Midterm Study Guide for Cardiac and Pulmonary Rehab
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
What does CVD stand for and what are some examples?
Cardiovascular Disease; examples include heart attack, stroke, arrhythmia, and hypertension.
What is the primary cause of death in the US?
Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) is the #1 cause of death in the US.
What is CAD and what does it involve?
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) involves blockage in the arteries.
What is the difference between a heart attack and cardiac arrest?
A heart attack occurs when an artery is blocked, preventing blood flow, while cardiac arrest is an electrical problem where the heart's rhythm is out of sync.
What was the purpose of the Framingham Heart Study?
To understand the impact of cardiovascular disease and the procedures and benefits of cardiac rehabilitation.
What are the five components of cardiac rehabilitation?
1) Exercise, 2) Heart-healthy diet, 3) Reduce stress, 4) Medical therapy, 5) Stop smoking.
What is the structure of cardiac rehabilitation phases?
Phase 1: Acute phase (inpatient monitoring), Phase 2: Sub Acute (outpatient conditioning), Phase 3: Training and Maintenance, Phase 4: Disease Prevention (Phases 3 and 4 are not covered by insurance).
What is the difference between primary and secondary prevention in cardiopulmonary rehab?
Primary prevention involves identifying and managing risk factors before an event occurs, while secondary prevention focuses on preventing further events after one has already occurred.
What is the definition of cardiovascular disease?
Atherosclerotic process characterized by thickening in the internal layer of blood vessel walls due to lipid accumulation.
What are Fatty Streaks and Plaque in relation to cardiovascular disease?
Fatty streaks are early signs of atherosclerosis, while plaque is a buildup that can block arteries.
What is myocardial ischemia and what does it cause?
Myocardial ischemia is a lack of blood flow to heart cells, causing pain due to insufficient oxygen supply.
What is angina and how does it relate to myocardial ischemia?
Angina is chest pain associated with myocardial ischemia, indicating that tissue connected to the affected artery is at risk.
What is stable angina?
Chronic external angina, predictable and occurs during exertion or psychological stress when oxygen demands increase.
What is unstable angina?
Considered an acute coronary syndrome, it is life-threatening and occurs unpredictably.
What causes Prinzmetal/Variant Angina?
It is caused by artery spasms and often occurs at rest, particularly in the early morning.
What is asymptomatic 'silent' angina?
Angina that occurs without noticeable symptoms, often detected during monitoring.
What is a myocardial infarction (heart attack)?
It is the death or necrosis of cardiac muscle due to sustained myocardial ischemia.
What are common contributors to myocardial infarction?
Ischemia, atherosclerosis, thrombus, and arterial spasm.
What percentage of myocardial infarctions are asymptomatic?
30% of all myocardial infarctions are asymptomatic.
What are common types of arrhythmias post-myocardial infarction?
Tachycardia (fast heart rate) and bradycardia (slow heart rate).
What is a thrombus and where can it form?
A thrombus is a blood clot; it can form in deep veins, typically in the calf, and can lead to pulmonary embolism.
What is congestive heart failure and what are its types?
Congestive heart failure is a condition where the heart cannot pump effectively; types include diastolic, systolic, acute, chronic, compensated, uncompensated, and intractable.
What is the pathway of air in the respiratory system?
Air enters the trachea, moves down to the bronchi, then to the bronchioles, and finally reaches the alveoli.
What is static lung volume and what are its components?
Static lung volume includes tidal volume, inspiratory reserve volume (IRV), expiratory reserve volume (ERV), residual lung capacity, and total lung capacity.
What are pulmonary function tests used for?
They are used to diagnose pulmonary diseases.
What are the different types of pulmonary tests?
Chest X Ray, Chest CT, Echocardiogram, Spirometry, Oximetry, Exercise Stress Test.
What characterizes obstructive pulmonary disease?
It affects the airways and includes conditions like COPD, chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and asthma. It is defined as difficulty expelling air, with air remaining in the lungs after each breath.
What is asthma and when does it typically start?
Asthma is a chronic condition that inflames and narrows the airways, usually starting in childhood.
What defines restrictive pulmonary disease?
Restrictive pulmonary disease affects the air sacs and includes conditions like interstitial lung disease, obesity, scoliosis, neuromuscular diseases, and COVID-19. It is characterized by difficulty fully expanding the lungs and reduced lung volume.
What is the difference between obstructive and restrictive pulmonary disease?
Obstructive pulmonary disease is characterized by difficulty getting air out (air trapping), while restrictive pulmonary disease involves a reduction in the ability to get air in (volume problem).
What is pulmonary rehabilitation used for?
It is used for individuals with chronic respiratory diseases to reduce symptoms, optimize functional status, increase participation, and reduce healthcare costs.
What are some non-invasive tests for cardiovascular disease (CVD)?
Resting ECG, King of Hearts, Holter monitoring, stress exercise tolerance test, echocardiogram, external counterpulsation, ankle brachial index for PAD patients.
What are some invasive tests for cardiovascular disease (CVD)?
Radionucleotide graded X test, medical or chemical stress test, cardiac catheterization, percutaneous transluminal coronary angiogram, coronary artery bypass graft.
What are non-modifiable risk factors for cardiovascular disease?
Age/gender, family history, ethnicity, cigarette smoking, hypertension, dyslipidemia.
What lifestyle changes can reduce cardiovascular disease risk?
Obesity management, regular exercise, and smoking cessation.
What are the key terms related to basic ECG?
Action Potential, Depolarization, Repolarization.
What does the P wave represent in an ECG?
The P wave represents the SA Node.
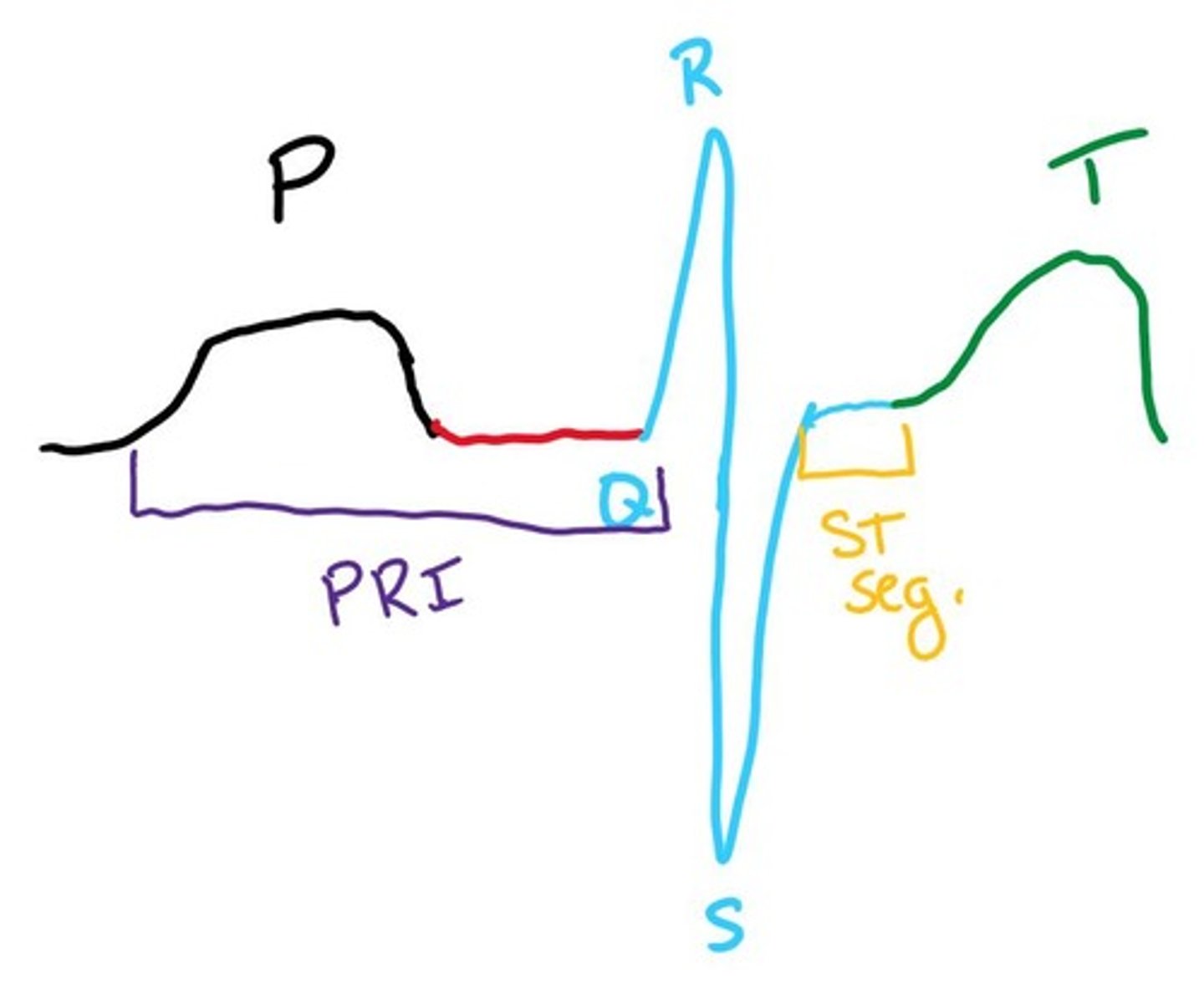
What does the QRS complex represent in an ECG?
The QRS complex represents ventricular contraction.
What does the T wave represent in an ECG?
The T wave represents ventricular relaxation.
What are common side effects of diuretics?
Loss of potassium and electrolytes, dehydration, increased urination, increased thirst, muscle cramps, low blood pressure.
What are beta blockers used for?
They are used for angina, SVT, rate control for Afib, MI, CHF, secondary hypertension, migraines, anxiety, and tremors.
What are common side effects of beta blockers?
Fatigue, decreased energy, nightmares, cold hands/feet, impotence, and potential triggers for asthma attacks.
What is the mechanism of action for calcium channel blockers?
They block calcium from entering cell walls, which decreases contractibility and promotes relaxation.
What are common side effects of calcium channel blockers?
Edema, constipation, dizziness, weakness, and decreased heart rate.
What is the mechanism of action for ACE inhibitors?
They prevent the creation of angiotensin II by inhibiting the angiotensin-converting enzyme, relaxing blood vessels and reducing water reabsorption by kidneys.
What are common side effects of ACE inhibitors?
Dry persistent cough, renal impairment, hyperkalemia, fatigue, dizziness, and headaches.
What are angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) used for?
They are used for hypertension, CHF, kidney failure in diabetes, and reducing the risk of stroke.
What is the mechanism of action for cardiac glycosides?
They act on the sodium-potassium pump, increasing output force and decreasing the rate of contraction.
What are common side effects of antiarrhythmics?
They can cause suppression of ectopic stimuli, redirect electrical activity, slow impulse generation, and decrease myocardial irritability.
What are nitrates used for?
They are used for angina, myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure, and hypertension.
What are common side effects of nitrates?
Decreased blood pressure, increased heart rate, dizziness, headaches, and facial flushing.
What is the purpose of exercise testing?
To diagnose abnormal physiological responses, assess risk for adverse events, and evaluate pre and post-operative status.
What are absolute contraindications for exercise testing?
Recent significant changes in resting ECG, recent MI, unstable angina, uncontrolled arrhythmias, aortic stenosis, decompensated heart failure, acute pulmonary embolus, and acute infections.
What should patients avoid before exercise testing?
Food, alcohol, caffeine, or tobacco for at least three hours prior to the test.
What are the characteristics of an athlete's heart?
Ventricular hypertrophy, enhanced cardiac output, lower resting heart rate, and improved vasovagal tone.
What is commotio cordis?
A condition caused by a blunt chest impact that can lead to sudden cardiac arrest, requiring precise timing of the impact.
What are the core components of cardiac rehabilitation?
Baseline patient assessment, nutrition, risk factor management, psychosocial management, activity counseling, exercise therapy, and outcome analysis.
What are some common psychological barriers to behavior change?
Fear of failure, lack of motivation, and low self-efficacy.
What is the Transtheoretical Model of Change?
A framework that includes stages: Precontemplation, Contemplation, Preparation, Action, and Maintenance.