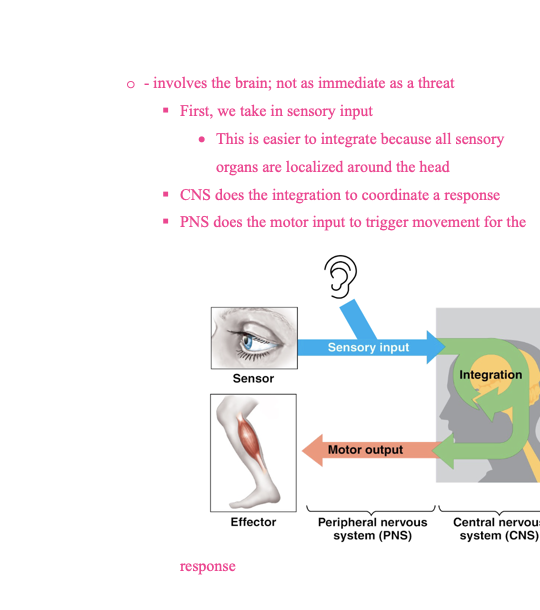
TOPIC 7- Control Systems
1/29
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
autocrine

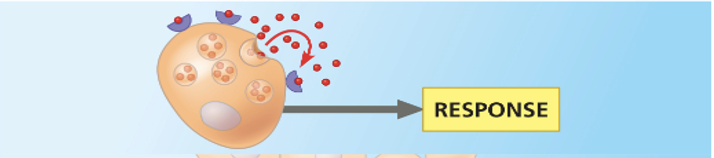
paracrine

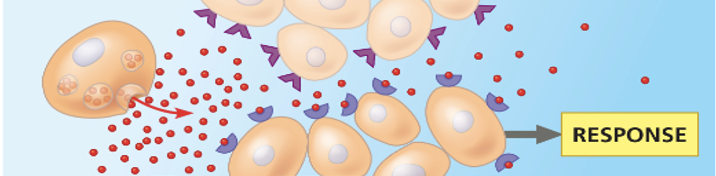
endocrine
signal (hormone) that travels to the target via blood

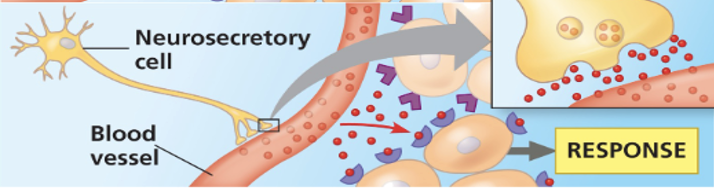
neuroendocrine
signal that originated from a neuron and travels to the target via blood stream
polypeptide hormone

amine hormone
modified amino acids that can be lipid-soluble or water-soluble
steroid hormone

tropic hormones
hormones that trigger the release of other hormones (in a hormone cascade)
high blood glucose
stimulus: _________
detected by pancreatic beta cells
response- secretion of insulin
target- liver, muscles, etc
response- decrease blood glucose via glycogen synthesis
low blood glucose
stimulus: _______
source- pancreatic alpha cells
target- liver
response- increase blood glucose via glycogen breakdown
insulin
facilitates glycogen synthesis; decreases blood glucose
glucagon
increases blood glucose through glycogen breakdown
prothoracicotropic hormone

ecdysteroid

juvenile hormones

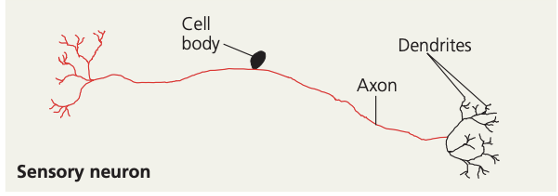
sensory neuron

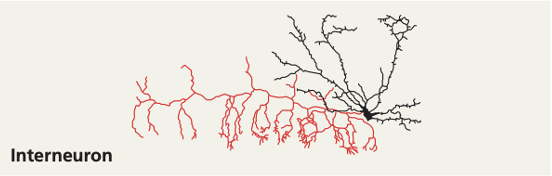
interneurons

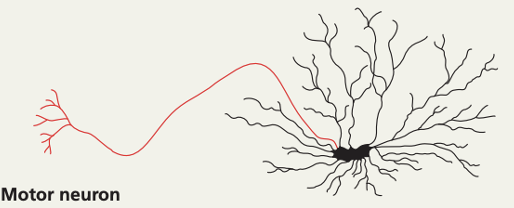
motor neuron

sodium potassium pump
______ always working to bring sodium ions out and bring potassium ions into the cell
means the intercellular environment is more negative
non-gated channel
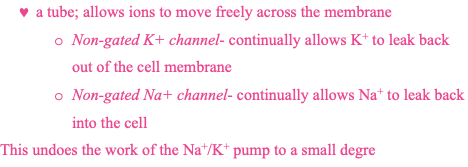
ligand-gated sodium channel

voltage-gated sodium channel
voltage-gated potassium channel

action potential steps
resting state- gated channels are closed
slow depolarization- stimulus opens up ligand-gated sodium channel
depolarization- opens most voltage-gated sodium channels and keeps the potassium channel closed
repolarization- voltage-gated sodium channels are closed, while voltage-gated potassium channels are opened
hyperpolarization- all sodium channels are now closed but potassium is still getting pumped
excitatory neurotransmitter

inhibitory neurotransmitter

temporal summation
one signal repeated over time
spatial summation

involuntary integration

voluntary integration