Hit to Lead Activities 1
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
what does lead optimisation produce?
produce a pre-clinical candidate where it is evaluated in a complex biological system for its toxicity and drug like properties to assess if its safe to advance for clinical development
what does a drug need to have a good balance of?
potency
stability
PK properties
safety
side effects
need to compromise to produce best balance
what are the different approaches to medicinal chemistry in drug discovery programme?
2 approaches:
we don’t know how good a compound is until you make it
we can utilise resources to predict enough data to ensure we make better compounds and succeed sooner
what is target validation?
verifies that the interactions with the target will impact the disease → identify biomarkers
what are the 3 ways in which a drug can be excreted?
faeces → if drug is not absorbed into blood then excreted here
urine → main route if drug enters blood
exhalation
what are the key properties to consider in hit to lead activities? (8)
aqueous solubility
lipophilicity (log P/D)
microsomal stability
P450 inhibition
cytotoxicity
Hep G2 hepatotoxicity
Caco-2 permeability (Papp)
MDR1-MDCK permeability (Papp)
why is aqueous solubility and lipophilicity important to consider in hit to lead activities?
too soluble: stays in aqueous phase
too lipophilic: stays in fatty tissue
why is microsomal stability important to consider in hit to lead activities?
organs will try to protect against foreign exogenous substance → mainly liver that does this :. detoxifies what you’re taking
liver = rich in microsomal enzymes → drug first exposed to liver :. defines what fraction of drug enters the systemic circulation
assay measures compound clearance and can give you an idea of how fast it will be cleared out in vivo
why is P450 inhibition important to consider in hit to lead activities?
CYP450 = main enzyme in liver → create hooks = functional groups (phase 1 metabolism) which increase polarity :. dissolves in water :. excreted in urine
drugs that exhibit CYP450 inhibition slows phase 1 metabolism of itself and other drugs metabolised using this enzyme
why is caco-2 permeability (Papp) important to consider in hit to lead activities?
caco 2 = intestinal epithelial cell line that forms a monolayer → used as a model to understand how well the drug crosses intestinal membrane :. assesses how well drug is absorbed from gut
why is MDR1-MDCK permeability (Papp) important to consider in hit to lead activities?
MDCK (man, die calvin klein) cells contain MDR1 gene which encodes p-glycoprotein efflux pump
mimics ejection of drugs from cells
can be used to predict intestinal and brain permeability
why is Hep G2 hepatotoxicity important to consider in hit to lead activities?
most drugs pass liver for metabolism → if drug is toxic to liver then this is reduced
hep G2 = liver cells
what is the target value for aqueous solubility?
less than 100 micromolar (microM)
what is the target value for lipophilicity (logD)
0-3 → for BBB penetration then 0-2
(>3 too lipophilic)
what is the problem with lipophilic drugs?
bind to many receptors :. many off target side effects
what is the target value for microsomal stability?
less than 30 microlitres/min/mg of protein
what is the target value for CYP450 inhibition?
more than 10 micromolar (microM)
what is the target value for caco-2 permeability
more than 1 × 10-6 cm-1
what is the target value for hep G2 hepatoxicity?
no effect at 50 x IC50 or EC50
what is the target value for cytotoxicity in suitable cell line?
no effect at 50 x IC50 or EC50
what do hit compounds look like?
functional groups arranged around a central core of scaffold
small
core will usually be flat, rigid, aromatic
why are hit compounds usually small?
during optimisation, adding substitutions will increase MW but aim is to stay beneath 500 Da :. if big, you cannot add freely
why are hit compounds usually aromatic?
allows points for modification :. rapid generation of many analogues
allows fine tuning of properties
can do template hopping = when screening compounds you find a hit which is already patented, you can make modifications whilst maintaining pharmacophore :. novel intellectual property for patent
what is the criteria for hits?
reproducible in vitro affinity/efficacy
favourable properties (MW, pKa, solubility etc)
chemical tractability = able to synthesise compound in sufficient quantities
structure-activity relationship established
patentable or strategy in place to enhance chemical novelty
no significant toxicity alerts from compounds or known metabolites
how was imatinib developed?
imatinib = tyrosine kinase BCR-ABL inhibitor
known protein kinase C inhibitor was taken → large number of analogues of this was prepared
these analogues maintained the core scaffold
x ray crystallography confirmed binding of imatinib to target :. imatinib found here
define bioavailability
fraction of unchanged dose reaching systemic circulation
measured on a scale of 0-1
what is absorption?
entry of drugs into the bloodstream from the site of administration.
comment on the importance of free drug in plasma
only free drug exerts pharmacological activity
free drug is in equilibrium across the system
drug is reversibly bound to tissues and in plasma
only free drug will be cleared
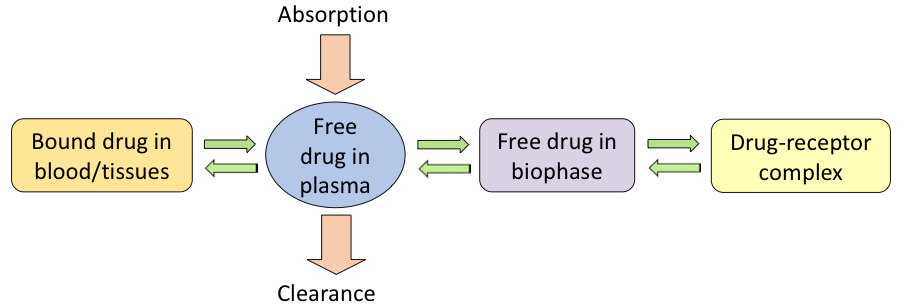
comment on the importance of plasma protein binding in hit to lead activities. what is its target value?
high binding affects dose, half-life and may have safety implications
PPB is expressed as fu = fraction unbound → value greater than 90% preferred
too high limits diffusion to the site of action
what is the criteria from hit to lead phase?
improved affinity/efficacy
selective over related targets (greater than 100 fold)
acceptable plasma protein binding, CYP inhibition/induction and hERG profiles
selectivity over non-related targets
efficacy in animal dose → dose-response relationship
no toxicity or mutagenicity at efficacious dose
define patent strategy
why is a balance during lead optimisation important?
drug experiences different environment before it reaches systemic circulation
optimising molecular properties are important to allow the drug to reach the target (but not getting renally or hepatically cleared from plasma)