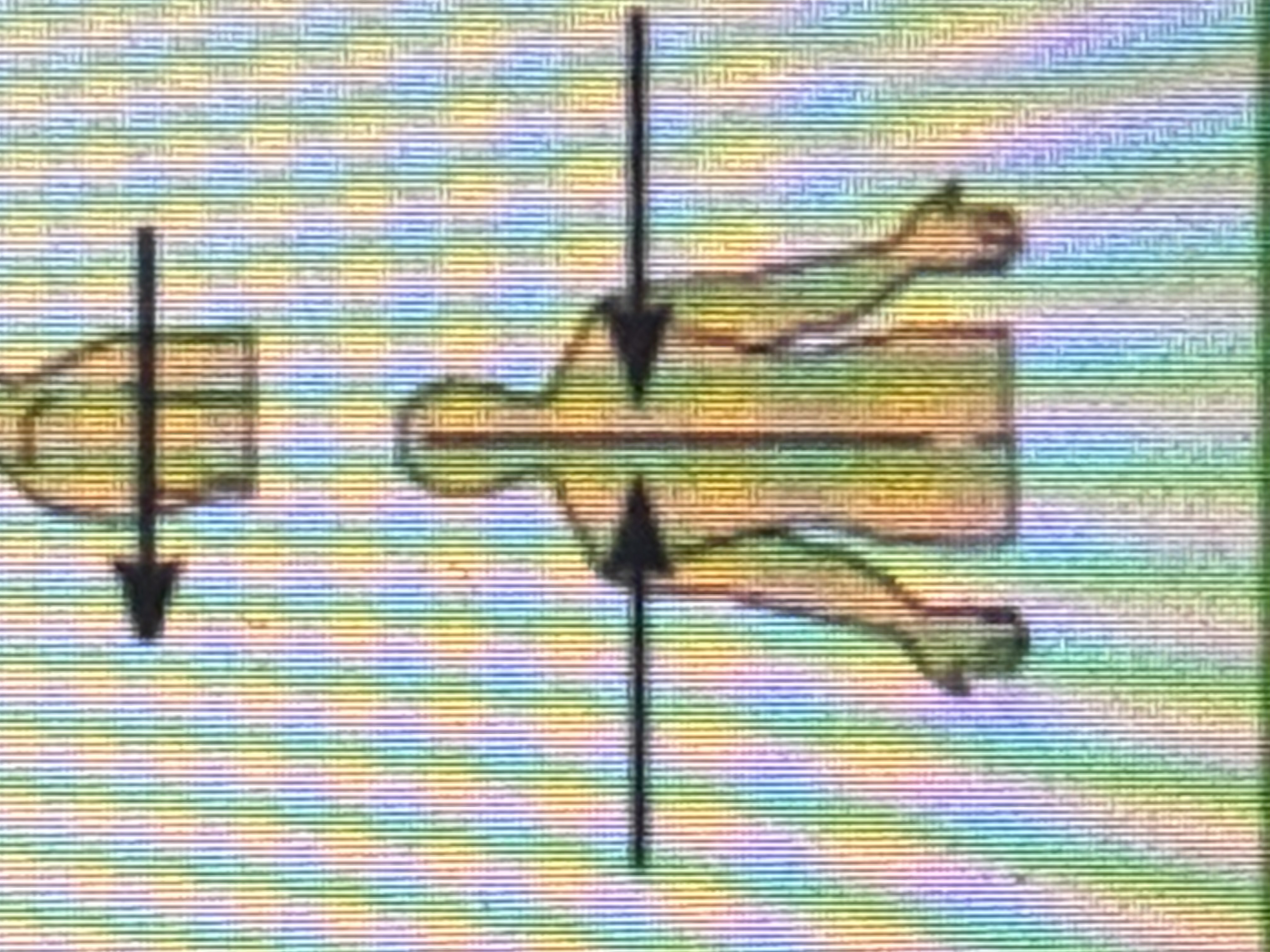
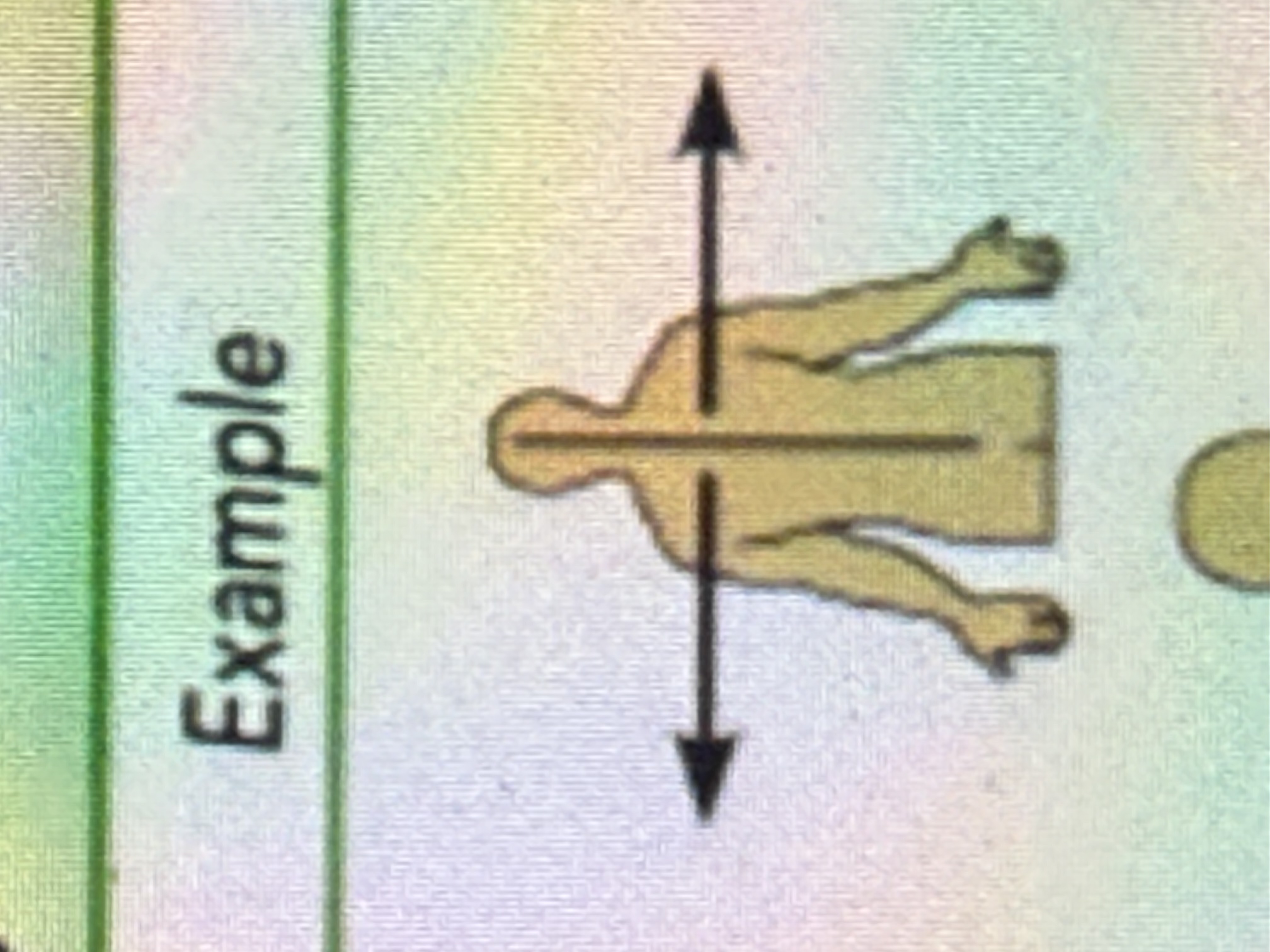
Lateral
Away from the midline; toward the outer side.
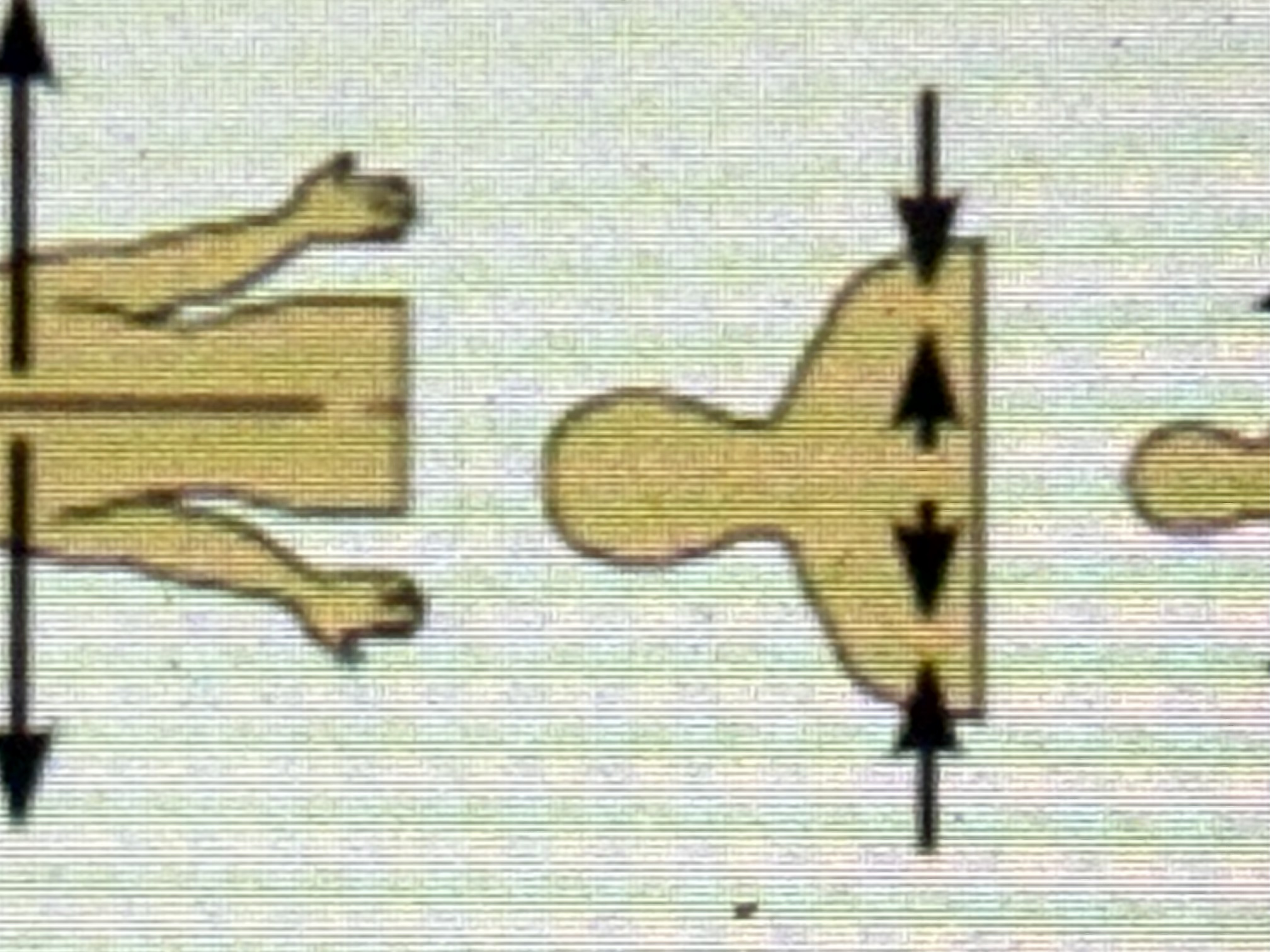
Intermediate
Between a more medial and a more lateral structure. Ex: The collarbone is intermediate between the beastbone and shoulder
Proximal
Closer to the origin of a body part or the point of attachment.
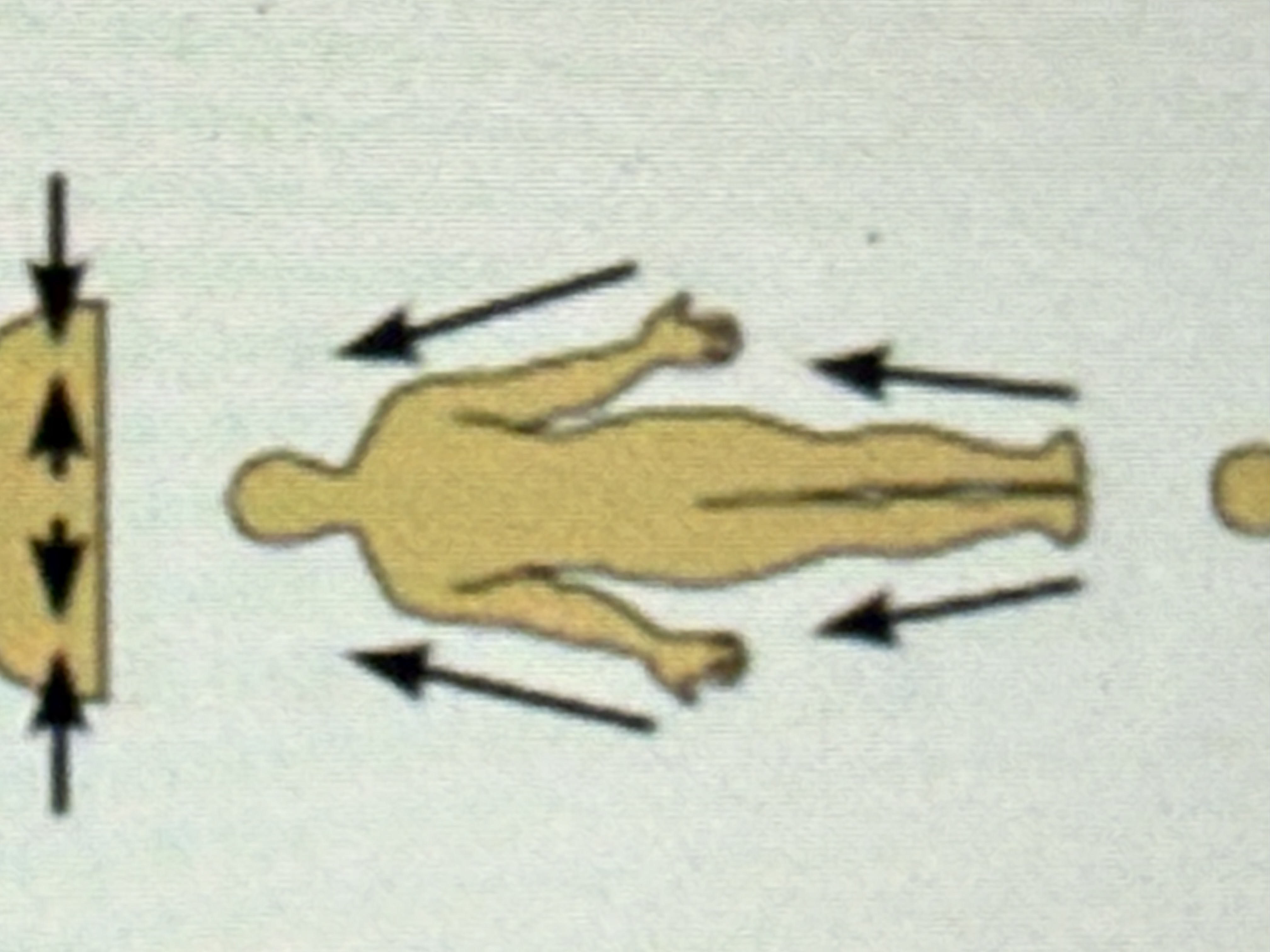
Distal
Farther from the origin of a body part or the point of attachment.
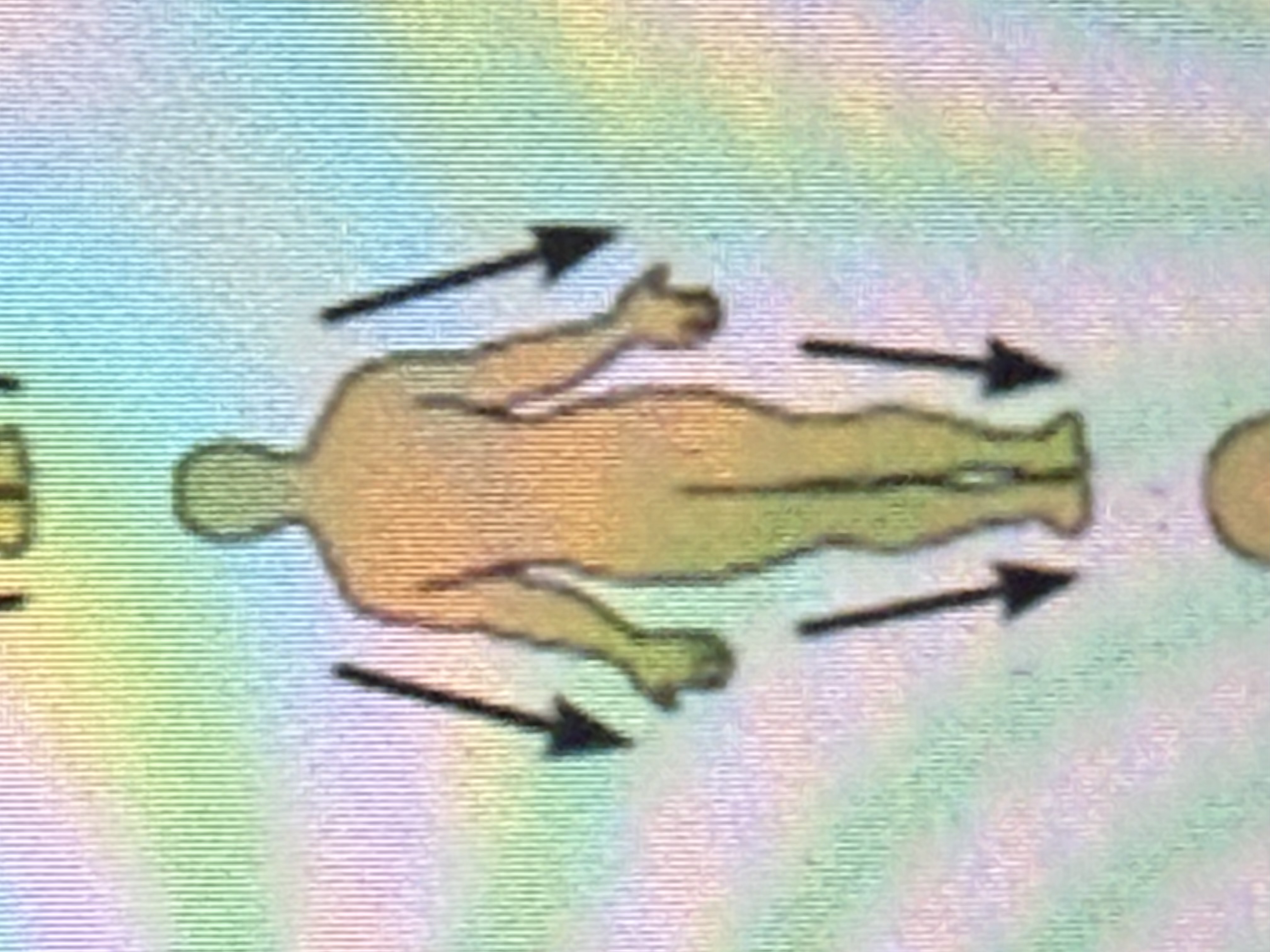
Superficial
Toward or at the body surface.(closer to skin)
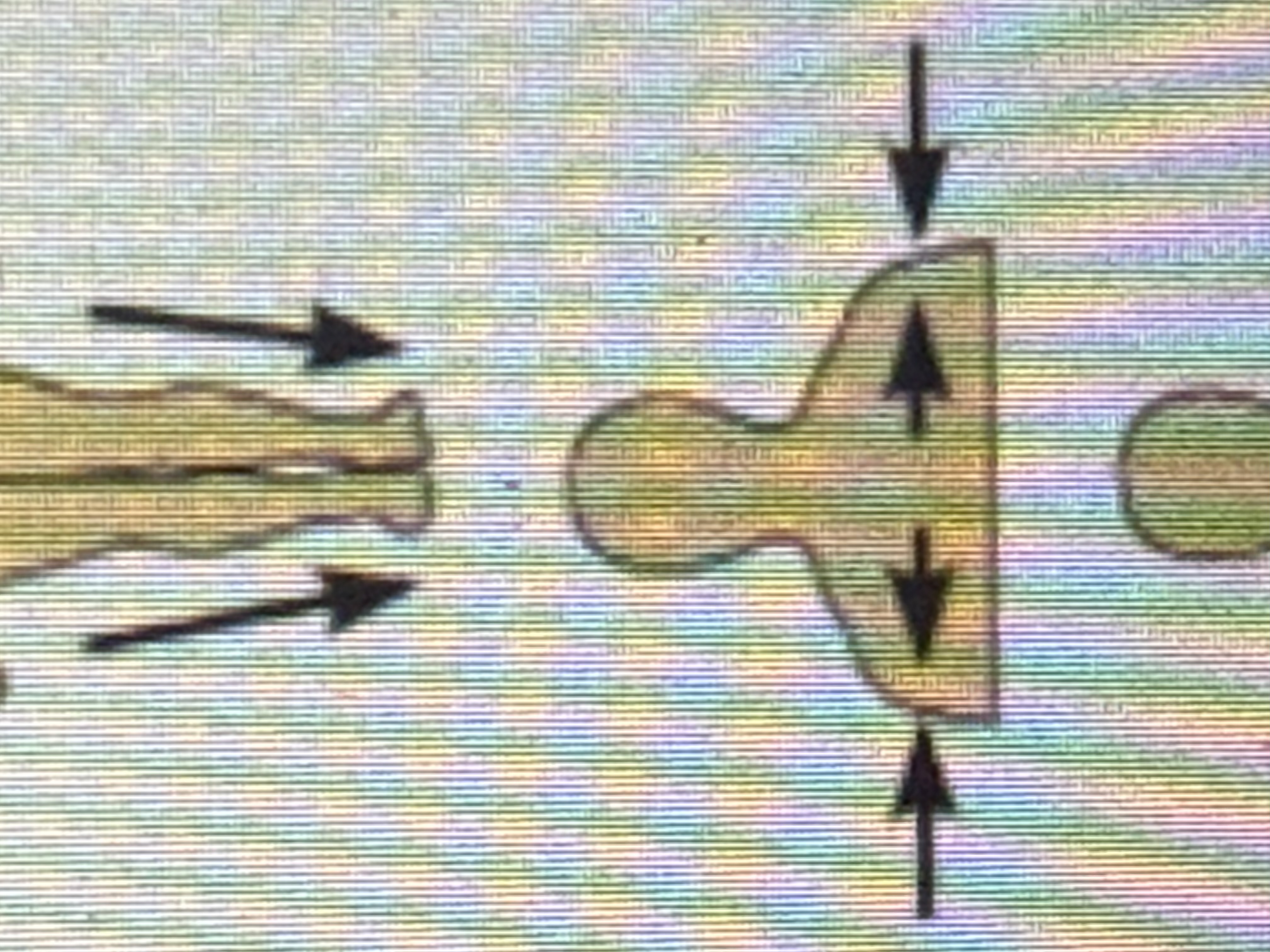
Deep
Away from the body surface; more internal.
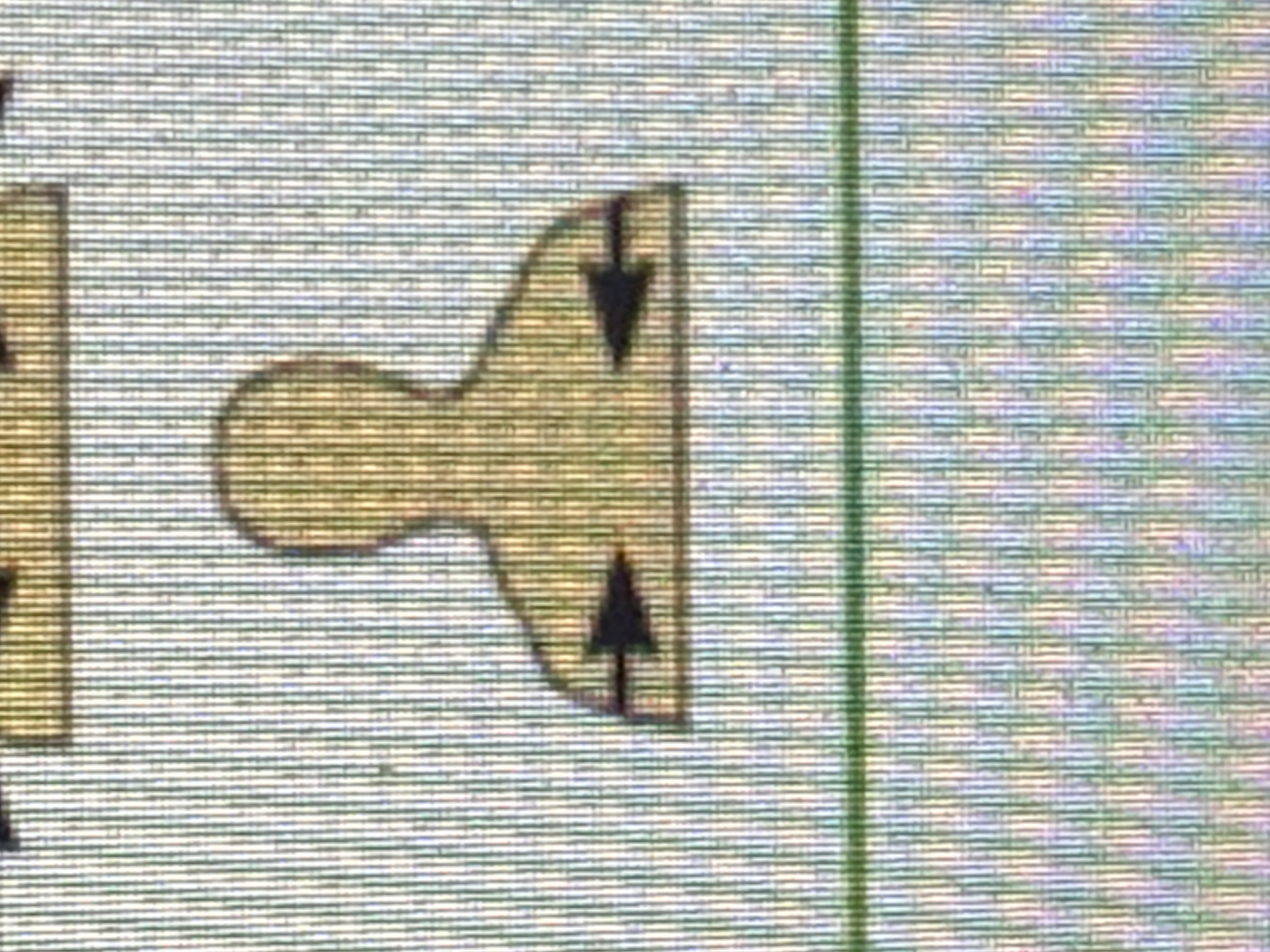

Axial
Head, neck, and trunk
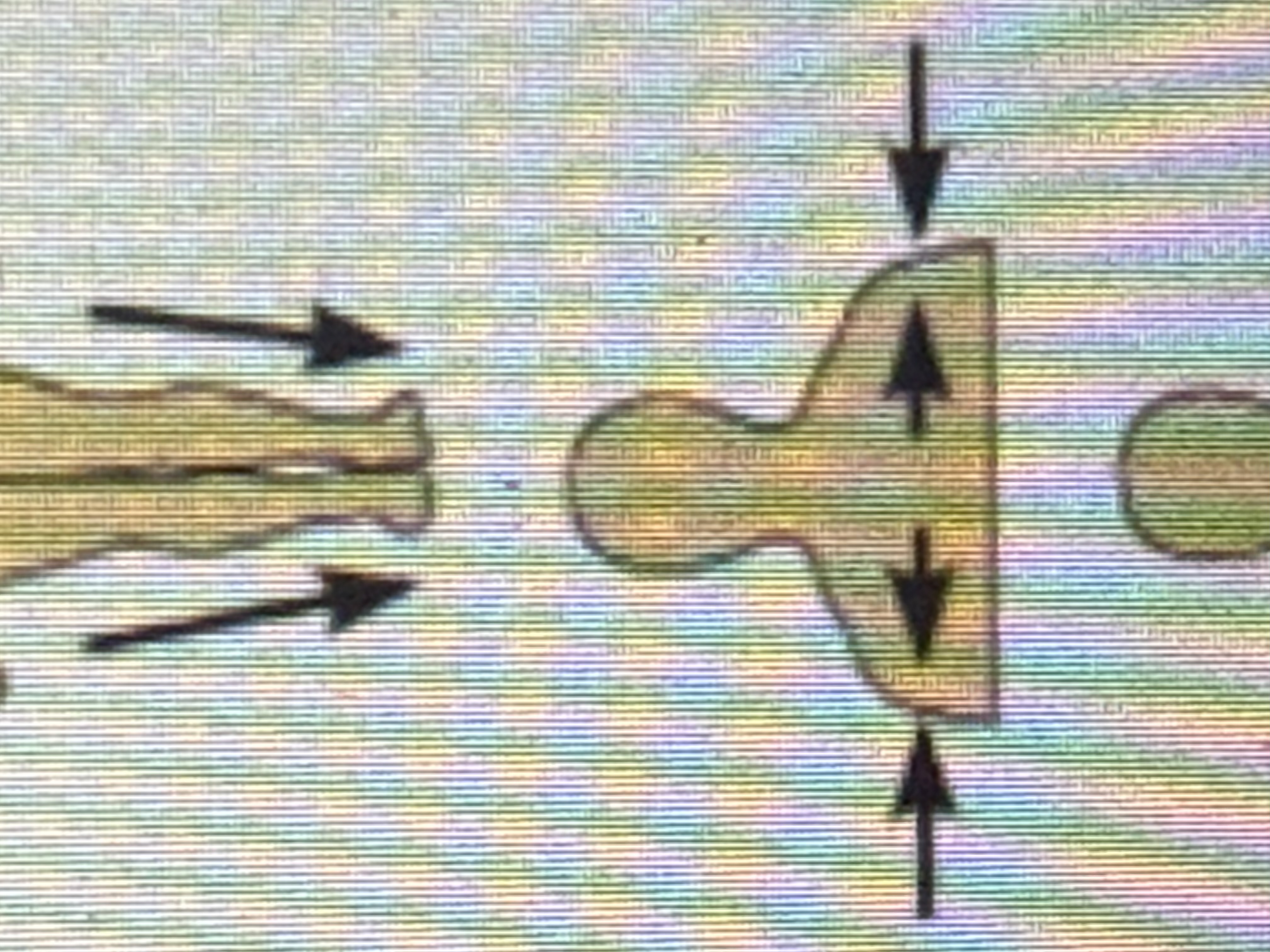
Appendicular
Appendages or limbs
Sagittal plane
Divides the body into right and left parts.
Midsagittal or medial plane
Sagittal plane that runs dire tly down the midline of the body
Parasagittal plane
Sagittal planes that are uneven (don’t cute directly in the middle of the body)
Frontal/Coronal plane
divides the body into anterior and posterior parts (front and back parts)
Transverse/horizontal plane
divides the body into superior and inferior parts(upper body & lower body)
Oblique section plane
Cuts made diagonally
Dorsal (posterior) cavity
protects the nervous system, and is divided into two subdivisions
Cranial Cavity
within the skull and encases the brain (type of dorsal cavity)
Vertebral cavity
runs within the vertebral column and encases the spinal cord (ttype of dorsal cavity)
Ventral (anterior) cavity
houses the internal organs (viscera), and is divided into two subdivisions:abdominopelvic & thoracic (seperated by diaphragm)
Parts of the Thoracic cavity
Pleural cavities – each houses a lung
§ Mediastinum – contains the pericardial cavity, and
surrounds the remaining thoracic organs
(“interpleural space”): trachea, thymus, great
vessels
§ Pericardial cavity – encloses the heart
Subdivisions of the Abdominopelvic cavity
Abdominal cavity – contains the stomach, intestines, spleen, liver, and other organs
Pelvic cavity – lies within the pelvis and contains the bladder, reproductive organs, and rectum
Ventral Cavity Membranes
§ Parietal serosa lines internal body walls
§ Visceral serosa covers the internal organs
§ Serous fluid separates the serosae
Abdominopelvic Regions & the organs in each one
Abdominal cavity – contains the stomach,
intestines, spleen, liver, and other organs
Pelvic cavity – lies within the pelvis and contains
the bladder, reproductive organs, and rectum