Hormone regulation in carbohydrate metabolism, fasting/fed state
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
How do endocrine hormones get to target cells
hormones enter blood stream to travel to targeted cells
What type of hormones bind to membrane receptors of targeted cells, and examples of the type
Peptide/protein and catecholamines hormones
Insulin, glucagon
epinephrine, norepinephrine, and growth hormone (GH)
how does hormones act on membrane receptors
second messenger enzyme cascade,
fast effects, activation of existing enzyme/protein and secretion of stored enzyme/protein
slow effects: transcription factor involved and gene transcription
What type of hormones bind to nuclear receptors and example
steroid and thyroid hormones
Steroid: cortisol
how do hormones act on nuclear receptors
hormone-bound receptor=transcription
plasma binding protein (lipid soluble) → cytoplasm nuclear receptors → gene transcription in hormone bound form
which hormone lowers blood glucose level
insulin
which hormone increases blood glucose level
several
which hormone is dominant in fed state condition
insulin
what is the difference in how liver, skeletal muscle, adipose, and most other cells process glucose under fed state/condition
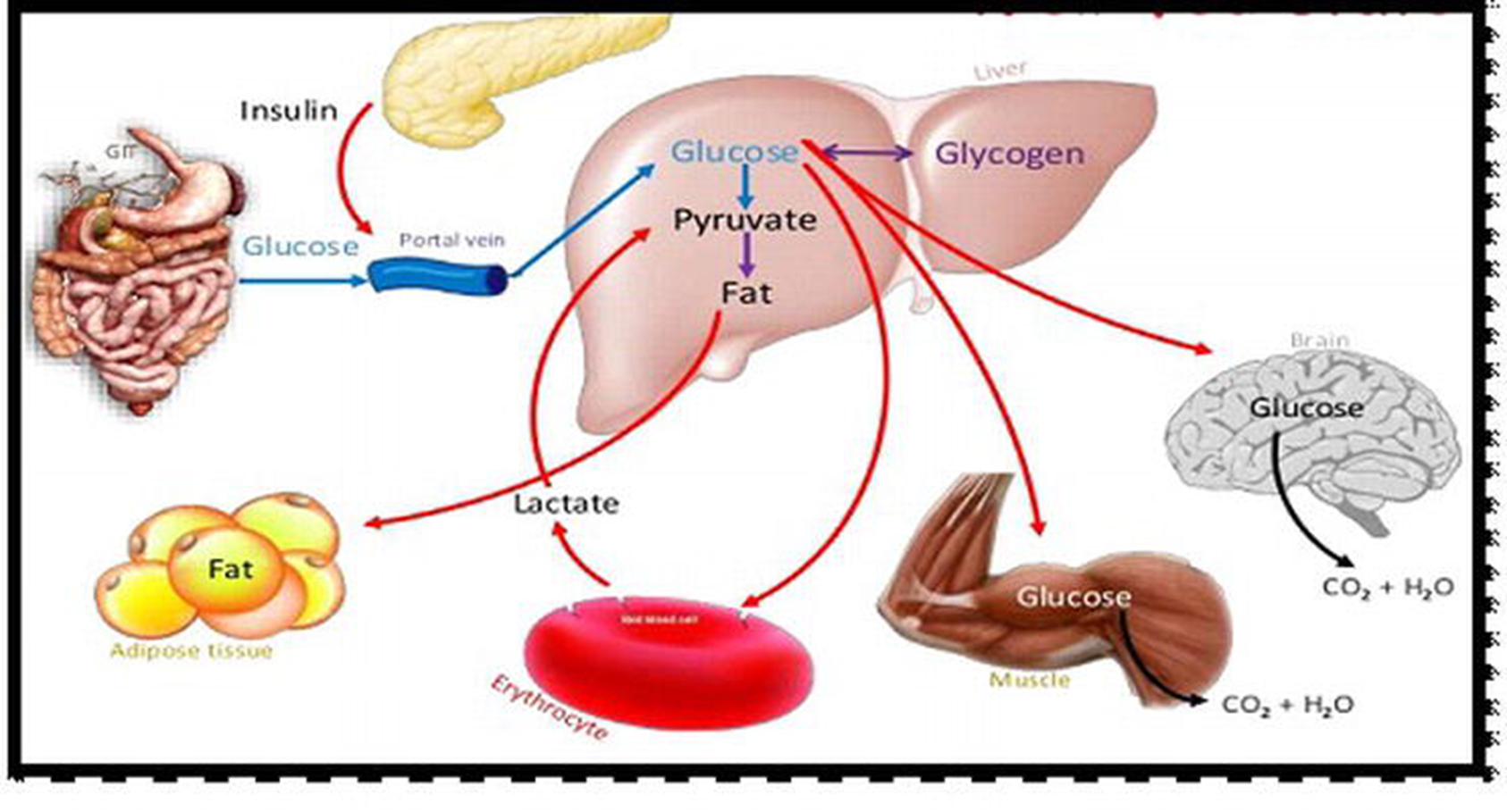
in fed state, which organ stimulates glucose
small intestine
What are incretin hormones present and fed state, and why are they important
GIP (k-cells) and GLP-1 (L cells)
important for post-meal insulin secretion
what is the difference in how liver, skeletal muscle, adipose, and most other cells process glucose in fasting state (post-absorptive)
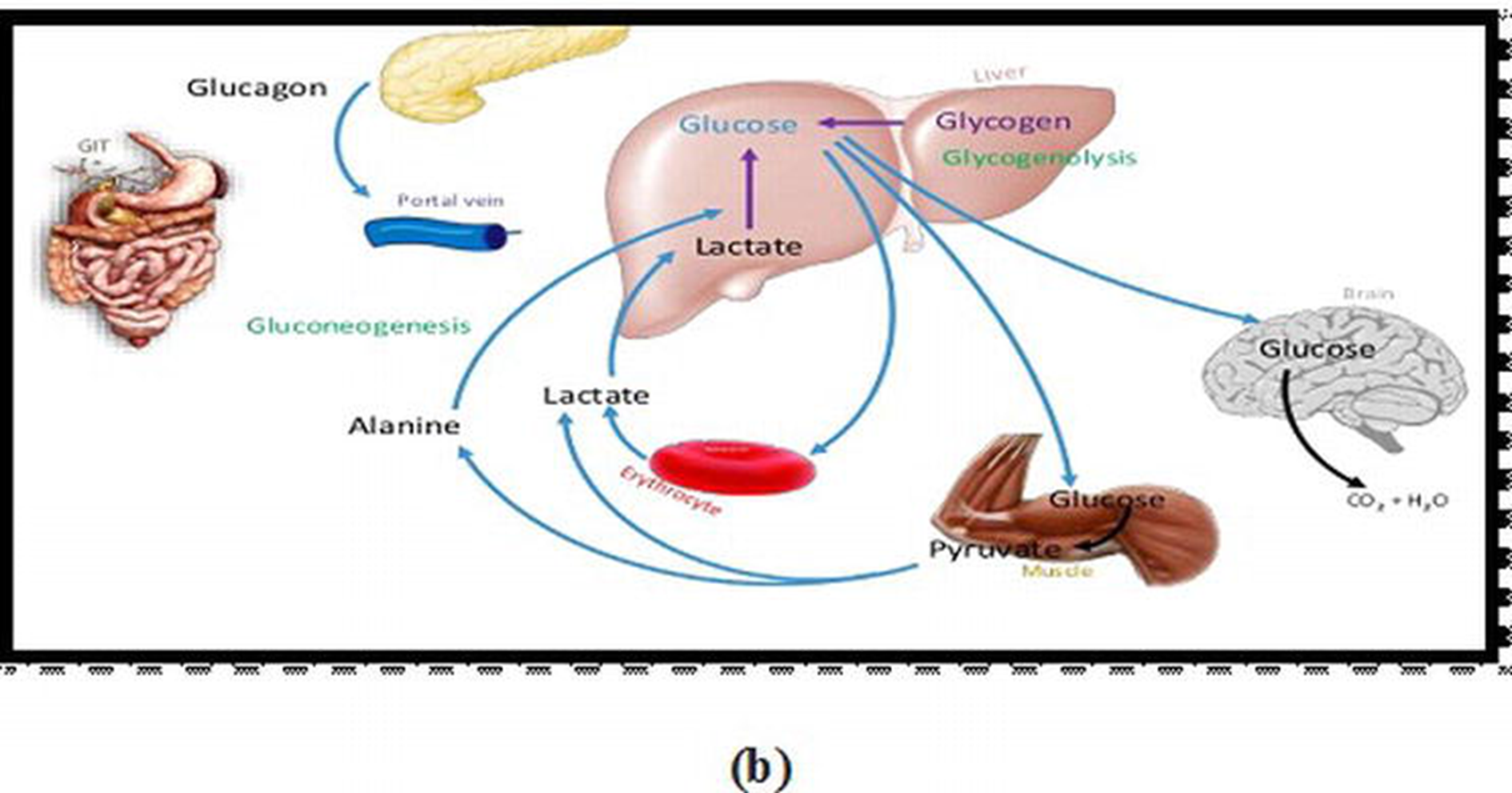
When is blood glucose level low (during what state)
Fasting
What hormone is dominant initially and afterwards during fasting state
initially: glucagon
afterwards: other hormones increase to maintain blood glucose
what stimulates the release of insulin
beta cells-high blood glucose levels
what stimulates the release of glucagon
low blood glucose, exercise and protein rich meals
how does insulin signals
binding to receptor on the cell’s surface, primarily involve protein phosphorylation including activation of enzymes PI3K and AKT (protein kinase)
What are major insulin signaling molecules in relevance of glycolysis
insulin receptor (IR)
insulin receptor substrates (IRS)
phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI3K)
protein kinase B (AKT)
What are major insulin signaling molecules of in relevance of glycogen synthesis
insulin receptor to activate PI3-kinase pathway
activates PKB/AKT, which inactivates GSK3) and protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) is activated to dephosphorylate and active glycogen synthase
how does glucagon signal
binding to G-protein coupled receptors on target cells in the liver
pancreatic islet alpha cells
What are major glucagon signaling molecules in relevance of gluconeogenesis
cAMP, PKA
What are major glucagon signaling molecules in relevance of inhibition of glycolysis
cAMP, PKA
What are major glucagon signaling molecules in relevance of glycogen synthesis
cAMP, PKA
how does insulin regulate key enzymatic steps in glycolysis
via translocation of GLUT4 transporters to plasma membrane, indirectly increase F2,6BiP, which activates PFK
how does insulin regulate key enzymatic steps in gluconeogenesis
suppressing PEPCK and G6Pase
how does glucagon regulate key enzymatic steps in glycolysis
decreasing concentration of F-2,6-BiP by activating enzyme FBP-ase2, which inhibits PFK1
indirectly downregulates PK
in glycogenolysis how does glucagon regulate key enzymatic steps
glucagon binding to G-protein coupled receptor—> increase in cAMP and activation of PKA—> PKA phosphorylates—> activates glycogen phosphorylase—> inactivates glycogen synthase
in gluconeogenesis, how does glucagon regulate key enzymatic steps
stimulates production of cAMP activating protein kinase A (PKA), which then phosphorylates and inhibits glycolytic enzymes, while promoting pyruvate kinase, PEPCK, and fructose 1,6-biphosphatase.
what multiple hormones regulate blood glucose
insulin and glucagon
epinephrine, cortisol, growth hormone (GH) somatostatin and amylin
Put hormone concentration changes in order, first to last, when blood glucose falls: GH increases, cortisol increases, insulin decreases, glucagon & epinephrine increase
insulin decreases
glucagon & epinephrine increase
GH increase
cortisol increases