BioChem: Transcription & Regulation
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What occurs in initiation?
Promoter recognition: transcription regulation is offered (rate-limiting step, sequence dependent)
Formation of closed-promoter complex: Promotor is bound, but energy for DNA separation hasn’t been used yet
Formation of open-promotor complex: DNA unwinds
What occurs during elongation?
Initiation site binds ATP and GTP, elongation site binds all four nucleotides; when both sites are bound, the enzyme catalyzes nucleophilic attack by the 3’ OH on the first NTP to alpha P on the second NTP
What are characteristics of the DNA complex during elongation?
the complex is not stable until ~9 nucleotides long, alpha subunit will be released and the elongation complex will become more stable, backtracking occurs after DNA is rewound
What occurs during backtracking?
RNA polymerase moves in reverse to correct errors
What occurs during termination?
factor independent: signaled by GC rich regions, RNA hairpins act as physical blocks
factor dependent: involves a ρ (rho) protein which is usually a hexamer and acs as a helicase, occurs less often
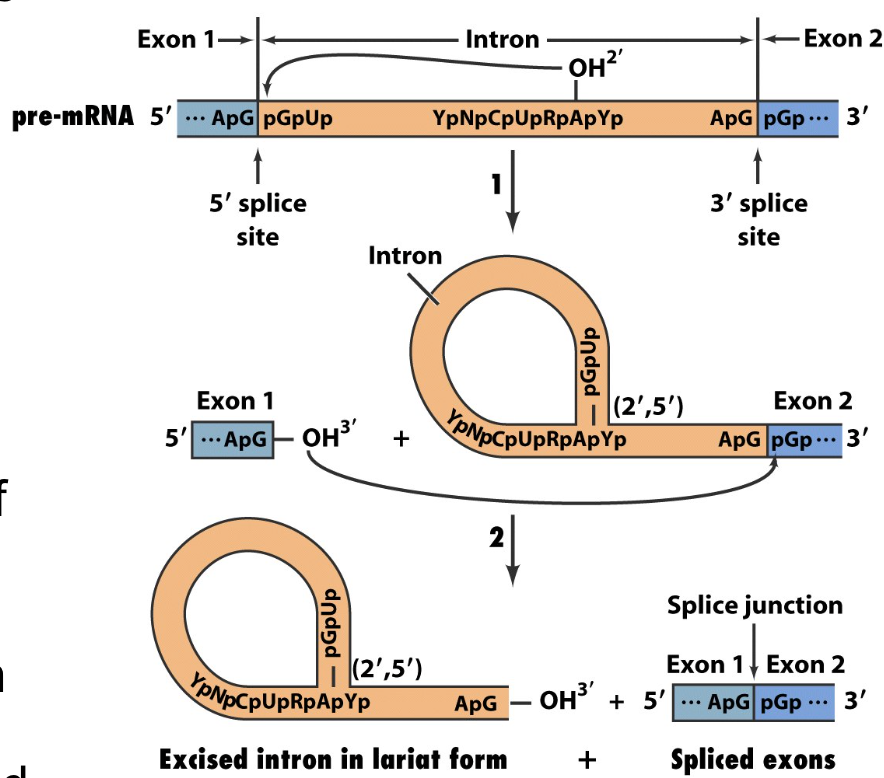
What nucleophilic reactions are involved in splicing?
OH2- attack on the 5’ splice site
3’ OH attack from the end of exon 1 on the 5’ edge of exon 2
What is an operon?
a set of contiguous prokaryotic structural genes that are transcribed as a unit as well as the adjacent regulatory elements that control their expression
What are products of the operon?
repressor specific for an inducer, mRNA through transcription, proteins through translation
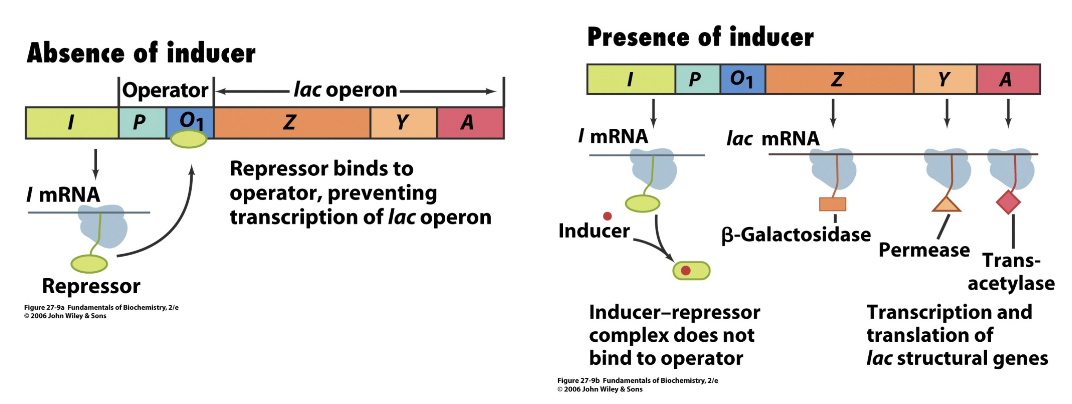
what is the function of the lac operon?
offers control over expression of beta-galactosidase (enzyme which hydrolyzes lactose, found in E. coli)
What occurs during induction?
an inducer inactivates the repressor, which leads to enzyme expression
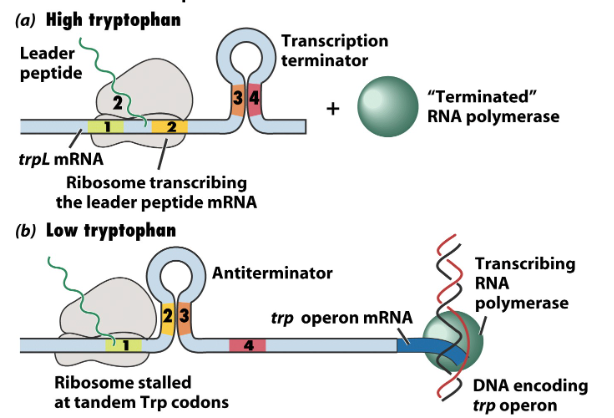
what is the function of the tryptophan operon?
controls gene expression of proteins that synthesize tryptophan
what are the two ways to control gene expression?
repressor system: trp repressor is activated by binding
attenuation system: leads to transcription termination
What is the difference between terminator and anti-terminator?
terminator: 3-4 “hair pin” forms, factor independent termination, high tryptophan, RNA polymerase comes off
anti-terminator: 2-3 “hair pin” forms, low tryptophan, RNA polymerase is transcribed
What occurs in transcription beyond the basal level?
a mechanism is created that is capable of transcribing at higher expression levels
What is translation?
Reading the mRNA made during transcription and assembling amino acids in the sequence indicated
What is required for translation to occur?
amino acids, tRNAs, ribosomes, mRNA
What is a codon?
a triple base sequence corresponding to a particular amino acid or stop
What is an anticodon?
the complement of the codon; a region on the tRNA which recognizes the codon
How do you read mRNA?
start codon is always AUG, which corresponds to Met (ignore the amino acids before AUG)
What is the acceptor stem of a tRNA structure?
segment at the top of the cloverleaf tRNA which attaches to the amino acid during “charging”, conserved CCA sequence
What is the Shine-Dalgarno sequence?
attachment sequence in the mRNA which aligns the ribosome for efficient and accurate attachment
What are ribosomes?
enzymes which catalyze protein synthesis by properly aligning the mRNA and respective tRNAs
What is the P site?
the site in which the extended peptide will “end up”
What is the A site?
the binding site for the incoming amino acid
What is the E site?
site where the “empty” tRNA molecule will exit