Psychology AOS Research Methods
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Things that influence the dependant variable
Independant, confounding, and extraneous variables.
Respect
Correlation
Does bot imply causation
Informed consent
Withdrawal rights
Confidentiality
Reliability
refers t9 the extent to which a measure produces results that are consistent, dependable, and stable.
Validity
refers to the extent to which a measure accurately measures what it is supposed to be measuring. Validity means that the results represent true findings among similar individuals in the population from which the sample was drawn.
Internal validity
refers to the extent to which an investigation actually investigates what is set out to investigate and/or claims to have investigated.
External validity
refers to the extent to which the results obtained for a study can be applied beyond the sample that generated them, specifically to individuals in a different setting and over time.
Generalisation
a decision about how widely the results of an investigation can be applied, particularly to other members of the population from which the sample was drawn.
Extraneous variable
A factor that could influence the dependant variable that is not the independent variable.
Confounding variable
A confounding variable may distort or mask the effects of another variable on the disease in question. For example, a hypothesis that coffee drinkers have more heart disease than non-coffee drinkers may be influenced by another factor.
•The aim
is a statement outlining the purpose of the investigation.
is a statement outlining the purpose of the investigation
What the aim needs to include/ doesn’t need to include.
The aim should clearly describe the investigation's purpose in a single, uncomplicated sentence, possibly expressed as a research question. Ensure it focuses on what the investigation seeks to find out and is related to any existing research questions.
•A research hypothesis
is a testable prediction of the relationship between two or more variables
A controlled experiment
is an experimental investigation to test the relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable, whilst controlling all other variables.
•A variable is
something that can change (‘vary’) in amount or type and is measurable.
A controlled variable
is one that is considered to have an effect on the dependent variable
independent variable (IV)
is the variable for which quantities are manipulated
dependent variable (DV)
is the variable the researcher measures
•Operationalising variables
refers to specifying exactly how the variables will be manipulated or measured in a particular controlled experiment.
A correlational study
is used to investigate the relationship that exists between variables without any control over the setting in which the relationship occurs or any manipulation by the researcher.
•A self-report
is a participant’s answers to questions presented by the researcher
An observational study
involves collection of data by carefully watching and recording behaviour as it occurs without any intervention or manipulation of the behaviour being observed.
A case study
is an intensive, in-depth investigation of some behaviour, activity, event or problem of interest in a single individual, group, organisation or situation. In psychology, the ‘case’ that is the subject of ‘study’ is usually a person.
Cross-sectional Method
•IA type of observational research method used to analyse data from a population at a specific point in time.
•t looks at the relationship between variables without manipulating the study environment
•It looks at the relationship between variables without manipulating the study environment
A Psychologist collects data from college students across different majors at the same time to study the relationship
Between academic stress levels and coping strategies.
A research method
that involves repeated observations of the same individuals over a long period of time
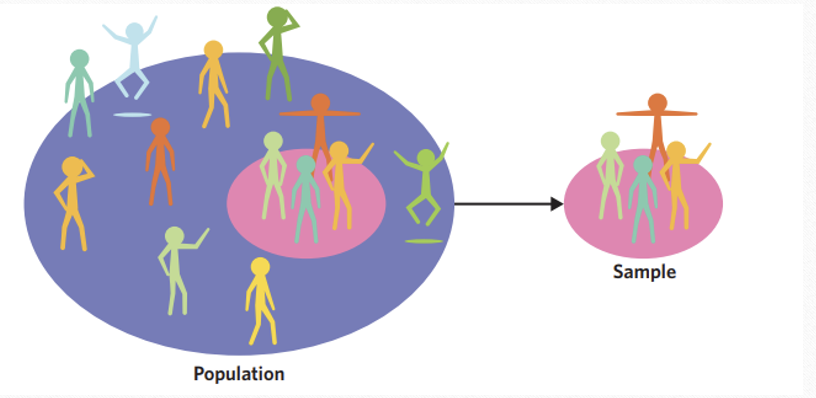
Population

refers to the entire group of research interest from which a sample is drawn and to which the researcher will seek to generalise (apply) the results of their investigation.
A sample
is a subset or part of the population that is selected for research purposes.
Sampling

is the process by which a subset or part of the population is selected for an investigation. The population of research interest is often referred to as the target population.
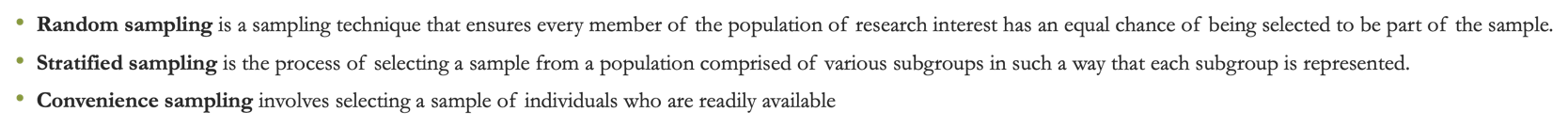
Sampling Techniques
•Random sampling is a sampling technique that ensures every member of the population of research interest has an equal chance of being selected to be part of the sample.
•Stratified sampling is the process of selecting a sample from a population comprised of various subgroups in such a way that each subgroup is represented.
•Convenience sampling involves selecting a sample of individuals who are readily available
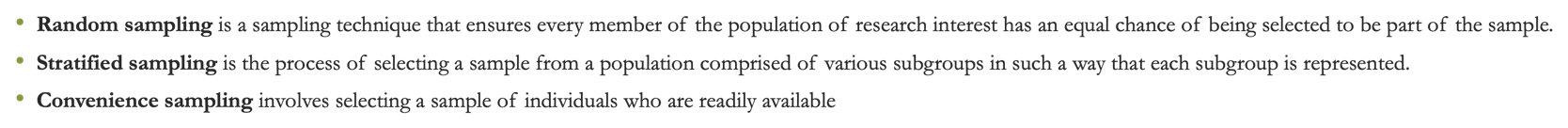
Random sampling

is a sampling technique that ensures every member of the population of research interest has an equal chance of being selected to be part of the sample.
•Stratified sampling
is the process of selecting a sample from a population comprised of various subgroups in such a way that each subgroup is represented.

Convenience sampling
involves selecting a sample of individuals who are readily available
•An extraneous variable

is a variable other than the IV that may cause a change in the DV and therefore may affect the results.
A confounding variable
is a variable other than the IV that has had an effect on the DV which cannot be separated from that of the IV.
Ethical Concepts

1.Beneficence:
2.Integrity
3.Justice
4.Non-maleficence:
5.Respect:
Beneficence:
The commitment to maximising benefits and minimising the risks and harms involved in taking a particular position or course of action.
1.Integrity
The commitment to searching for knowledge and understanding, the honest reporting of all sources of information and results, whether favourable or unfavourable, in ways that permit scrutiny and contribute to public knowledge and understanding.
Justice:
The moral obligation to ensure that there is fair consideration of competing claims; that there is no unfair burden on a particular group from an action; and that there is fair distribution and access to the benefits of an action.
Qualitative Research:
Focus: In-depth understandings of social phenomena, experiences, and meanings.
Data: Non-numerical, + interviews, observations, or focus groups.
Purpose: Understanding perspectives, behaviours, and the "why" behind actions.
Quantitative Research:
Focus: Measuring and analyzing numerical data to identify patterns and relationships.
Data: Numerical data, like survey responses or experimental results.
Purpose: Testing hypotheses, generalizing findings, and determining the "how much" or "how often".
3. Mixed Methods Research:
Focus: both qualitative and quantitative approaches for a more comprehensive understanding.
Data: both numerical and non-numerical data.
Purpose: Utilising the strengths of both methods to provide a richer and more nuance interpretation of research questions.
d
Cross-sectional method
Helps understand a current situation or phenomenon
without the need for long-term
longitudinal study
observing the same individuals or groups over an extended period of time- changes, patterns, and long term effects.
Descriptive methods
Data collection by observing and recording behavior without manipulation of variables. surveys, observations, and case studies
Correlation studies
Correlation studies examine the relationship between two or more variables to see if they change together and in what way.
DV
being measured
IV
being changed
explain how fMRI is used to examine brain structure in developmental and psychological research.
measures brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow, which reflects neuronal activity.