Kinesiology Notes and Vocab - Unit.6
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Neuro system
Controls the function of every other system in the body by communicating with body systems/organs
coordinates performance using electrical and chemical means
Somatic ns and Autonomic ns
From autonomic is sympathetic ns and parasympathetic ns
How is the peripheral nervous system divided?
Brain and spinal cord
How is the central Nervous system divided?
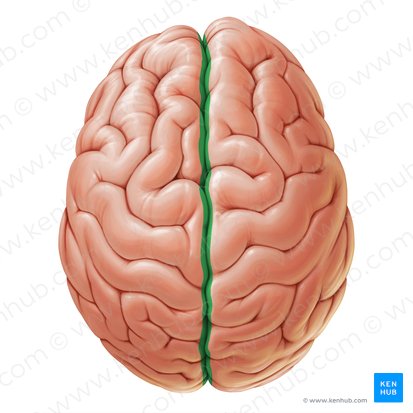
Fissure
The deep grooves in the cerebral cortex
Sulci
The shallow grooves in the cerebral cortex
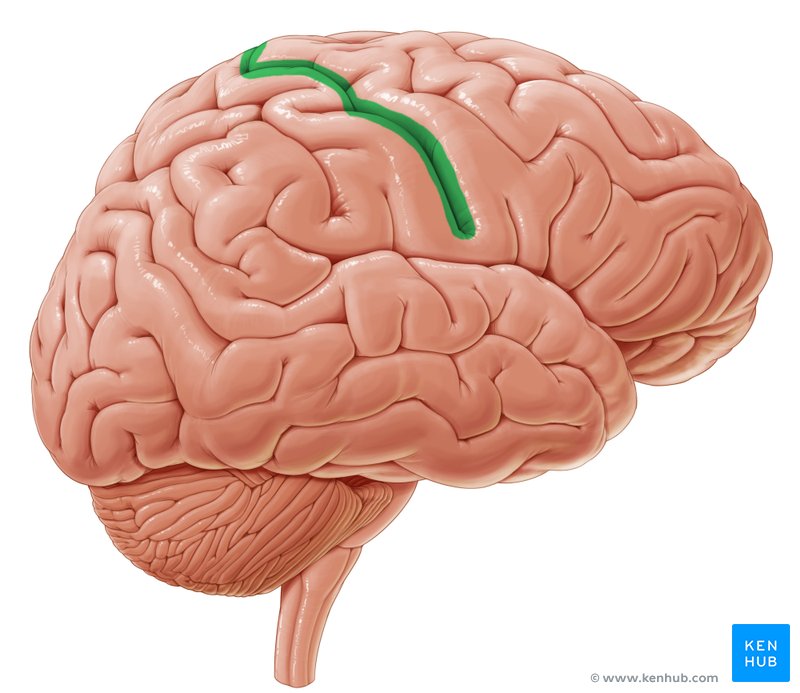
Gyri
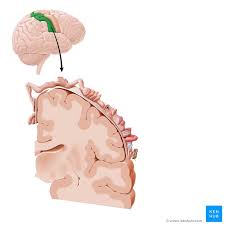
The ridges between the sulci on the cerebral cortex
As the cortex expanded, our brain created folds to maximize the volume that could fit inside our skull.
Why do we have ridges in our brain?
Volume theory
Conscious thought
white matter
Myelinated axons
Sends out signals to the body
Connects regions that send and receives signals
Affects learning and focus abilities
Gray Matter
Cell bodies of neurons
Unmyelinated axon (slower processes)
Larger areas indicates higher intelligence
Enables individuals to control movement, memory, and emotions
Brainstem (reptilian brain)
Oldest part of the brain and connects the brain to the SPINAL CORD
Controls breathing, heart rate, digestion, and sleep
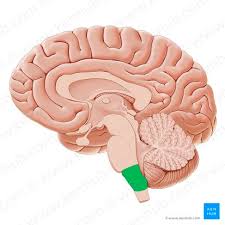
Cerebellum
Coordinates voluntary movements
Maintains balance and posture
Fine-tunes motor skills
Muscle memory
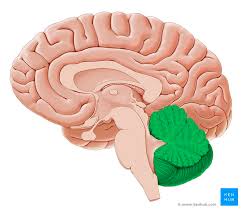
Cerebrum
The largest part of the brain, making up the lobes
Divided into left (Analytical) and right (Intuitive) hemispheres by longitudinal fissure
Initiates and coordinates movement and regulates temperature
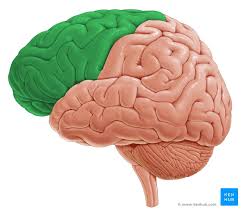
Frontal
What Lobe is This?
Functions: Higher-level thinking and controlling some voluntary motor movement
EX: Personality, memory, learning, planning, motivation, problem-solving
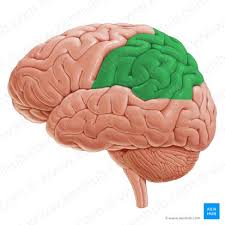
Parietal
What Lobe is This?
Function: Somatosensory (senses)
EX: Touch, pain, temperature, aching, awareness of somatic sensation, processing somatic sensation, proprioception (coordination of visual, auditory, and Somatosensory stimuli, and spatial/body awareness)
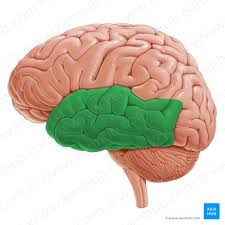
Temporal
What Lobe is This?
Function: Auditory
Stores memories
EX: Awareness of auditory stimuli (Hearing sounds, pitch, frequency…) and processing auditory stimuli (analyzing, memory, and recognizing)
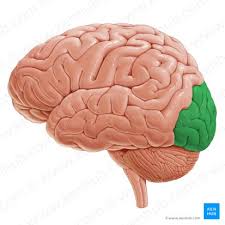
Occipital
What Lobe is This?
Function: Visual
EX: Awareness of visual stimuli (seeing objects) and processing visual stimuli (analyzing, recognizing, memory, shapes, colors sizes…)
Weighs 3 lbs
Contains 100B cells
feels no pain
Produces electricity
Develops back to front
What are the five facts of the brain?
Hippocampus
Located in the temporal lobes
Functions: Memory formation, spatial navigation, and learning
Amygdala
Located within the temporal lobe
Functions: Processing emotions and recognizing emotions in others
Thalamus
Function: A relay system for sensory information; takes sensory information (except smell) to the cerebral cortex
Corpus callosum
Connects the left and right brain
Function: allows for communication between the left and right hemispheres
Spinal Cord
A long bundle of never protected by the vertebrae
Function: Carries never impulses back and forth between the body and brain
Somatic NS
Functions: Helps you perceive the environment and react to it
Ex: Picking up a cup, walking, knee reflex
Autonomic NS
Function: Involuntary bodily functions
EX: Breathing, heat beat, pupil dilation
Sympathetic NS
Fight or flight—confront or flee from danger
Body’s natural response to stress
Parasympathetic
Rest and digest
Helps you relax
Neuron
The functional and structural unit of the nervous system
3 types
Afferent 2. Efferent 3. Inter-neurons
Afferent Neurons (Sensory)
Function: Carry sensory information TO brain and spinal cord
Sensory detection
Efferent Neurons (Motor)
Function: Carry motor commands AWAY from brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands
Inter-neurons
Function: Connects one neuron to another to transfer messages (middle man)
ONLY in the CNS; originate or terminate In the brain or spinal cord
Dendrites
Receptive region (receives input)
Function: Receives the messages from another neuron
Branch like fibers
Soma (Cell Body)
Function: Houses the nucleus and organelles! Essential for the neuron's metabolic activities and processing information.
Receptive region (receives input)
Axon
Function: Transmits messages away from the cell body to other neurons or muscles.
Conductive region
An extension of the cell body
Myelin Sheath
Fatty covering that wrap around the axon insulator
Function: Protects and insulates the axons so message can travel quicker and efficiently
Schwann cell makes the myelin sheaths
Nodes of Ranvier
The gaps between the myelin sheath
Function: Speeds up the conduction/sped of message
Terminal Endings
The end of the axon where neurotransmitters are released and stored
Function: Sends the signal to other neurons to communicate
Transmissive region (transmits message out to neurons)
Synaptic Transmission
Movement of neural impulse across the synapse
Gates are designed for specific neurotransmitters

Neurotransmitters
A chemical message—At least 100 are known!
EX: Dopamine, serotonin, histamine, adrenaline, epinephrine
Hypothalamus
Function: regulating various bodily functions
EX: hormone regulation, body temperature, thirst and hunger, emotional responses, and sleep-wake cycle
Receptive
Conductive
Transmissive
What are the three regions of a neuron?
Resting Potential
Membrane potential of a neuron that isn’t transmitting signals
Negatively charged at this stage
Action Potential
When the total input of neurotransmitters reaches a threshold of -55mV
Neuron fires an action potential
Glial Cells
Provide physical and chemical support to neurons and maintain their environment
non-nerve cells