Lesson 66: Structure and Function of the Pharynx and Esophagus
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
nasopharynx
1
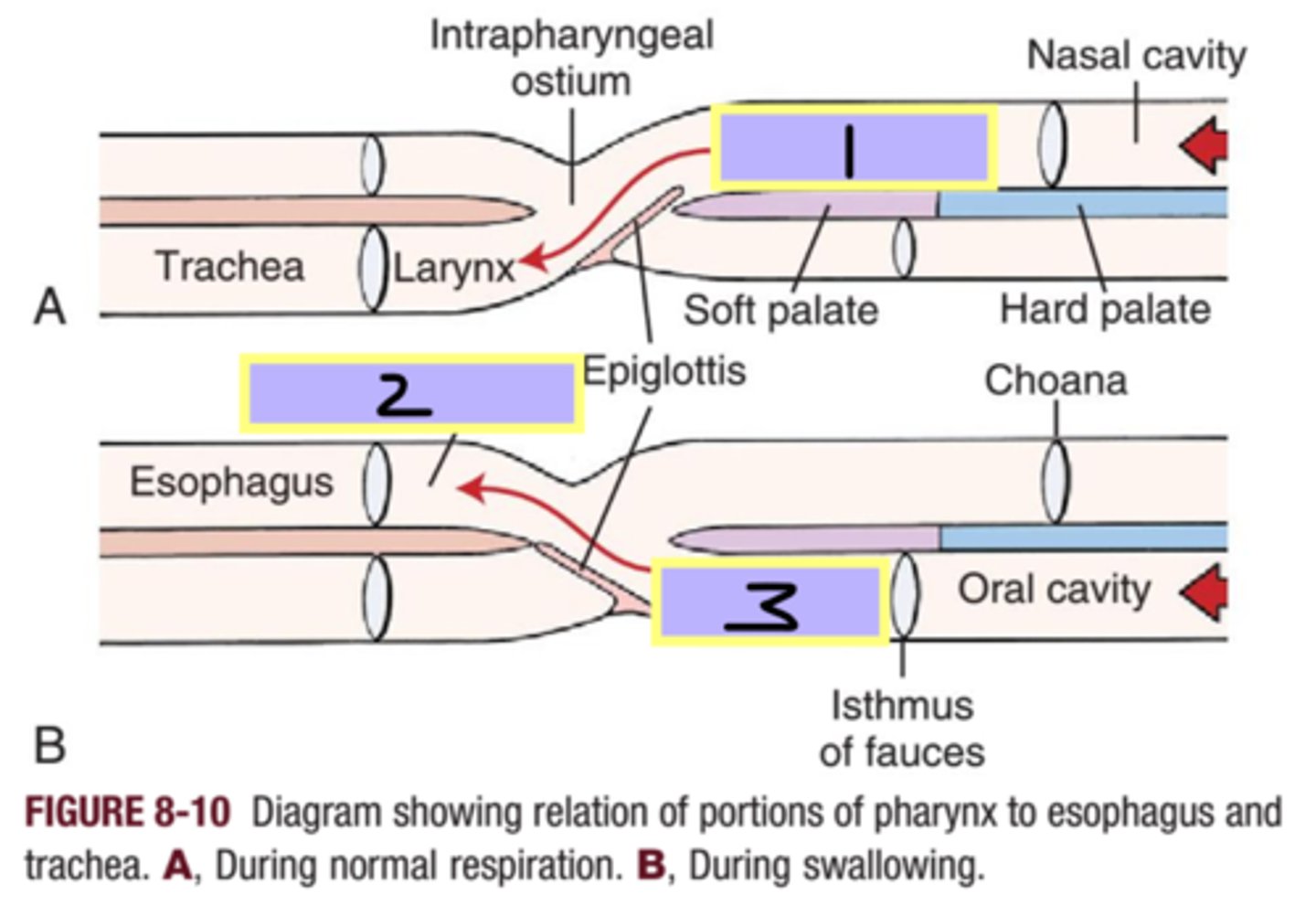
nasopharynx
laryngopharynx
2
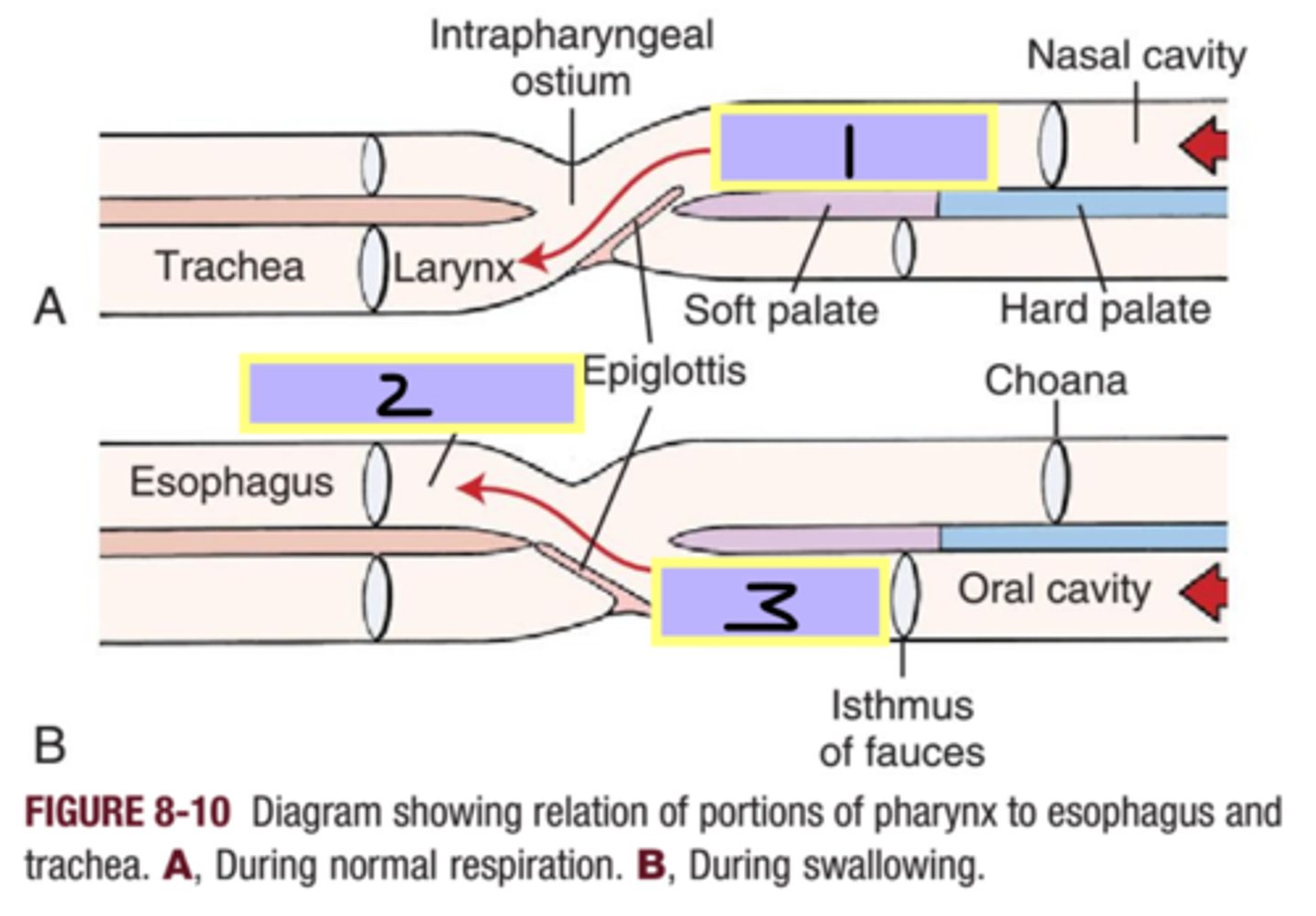
laryngopharynx
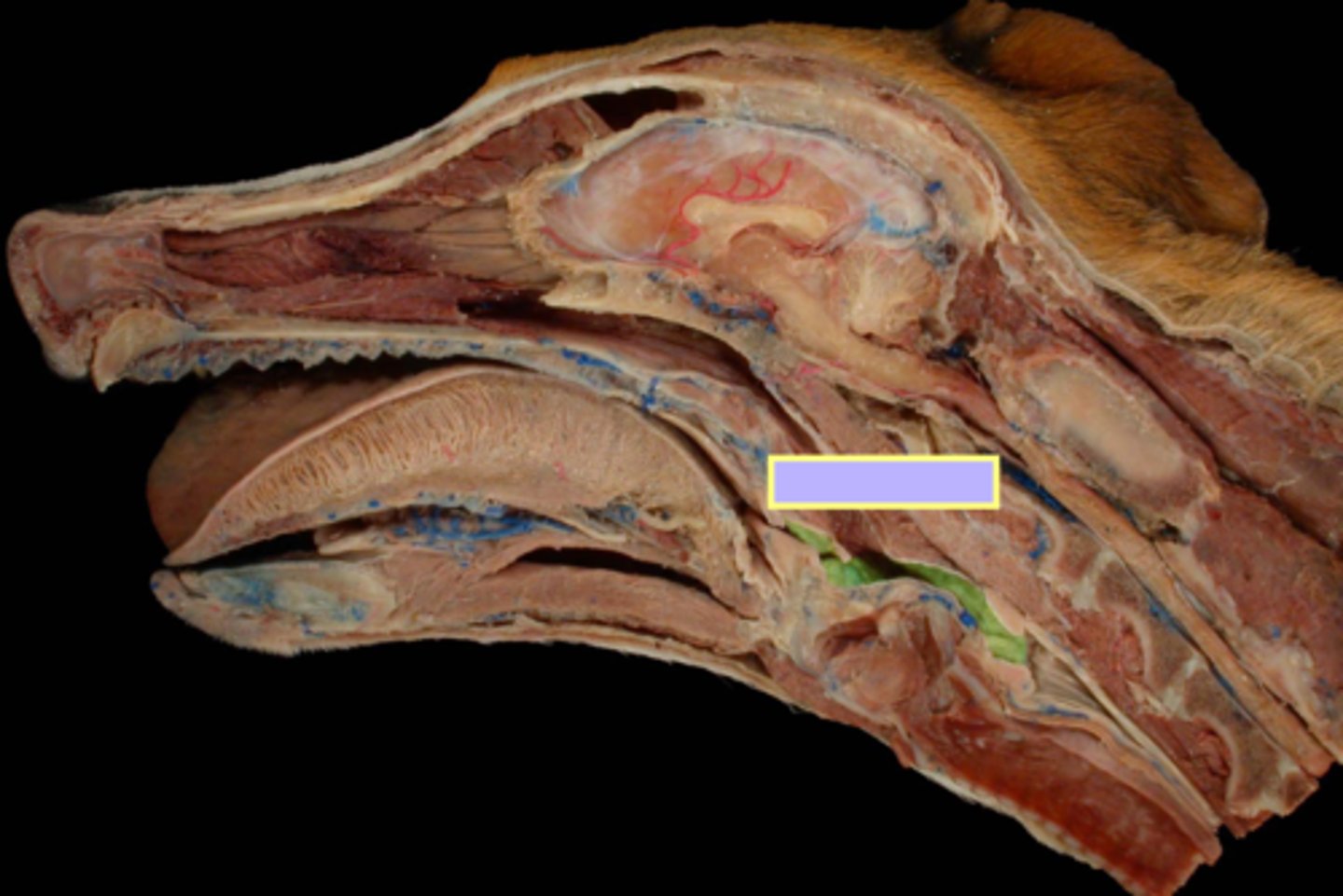
oropharynx
3
oropharynx
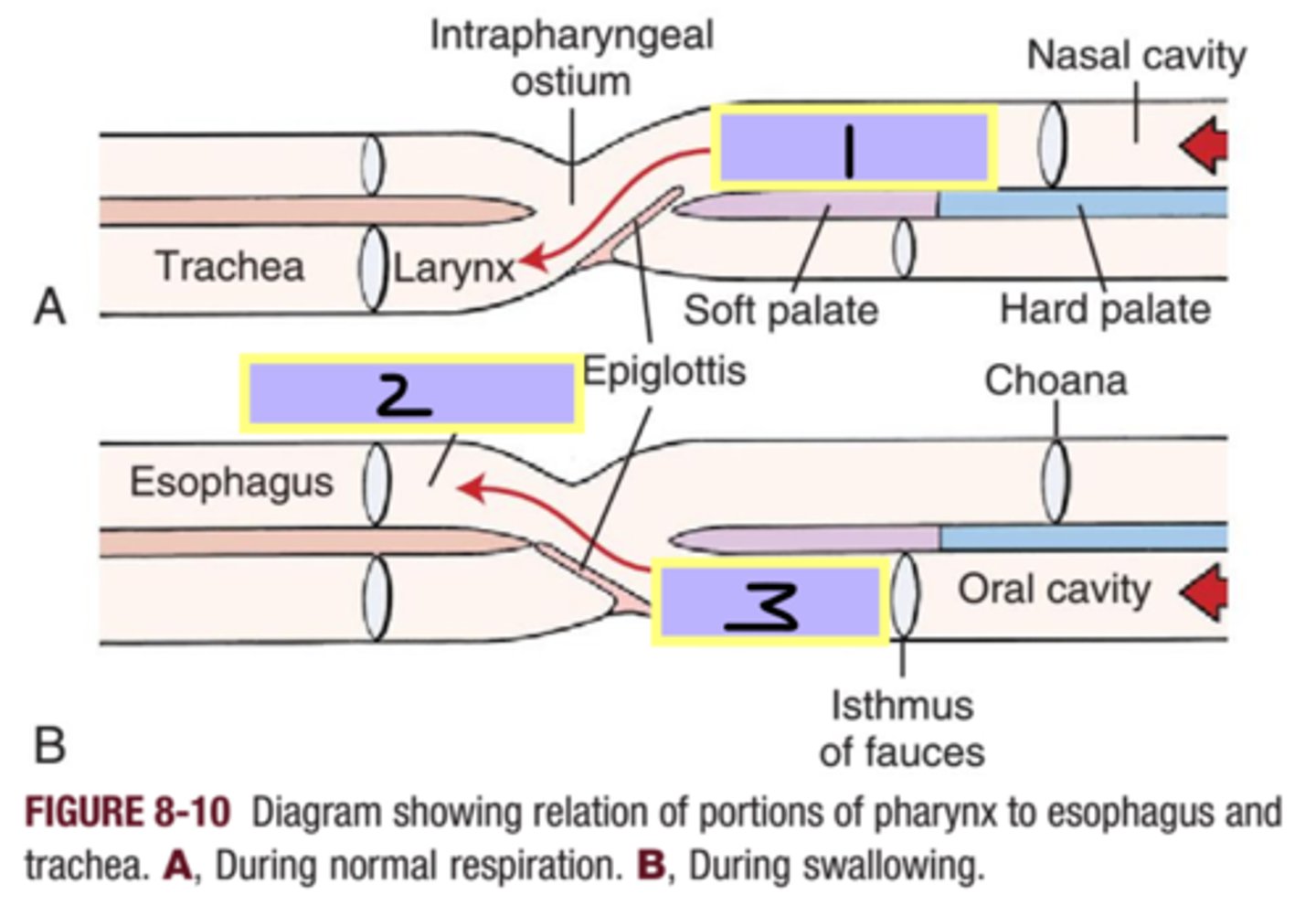
epiglottis
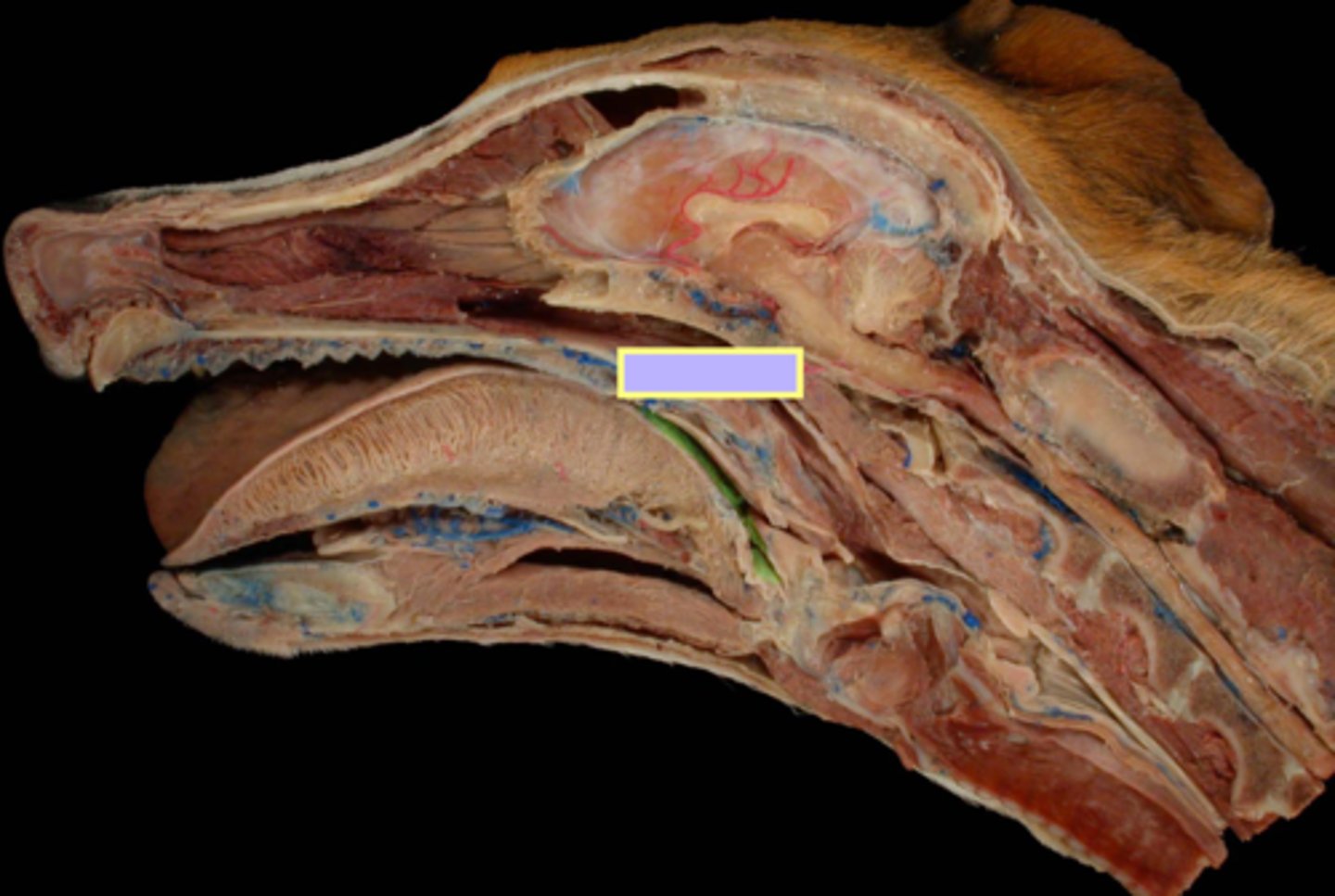
hyopharyngeus muscle
Muscles of the pharynx:
2
contract to push food into the esophagus (collapsing passage)
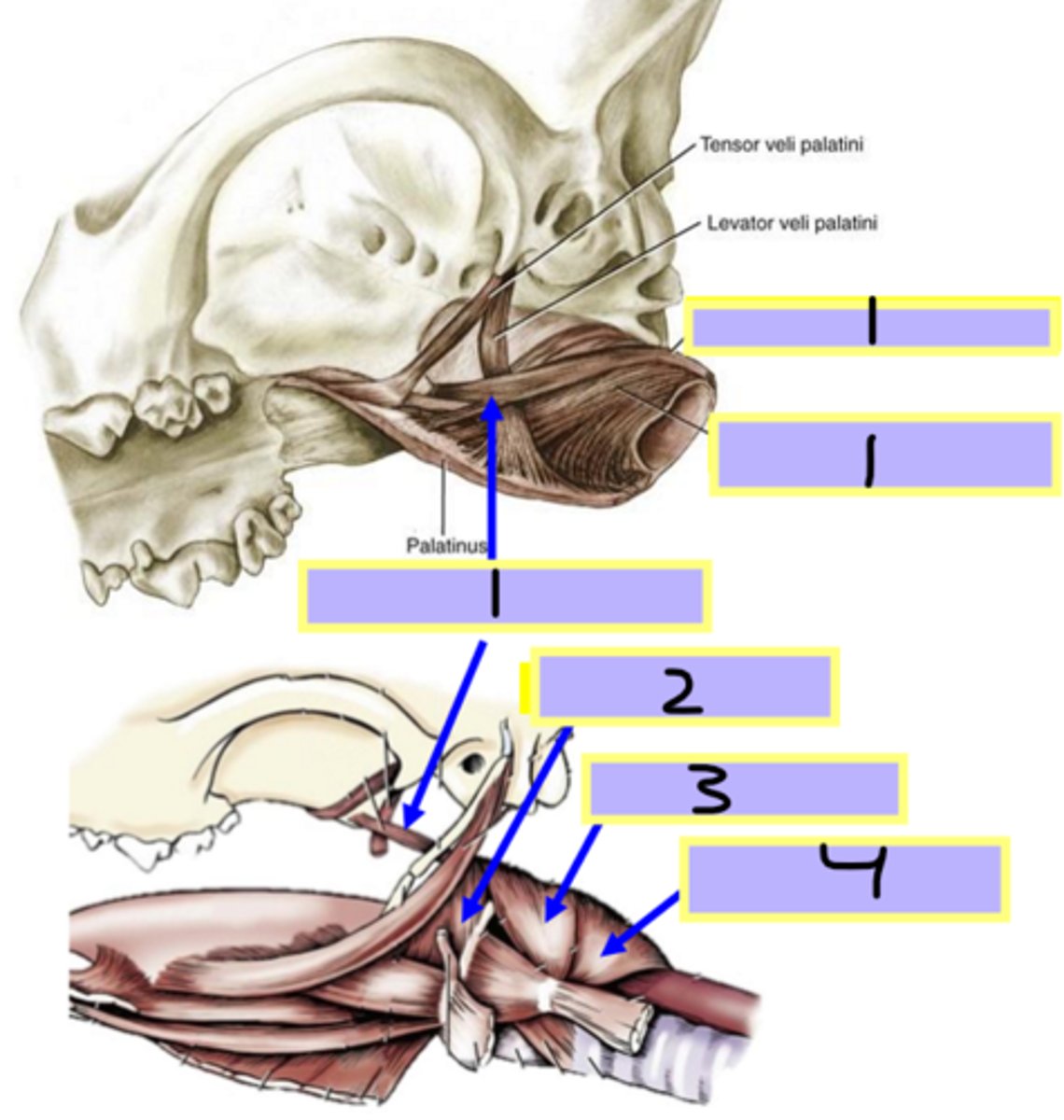
hyopharyngeus muscle
Muscles of the pharynx:
contract to push food into the esophagus
(collapsing passage)
thyropharyngeus muscle
Muscles of the pharynx:
3
contract to push food into the esophagus
(collapsing passage)
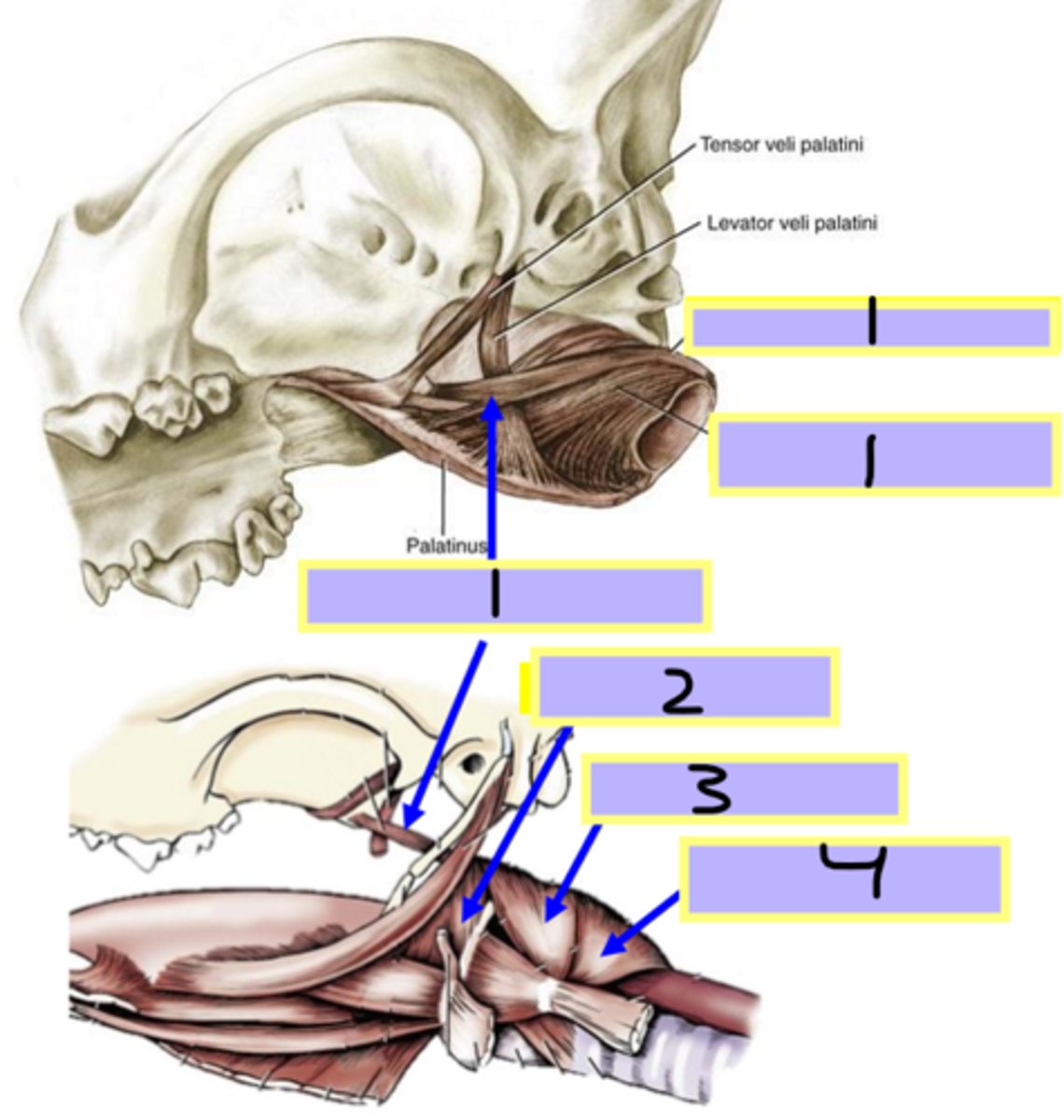
thyropharyngeus muscle
Muscles of the pharynx:
contract to push food into the esophagus
(collapsing passage)
cricopharyngeus muscle
Muscles of the pharynx:
4
contract to push food into the esophagus
(collapsing passage)
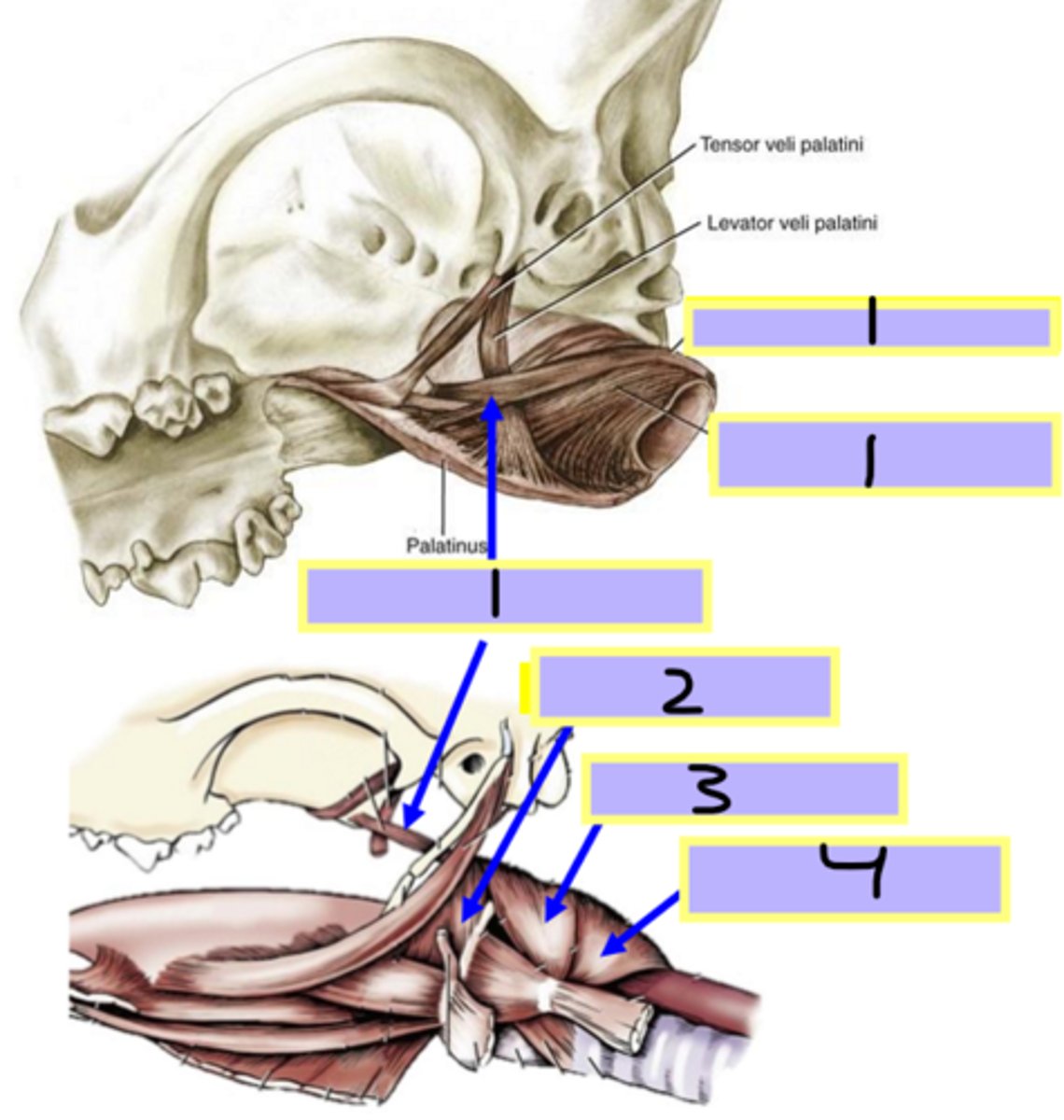
cricopharyngeus muscle
Muscles of the pharynx:
contract to push food into the esophagus
(collapsing passage)
pterygopharyngeus muscle
Muscles of the pharynx:
1
pharyngeal shorteners (swallowing)
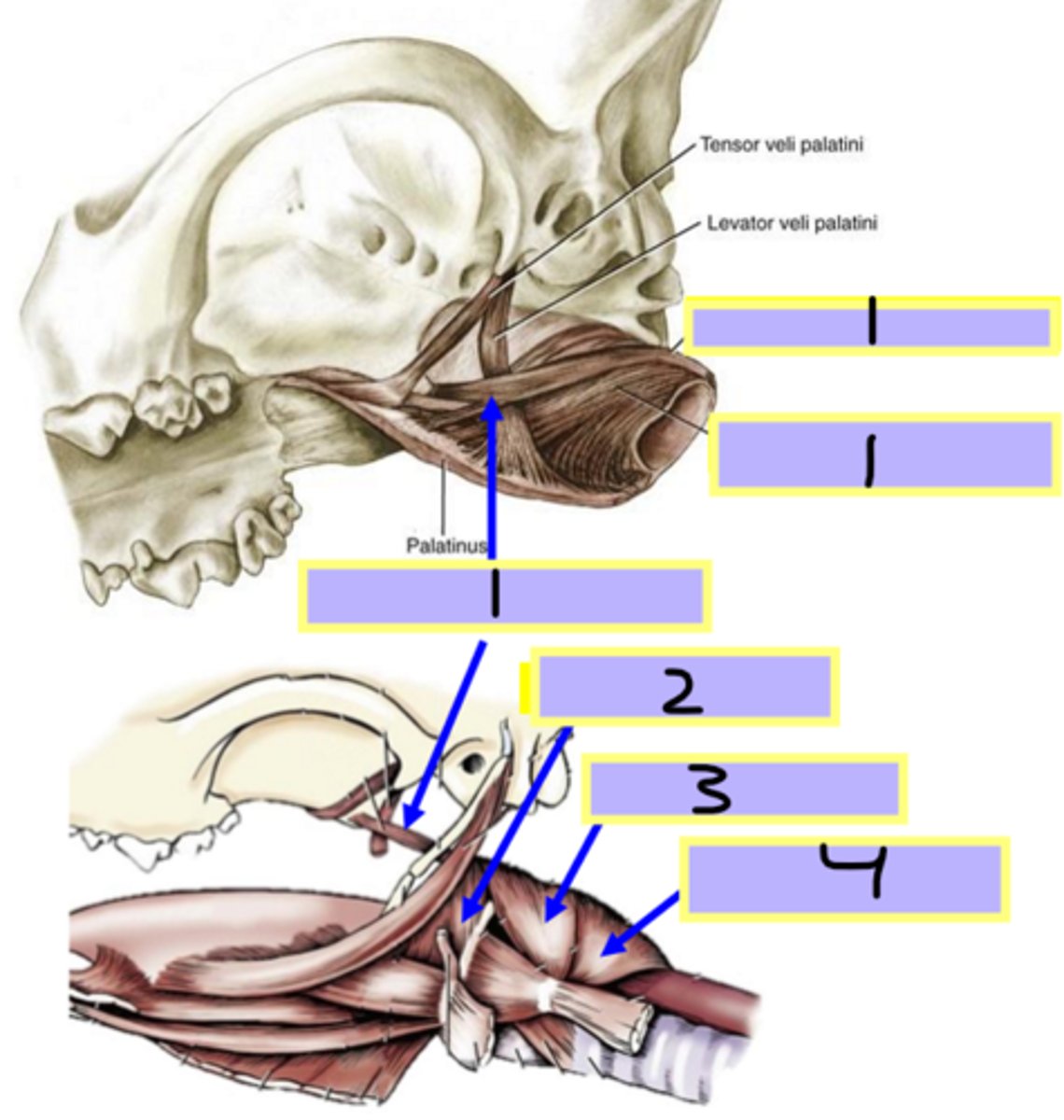
palatopharyngeus muscle
Muscles of the pharynx:
pharyngeal shorteners (swallowing)
stylopharyngeus muscle
Muscles of the phaynx:
enlarges the pharynx during swallowing
vagus nerve (CN X)
Nerve supply to the pharynx:
motor innervation to the muscles and sensory innervation to the lumen
glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
Nerve supply to the pharynx:
motor innervation to the muscles and sensory innervation to the lumen
trigeminal nerve (CN V, maxillary branch)
Nerve supply to the pharynx:
sensory innervation to the lumen
external carotid artery
Blood supply to the pharynx:
1
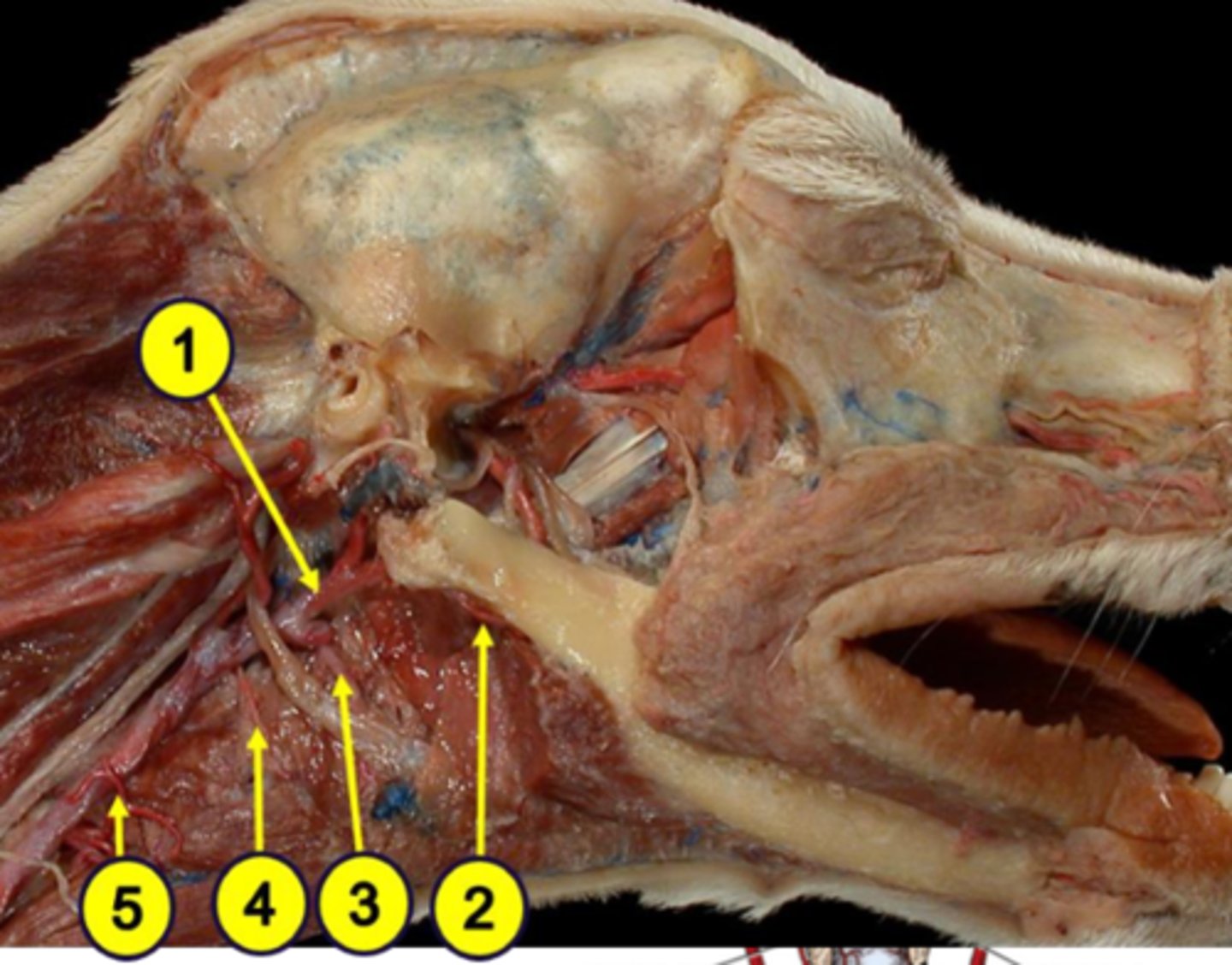
facial artery
Blood supply to the pharynx:
2
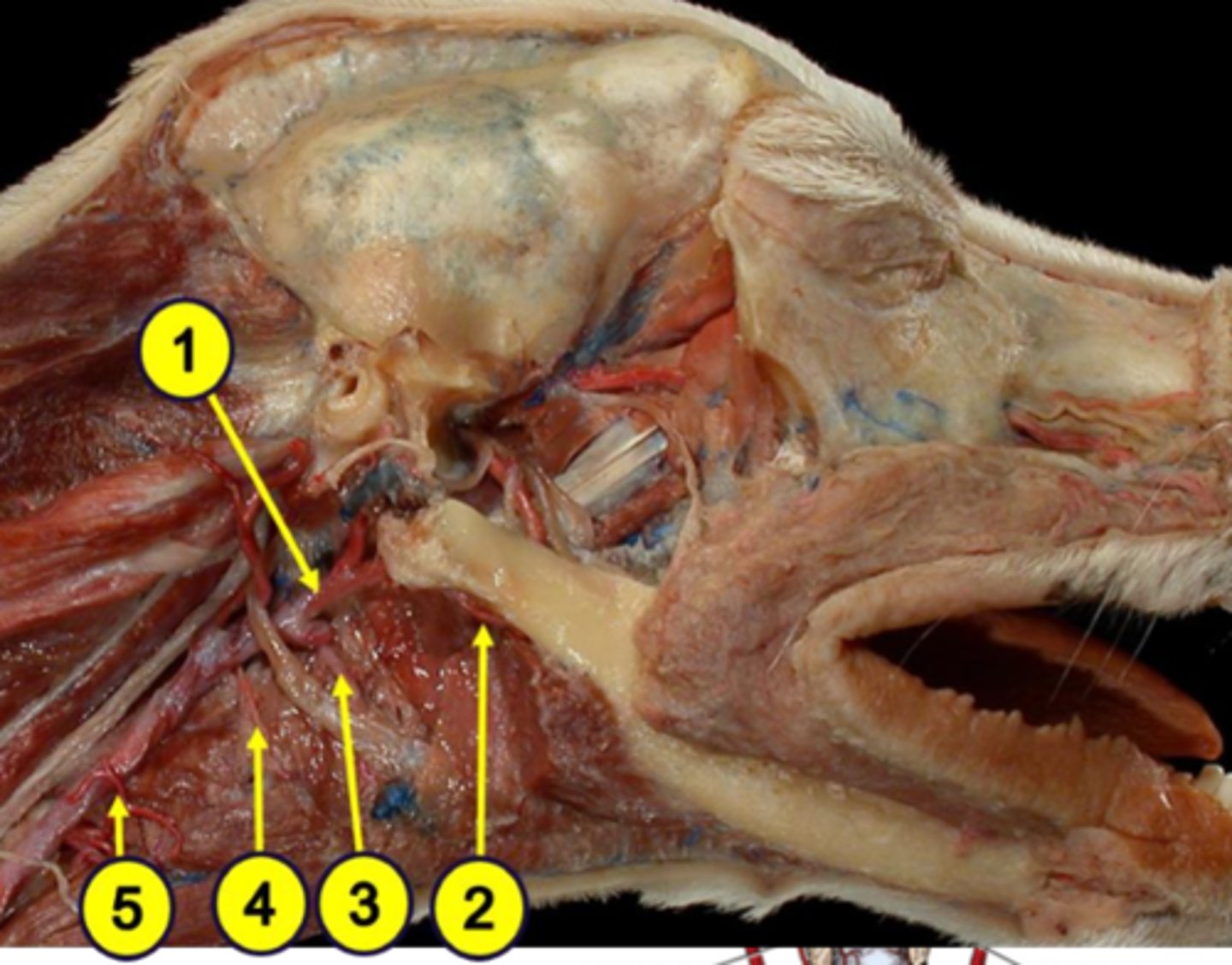
lingual artery
Blood supply to the pharynx:
3
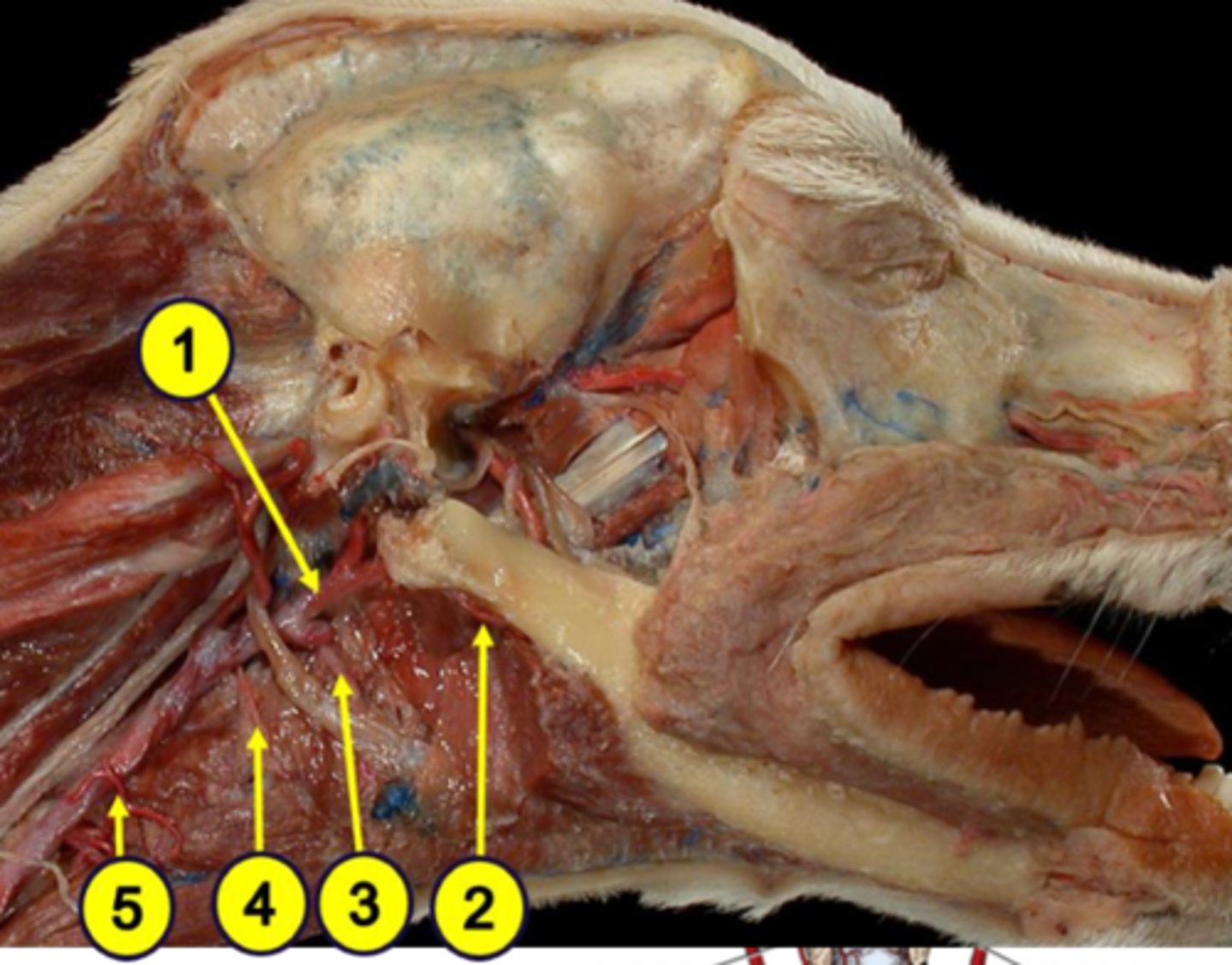
cranial laryngeal artery
Blood supply to the pharynx:
4
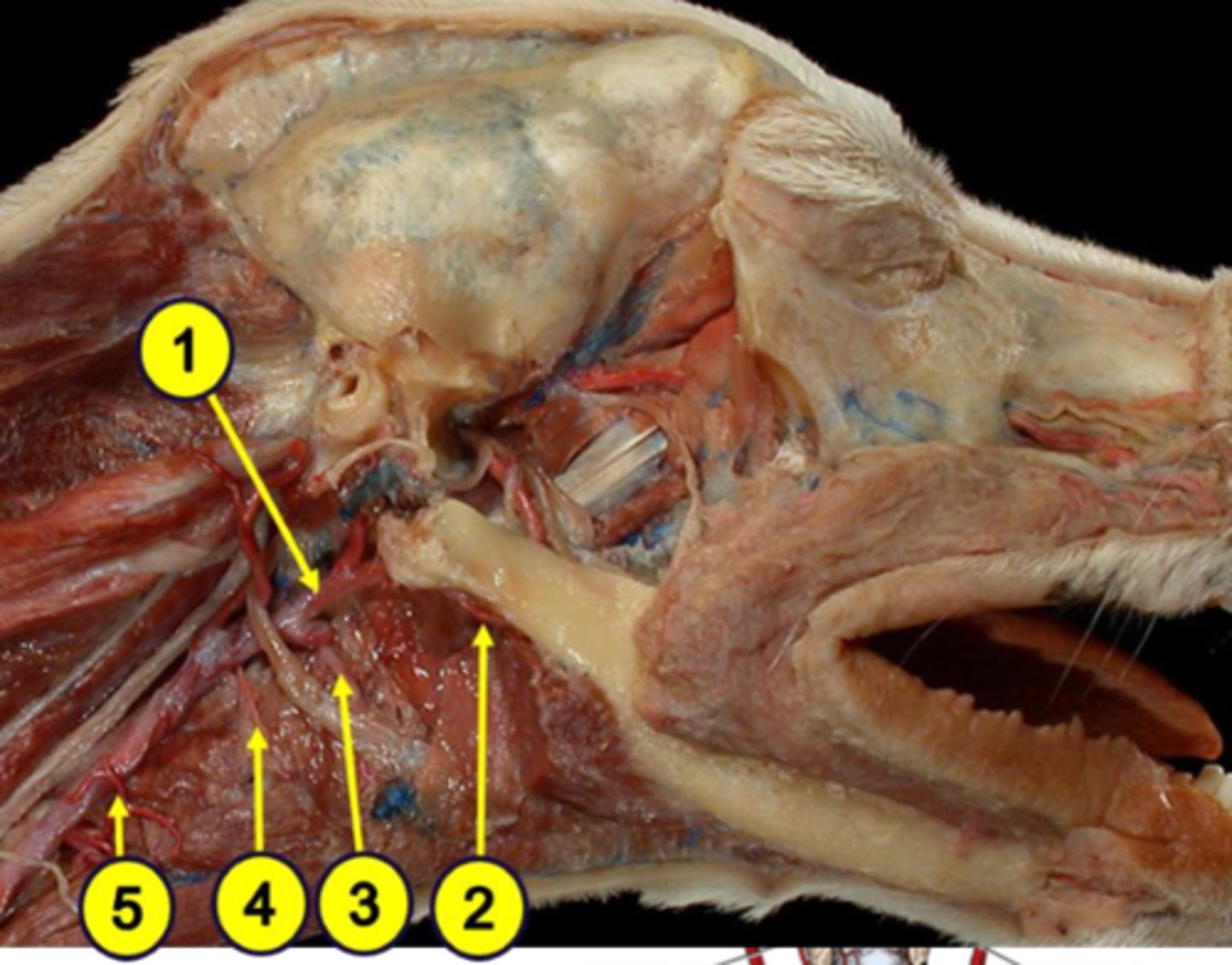
cranial thyroid artery
Blood supply to the pharynx:
5
horse
Species differences:
- long, narrow pharynx
- longer soft palate that lies beneath the epiglottic cartilage (preventing oral breathing)
- modified auditory tubes connected to the nasopharynx called the guttural pouch
ruminants
Species differences:
- supports rumination (regurgitation, remastication, re-swallowing)
- wide pharynx for large boluses
- limited oral breathing
pigs
Species differences:
- larger pharynx relative to head size
- pharyngeal diverticulum
nasopharynx
- ciliated epithelium to trap and clear debris
- involved in respiration
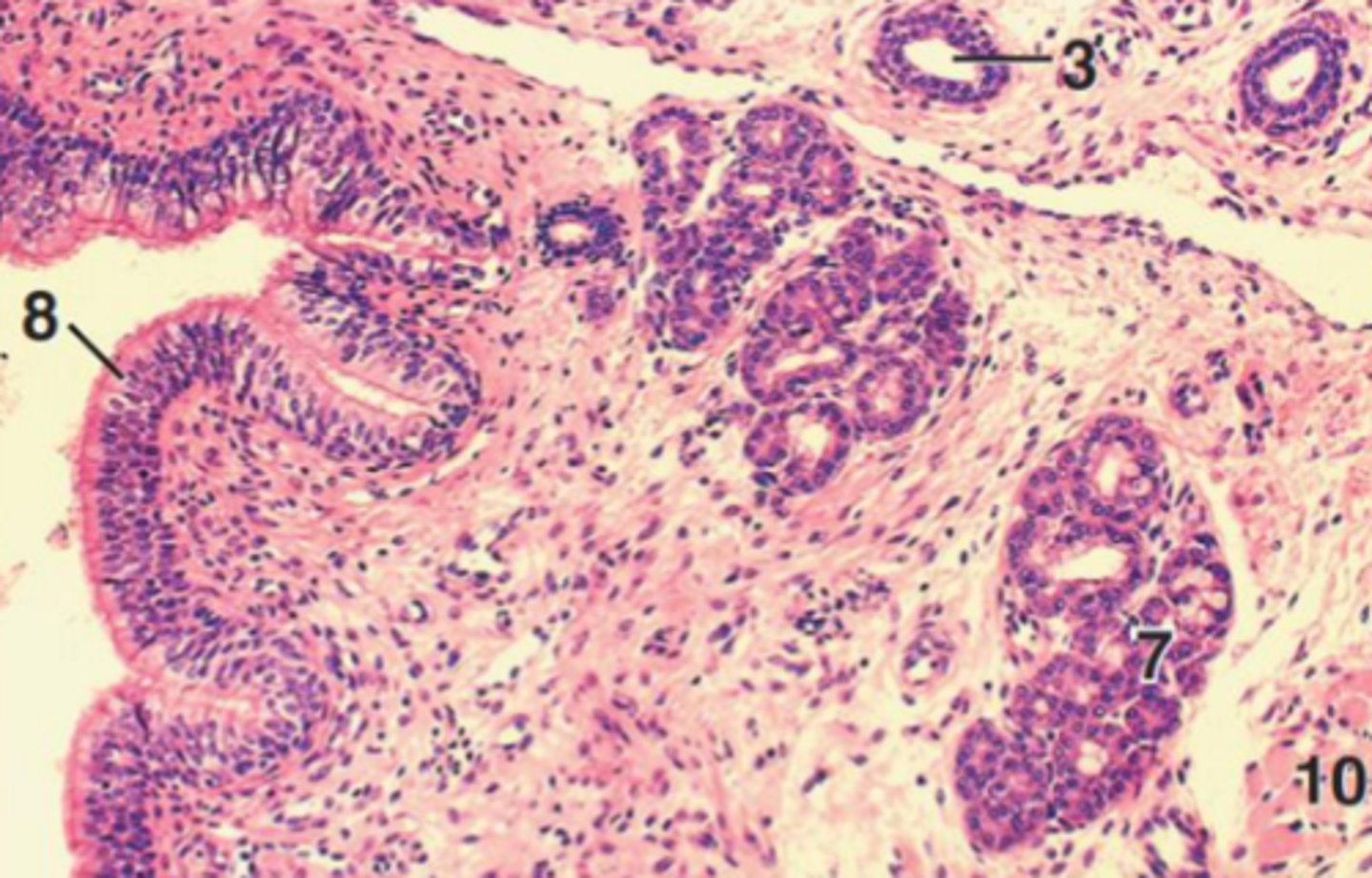
oropharynx (and laryngopharynx)
- protective stratified squamous epithelium to withstand mechanical stress
- involved in swallowing
tonsils
lymphoid tissue of the pharynx
MALT (mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue)
- lymphoid tissue embedded within the mucosa, not visible
pharyngeal tonsils
- lymphoid tissue of the pharynx associated with the nasopharynx
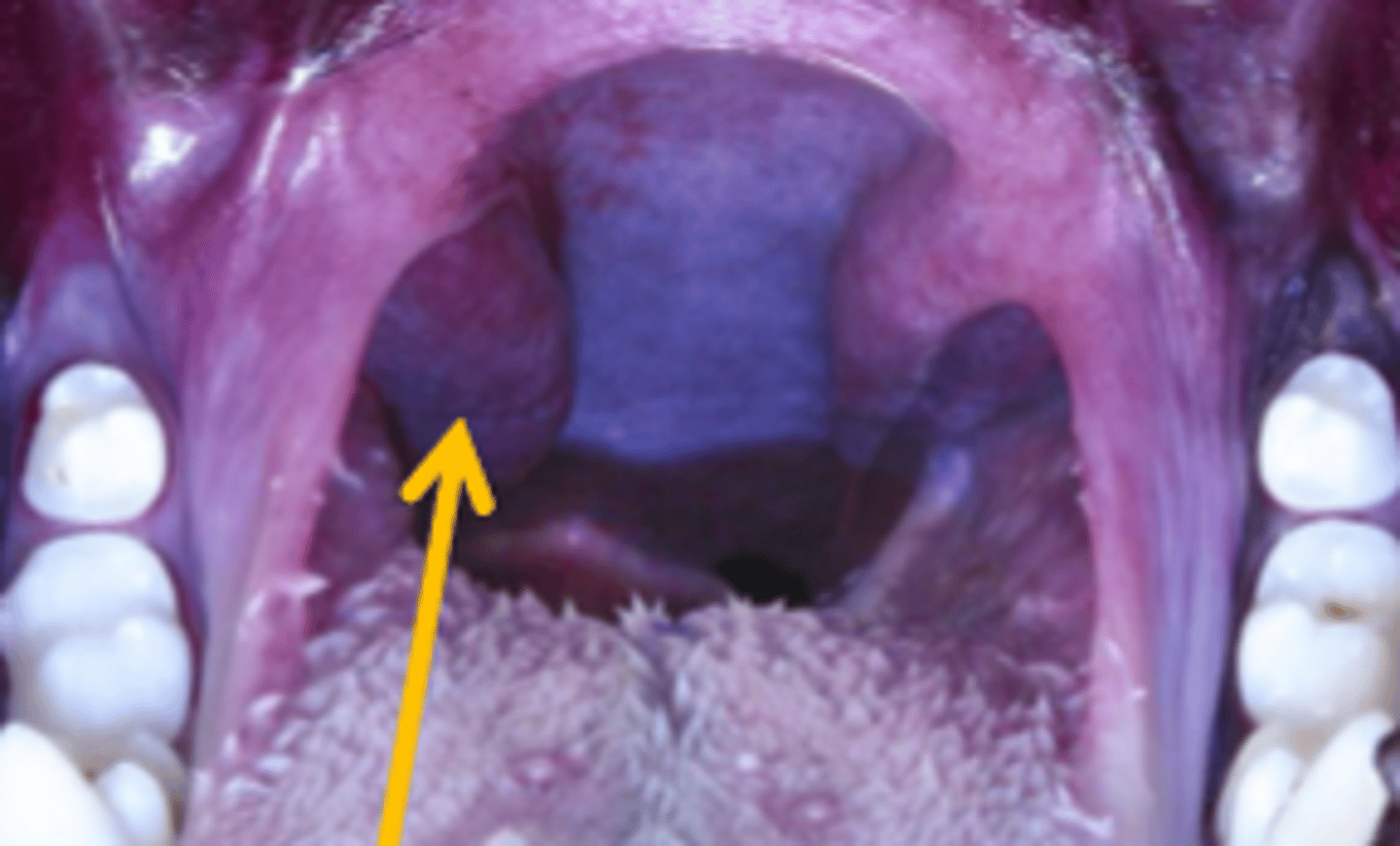
palatine tonsils
- lymphoid tissue of the pharynx associated with the oropharyngeal surface
- visible in dog, cat, and bovine
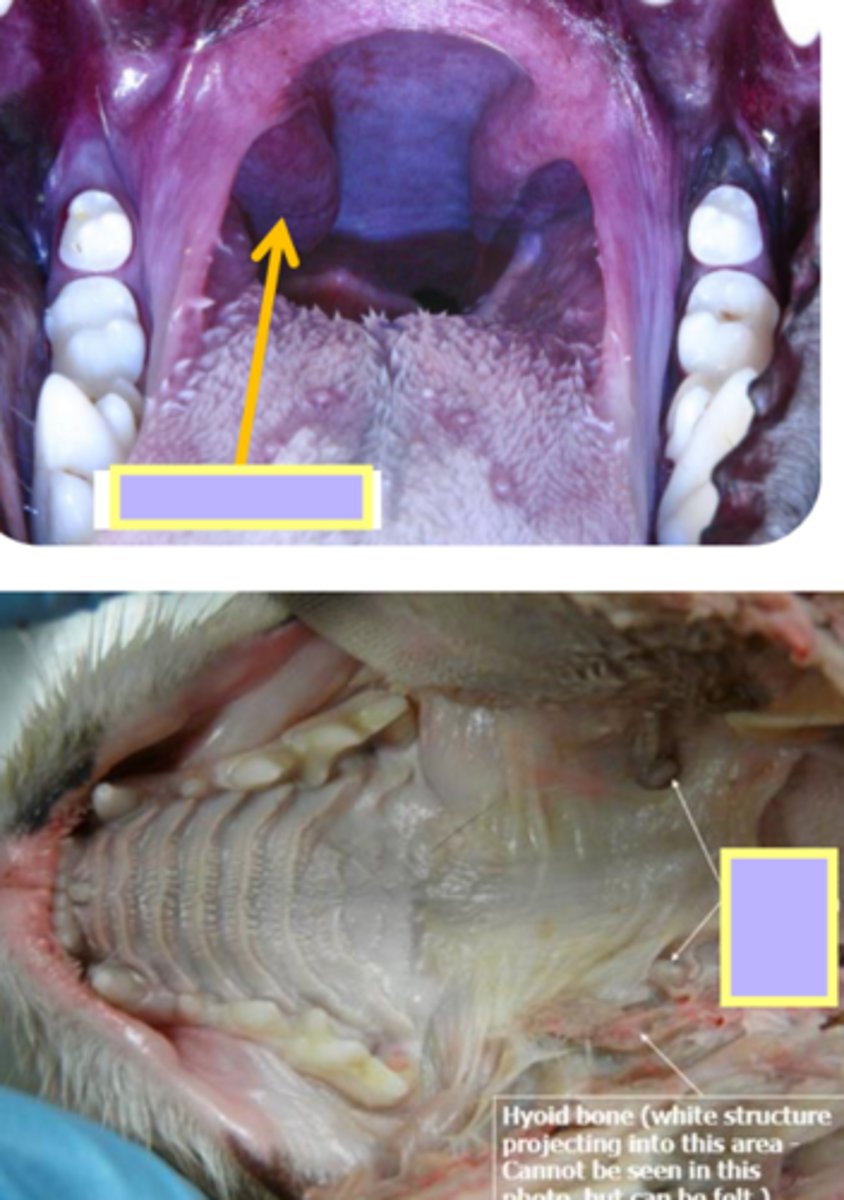
lingual tonsils
- lymphoid tissue of the pharynx embedded in the mucosa of the tongue (root)
- well developed in bovine
scattered lymphoid tissue
horses have ___________________ rather than a well-defined tonsillar structure
large palatine tonsils
ruminants and pigs have _________________ with deep crypts for antigen trapping
deep crypts
dogs have ________________ in the palatine tonsils, making them more prone to tonsilitis
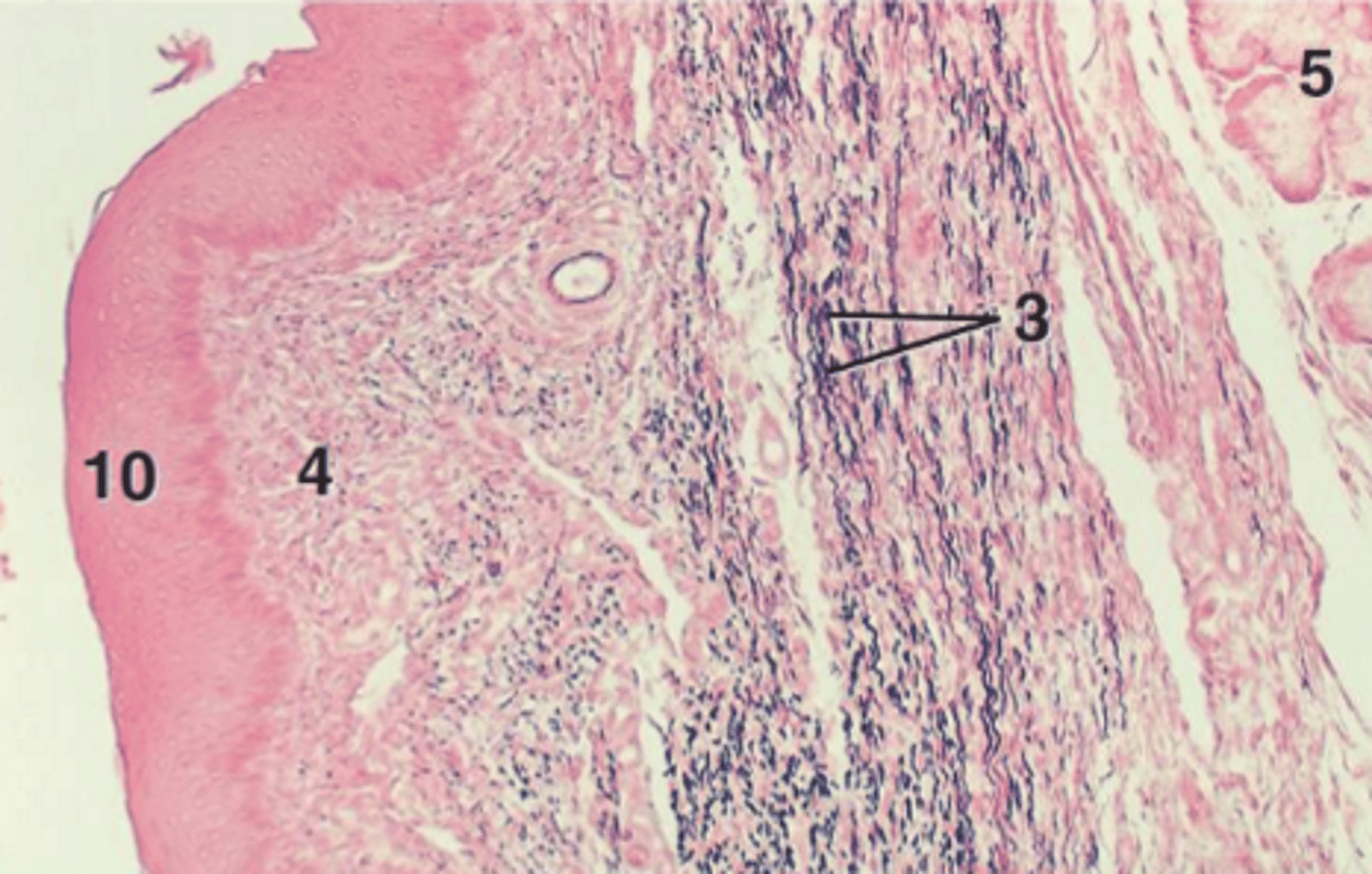
dorsal
cervical portion of the esophagus position
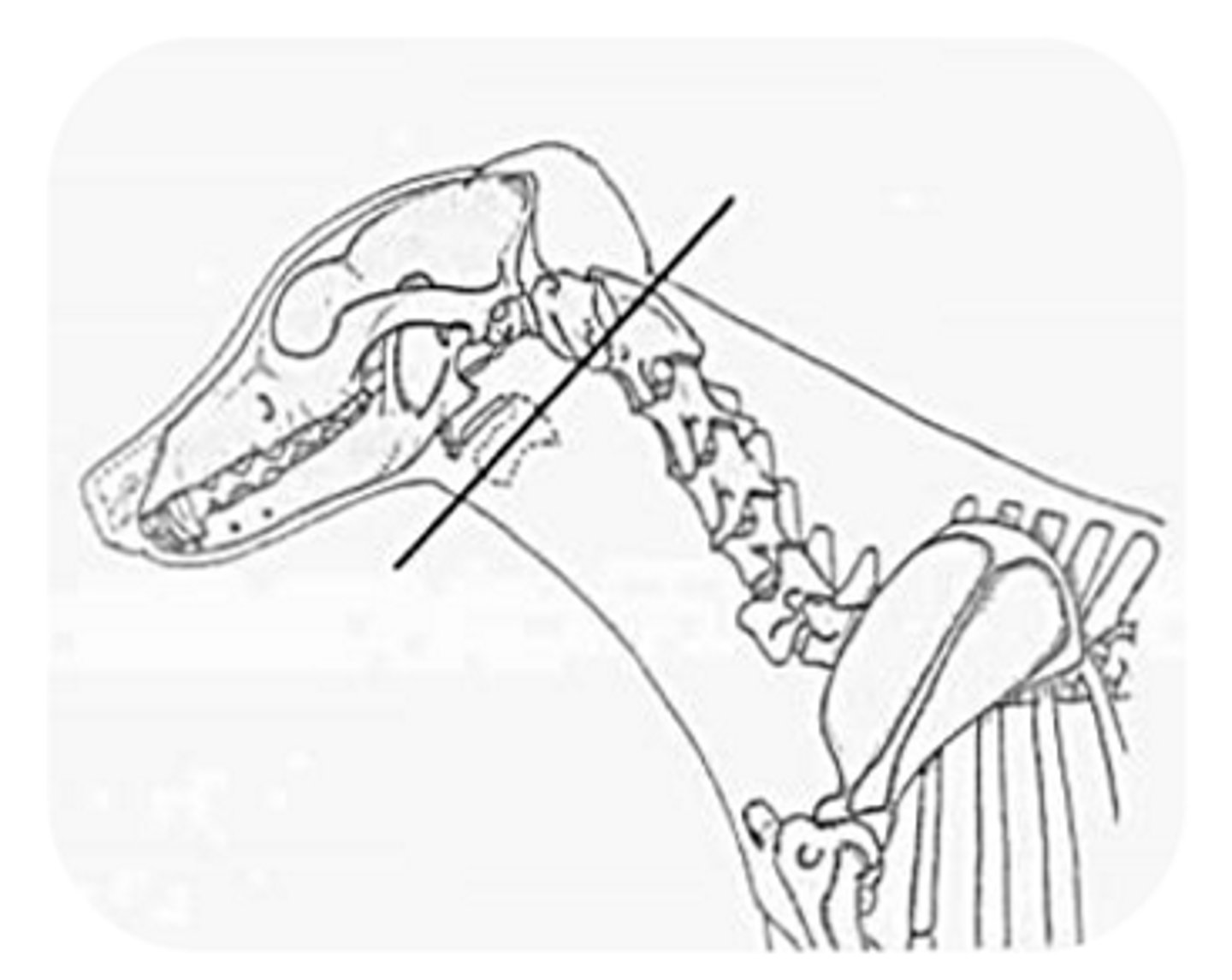
left lateral
cervical portion of the esophagus position
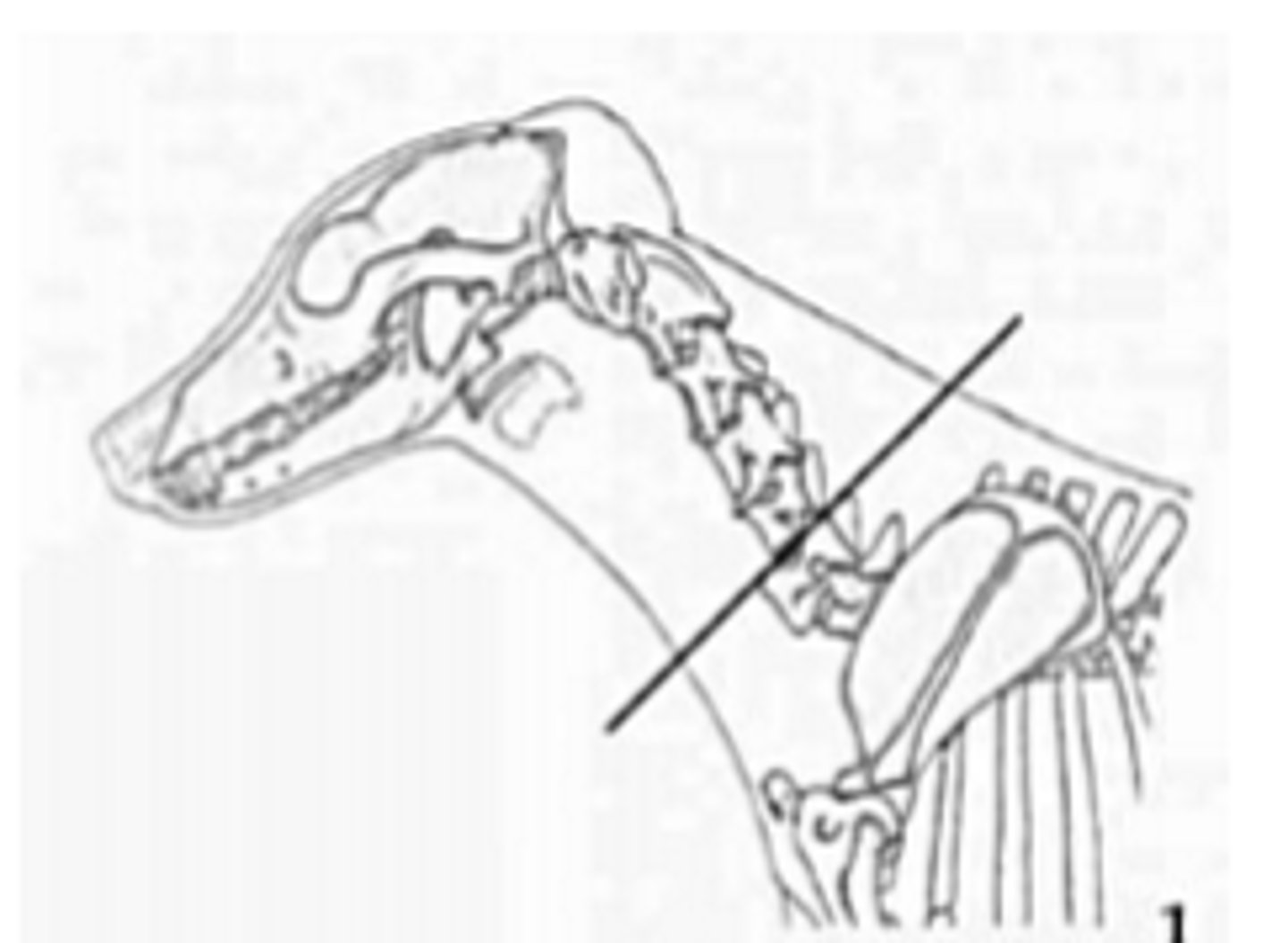
base of heart and diaphragm
Thoracic part of the esophagus:
points most likely to cause obstruction
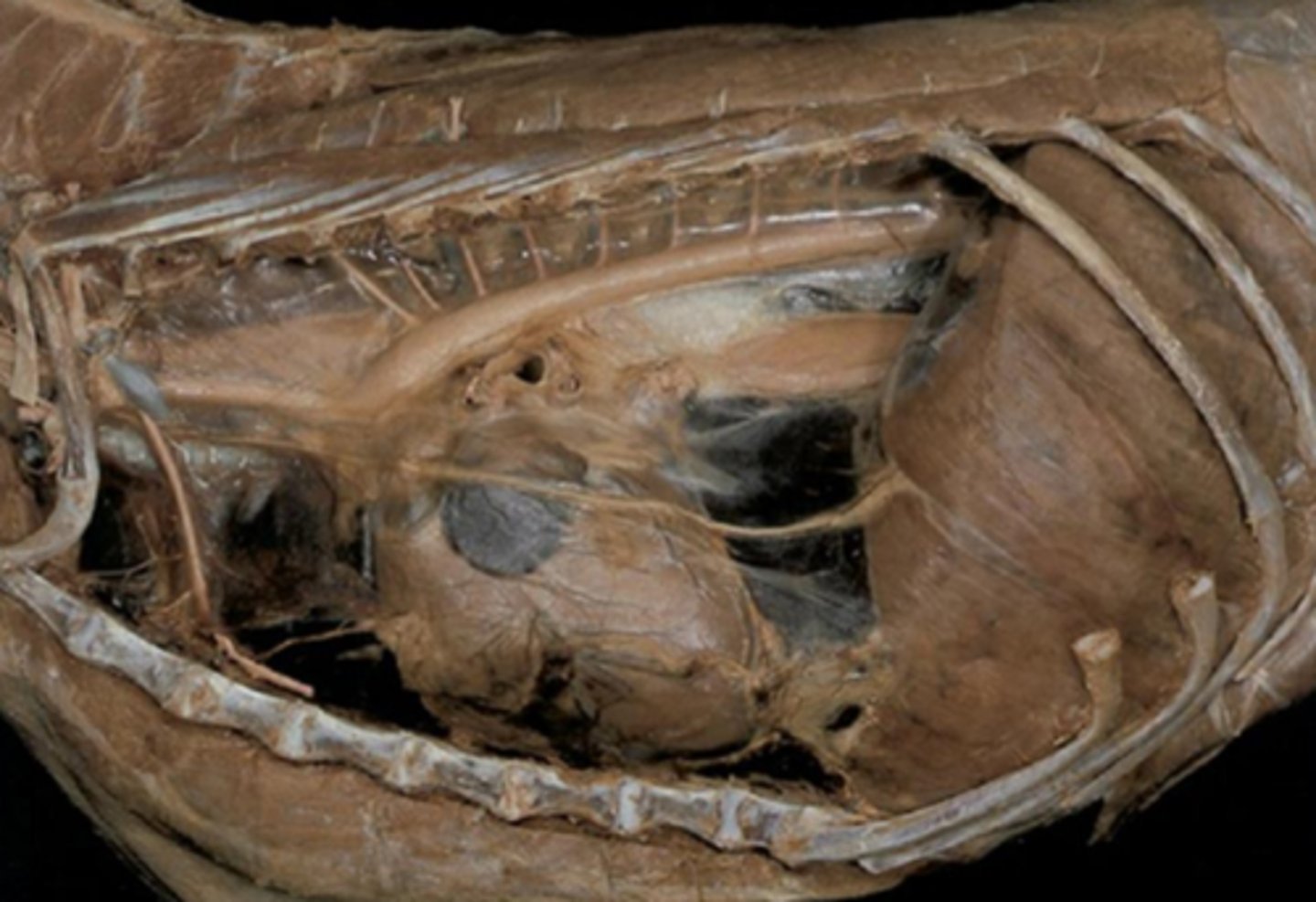
vagus nerve (CN X)
Nerve supply to the esophagus:
- motor
- somatic control of striated muscle portions
- autonomic control of smooth muscle portions
thyroid arteries (cranial and caudal)
Blood supply of the esophagus:
- 1 and 4
- cervical esophagus (neck region)
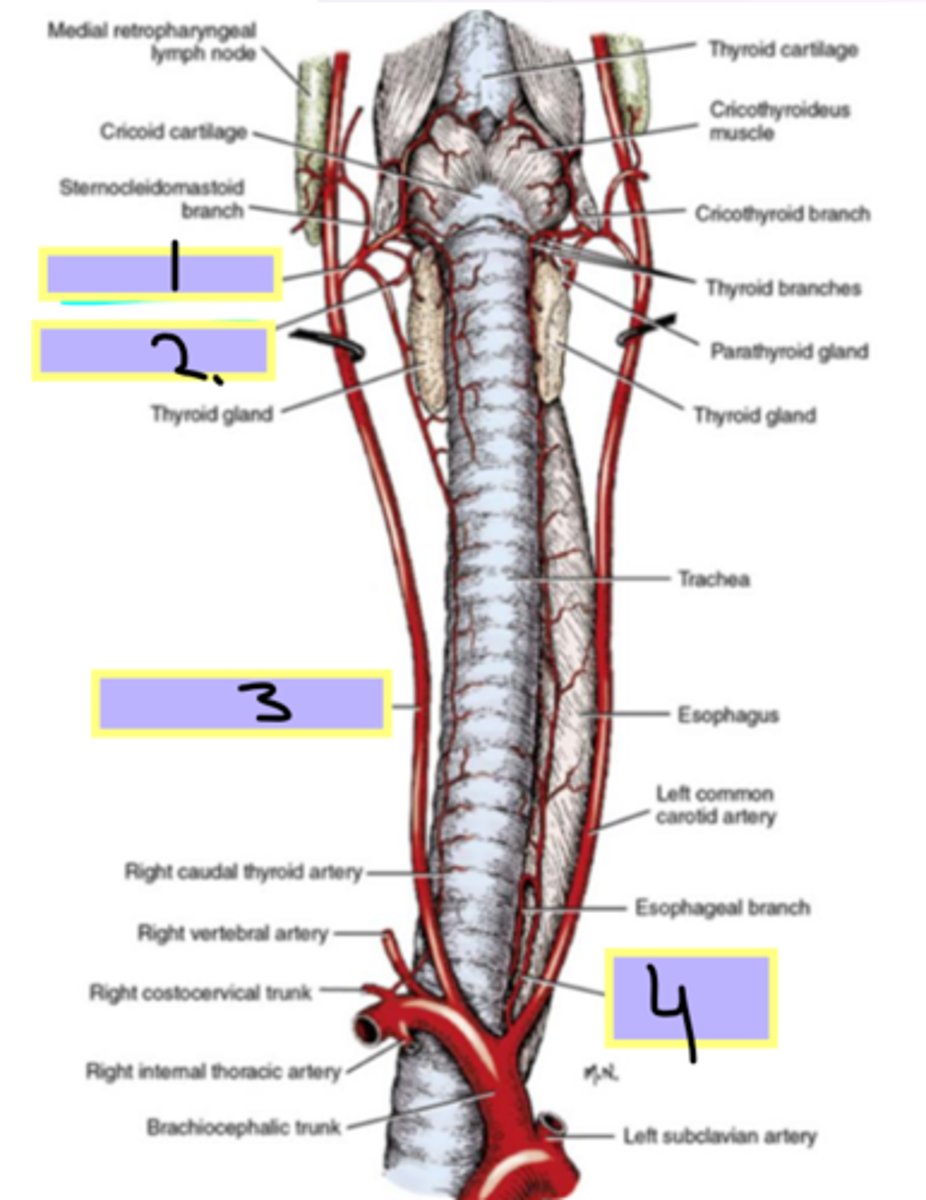
bronchoesophageal artery
Blood supply of the esophagus:
- thoracic esophagus (chest region)
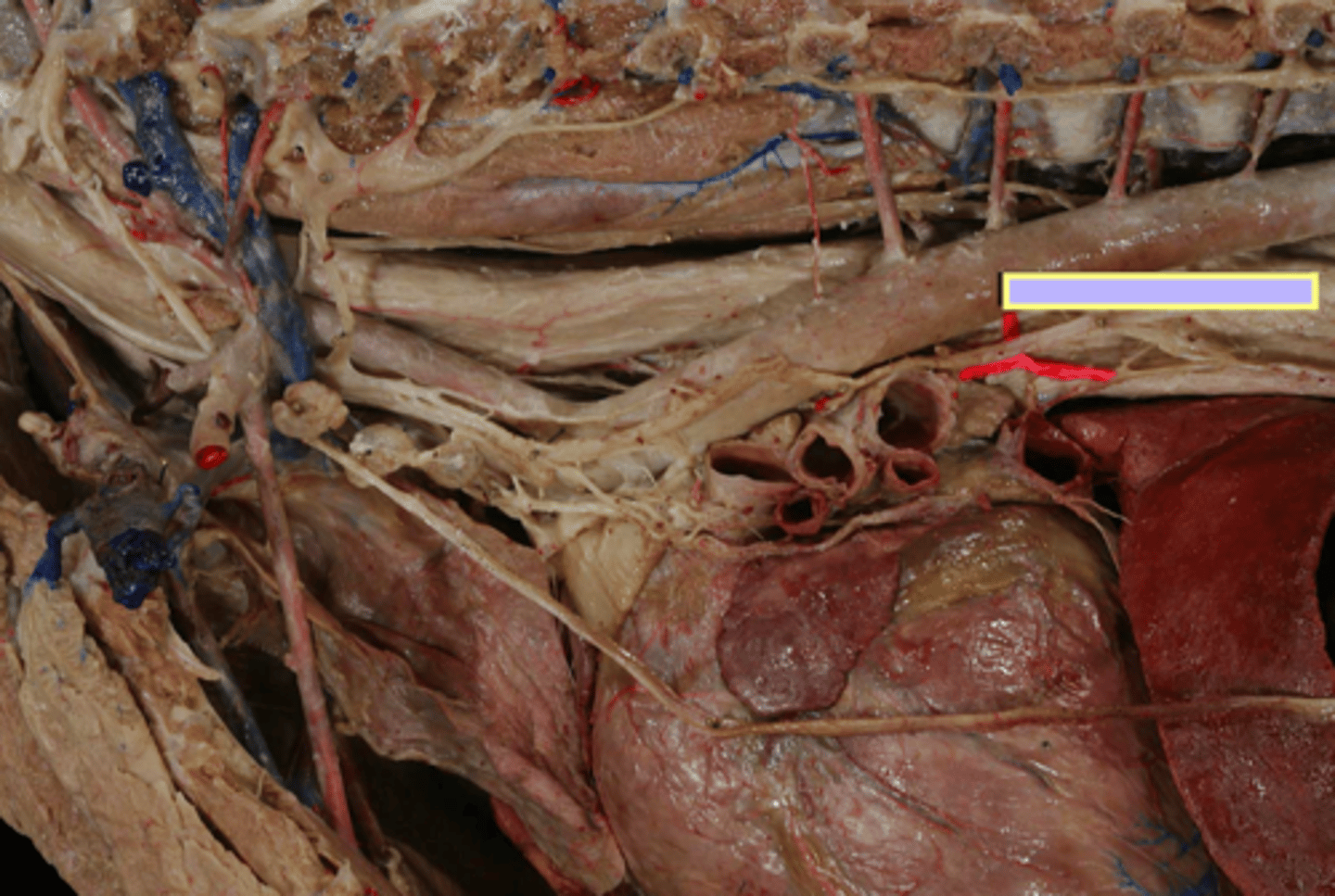
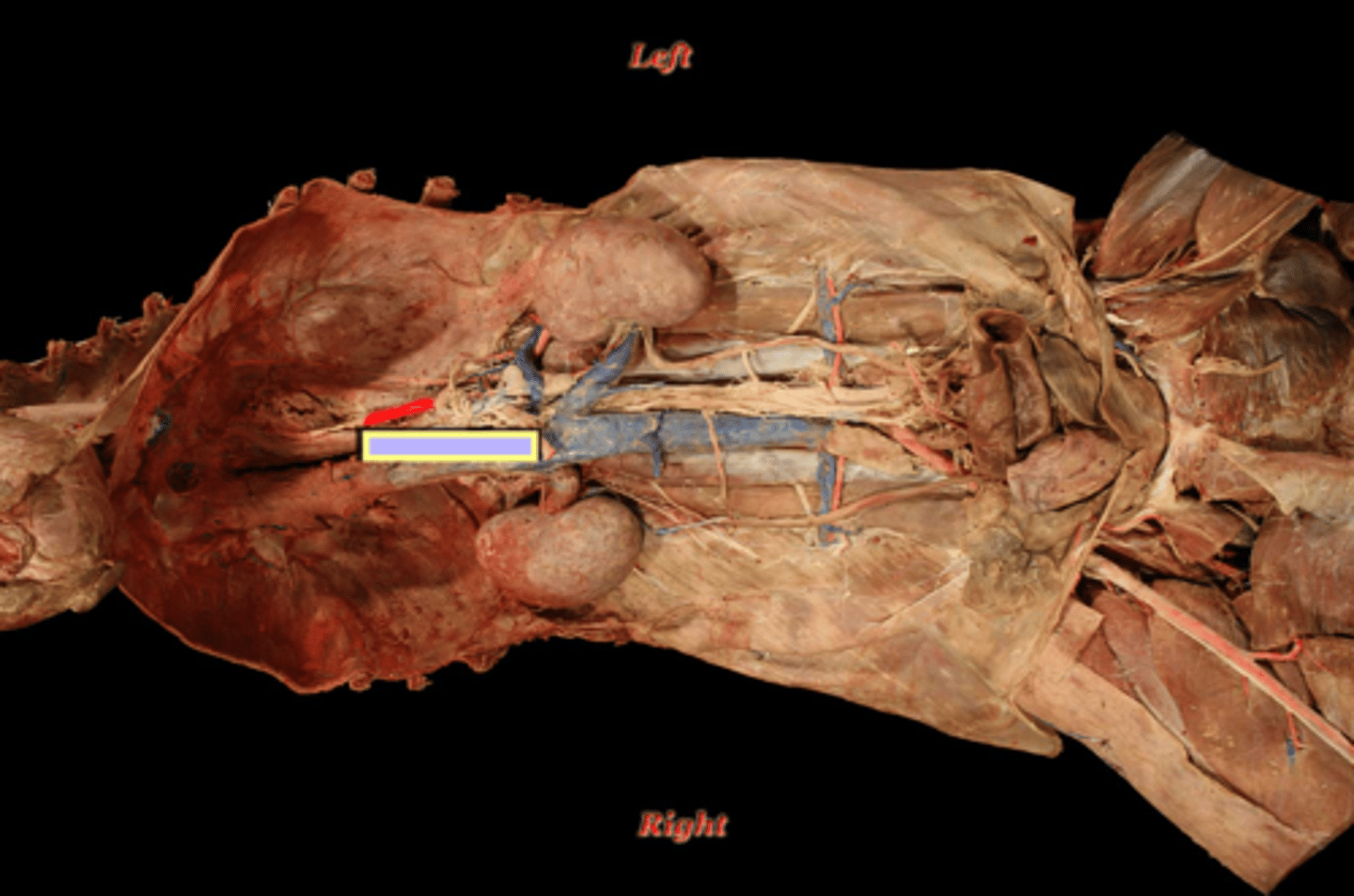
left gastric artery
Blood supply of the esophagus:
- abdominal esophagus (near stomach)
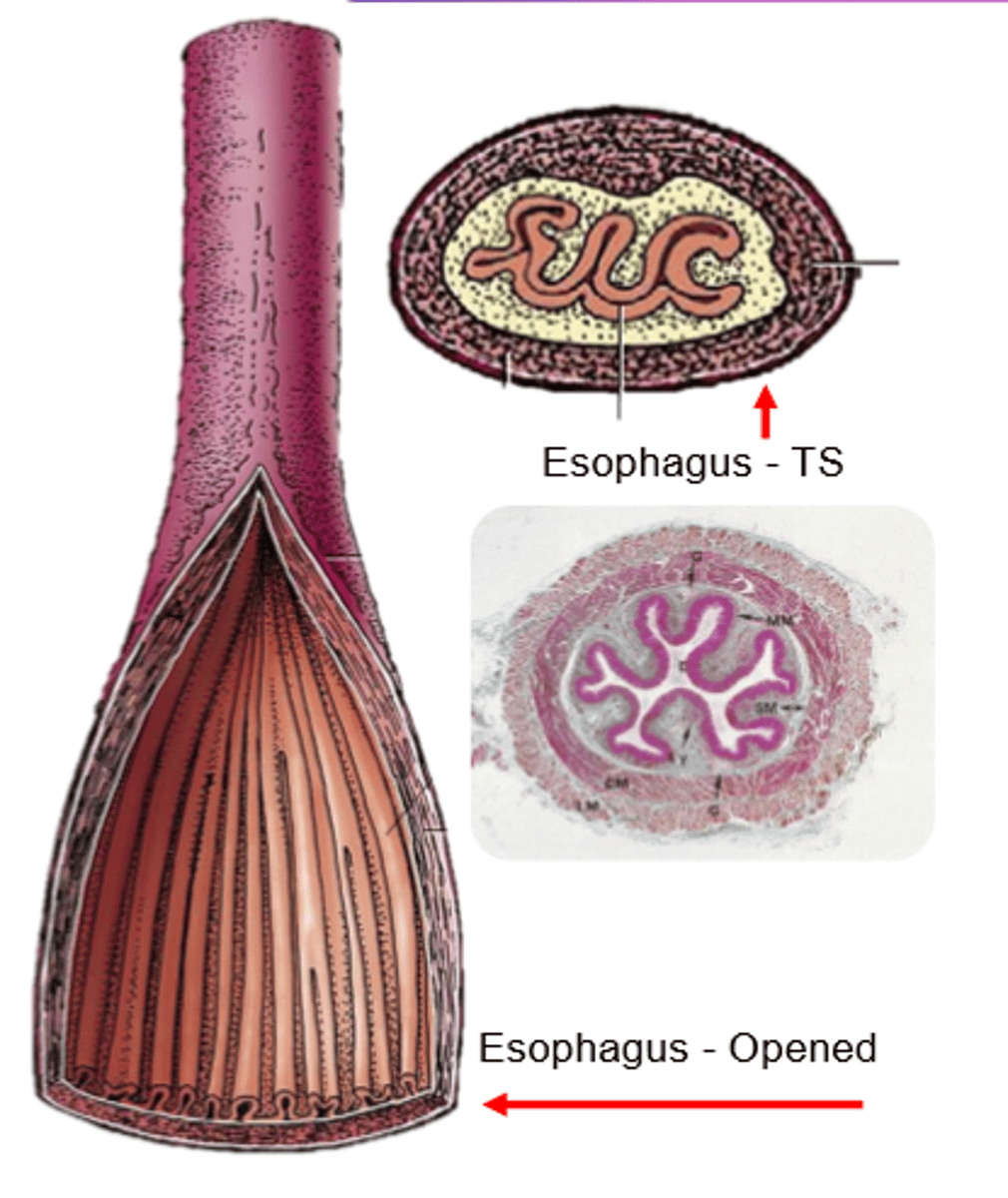
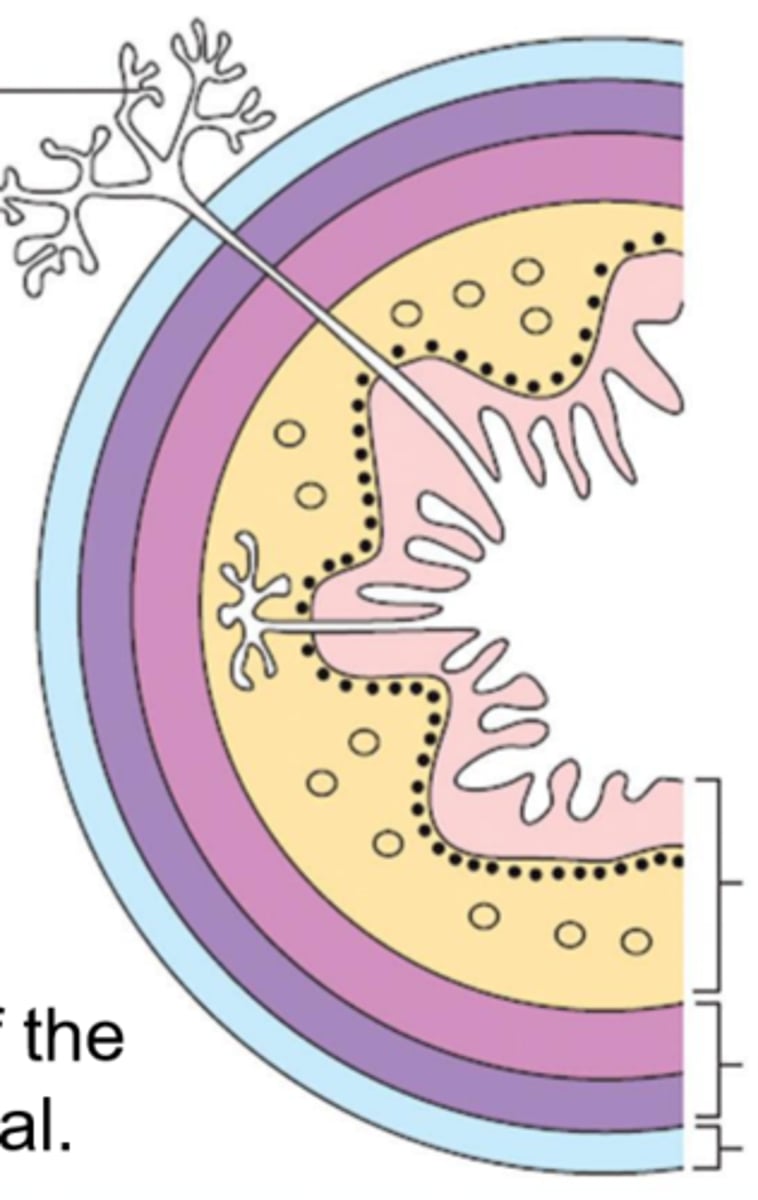
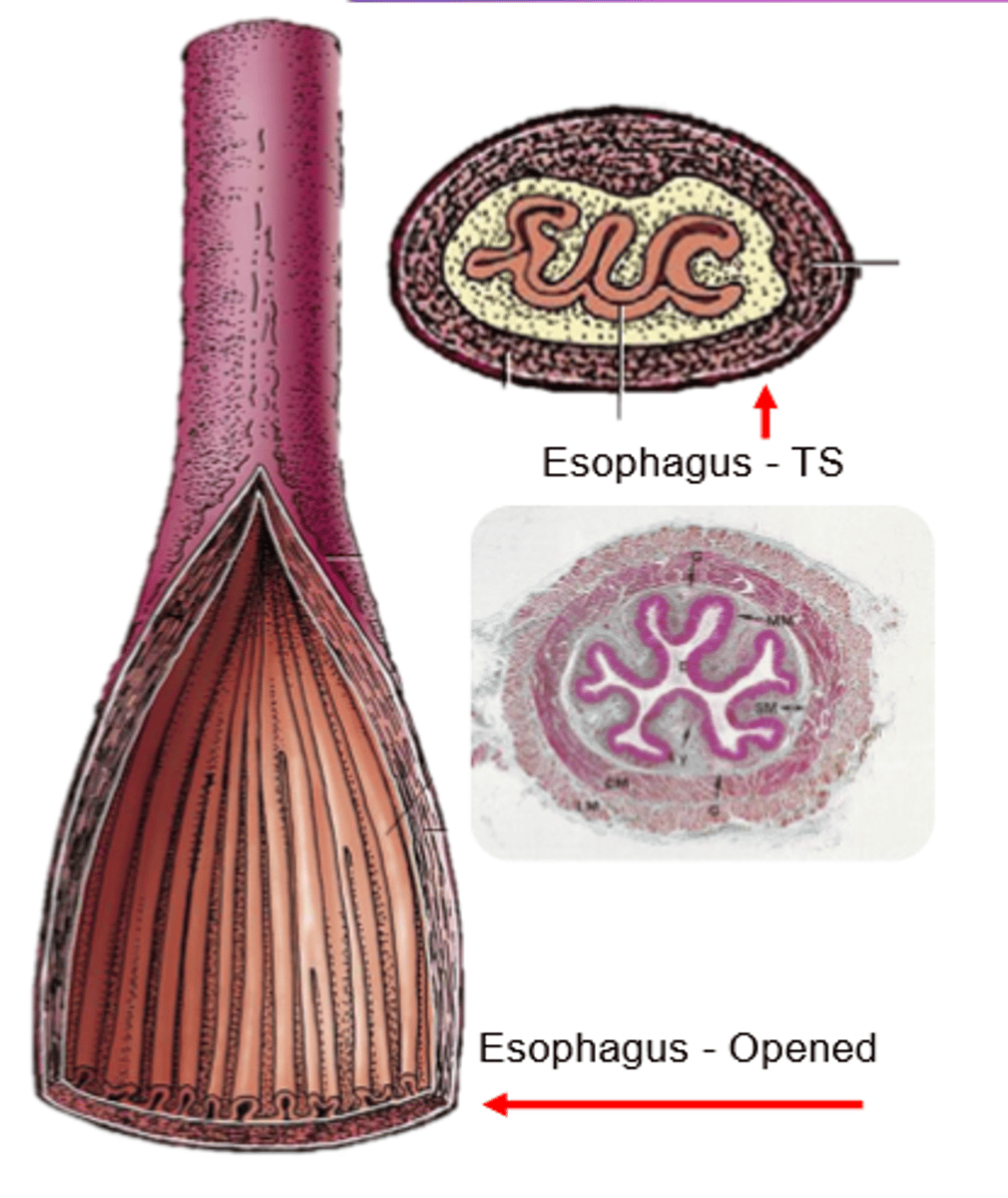
mucosa
Esophageal wall:
light pink
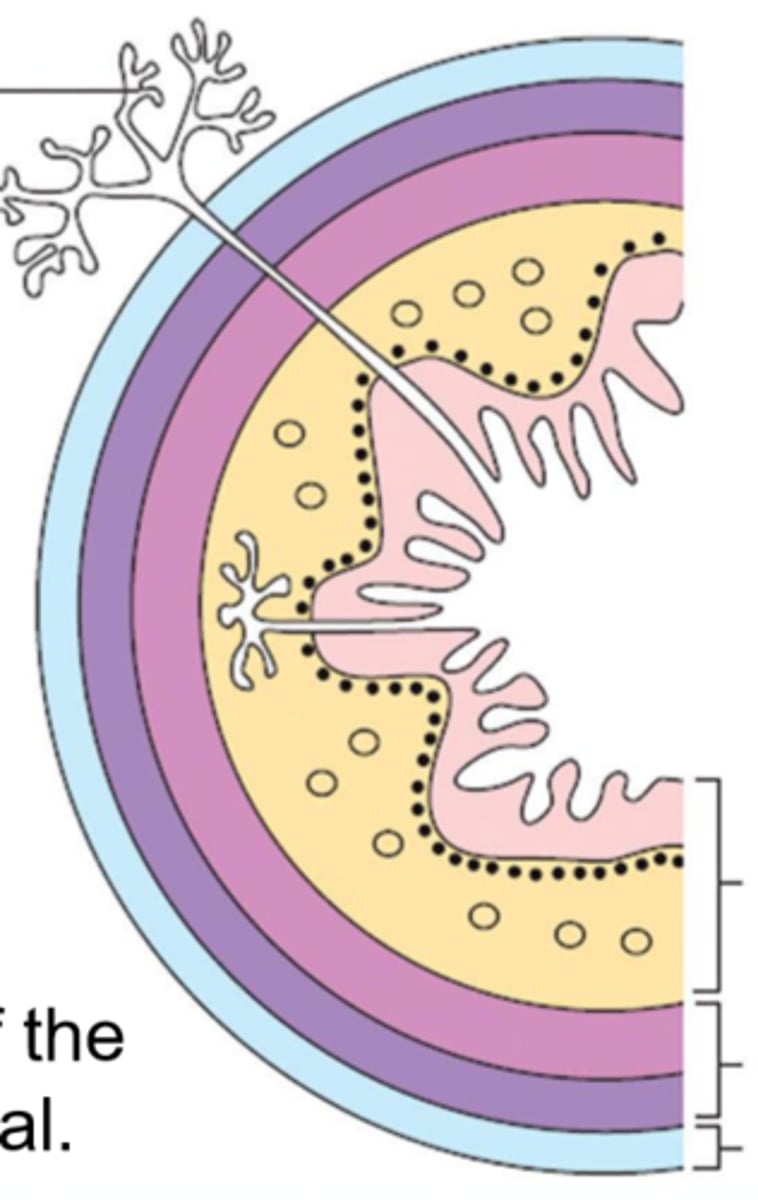
submucosa
Esophageal wall:
yellow
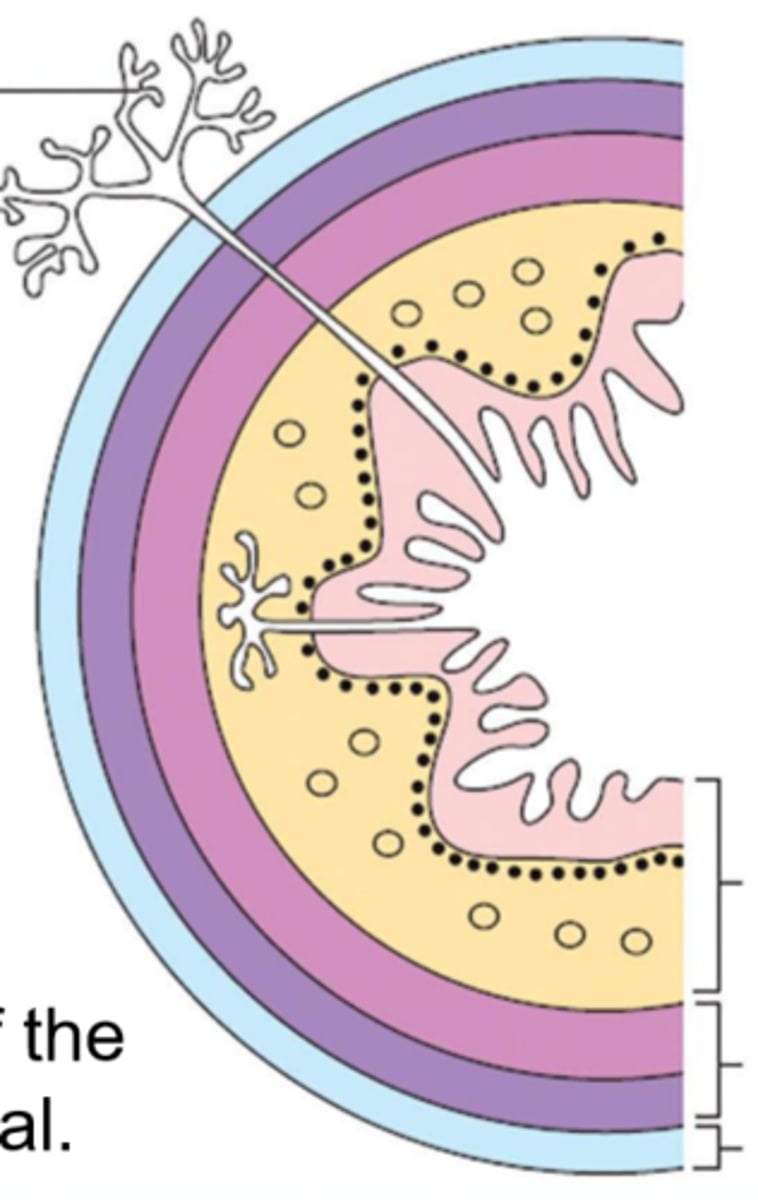
muscularis
Esophageal wall:
dark pink and purple
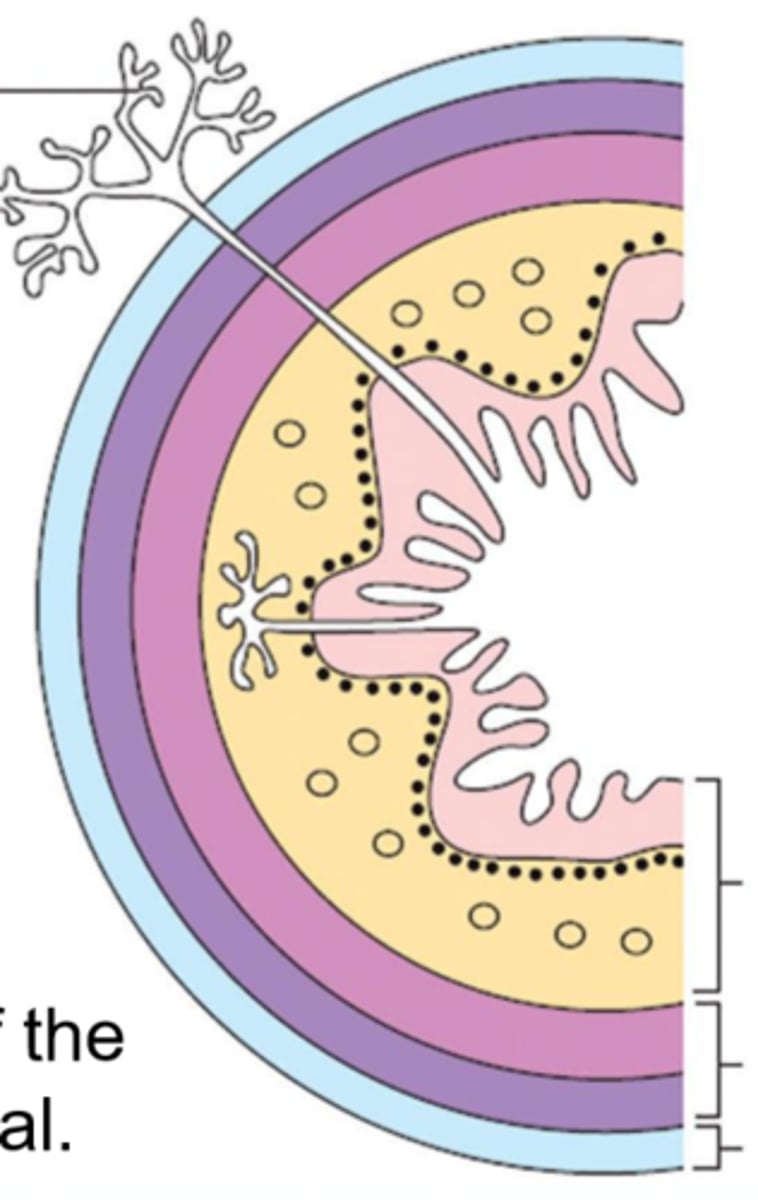
serosa (adventitia)
Esophageal wall:
light blue
non-keratinized
Esophagus:
epithelium of cat and dog
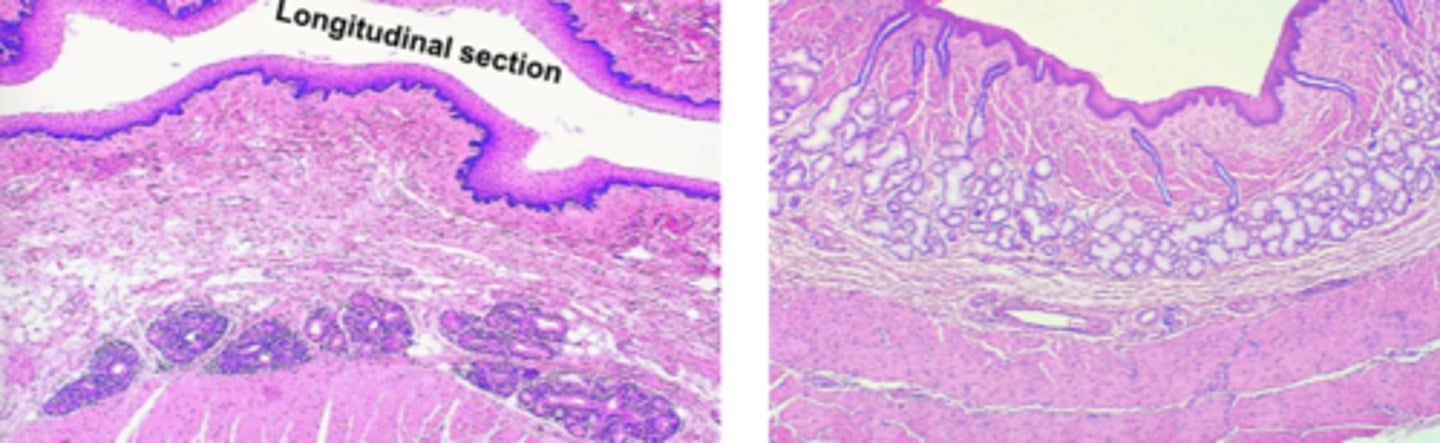
keratinized
Esophagus:
epithelium of horse and pig
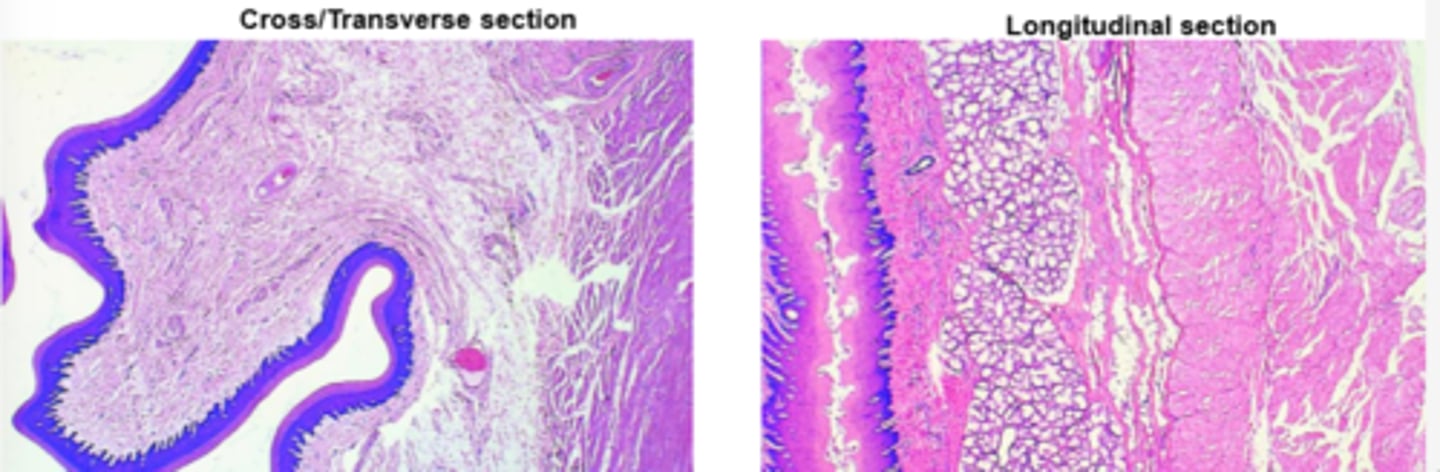
ruminants and dogs
Species differences of muscular coat:
entirely skeletal muscle, allowing voluntary control
horses, pigs, cats
Species differences of muscular coat:
upper part is skeletal muscle, transitioning to smooth muscle towards the stomach