2.4 Assesment of intelligence
1/61
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
A good intelligence test includes
Standardization of administration
Variety of task
Norm referencing
What are intelligence tests used for?
Selection
Diagnosis
Evaluation
Remember is the test?
reliable
validated
useful
Reliability
Internal: Items that measure the same construct
Measures the consistency of test results
Test-retest → Similar IQ scores in different times
- IQ scores can fluctuate (± 15)
- Is it accurate to assign a single IQ score based on one test administration? NO
The test provides consistent results over time and across different settings.
Test-retest:
Similar IQ scores in different times
(Consistency of a test over time.)
Validity
intelligence tests may not measure all aspects of intelligence (multiple intelligences theories vs singular intelligence)
intelligence is influenced by cultural and contextual factors
refers to how well a test measures what it is supposed to measure
Usefulness
Intelligence tests predict academic/ job performance but their predictive power diminishes over time and is affected by situational factors
Present limitations guiding educational interventions
refers to how well a test serves its intended purpose in real-life settings — whether in education, clinical practice, job placement, or research.
Instruments for measuring intelligence
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS
four different versions
scales have been revised to incorporate improvements and adapt scales to the current population
1st version Wechsler
He designed and standardized among a sample of 1,500 adults
known as Wechsler Intelligence Scale
In 1955 Wechsler introduced two tests
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS)
Wechsler Scale for Children (WISC)
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS
adults aged between 16 and 75
Wechsler Scale for Children (WISC)
children aged between 5 and 16 years.
importance of including verbal & nonverbal tests
✓ Verbal scale
✓ Manipulative scale
✓ Total IQ
Wechsler's original test
assess intellectual ability
such as:
Verbal comprehension
Abstract reasoning
Perceptual organization
Quantitative reasoning
1st version WAIS (Wechsler)
WAIS (Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale, 1955).
Evaluates: total IQ, verbal IQ, manipulative IQ
Includes 11 tests:
Information, Comprehension, Arithmetic, Similarities, Digits, Vocabulary, Number Key, Incomplete Figures, Cubes, Comic Books and Puzzles.
The 1st version includes, how many tests?
Includes 11 tests:
Information, Comprehension, Arithmetic, Similarities, Digits, Vocabulary, Number Key, Incomplete Figures, Cubes, Comic Books and Puzzles.
2nd version WAIS (Wechsler):
- WAIS - R
3rd version WAIS (Wechsler)
WAIS - III
4th version WAIS (Wechsler)
the version of test which we use today
Includes 1 general scale (total IQ) and 4 subscales:
Verbal Comprehension Scale
Perceptual Reasoning Scale
Working Memory Scale
Processing speed scale
Materials
Technical and interpretation manual.
Application and correction manual.
Stimulus booklets
Response booklet
Bicolor cubes
Correction templates
Qualification level in the test? Must be introduced by who?
a person with from an advanced degree in Psychology
Questionnaire description (purpose, application, age, duration)
to assess the intellectual aptitude of adults
individual
16 -89 years old
60 minutes for 10 main tests
90 minutes for complete application
Cognitive areas evaluated in the test (the scales)
• Verbal comprehension
• Perceptual reasoning
• Working memory
• Processing speed
General intellectual aptitude (total IQ)
Verbal comprehension scales main tests:
Similarities
Vocabulary
Information
Verbal comprehension scales optional test
Comprehension
Similarities
verbal comprehension scale
18 items
Composed of words of common objects or concepts
AIM: evaluate verbal reasoning and concept formation
Example of similarities:
How are they similar?
orange - pear;
dog - lion;
table - chair
Vocabulary
verbal comprehension scale
Task 1: name object presented on the picture.
Task 2: define words that the examiner names.
Aim: to evaluate the subject's lexicon and formation of
verbal concepts.
the range of words gets harder to define
Example of Vocabulary
What does the word rivalry mean.
what does an apple mean?
Information
Verbal comprehension scale
Task: To answer orally questions about general
knowledge.
Aim: To assess the ability to acquire, store and retrieve
knowledge.
example of information test
What is the capital of Spain?
The index of Verbal comprehension assesses
the ability to understand, generate and transfer verbal information.
(how well a person thinks and learns using language)
Perceptual reasoning scales main tests
Cubes
Matrices
Visual puzzles
Perceptual reasoning scales optional tests
Scales
Incomplete figures
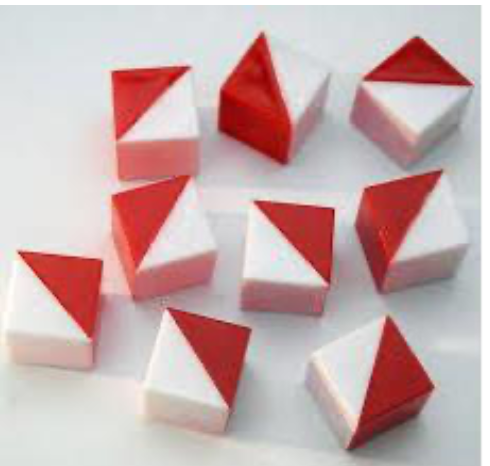
Cubes test
Perceptual reasoning scales
14 items
30 seconds to complete
Task: to reproduce with colored cubes the models represented in plates.
Aim: to evaluate the ability to analyze and synthesize abstract visual stimuli.
Example of Cubes test
the person observes the psychologist creating a image of the cubes, the task is to create as similar image of the cubes as the psychologist

Matrices
Perceptual reasoning scales
26 items
Task: to observe a matrix or an incomplete series and select the correct one among different options.
Aim: to evaluate fluid intelligence, general visual intelligence, spatial aptitude and classification
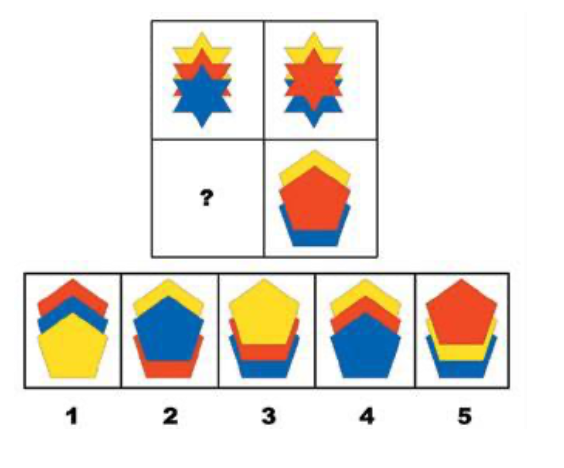
Example of Matrices
the person must complete the photo by selecting the correct item to the rest
Visual puzzles
Perceptual reasoning scales
26 items
Task: the examiner shows a puzzle that the subject must reproduce by selecting the 3 images that complete it.
Objective: to evaluate non-verbal reasoning, ability to analyze & synthesize visual stimuli.
The index of Perceptual reasoning measures
The ability to process visual and spatial information, as well as to reason and solve problems with that information
Working memory scales main test
Digit span
Arithmetic
Working memory scales optional tests
Letters and numbers sequencing
Digits span
Working memory scales
24 items
Task 1: digits in direct order.
Task 2: digits in reverse order.
Task 3: digits in increasing order
Aim: to evaluate learning, memory, attention,
auditory processing of information
Example of digit span (photo)

Arithmetic
Working memory scales
22 items
Task: mentally solve a series of arithmetic problems and give an answer in the time limit.
Aim: to evaluate mental representations, concentration, attention,
short and long term memory.
Example of Arithmetic
Arithmetic problems
Paula is 23 years old and Mario is 15 years older. How old is Mario?
The index of Working memory assesses
The ability to retain and manipulate information in short-term memory.
Processing speed scales main tests:
Digital symbol-coding
Symbol search
Processing speed scales optional tests
Cancellation
Symbol search
Processing speed scales
60 items
Task: to observe two model symbols & determine whether or not they are among another group of symbols in a limited time.
Aim: to evaluate visual short-term memory, visual-motor coordination, cognitive flexibility, visual discrimination
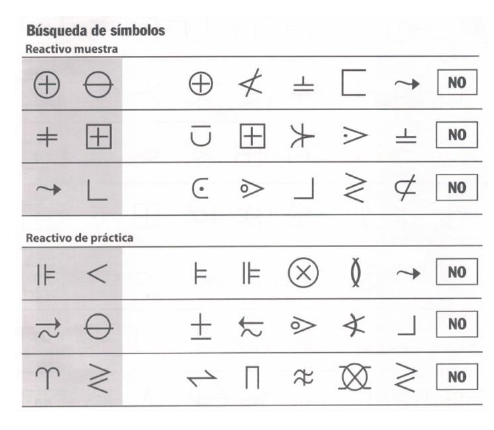
Example of symbol search test
the time is limited
identify if the items corresponds to the table
Digital symbol-coding
Processing speed scales
135 items
Task: copy symbols matched to numbers in a limited time.
Aim: to assess processing speed, visual short-term memory, learning ability, and psychomotor speed.
Example of Digital symbol-coding
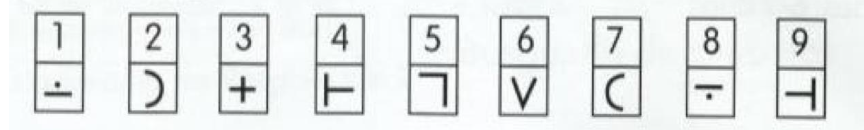
The index of Processing speed measures
duration: 1 min 30 seconds
the speed with which visual information can be processed efficiently.
Punctuation of EACH TEST
The direct scores obtained in each of the tests are transformed into scalar scores:
- Mean (M)= 10
- Standard deviation (SD) = 3
Punctuation of the 4 general scales & IQ
4 general scales & IQ:
M = 100 & SD = 15
Ecological validity
General intelligence related to work performance, psychological well-being.
Specific domains not clearly related to other aspects.
how well the results of a test or study apply to real life or everyday situations.
Practical WAIS applications
most universal test applied
Great practical and clinical utility.
Used for more than 70 years in different contexts:
• Identification of intellectual disabilities
• Learning disorders
• Clinical intervention
• Neuropsychological evaluation.
The results of intelligence assessment tests can help in
early detection of cognitive impairment:
✓ First signs impairment: 20-29 years.
✓ Significant impairment: > 55 years.
we can therefore evaluate cognitive impairment in the patient
Areas of cognitive impairment
Processing speed.
Executive functioning
Sensory acuity
Psychomotor aptitude.
Working memory
Attention
Scores obtained on the tests may be invalidated due to:
Application errors
Recent exposure to the items
Physical and sensory limitations of the subject
Erroneous response patterns (I don't know, always the same answers).