(12) geo: water resources
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
what is the total of moisture balance in the world surface area?
71% water, 29% continents
where is all of earth’s water located?
97% is in the ocean, 2.8% is drinkable and 68.7% is locked in glaciers
the largest components of surface freshwater are…
glaciers and snow, aka snowpacks (himalayas, tibetan plateau, california)
what is the hydrologic cycle?
the movement of water in all forms (through processes like evaporation, precipitation, etc.)
are surface water resources evenly spread across the earth?
no because of the ITCZ and climate change
countries have abundant rainfall due to the amount of?
freshwater access
what is water that is in the atmosphere called?
water vapor
what two processes add water to the atmopshere?
evaporation and transpiration
evaporation
water from the ground
ex: (puddles drying up) is most important in water
transpiration
the movement and evaporation of water by plants
(most important in continents)
what is evapotranspiration?
transpiration + evaporation
what does water interact with first when it travels to the subsurface?
soil
when soil becomes saturated…
the water moves further into the soil and becomes groundwater
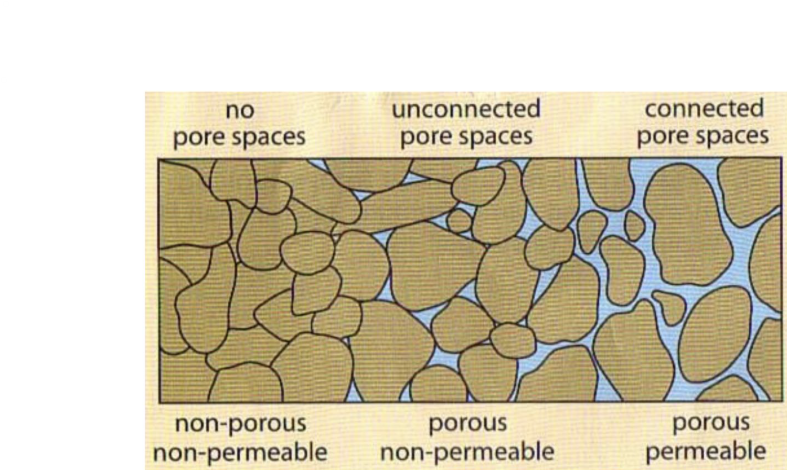
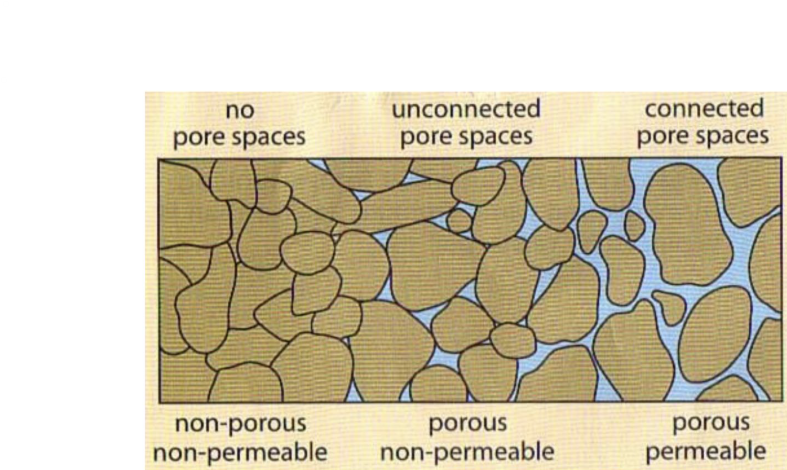
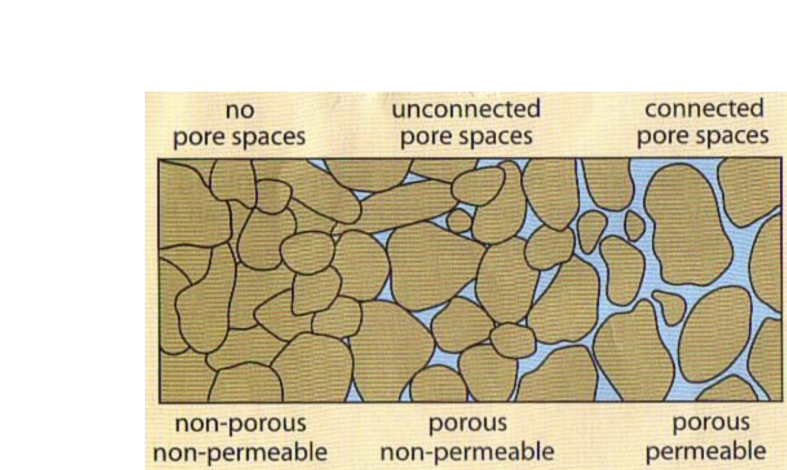
what is soil made of?
physical particles and pore space
porosity
empty spaces in soil
what is high porosity?
higher potential to hold water
what is low porosity?
lower potential to hold water
permeability
how connected the empty spaces in soil are
important in oil and gas exploration
porosity = ?
volume of voids / total volume
what is the goal of fracking?
to increase the permeability of rocks
what is gravitational water?
water that is unavailable for plants because it fills the pore space with soil, but the soil doesn’t have enough strength. causing it to move downward
what is capillary water?
water that is held on to soil particles by capillary action (available)
ex: putting a drop of water on a coin to see how much water it can hold
what is hydroscopic water?
water that is held on to soil particles by capillary action, but beyond what can be accessed by plant roots (unavailable)
what type of water does the left image represent?
hydroscopic waters
what type of water does the middle image represent?
capillary waters
what type of water does the right image represent?
gravitational waters
what is field capacity?
the maximum capacity of soil to hold water
what will water added to soil after it reaches field capacity turn into?
groundwater
what is the wilting point?
the point where all water available is hygroscopic and unavailable to plants
field capacity soil is…
saturated, and gravitational water filters into groundwater
available water is…
not saturated, and capillary water is accessible to plants
the wilting point soil is…
not saturated, all water is hydroscopic and inaccessible to plants
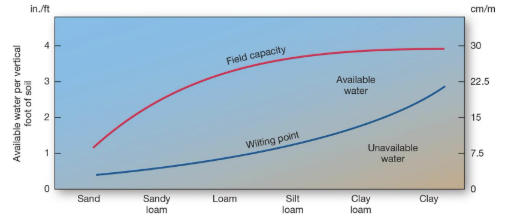
what is the water above the red line called?
gravitational water
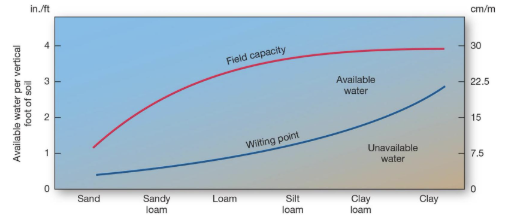
what is the water below the red line called?
capillary water
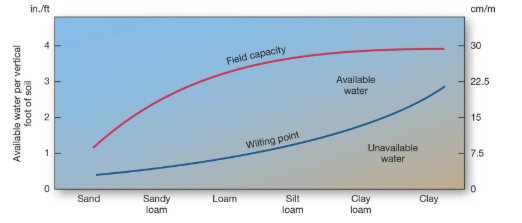
what is water below the blue line called?
hydroscopic water