A&P101 Lecture 16 Quiz Sarcomere structure
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
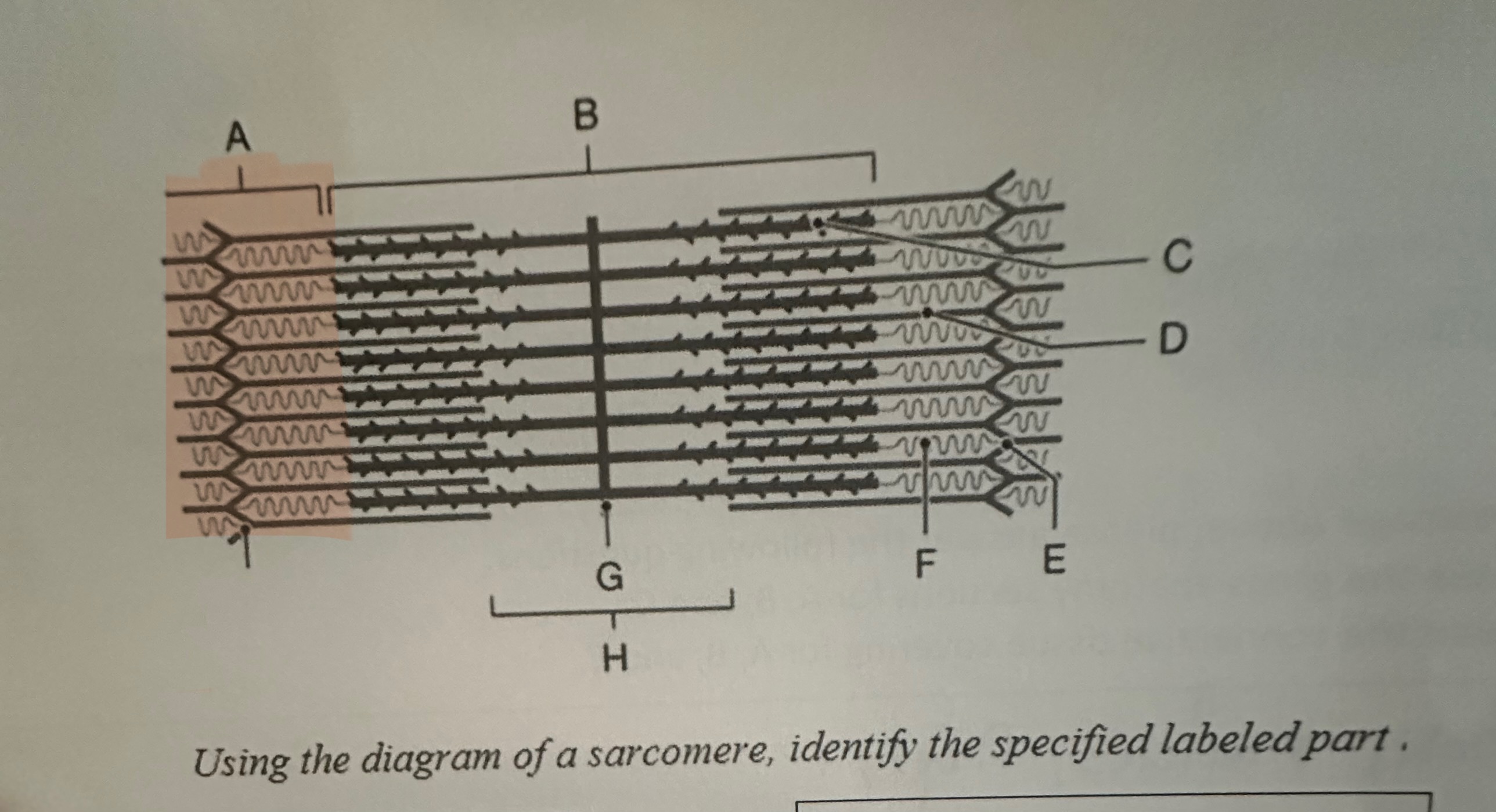
A
I Band
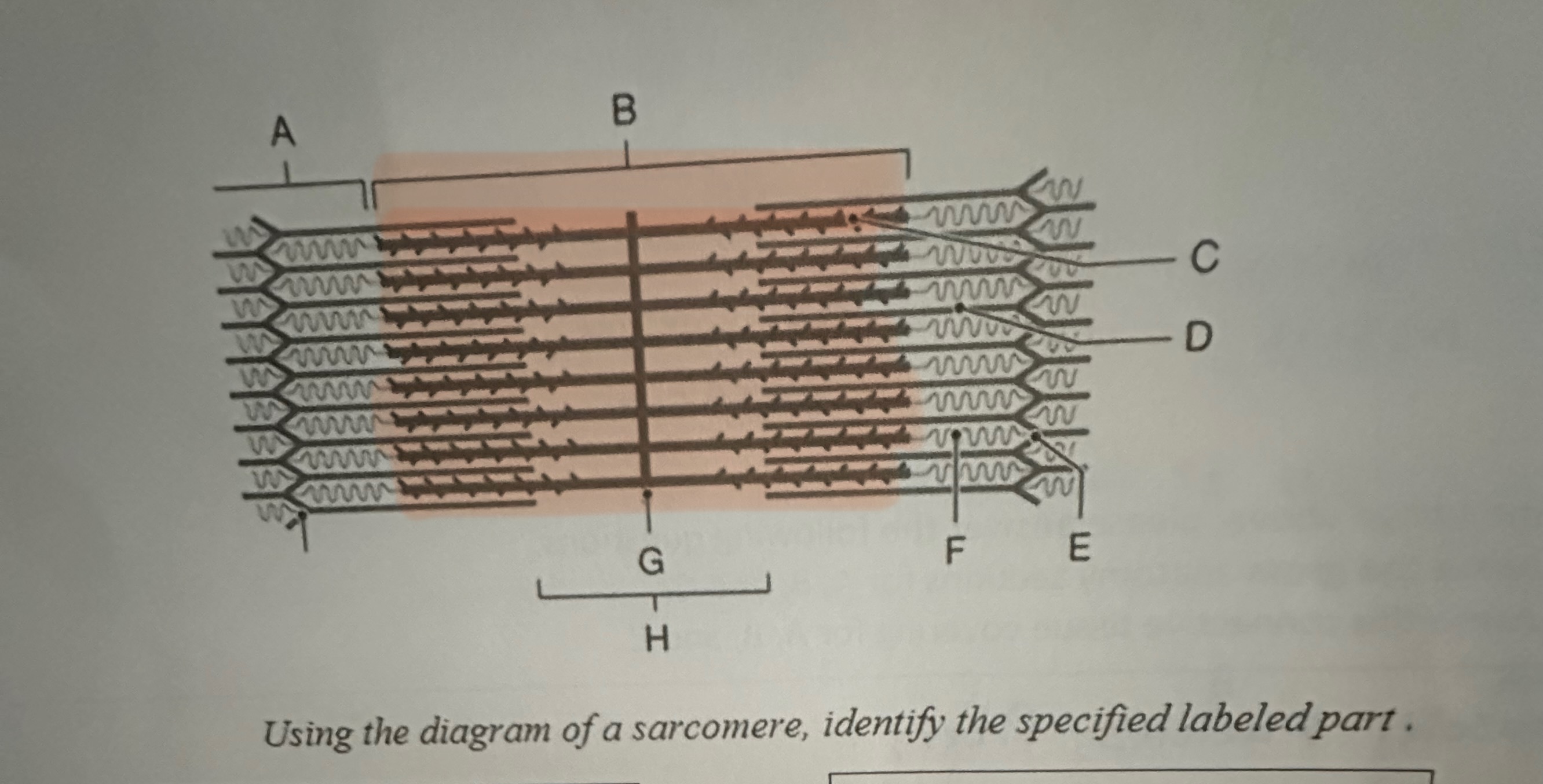
B
A- Band
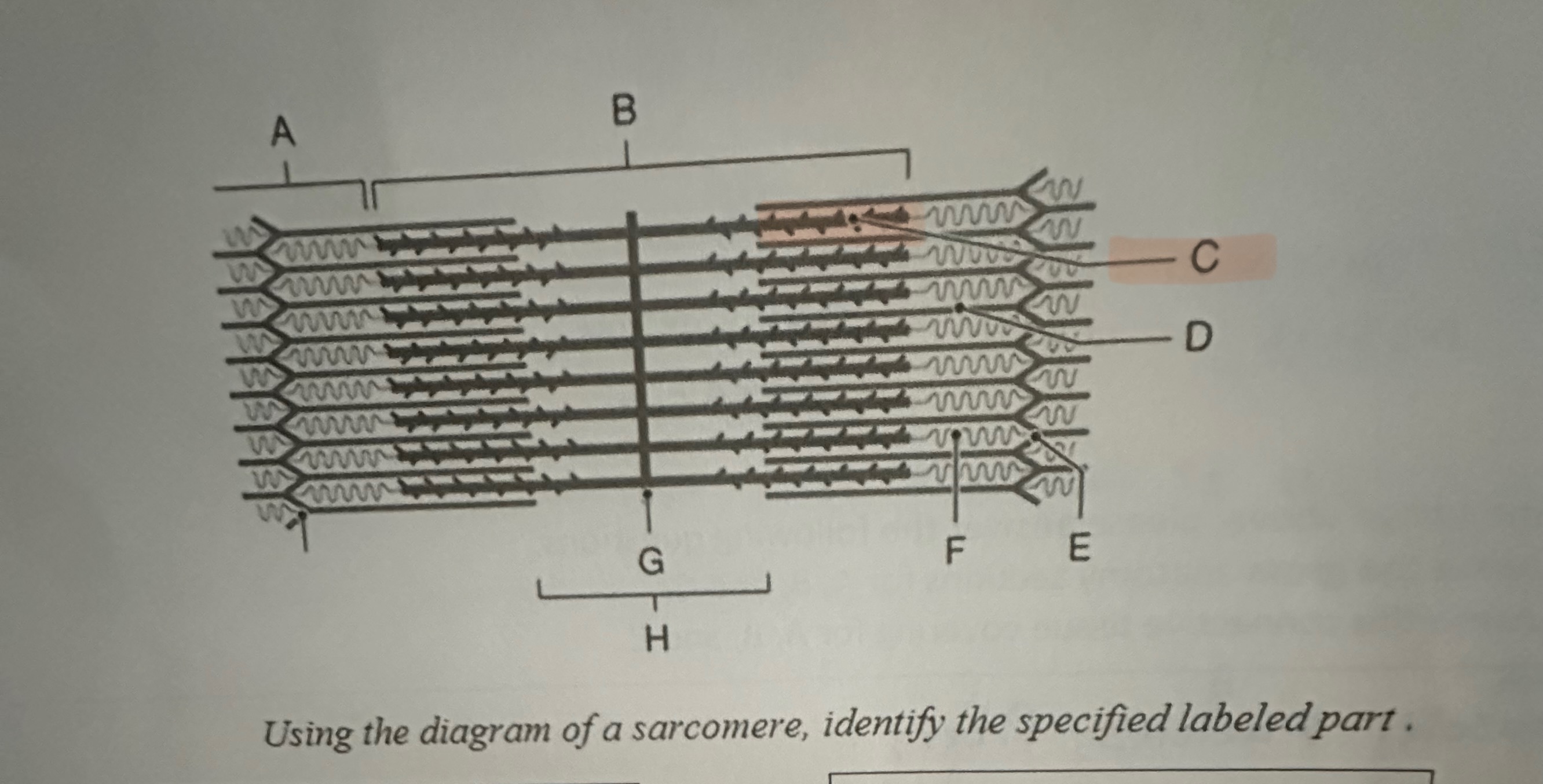
C
Myosin
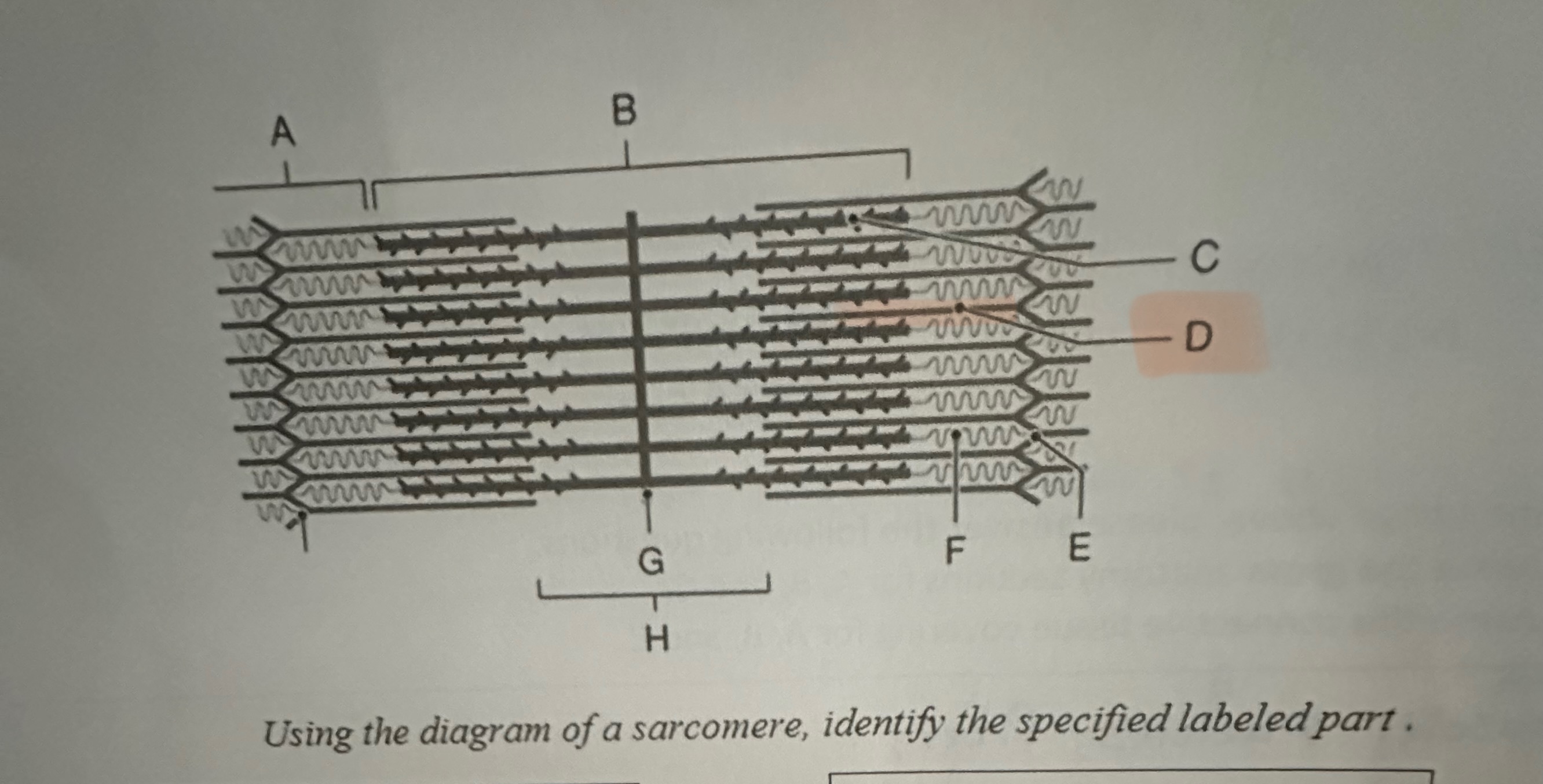
D
Actin
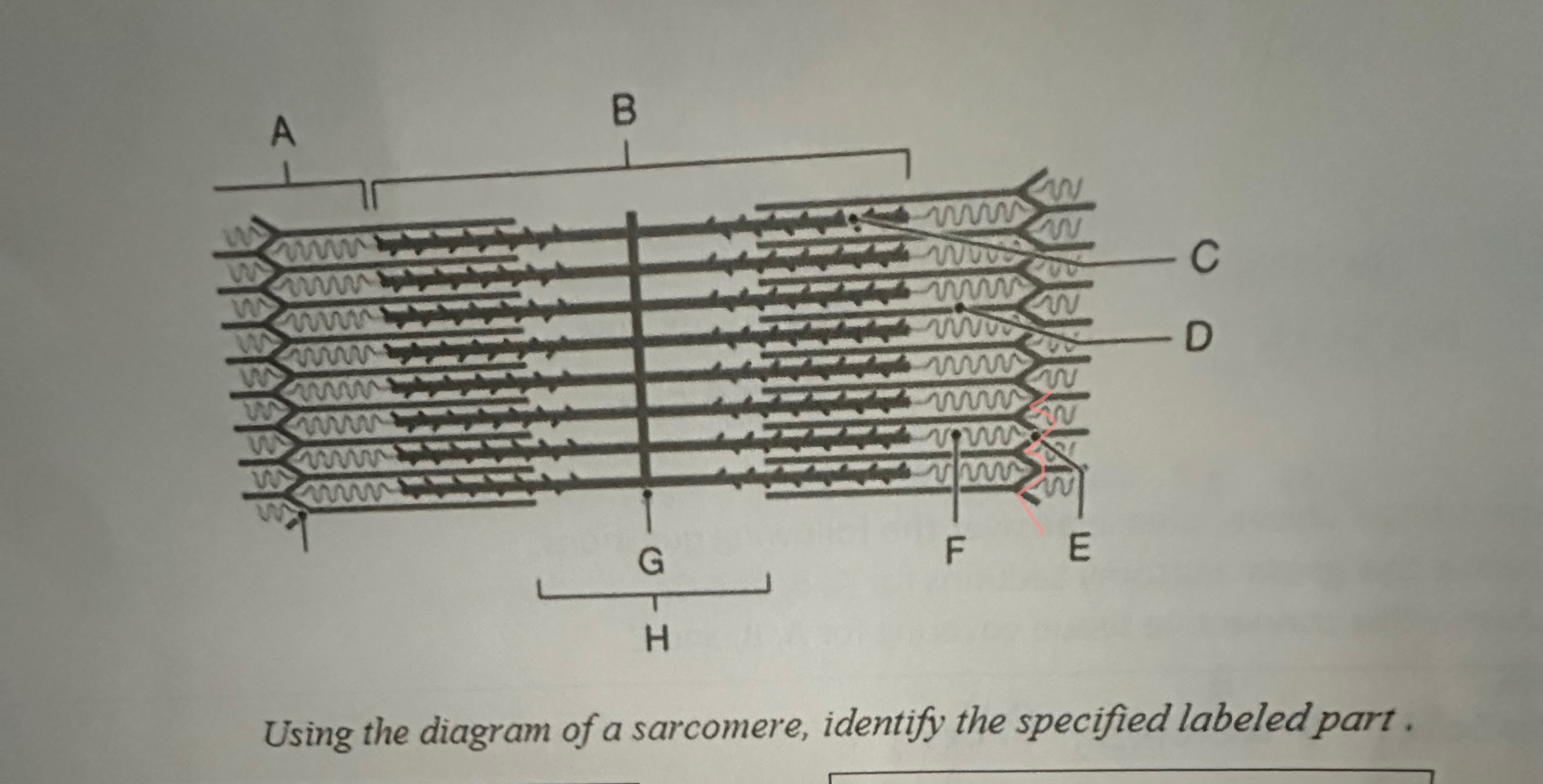
E
Z-Line
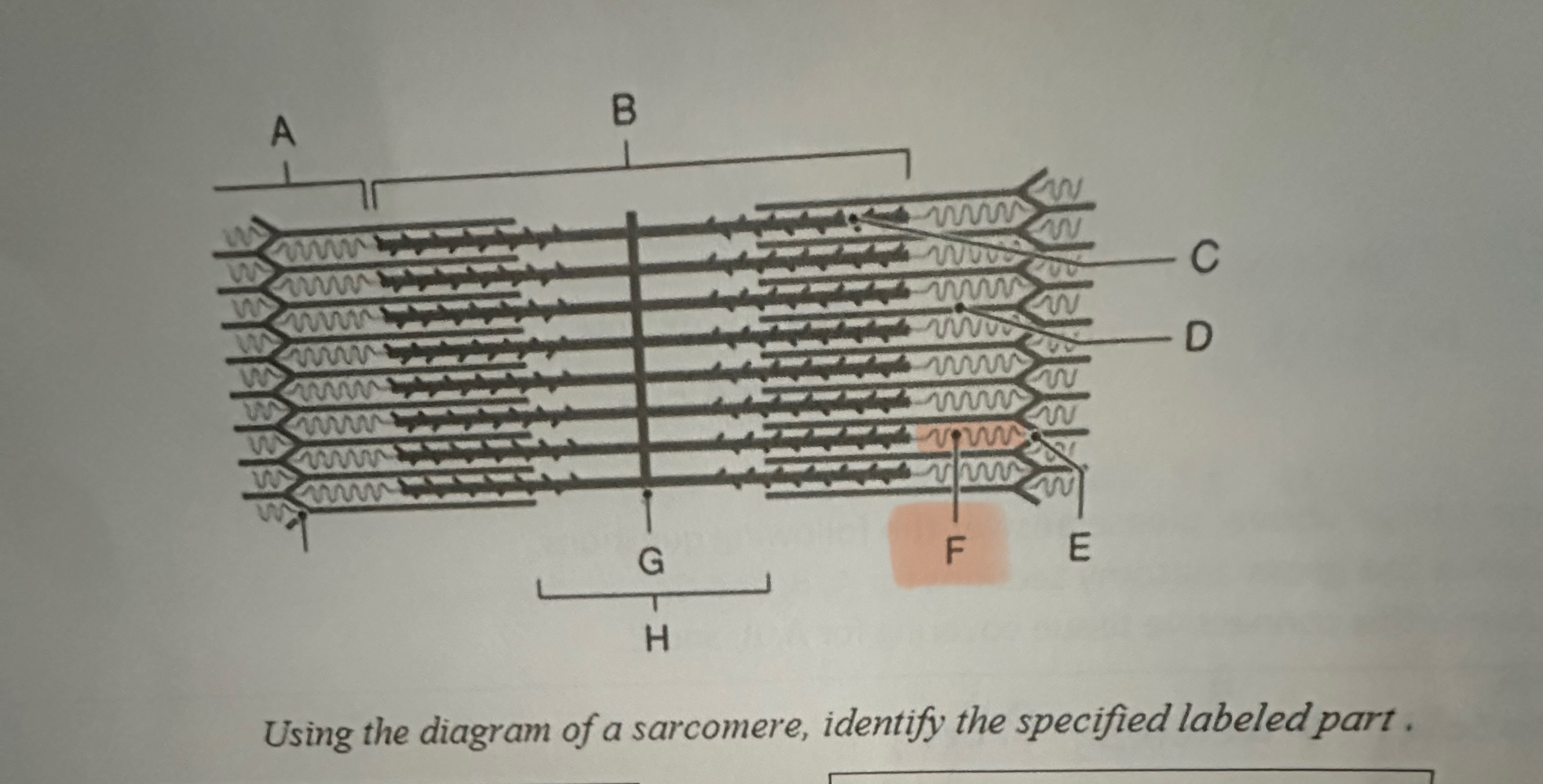
F
Titin
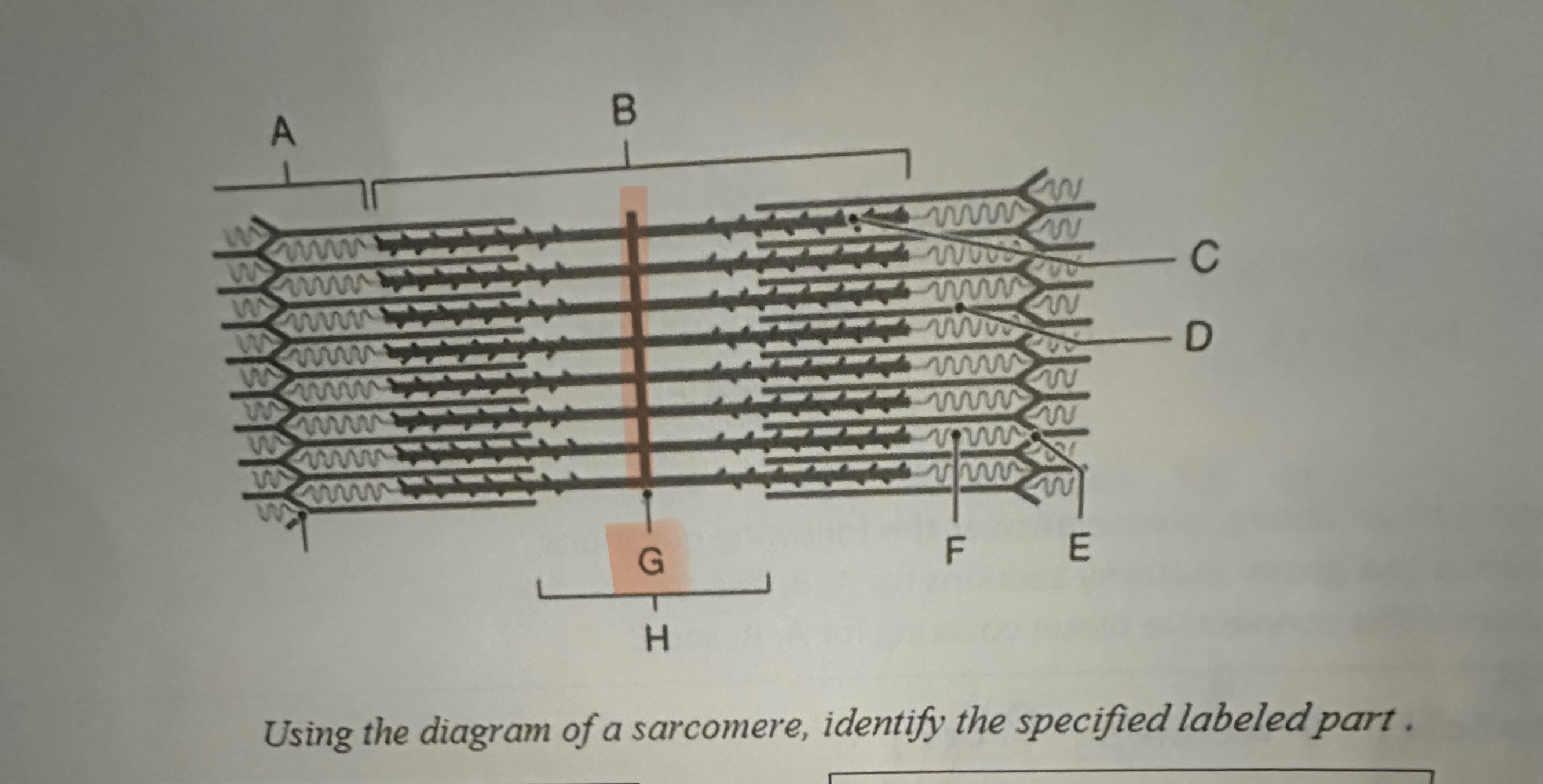
G
M -Line
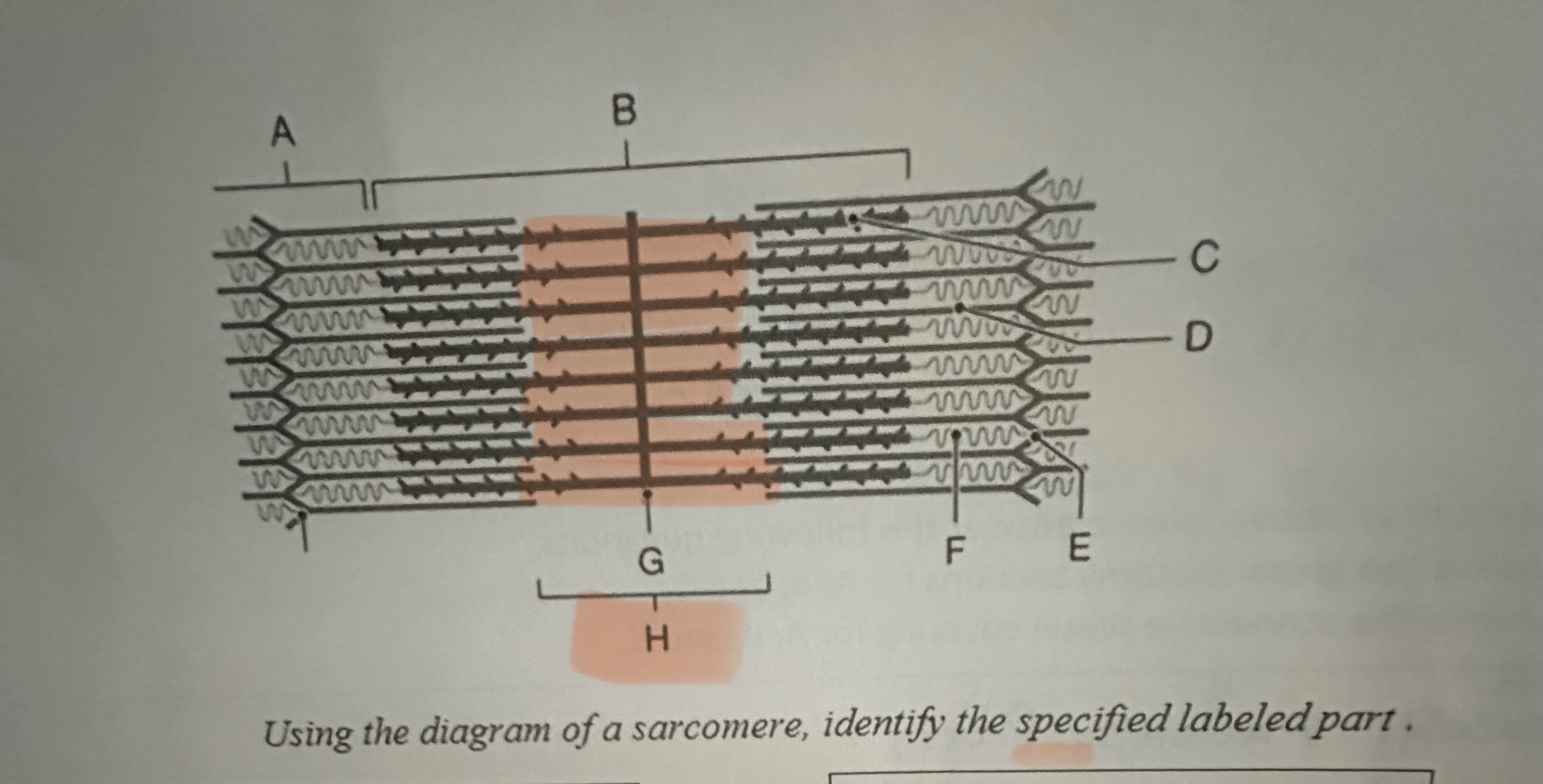
H
H- Band
What is the sarcolemma?
plasma membrane of the Muscle cell.
What is the T-tubule?
extension of the sarcolemma
Which organelle in the sarcoplasm is functionally linked to the T-tubule?
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
What is another function of the Organelle in part C ?
Calcium storage.
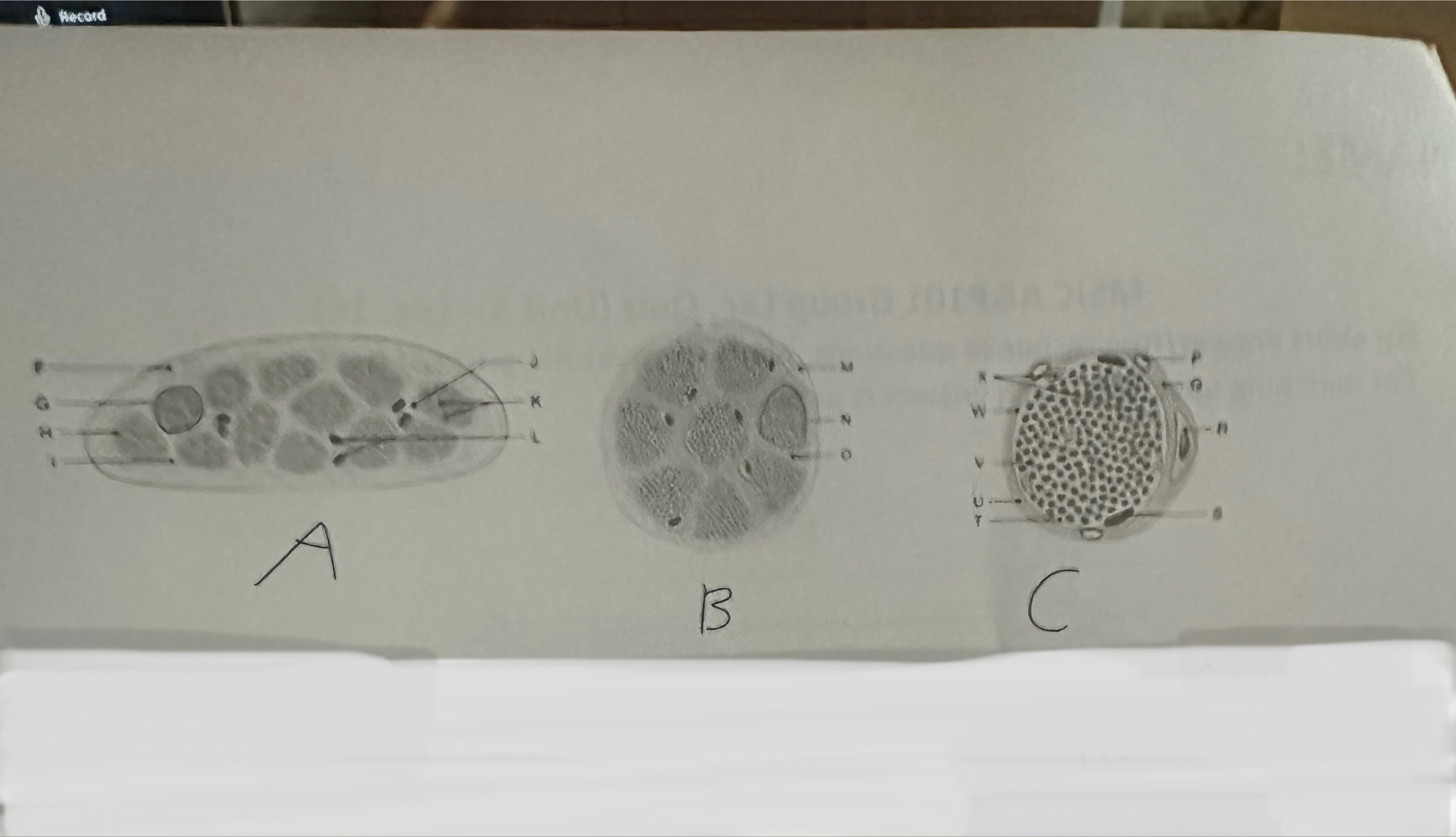
Please name the Gross Anatomy sections for A, B, and, C
A) Muscle B) Facicles C) Fiber
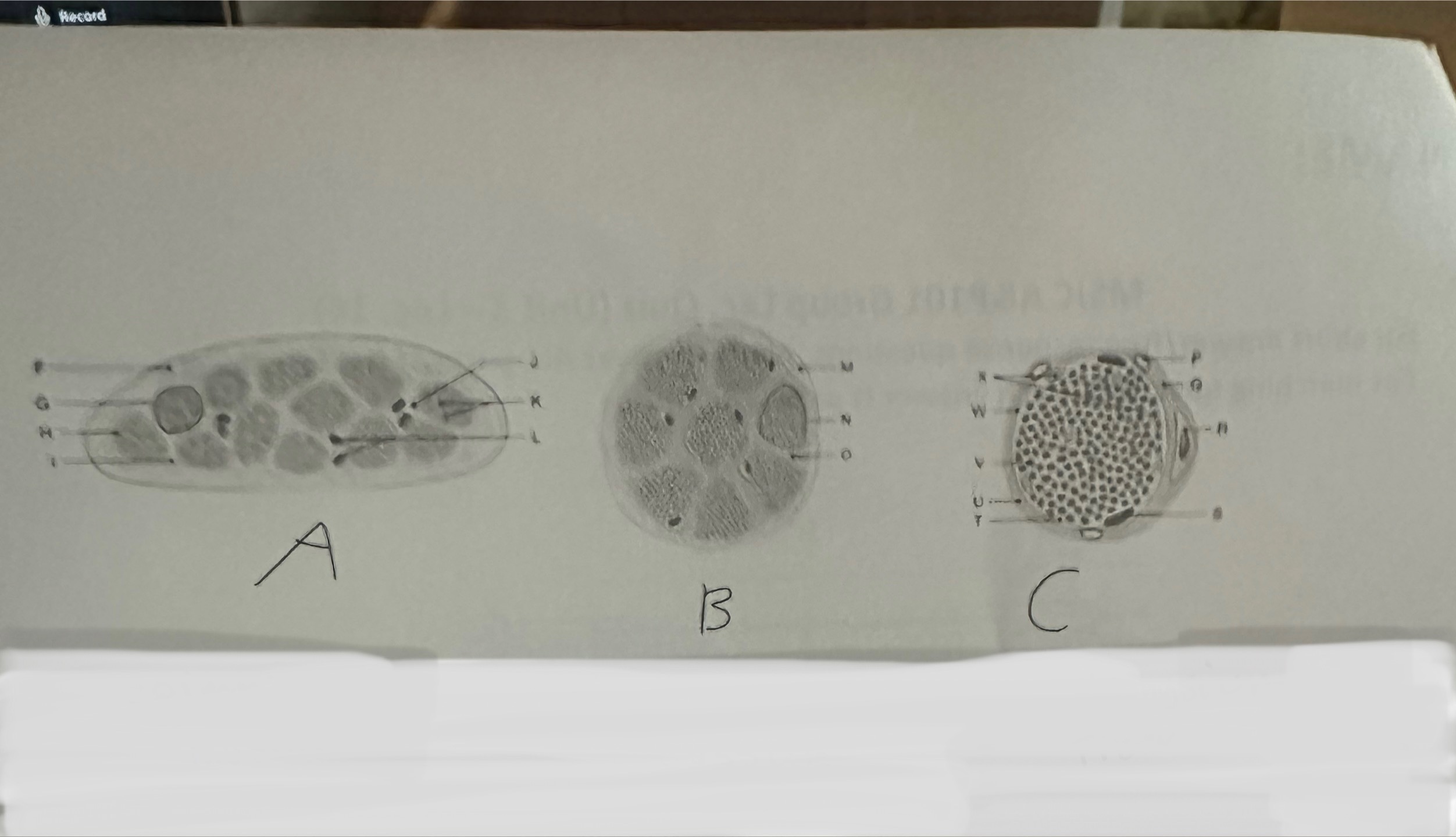
Please name the connective tissue covering for A , B, and, C
A) Epimysium B) Perimysium C) Endomysium
If someone has no actin, how would this affect a persons muscles ability to contract. AND WHY ?
No contraction because Myosin can't be Pulled on anything.
What is rigor mortis? Please explain the mechanism of this the same way Prof. Joe discussed it.
Its a Post-death muscle stiffening caused by lack of ATP.
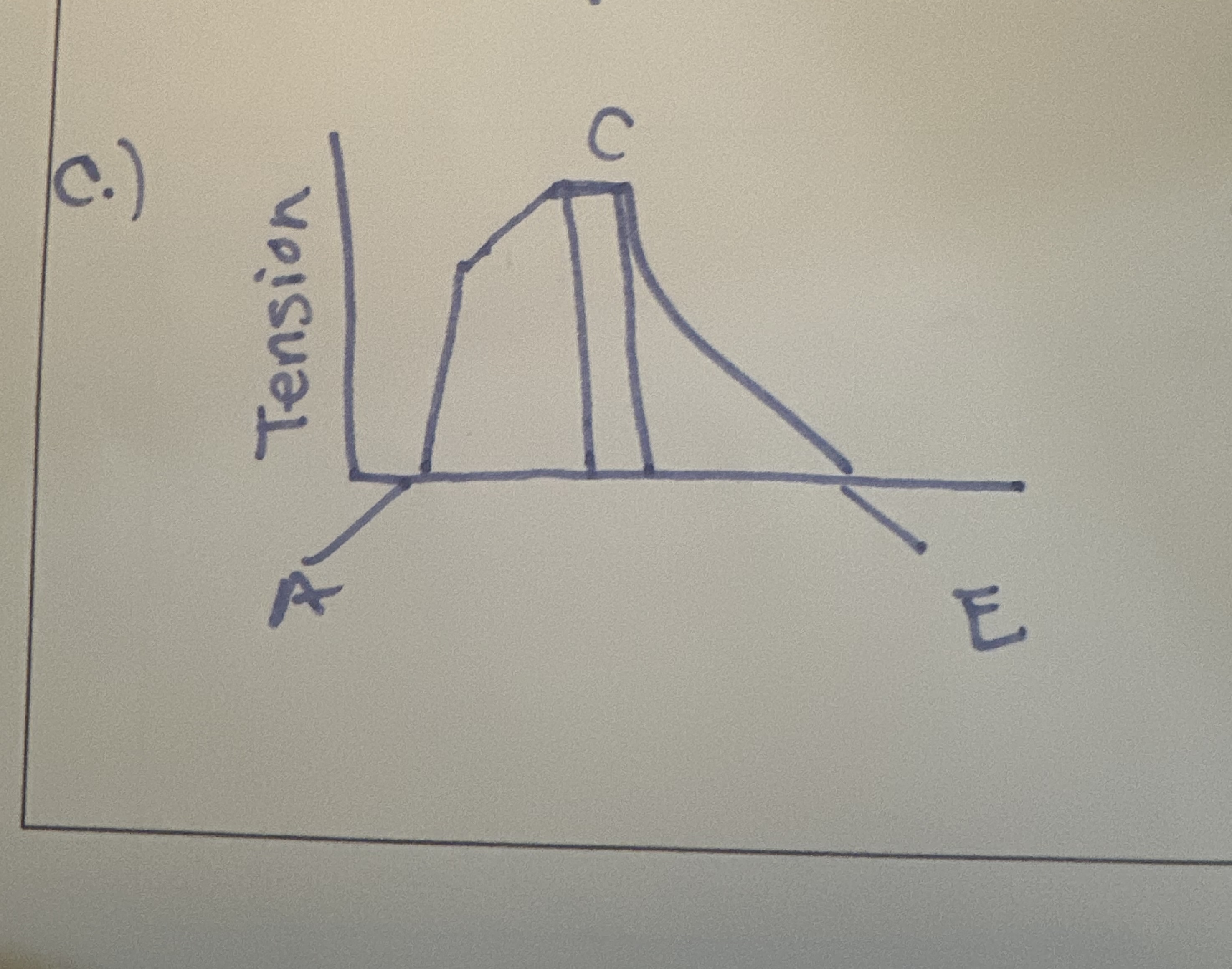
Explain (or draw out ) the concept of stretching/ flexibility in relation to protein filament.
A - extreme shortening (over lap)
B - No overlap ( Extreme Lengthening)
C - Perfect, Little Overlap
Why is ATP needed for muscle contraction? Please have a detailed explanation.
crossbridge detachment.
ATP breaks crossbridge to allow contraction cycle to continue.
Why is calcium needed for muscle contraction? Please have a detailed explanation.
Calcium is the key.
The Key Hole is troponin and
The Door is actin.
Calcium binds to troponin.
What is the name of the cell that interacts with a muscle fiber to initiate muscle action potentials?
Motor neurons.
What chemical does cell A ( motor neuron) send to the muscle fiber to initiate muscle action potentials?
ACH
Where does the muscle action potential travel to?
T-tubule
How does the muscle action potential cause calcium release? ( Provide 2 key details for this question)
It travels through T-tubules, causing protein changes that OPEN RyR receptors in the SR. The SR releases calcium( DHP to RYR)