A&P II Exam #2 (CH 18 and 19) - Questions
1/94
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The Cardiovascular System (Heart) and The Lymphatic System
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
name the coverings of the heart and describe the functions of the fibrous pericardium
pericardium - double-walled and surrounds the heart
fibrous pericardium
superficial layer
protection
anchors heart to surrounding structures
prevents overfilling
serous pericardium
deep, double-layered
parietal layer - lines internal surface of fibrous pericardium
visceral later (epicardium) - external surface
pericardial cavity - filled with serous fluid (allows for heart to work without friction
describe the three layers of the heart wall. What is the function of the myocardium
epicardium - visceral layer of serous pericardium
myocardium - layer that actually contracts
endocardium - sheet of squamous endothelium
describe the functions of the four heart chambers
2 atria - entryways
receives blood
small and thin-walled (only needs to push to ventricles, gravity also helps)
sits above ventricles
contains auricles - small, wrinkled, protruding appendages, increases atrial volume
2 ventricles - underside
discharging chambers - actual pumps of heart
thicker myocardium (pump to rest of body)
trabeculae carneae - irregular ridges of muscles that mark the internal walls
papillary muscles - plays a role in valve function, project into the ventricular cavity
name each chamber and provide the name and general route of its associated great vessel(s)
RA
posterior wall is smooth
anterior wall contains pectinate muscles
may contain fossa ovalis
superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, coronary sinus
LA
mostly smooth
pectinate muscles found only in the auricles
may contain fossa ovalis
four pulmonary veins - blood from the lungs to heart
RV
chamber closest to the surface
pumps blood to pulmonary trunk
LV
majority of posteroinferior surface of heart
pumps blood to aorta
name the three veins which return blood to the RA
superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, and coronary sinus
name the heart valves and describe their location, function, and mechanism of operation
atrioventricular (AV) valves - prevents backflow to atria when ventricles contract
tricuspid - right AV, 3 cusps
bicuspid (mitral) left AV, 2 cusps
BOTH contains chordae tendineae (heart strings)
semilunar (SL) valves - prevents backflow from major arteries back to ventricles
pulmonary SL valve - RV to pulmonary trunk, 3 cusps
aortic SL valve - LV to aorta, 3 cusps
what is the function of the chordae tendineae
anchors cusps of AV valves to papillary muscles
hold valve flaps in closed position
prevents flaps from everting back to atria
allows unidirectional blood flow
trace the pathway of blood through the heart
pulmonary circuit
SVC and LVC and coronary sinus → RA → tricuspid valve → RV → pulmonary semilunar valve → pulmonary trunk → pulmonary arteries → lungs
systemic circuit
four pulmonary veins → LA → mitral/bicuspid valve → aortic semilunar valve → aorta → body
true or false - veins always carry oxygen-poor blood, and arteries oxygen-rich blood
false
pulmonary arteries does not contain oxygen rich blood (away from heart, towards lungs)
pulmonary veins contain oxygen rich blood (away from heart, towards body)
name the major branches and describe the distribution of the coronary arteries
what is their function
coronary arteries
left coronary arteries
anterior interventricular artery - supplies interventricular system and septum and anterior walls of both ventricles
circumflex artery - supplies LA and posterior wall of LV
right coronary arteries
right marginal artery - supplies myocardium of lateral right of heart
posterior interventricular artery - runs to apex of heart and supplies posterior interventricular walls (merges with AIA at the apex of the heart)
coronary veins
cardiac veins collect blood from capillary beds
coronary sinus - empties into RA
great cardiac vein - anterior interventricular sulcus
middle cardiac vein - posterior interventricular sulcus
small cardiac vein - right interior margin
what is the result of coronary artery blockade
myocardial infarction (heart attack)
prolonged coronary blockage
cells die - amitotic heart cells are replaced with noncontractile scar tissue
*angina pectoris (choked chest)
thoracic pain due to fleeting deficiency in blood delivery to myocardium
weakened cells, not dead
what is the coronary sinus
returns deoxygenated blood from coronary veins, drained into the RA
how does the structure and function of cardiac muscle cells differ from skeletal muscle fibers
not in-depth explanations
some cardiac muscle cells are self-excitable
heart contracts as a unit
uses both SR and EF calcium to contract
skeletal only uses SR to contract
NO tetanic contractions (build up) in cardiac muscles
heart relies on O2 respirations
can use other pathways, but NEEDS O2
what structures can you find in the intercalated discs of cardiac cells
what is their function
gap junctions
allows ions to pass cell to cell, electrically couple adjacent cells
allows heart to be a functional syncytium (single coordinated unit)
desmosomes
holds cells together, prevents cells from separating from contraction
what is a functional syncytium
which structures of the intercalated discs allow the myocardium to function as a functional syncytium
a single coordinated unit - gap junctions (passage of ions, electrically connected)
calcium is needed for muscle contraction, what is the source of calcium for skeletal and cardiac muscle fiber contraction
cardiac muscle cells use both SR and EF for contraction
skeletal muscle does not use EF calcium for contraction
what are the cardiac pacemaker cells and what is their function
specialized cells that have the ability to depolarize spontaneously
unstable resting potential - continuously depolarize
pacemaker potential - the spontaneously changing membrane potential that initiate action potential trigger rhythmic contractions
name the function of the SA node
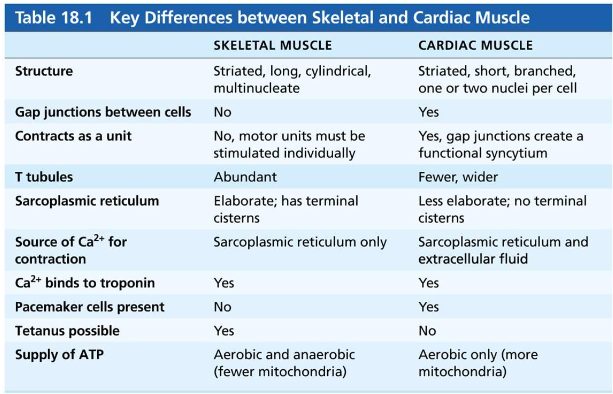
name the components of the conduction system of the heart and their location trace the conduction pathway
sinoatrial node, pacemaker, sinus rhythm
initiates action potential
why are the impulses delayed at the AV node
which modifications are responsible for this delay
due to lower number of gap junctions and small diameter of muscle fibers
allows atria to complete their contraction before ventricles contract
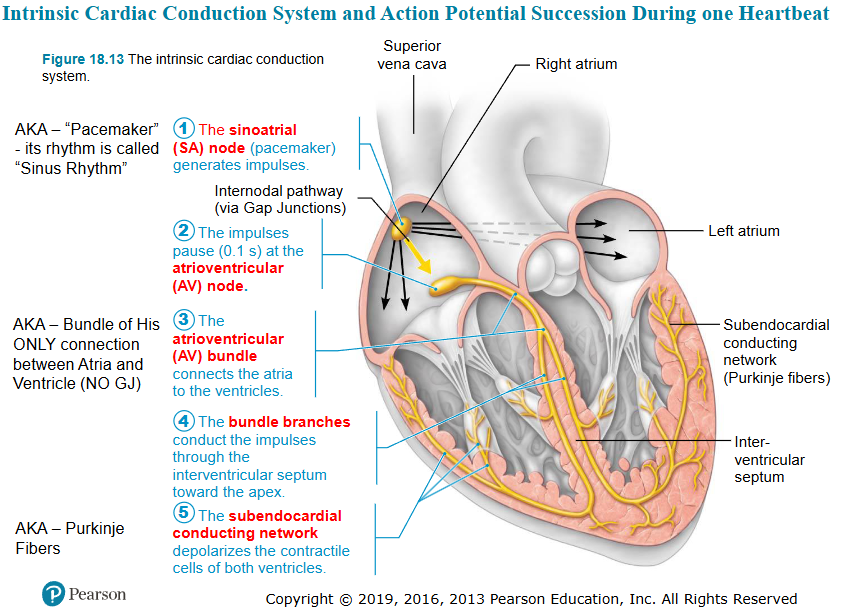
draw the pacemaker and action potentials of cardiac pacemaker cells
indicate which ion channels are open/closed during:
pacemaker potential
depolarization
repolarization
pacemaker potential
slow sodium channels open, NA+ enters cell
potassium channels are closed
membrane potential becomes less negative
depolarization/action potential
calcium channels open (Ca2+ enters cell) - voltage gated (sodium channels)
membrane potential becomes less negative FASTER
repolarization
calcium channels close
potassium channels open, K+ leaves cell
membrane potential becomes more negative
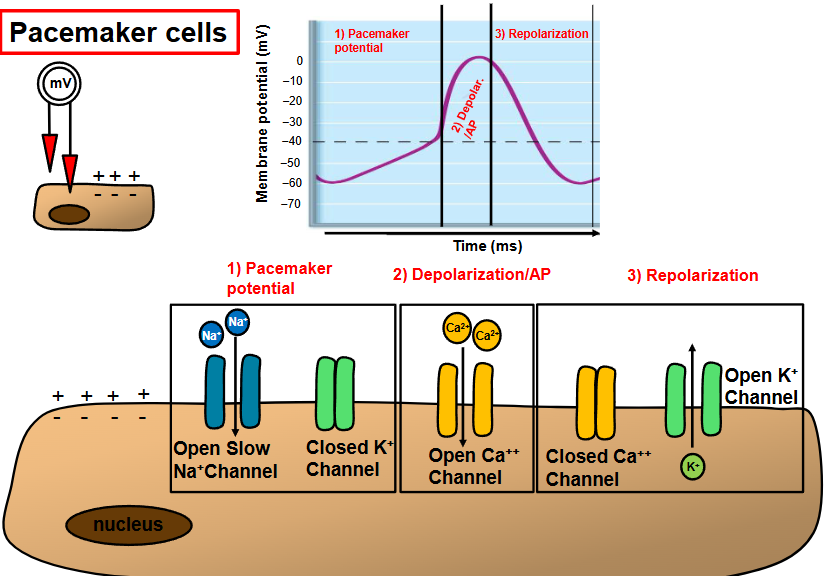
define the pacemaker potential
which event causes the pacemaker potential
the spontaneously changing membrane potential that initiate action potential trigger rhythmic contractions
opening of slow sodium channels
draw the action potential of contractile cardiac muscle cells
indicate which ion channels are open/closed during:
depolarization
plateau phase
repolarization
depolarization/action potential
fast voltage gated sodium channels open
Na+ enters the cell
MP becomes less negative, more positive
immediate depolarization
plateau
potassium channels start opening (exits cell)
slow calcium channels open (enters cell)
MP SLOWLY becomes more negative
allows for a longer refractory period
prevents tetanic contractions
repolarization
inactivated Ca2+ channels
potassium channels open up (K+ leaves the cell)
MP becomes more negative
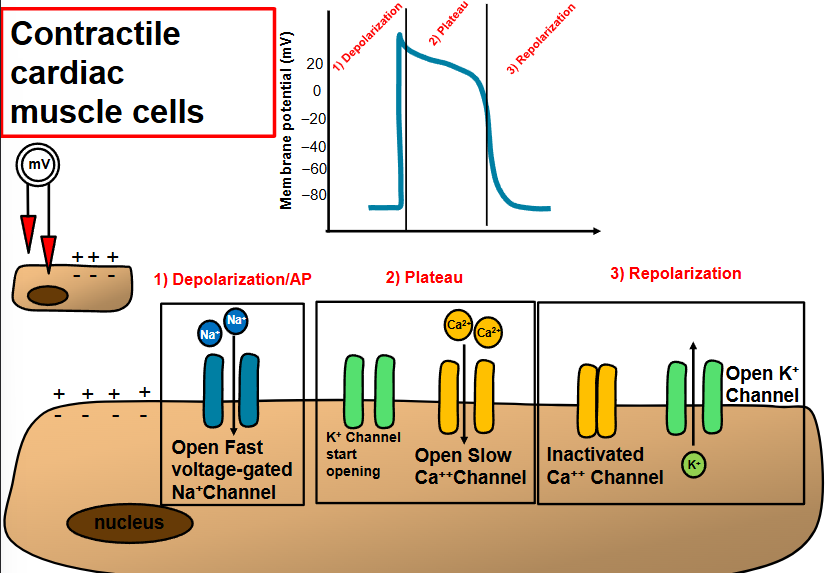
describe and compare action potentials in cardiac pacemaker and contractile cell
the influx of Ca2+ that produces rising phase of action potential
pacemaker cells → slow, Ca2+
contractile cell → fast, Na+
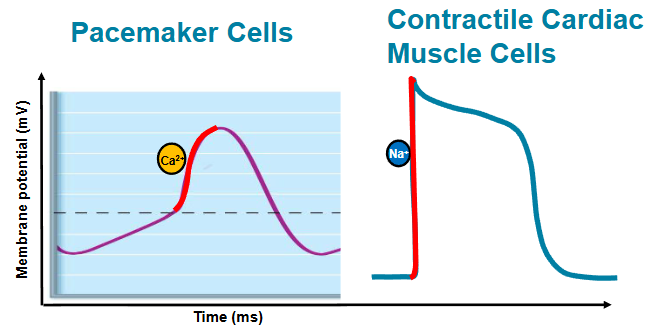
compare the actions potential in cardiac and skeletal muscle fiber
skeletal - action potential is 1-2 milliseconds
cardiac - AP is >200 milliseconds
plateau - slow Cs2+ entering the cell
allows for an effective pump
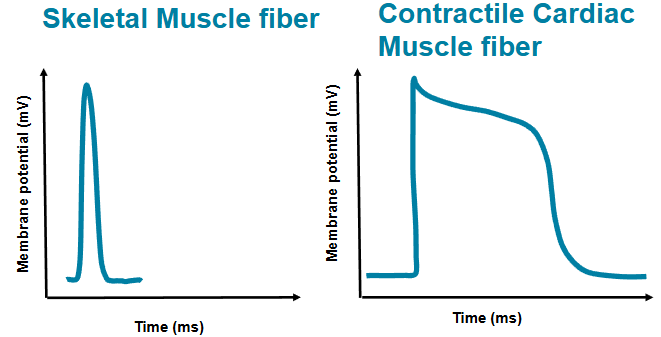
name one important consequence of the long plateau phase observed in contractile cell
cardiac muscle stays contracted longer due to Na+ channels staying in a longer inactive state
allows for efficient ejection of blood
prevents tetanic contractions
slow calcium channels also plays a role (Ca2+ flows in)
can the basic rhythm of the heart be modified
yes - changes in lifestyle (ex: exercise), medications, pacemakers, AED, caffeine, alcohol, body temperature
autonomic nervous system - cardiac centers in medulla oblongata
cardioacceleratory center - sympathetic trunk to increase heart rate and force (innervates SA and AV nodes, heart muscles and coronary arteries
cardioinhibitory center - parasympathetic signals via vagus nerve to decrease rate (innervate mostly the SA and AV nodes)
which parts of the conduction system are innervated by the autonomic nervous system
cardioacceleratory center
medulla oblongata → thoracic spinal cord → sympathetic trunk → SA and AV nodes, heart muscles and coronary arteries
cardioinhibitory center
cardioinhibitory center
medulla oblongata (dorsal motor nucleus of vagus) → SA and AV nodes
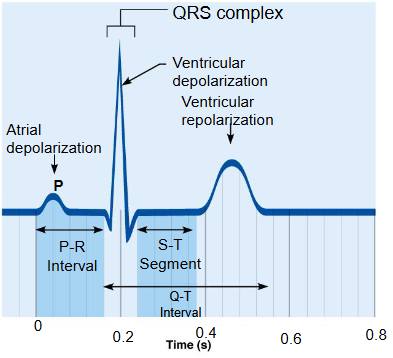
what is an electrocardiogram
draw a diagram of a normal electrocardiogram tracing
name the individual waves and intervals, and indicate what each represents
a graphic recording of electrical heart activity
P wave: depolarization of SA node and atria
QRS complex: ventricular depolarization and atrial repolarization
T wave: ventricular repolarization
P-R interval: beginning of atrial excitation to beginning of ventricular excitation
S-T segment: entire ventricular myocardium depolarized
Q-T interval: beginning of ventricular depolarization through ventricular repolarization
heart abnormalities can be detected on an ECG tracing, how would enlarged ventricles, a heart attack and an nonfunctional SA node show in an ECG tracing
enlarged ventricles - enlarges R waves
heart attack- electrical activity is disorganized
nonfunctional SA node - P waves are absent, AV node paces heart (slower bpm - 40 to 60 bpm)
true or false - the cardiac cycle includes all events associated with the blood flow through the heart during one complete heartbeat - atrial systole and diastole followed by ventricular systole and diastole
true
name the phases of the cardiac cycle and describe the events that take place during every phase
first half of first step
ventricle filling (passive)
the heart in the aorta is 120-80 mmHg
pressure in the heart is low
as the atrium and ventricle fill with blood (AV valves are open) the pressure in both chambers increases
80% of ventricular filling occurs
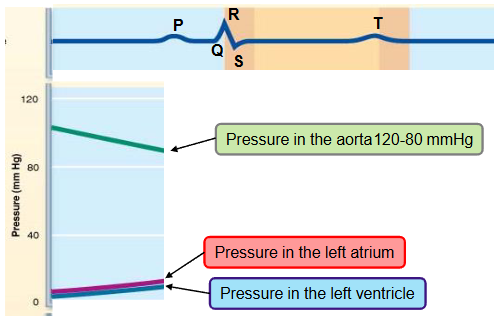
name the phases of the cardiac cycle and describe the events that take place during every phase
second half of first step
ventricular filling (atrial systole)
the P wave occurs - atrial systole
the atria depolarize and contract
the atria pump some extra blood into the ventricles and the pressure in both chambers slightly increases
remaining 20% of ventricular blood is pumped here
last part of ventricular diastole (end diastolic volume)
atria relax for the remainder of cardiac cycle
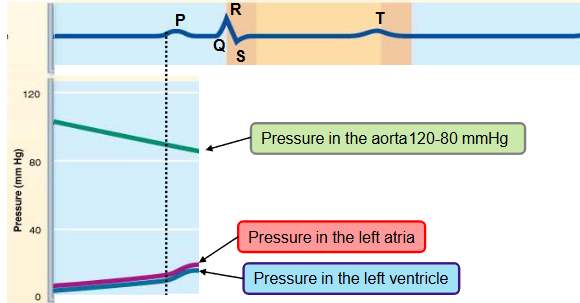
name the phases of the cardiac cycle and describe the events that take place during every phase
second step
ventricular isovolumetric contraction
the QRS complex occurs
the ventricle starts contracting → the pressure in the ventricle progressively increases
a small volume of blood is pushed into the atrium, closing the AV valve temporarily increasing the pressure in the atrium
split second phase - ventricles are completely closed, and volume in unchanged
the pressure in the aorta is higher than the pressure in the ventricle, the blood is still not ejected into the aorta (pressure goes from high to low)
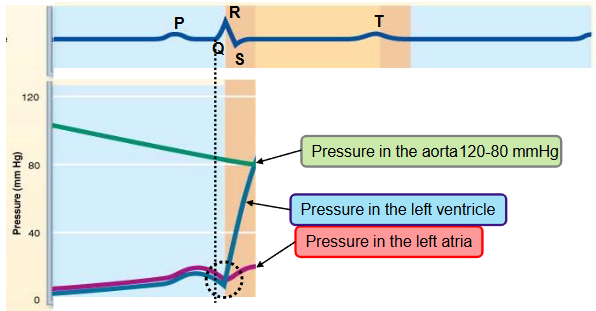
name the phases of the cardiac cycle and describe the events that take place during every phase
first half of third step
ventricular ejection
the ventricle pressure exceeds the aortic pressure (diastolic pressure ~ 80mmHg)
the semilunar valve opens
blood in the ventricle is ejected into the aorta
pressure in ventricle and aorta keeps increasing
as the pressure increases within aorta, the aorta distends
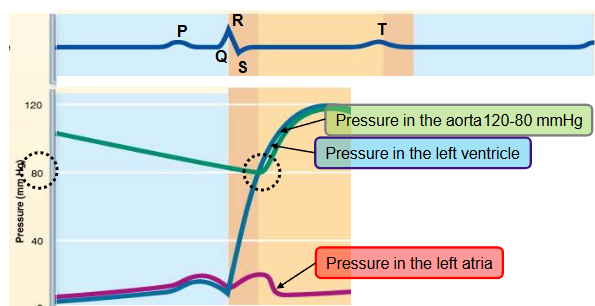
name the phases of the cardiac cycle and describe the events that take place during every phase
second half of third step
ventricular ejection
pressure in aorta reaches maximum (systolic pressure ~ 120mmHg)
T wave occurs, the ventricles begins to repolarize
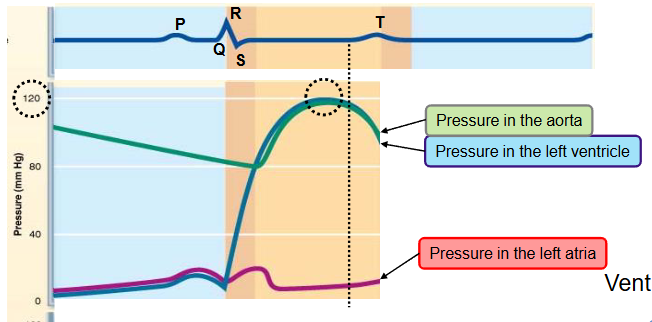
name the phases of the cardiac cycle and describe the events that take place during every phase
fourth step
ventricular isovolumetric relaxation
ventricles relax - early diastole
blood remaining in the ventricles after contraction - end systolic volume (ESV)
ventricular pressure falls below aortic pressure → semilunar valves close
closure of aortic valve raises aortic pressure as backflow rebounds off close valve cusps (dicrotic notch)
causes back flow of blood that fills the coronary arteries
the pressure in the filling atrium keeps increasing
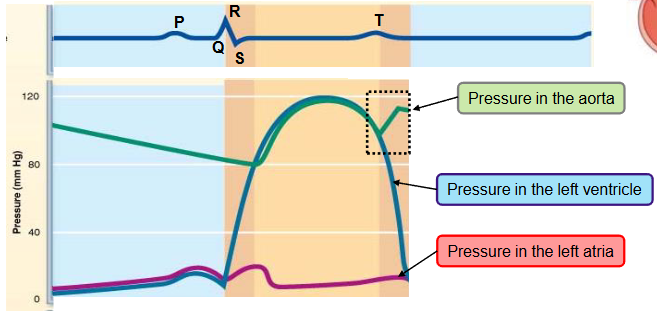
name the phases of the cardiac cycle and describe the events that take place during every phase
‘last’ step going back to first step
ventricular filling (passive)
the pressure in the relaxing ventricle falls below the pressure in the atrium
AV valve opens
blood flows from the atrium to the ventricle
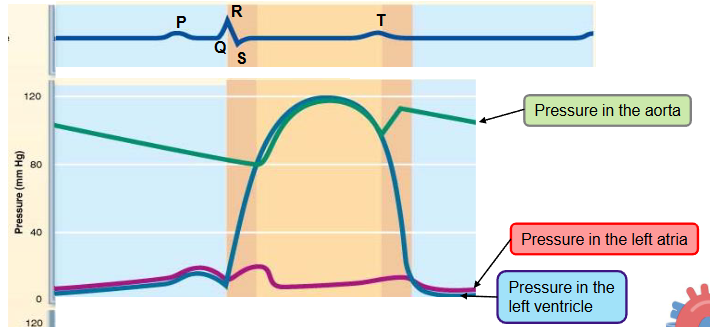
which phases of the cardiac cycle overlap with ventricular contraction and which with ventricular relaxation
isovolumetric contraction phase - AV valves close and SL valves open
systole, first heartbeat is heard
isovolumetric relaxation phase - SL valves open and AV valves close
diastole, second heartbeat is heard
define end diastolic volume (EDV) and end systolic volume (ESV)
EDV: volume of blood in each ventricle at end of ventricular diastole
ESV: volume of blood remaining in each ventricle after systole
when do the valves open/close during the cardiac cycle? When does the dicrotic notch occur
in order of cardiac cycle:
AV valves close when the ventricular pressure exceeds the atrial pressure
SL valves open when the ventricular pressure exceeds the aortic pressure
SL valves close when the ventricular pressure drops below aortic pressure
slight raise in aortic pressure due to backflow rebounding off of closed valve cusps (dicrotic notch)
AV valves open when the ventricular pressure drops below the atrial pressure
during which phase of the cardiac cycle do the heart sounds occur
first heart beat:
isovolumetric contraction phase (systole)
as the AV valves close
second heart beat:
isovolumetric relaxation phase (diastole)
as the SL valves close
define cardiac output (CO) and stroke volume (SV)
CO: amount of blood pumped out by each ventricle in one minute
equals heart rate (HR) times stroke volume (SV)
SV: volume of blood pumped out by one ventricle with each beat
correlates with force of contraction
name 3 factors that influence stroke volume, explain how
preload (intrinsic influence)
degree of stretch of heart muscle
preload: degree to which cardiac muscle cells are stretched just before they contract
high preload = higher SV
relationship between preload and SV is called Frank-Starling law of the heart
stretching leads to dramatic increase in contractile force
venous return - amount of blood returning to heart
slow heartbeat and exercise increase venous return
increased venous return distends (stretches) ventricles and increases contraction force
increase in venous return → increase in EDV → increase in SV → increase in CO
increase in EDV → increase in SV = Frank-Starling law of the heart
name 3 factors that influence stroke volume, explain how
contractibility (extrinsic influence)
contractile strength at given muscle length
independent of muscle stretch and EDV
increased contractility lowers ESV caused by:
sympathetic epinephrine release stimulants increased Ca2+ influx, leading to more cross bridge formations
sympathetic stimulation (NE/E) → more Ca2+ in the cardiac myocytes → increased force of contraction (contractility) → increased SV
name 3 factors that influence stroke volume, explain how
afterload
afterload: pressure that ventricles must overcome to eject blood
back pressure from atrial blood pushing on SL valves
aortic pressure is around 80mmHg
healthy individuals: afterload is not a major determinant of SV since remains constantly
hypertension increases afterload, reducing the ability of ventricles to eject blood
what is venous return and how does it influence the stroke volume
venous return: amount of blood returning to heart
increased VR distends (stretches) ventricles and increases contraction force
increase in venous return → increase in EDV → increase in SV → increase in CO
increase in EDV → increase in SV = Frank-Starling law of the heart
which mechanism results in an increased stroke volume during exercise? (hint: increased venous return
contraction of skeletal muscles ‘milks’ blood back towards heart (muscular pump), increasing venous return, increasing preload, increasing SV
how is the contractility of the myocardium regulated (hint: sympathetic nervous system)
compare and contrast preload and contractility
sympathetic epinephrine release stimulants increased Ca2+ influx, leading to more cross bridge formations
sympathetic stimulation (NE/E) → more Ca2+ in the cardiac myocytes → increased force of contraction (contractility) → increased SV
preload: degree to which cardiac muscle cells are stretched just before the contract
contractility: the intrinsic strength and ability of the myocardium to contract, independent of the initial fiber length
how does high blood pressure affect the stroke volume and why
hypertension increases afterload, reducing the ability of ventricles to eject blood
heart has to work harder to pump blood against the elevated resistance in the arteries
how is the heart rate regulated by the sympathetic and parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system
sympathetic
stress → sympathetic stimulation → release of NE → faster depolarization of the pacemaker cells (SA and AV nodes) and increased Ca2+ influx in cardiac myocytes (contractile cells) → increased HR (positive chronotropism) and increased contraction force (positive inotropism)
how is the heart rate regulated by the sympathetic and parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system
parasympathetic
after the stress has passed → parasympathetic stimulation → release of ACh → pacemaker cells (SA and AV nodes) hyperpolarize (binding of ACh to its receptor initiates signaling cascade that opens K+ channels in node cells) → decreased HR (negative chronotropism)
explain the role of the autonomic nervous system in regulating cardiac output
controlling heart rate and contractility through two branches: sympathetic and parasympathetic systems
cardioinhibitory and cardioacceleratory Center
what is coronary atherosclerosis
clogged arteries caused by fat buildup; impairs oxygen delivery to cardiac cells
t or f: a succession of heart attacks might decrease the pumping efficiency of the heart because dead heart cells are replaced by non-contractile scar tissue.
true
compare and contrast pulmonary and systemic congestion
systemic (peripheral) congestion
right side fails
right side of the heart is unable to pump blood efficiently, causing it to back up into the body
blood stagnates in body organs
fluid leaks into tissue spaces
pulmonary congestion
left side fails
LV cannot effectively pump blood into the body, causing blood and fluid back into the lungs
pressure in blood vessels of lung increases
fluid leaks from vessels into lung tissue
pulmonary edema leads to suffocation (lungs fill w/fluid and not O2)
describe the three layers that typically form the wall of a blood vessel and state the function of each
tunica intima
endothelium - simple squamous epithelium that lines lumen of all vessels
subendothelial layer
internal elastic membrane
allows a slick surface that reduces friction
continuous with the endocardial lining of the heart chambers
tunica media
smooth muscle and elastic fibers
plays a role in vasoconstriction and vasodilation
bulkiest layer - responsible for maintaining blood flow and blood pressure in arteries
tunica externa
loose collagen fibers - protect and reinforce wall and anchor it to surrounding structures
contains nerve fibers, lymphatic vessels and vasa vasorum
define vasoconstriction and vasodilation
vasoconstriction: decreased lumen diameter
reduced heat loss through skin, makes blood vessels smaller → away from skin surface
increased BP
vasodilation: increased lumen diameter
release heat through the skin → BV are closer to the surface of skin
decreases BP
compare and contrast the structure and function of the three types of arteries
elastic arteries (conducting arteries)
thick-walled, largest in diameter, most elastic
near the heart (aorta and major branches)
largest in diameter: 2.5mm to 1cm
elastin found in all three tunics, mostly tunica media
contain substantial smooth muscle, but inactive in vasoconstriction
function: acts as pressure reservoirs that expand and recoil as blood ejected from heart
allows for continuous blood flow downstream even between heartbeats
compare and contrast the structure and function of the three types of arteries
muscular arteries
distribute blood to major organs
aka distributing arteries
account for most of named arteries
diameter range: pinky finger to a pencil lead
has the thickest tunica media, with more smooth muscle and less elastic fibers than elastic arteries
less capable of stretching
function: active in vasoconstriction, deliver blood to body organs
compare and contrast the structure and function of the three types of arteries
arterioles
smallest of all arteries
aka resistance vessels - since changing diameters changes resistance to blood flow
diameter range: 0.33mm to 10uM
larger arterioles contain all three tunics
smaller arterioles are mostly single layer of smooth muscle surround endothelial cells with very little elastic fibers
function: control flow into capillary beds via vasodilation and vasoconstriction of smooth muscle
leads to capillary beds
describe the structure and function of a capillary bed
interwoven network of capillaries between arterioles and venules
terminal arteriole: branches into 10 to 20 capillaries (exchange vessels) that form capillary beds and drain to postcapillary venules
microscopic vessels; diameter is so small only one RBC can pass through at a time
1mm in length and 8-10uM in diameter
pericytes: contractile stem cells, lie along the outer surface for generation of new vessels, stability and permeability control
function: exchange of gases, nutrients, wastes, and hormones
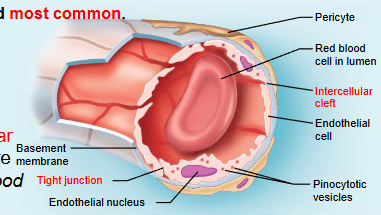
name the 3 types of capillaries
continuous capillary, fenestrated capillary, and sinusoid capillary
least permeable:
continuous capillary
largest fenestrations and intercellular clefts:
largest fenestrations - fenestrated capillary
large intercellular clefts - sinusoid capillary
present in the CNS, kidneys, intestine, and bone marrow:
CNS - continuous capillary
kidneys, intestine - fenestrated
bone marrow - sinusoid
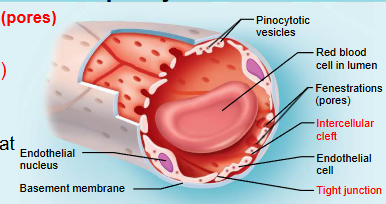
continuous capillary
least permeable and most common
abundant in skin, muscles, lungs and CNS
often have associated pericytes
pinocytotic vesicles ferry fluid across the endothelial cell
brain capillary endothelial cells lack intercellular clefts and have tight junctions around their entire perimeter (blood brain barrier)
fenestrated capillar
large fenestrations (pores) that increase permeability
occurs in areas of active filtration (kidneys) or absorption (small intestine) and areas of endocrine hormone secretion
fenestrations - holes that tunnel through endothelial cells
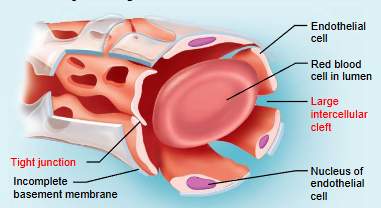
sinusoid capillary
most permeable and occur in limited locations
occur in liver, bone marrow, spleen, and adrenal medulla
have large intercellular clefts as well as fenestrations
few tight junctions
have incomplete basement membranes
allow for large molecules and even cells to pass across their walls
is blood always flowing freely through the capillaries
what happens with the capillary beds in muscles and intestine:
when you exercise
after you eat
blood does not always flow freely though the capillaries
vascular shunts for bypass
directly connect the terminal of arteriole to the postcapillary venules
precapillary sphincters
acts as a valve to regulate blood flow into the capillary bed
muscles:
when you exercise: capillary beds open → more blood flow for oxygen and nutrients
after you eat: capillary beds less active (blood is directed to the gut instead)
intestine:
when you exercise: capillary beds constrict (blood diverted to muscles)
after you eat: capillary beds open → more blood flow for digestion and absorption
describe the structure and function of veins and explain how veins differ from arteries
venules
diameter range from 8-100uM
extremely porous, like capillaries, to allow fluid and WBC to move easily into tissues
most have only tunica intima, with larger venules gaining a think tunica media and externa
describe the structure and function of veins and explain how veins differ from arteries
veins
have all tunics, but thinner walls with larger lumens
tunica media is thin, but tunica externa is thick
tunica externa contains collagen fibers and elastic networks
large lumen and thin walls make veins good storage vessels
called capacitance vessels (blood reservoirs) because they contain up to 65% of blood supply
explain how veins differ from arteries
arteries
carry oxygenated blood away from heart
thicker, more tunica media (smooth muscle) due to high pressure of blood flow
ratio of smooth muscle to collagenous tissue will always be greater
does not contain valves (other than pulmonary artery)
closer to major organs
veins
carry deoxygenated blood towards heart
thinner, less muscular wall, lower BP
contains venous valves
prevent backflow of blood
formed from folds of tunica intima
resemble SL valves
most abundant in veins of limbs
define blood flow, blood pressure, and resistance
blood flow: volume of blood flowing through vessel, organ, or entire circulation in given period
ml/min
equivalent to cardiac output for entire vascular system
flow through individual organs may vary
blood pressure: force per unit area exerted on wall of blood vessel by blood
mmHg
measured as systemic arterial BP in large arteries of heart
pressure gradient provides driving force that keeps blood moving from higher to lower pressure areas
resistance (total peripheral resistance/TPR): opposition to flow (most friction occurs in periphery)
measurement of amount of friction blood encounters with vessel walls
three important sources of resistance
blood viscosity
total blood vessel length
blood vessel diameter
explain the relationships between blood flow, blood pressure, and resistance
blood flow is directionally proportional to the difference in pressure between two points (pressure gradient)
as difference in pressure changes, BF follows the same direction
more blood pumping = more blood pushing against vessels
blood flow is inversely proportional to total peripheral resistance (TPR)
as TPR increases, blood flow decreases
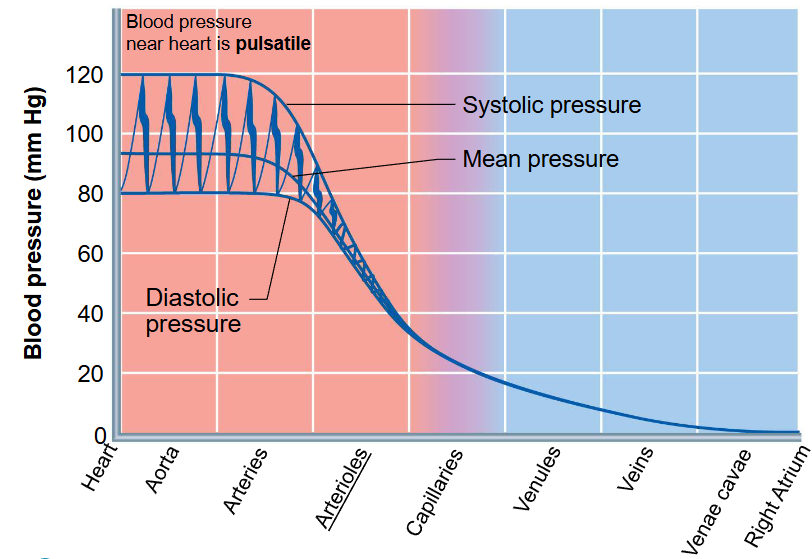
describe how blood pressure differs in the arteries, capillaries, and veins
blood is driven through the body by a pump through a closed circuit under pressure
nearer the pump, the greater the pressure
pumping action of the heart generates blood flow, while pressure is established from resistances
greatest pressure to least pressure:
heart → aorta → arteries → arterioles → capillaries → venules → veins → venae cavae → right atrium
name three structural adaptations that are important for maintaining venous return
muscular pump: contraction of skeletal muscles ‘milks’ blood back towards heart
respiratory pump: pressure changes during breathing, moves blood towards heart by squeezing abdominal veins (diaphragm contracts and the thoracic cavity expands - lowering pressure in chest cavity, lower pressure in chest = pushes blood from abdomen into thorax and towards heart)
sympathetic venoconstriction: under sympathetic control, smooth muscle constrict, pushing blood back towards heart
all methods increase venous return → increasing stroke volume and cardiac output
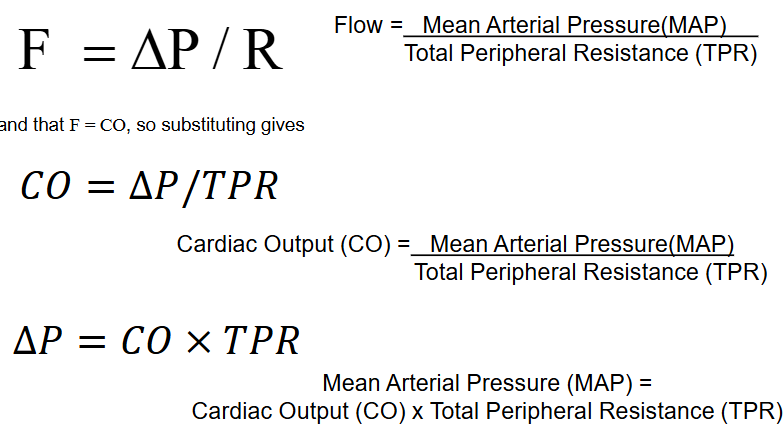
list and explain the factors that influence blood pressure
cardiac output
peripheral resistance (PR)
blood volume
MAP = stroke volume x heart rate x TPR
anything that increases SV (venous return), HR (medullary centers), or R (mostly vessel diameters) also increases pressure
Short-term regulation of blood pressure is mediated by _________ and _________.
Short-term regulation alters blood pressure by changing ____/______.
Long-term regulation is mediated by______/_ ____.
Long-term regulation alters blood pressure by changing ________
neural; hormonal controls
TPR; CO
renal; hormonal controls
blood volume
where is the location and what is the function of the vasomotor center
what is the vasomotor tone
vasomotor center: controls diameter of blood vessels
found in the medulla oblongata
sends steady impulses via sympathetic efferent to blood vessels
vasomotor tone: continuous moderate constriction of arterioles
helps regulate BP and BF
list the events which help to maintain the blood pressure by the baroreceptor reflex (short-term blood pressure regulation)
stimulus: BP rises above normal
baroreceptors in carotid sinuses and aortic arch are stimulated
increased impulses from baroreceptors
stimulate cardioinhibitory center
inhibit cardioacceletory center
inhibit vasomotor center
decreased vasomotor impulses - causing vasodilation (causing reduced TPR) and decreased sympathetic impulses to heart cause decreased HR, contractility, and CO
reduced CO and TPR return blood pressure to homeostatic range
Describe the effects (stimulatory/inhibitory) of activated baroreceptors on
cardiovascular centers (cardioacceleratory, cardioinhibitory and vasomotor centers) in the
medulla oblongata
stroke volume, heart rate, total peripheral resistance, and blood pressure
cardioacceletory: inhibited → causes the heart to pump less, decreasing BP (reduces the force and volume of blood circulating in the arteries)
cardioinhibitory: stimulated → slows heart rate
vasomotor center: inhibited → uses sympathetic efferent (cardioacceleratory), vasodilation of arterioles and veins
SV: decreases (less sympathetic simulation → less contractility → smaller SV)
HR: decreases
TPR: decreases (vasodilation from reduced vasomotor tone
BP: decreases to normal range
describe the direct and indirect renal/hormonal mechanisms of blood pressure regulation. Name the 4 mechanisms activated by angiotensin II in the indirect renal blood pressure regulation (long-term blood regulation)
direct: decreased arterial pressure → decreased filtration by kidneys → decreased urine formation (keeping fluid in) → increasing blood volume → increase in MAP
natural function the kidney does - does not require a signal
indirect: decreased arterial pressure → inhibits baroreceptors → increased sympathetic nervous system activity → increased renin release from kidneys
renin turns angiotensinogen to angiotensin I, angiotensin converting enzyme turns I into II
II signals adrenal cortex → release aldosterone → increase sodium reabsorption by kidneys → H2O reabsorption by kidneys → increase blood volume → increased MAP
II signals to increase ADH release by posterior pituitary gland → H2O reabsorption by kidneys → increase blood volume → increased MAP
II increases thirst via hypothalamus → increase in water intake → increase blood volume → increased MAP
II increases vasoconstriction = increase in TPR → increase MAP
define hypertension and describe the effects of prolonged hypertension on the heart
hypertension: high blood pressure
damages the heart by causing the left ventricle to thicken and enlarge = strains the heart and makes it less effective at pumping blood
can lead to reduced blood supply to heart muscle, which can cause heart failure
name the 2 types of intrinsic controls of blood flow
intrinsic controls (autoregulation) - within tissue or organ; uses paracrines or muscle tissue properties
metabolic or myogenic controls
distribute blood flow to individual organs and tissues as needed
vasodilators: low O2, high CO2, high H+, high K+, prostaglandins, adenosine, nitric oxide
vasoconstrictors: myogenic (stretch); metabolic (endothelin)
name the 2 types of extrinsic controls of blood flow that cause vasoconstriction
extrinsic controls - outside tissue or organ
neural or hormonal controls
maintain MAP
redistribute blood during exercise and thermoregulation
vasodilation: neural → decreases sympathetic tone; hormonal → atrial natriuretic peptide
vasoconstriction: neural → increase sympathetic tone; hormonal → angiotensin !!, antidiuretic hormone, epinephrine, and norepinephrine
how would O2, CO2 and sympathetic stimulation influence blood flow
O2 vasodilates at high levels but can cause systemic vasoconstriction under severe systemic hypoxia
CO2 vasodilates in most tissues and sympathetic stimulation generally causes vasoconstriction, except the brain
explain how blood flow through muscles and intestine is regulated during exercise.
active or exercise hyperemia: during muscle activity, blood flow increases in direct proportion to metabolic activity
blood flow in muscles: metabolic factors induce vasodilation
blood flow in kidneys, intestine: inhibited by sympathetic vasoconstriction
what is the relationship between cross-sectional area of vessels and blood flow velocity
velocity of flow changes as blood travels through systemic circulation
velocity = flow rate/total cross-sectional area
speed is inversely related to total cross-sectional area
capillaries have largest area so slowest flow
ex: highway system
fewer lanes = cars move faster
big freeway (aorta): one or two wide lanes → all the cars (blood) funnel through a small cross-sectional area → cars move fast
more lanes = cars slow down
exiting roads (venules/veins): the little roads merge back into bigger streets → fewer total lanes → cars pick up speed again, but not quite as fast as on the freeway.
why is the blood flow in the capillaries slow compared to the blood flow in the aorta?
capillaries have massive area - millions of tiny capillaries, total area of the vascular bed is much larger than the aorta, causing the blood to move slower
why is a slow blood flow in the capillaries beneficial
allows adequate time for exchange between blood and tissues
describe the four routes of transport across the endothelial cell wall of capillaries
diffusion through plasma membrane (lipid-soluble substances)
movement through intercellular clefts (water-soluble substances)
movement through fenestrations (pores - water-soluble substances)
transport via vesicles (large substances; endocytosis or exocytosis)
define bulk flow
why is it important
fluid is forced out of clefts of capillaries at arterial end, and returns to blood at venous end
important in determining relative fluid volumes in blood and interstitial space
refreshes/maintains interstitial environment
define hydrostatic pressure and osmotic pressure
hydrostatic pressure: force exerted by fluid pressing against wall
in capillary: pushes fluid out of capillary
in interstitial fluid: pushes fluid into capillary
osmotic pressure: sucking pressure created by nondiffusible plasma proteins (albumin) pulling water back into capillary (encouraging osmosis
in capillary: pulls fluid into capillary
in interstitial fluid: pulls fluid out of capillary
describe the different types of pressures that are implicated in bulk flow
explain how these pressures determine the exchange of fluid between blood and the interstitial space along the capillaries
arteriolar end of capillary:
NFP = 10mmHg out of capillary (fluid moves from capillary into the interstitial space)
hydrostatic pressure in capillary: 35mmHg out of capillary
osmotic pressure in capillary: 26mmHg into capillary
hydrostatic pressure in IF: 0mmHg into capillary
osmotic pressure in IF: 1mmHg out of capillary
venous end of capillary:
NFP = -8mmHg (fluid moves from the interstitial space into capillary)
hydrostatic pressure in capillary: 17mmHg out of capillary
osmotic pressure in capillary: 26mmHg into capillary
hydrostatic pressure in IF: 0mmHg into capillary
osmotic pressure in IF: 1mmHg out of capillary
net filtration is occurring at the arteriolar end of the capillary, while reabsorption is taking
place at the venous end of the capillary
describe what “filtration” and” reabsorption” is
filtration: fluids are forced through capillary walls, leaving proteins and cells behind
WBC leaves from venules, does not leave from capillaries
reabsorption: fluids move back into capillary
what happens with fluid that is lost from the capillaries
not all fluid filtered out of the capillaries gets reabsorbed at the venous end (20L of fluid from capillaries at their arteriolar end and flows through interstitial space; 17L is reabsorbed back to venous end)
lymphatic system picks up extra fluid
define edema
describe potential causes of an edema
edema: abnormal increase in amount of interstitial fluid
an increase in outward pressure (driving fluid out of the capillaries)
a decrease in inward pressure
a decrease in drainage of interstitial fluid through lymphatic vessels
describe the general functions of the pulmonary and systemic circuit
pulmonary circuit: moves blood between heart and lungs
turn deoxygenated blood into oxygenated blood
systemic circuit: move blood between heart and body
deliver oxygen and nutrients into body