BIO 202 chapter 6
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/100
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
1
New cards
integumentary system
hair, nails, cutaneous glands
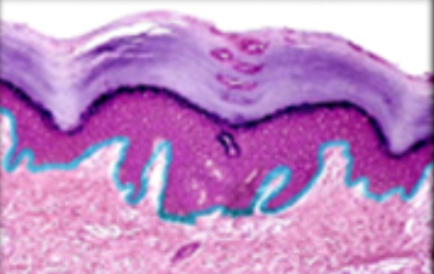
2
New cards
stratum basale
3
New cards
most vulnerable organ
skin
4
New cards
skin
largest and heaviest organ
5
New cards
epidermis
stratified squamous epithelium
6
New cards
dermis
deeper connective tissue layer
7
New cards
hypodermis
adipose tissue layer below the skin
8
New cards
dermatology
scientific study and medical treatment of integumentary system
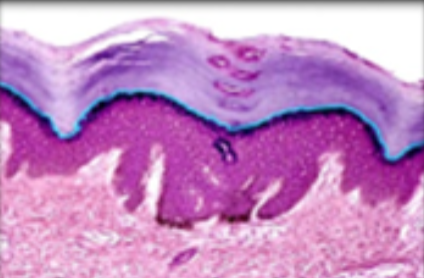
9
New cards
stratum lucidum
10
New cards
stratum granulosum
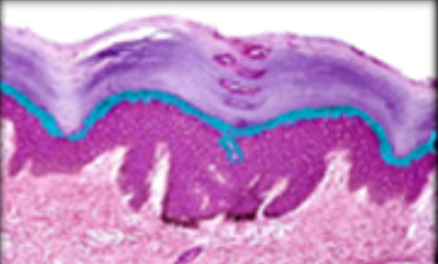
11
New cards
stratum spinosum
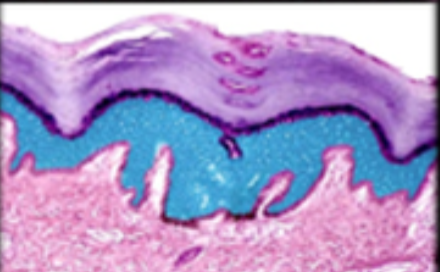
12
New cards
resistance to trauma and infection
keratin, dermic and defense's, acid mantle
13
New cards
thin skin
hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands
14
New cards
skin barrier functions
water, UV radiation, harmful chemicals
15
New cards
vitamin D synthesis
skin carries out first step-- liver and kidneys complete rest
16
New cards
sensation
skin extensive sense organ; receptors for temp, touch, pain, and more
17
New cards
thermoregulation
thermoreceptors, vasoconstriction/ vasodilation, perspiration
18
New cards
stratum corneum
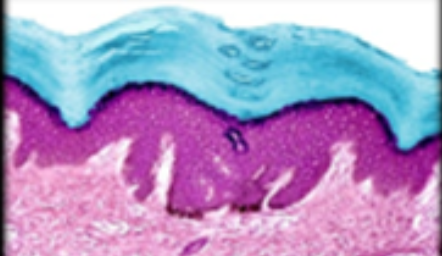
19
New cards
nonverbal communication
facial expression; important in social acceptance and self image
20
New cards
thick skin
sweat glands, but no hair follicles or sebaceous (oil) glands
palms of hands and soles of feet
palms of hands and soles of feet
21
New cards
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
includes dead cells at skin surface packed with keratin proteins
22
New cards
avascular
lacks blood vessels
Depends on the diffusion of nutrients from underlying connective tissue
Depends on the diffusion of nutrients from underlying connective tissue
23
New cards
five epidermal cell types
stem cells, keratinocytes, melanocytes, tactile cells, dendritic cells
24
New cards
stem cells
undifferentiated cells that give rise to keratinocytes
25
New cards
keratinocytes
great majority of epidermal cells, synthesize keratin
26
New cards
melanocytes
synthesize melanin that shields DNA from UV radiation
27
New cards
tactile cells
light touch receptor cells associated with dermal nerve fibers
28
New cards
dendritic cells
macrophages originating in bone marrow that guard against pathogens
29
New cards
4 events in stratum granulosum
1. Keratohyalin granules release filaggrin—a protein that binds keratin into tough bundles
2. Cells produce tough envelope proteins beneath their membranes
3. Membrane-coating vesicles release lipid mixture that spreads out over cell surface and waterproofs it
4. Keratinocytes’ organelles degenerate and the cells die
2. Cells produce tough envelope proteins beneath their membranes
3. Membrane-coating vesicles release lipid mixture that spreads out over cell surface and waterproofs it
4. Keratinocytes’ organelles degenerate and the cells die
30
New cards
epidermal water barrier
water retention is fostered by tight junctions between skin cells and the waterproofing that occurs in the stratum granulosum
31
New cards
papillary layer
thin zone of areolar tissue in and near the dermal papilla
rich in small blood vessels
rich in small blood vessels
32
New cards
reticular layer
thicker layer of dense, irregular connective tissue
stretch marks (striae)
stretch marks (striae)
33
New cards
hypodermis
contains more areolar and adipose tissue
pads body and binds skin to underlying tissues
common site of drug injection due to many blood vessels
pads body and binds skin to underlying tissues
common site of drug injection due to many blood vessels
34
New cards
melanin
Most significant factor in skin color
Produced by melanocytes, accumulates in keratinocytes
Produced by melanocytes, accumulates in keratinocytes
35
New cards
eumelanin
brownish black
36
New cards
pheomelanin
reddish yellow (sulfur containing)
37
New cards
hemoglobin
pigment in red blood cells; adds reddish to pink hue in skin
38
New cards
carotene
Yellow pigment acquired from egg yolks and yellow/orange
vegetables; Concentrates in stratum corneum and subcutaneous fat
vegetables; Concentrates in stratum corneum and subcutaneous fat
39
New cards
UV light harmful effects
causes skin cancer, breaks down folic acid
40
New cards
UV light benefits
stimulates vitamin D synthesis
41
New cards
cyanosis
blueness due to oxygen deficiency (Grandmas fingers turn blue)
42
New cards
erythema
redness due to increased blood flow to skin
43
New cards
pallor
paleness due to decreased blood flow to skin
44
New cards
jaundice
yellowing due to bilirubin in blood (can be caused by liver)
45
New cards
hematoma
bruising; clotted blood under skin
46
New cards
friction ridges
Markings on the fingertips that leave oily fingerprints (unique pattern, remains unchanged throughout life)
47
New cards
flexion lines (creases)
Lines on the flexor surfaces of the digits, palms, wrists, elbows
48
New cards
Hemangiomas
(birthmarks) Patches of discolored skin caused by benign tumors of dermal capillaries
49
New cards
accessory organs
Hair, nails, and cutaneous glands
50
New cards
Pliable soft keratin
makes up stratum corneum
51
New cards
compact hard keratin
makes up hair and nails
52
New cards
Pilus/ Pili
aka hair follicle
53
New cards
3 hair zones
bulb, root, shaft
54
New cards
bulb
swelling at the base where hair originates in
dermis or hypodermis
dermis or hypodermis
55
New cards
root
remainder of the hair in the follicle
56
New cards
shaft
portion of hair above the skin surface
57
New cards
dermal papilla
Bud of vascular connective tissue encased by bulb
Only source of nutrition for hair
Only source of nutrition for hair
58
New cards
hair matrix
Region of mitotically active cells immediately above
papilla
Hair’s growth center
papilla
Hair’s growth center
59
New cards
3 layers of hair
medulla, cortex, cuticle
60
New cards
medulla
Core of loosely arranged cells and air spaces
61
New cards
cortex
Constitutes bulk of the hair
Consists of several layers of elongated keratinized cells
Consists of several layers of elongated keratinized cells
62
New cards
cuticle
Composed of multiple layers of very thin, scaly cells that overlap each other
Free edges directed upward
Free edges directed upward
63
New cards
follicle
diagonal tube that extends into the dermis and possibly
hypodermis, contains the hair root and has two principal layers
hypodermis, contains the hair root and has two principal layers
64
New cards
epithelial root shaft
Extension of the epidermis lying adjacent to hair root
Widens at deep end into bulge—source of stem cells for
follicle growth
Widens at deep end into bulge—source of stem cells for
follicle growth
65
New cards
connective tissue root sheath
Derived from dermis but a bit denser
Surrounds epithelial root sheath
Surrounds epithelial root sheath
66
New cards
hair receptors
sensory nerve fibers entwining follicles
67
New cards
piloerector muscles
(erector pili) smooth muscle attaching follicle to dermis
68
New cards
black and brown hair
eumelanin
69
New cards
red hair
pheomelanin
70
New cards
blond hair
intermediate amount of pheomelanin and very little eumelanin
71
New cards
gray and white hair
hair have little or no melanin
72
New cards
nail plate
hard part of nail
73
New cards
free edge
overhangs the fingertip
74
New cards
nail body
visible attached part of nail
75
New cards
nail root
extends proximally under overlying skin
76
New cards
apocrine sweat glands
groin, anal region, axilla, areola of nipple beard area of men
Produce sweat that is milky and contains fatty acids
Produce sweat that is milky and contains fatty acids
77
New cards
bromhidrosis
Disagreeable body odor produced by bacterial action on sweat from apocrine glands
78
New cards
merocrine sweat glands
Simple tubular glands; Watery perspiration that helps cool the body
MOST NUMEROUS SKIN GLAND
MOST NUMEROUS SKIN GLAND
79
New cards
myoepithelial cells
Found in both apocrine and eccrine glands
Contract in response to stimulation by sympathetic nervous system and squeeze perspiration up the duct
Contract in response to stimulation by sympathetic nervous system and squeeze perspiration up the duct
80
New cards
acid mantle
inhibits bacterial growth
81
New cards
diaphoresis
Sweating with wetness of the skin
• 1 L sweat per hour may be lost during exercise
• 1 L sweat per hour may be lost during exercise
82
New cards
cutaneous transpiration
Water loss from skin not due to sweating
• Water diffuses between the keratinocytes and evaporates from the skin surface
• Water diffuses between the keratinocytes and evaporates from the skin surface
83
New cards
sebaceous glands
flask-shaped and have short ducts opening into hair follicles
holocrine secretion style
holocrine secretion style
84
New cards
sebum
oily secretion of sebaceous glands
85
New cards
ceruminous glands
secrete a combination of both sebum and dead epithelial cells to form cerumen
86
New cards
mammary glands
Produce milk
87
New cards
mammary ridges
(milk lines) Two rows of mammary glands in most mammals
88
New cards
basal cell carcinoma
Most common skin cancer
Least dangerous because it seldom metastasizes
forms in stratum basale
Least dangerous because it seldom metastasizes
forms in stratum basale
89
New cards
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Arises from keratinocytes of stratum spinosum
Tends to metastasize to lymph nodes and may become lethal
Tends to metastasize to lymph nodes and may become lethal
90
New cards
Melanoma
arises from melanocytes
less than 5% of skin cancers
less than 5% of skin cancers
91
New cards
burns
leading cause of accidental deaths
92
New cards
burn deaths
Fluid loss, Infection, Toxic effects of eschar (burned, dead tissue)
93
New cards
debridement
removal of eschar
94
New cards
first degree burn
Only involves the epidermis
• Redness, slight edema, and pain
• Heals within days
• Redness, slight edema, and pain
• Heals within days
95
New cards
second degree burn
(partial-thickness burn) Involves part of dermis, May appear red, tan, or white; blistered and painful, Two weeks to several months to heal and may leave scars
96
New cards
third degree burn
(full-thickness burn) Involves all of dermis and often some deeper tissues, Often requires skin grafts, Needs fluid replacement, infection control, supplemental nutrition
97
New cards
autograph
tissue from another location on the same person’s body
98
New cards
split-skin graft
involves taking epidermis and part of the dermis from undamaged area such as the thigh or buttocks
99
New cards
isograft
tissue from identical twin
100
New cards
homograft
(allograft) tissue from unrelated person