Biodiversity chapter 17
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
What are the mechanisms of evolution
natural selection
mutation
migration
drift
is non random mating a mechanism of evolution
no it is not
What is a population?
a group of organisms that includes all of the individuals of a single species that live together in the same place and time
what is microevolution
how populations change over time because of changes in how common specific gene variants (alleles) are within the population.
What is phenotypic variation?
heritable variation in appearance and/or function
what is phenotypic plasticity?
expression of a different phenotype with the same genotype
What is quantitative variation? what is an example?
individuals differ in small incremental ways. ex. lengh
what is qualitative variation? what is an example?
characters with discrete state. ex colour
What is polymorphisms
discrete variants of a character (phenotypic definition but there is a genotypic version)
what is a high narrow curve with little variation among individuals suggest?
that selection of some sort is probably occurring
what is a broad low curve with a lot of variation among individuals suggest?
that selection may not be strong because no phenotypes are “winning”
What may impact phenotype variation?
genetics, environment, or an interaction of the two
what is the difference between genetics vs environment affecting the phenotype?
genetics are heritable and will be passed down
how can you determine if phenotypes are due to genes or environment
experiments such as: keeping genetics constant but changing the environment or breeding experiments (Mendels)
if there is alot of phenotypic variation then the cause is probably ________
environmental
if there is not alot of phenotypic variation the cause is probably ______
genetic
The Hardy-Weinberg principal is a null hypothesis that defines:
a population that is not evolving
What is evolution redefined
a change in allele frequencies from one generation to the next, changing how common a particular allele is within a population (frequency) changing the genetic make up of a population
populations often contain substantial ______ variation
genetic
what is population genetics
studying the genetic variation that exists in a population and how the genetic variation changes over time due to evolution
why does genetic variation occur?
because individuals contain different versions of the same genes (different individuals may carry different alleles for one or more genes) and as they reproduce the offspring gets some of those genes resulting in variations
What is a locus?
location of a gene on a chromosome
what is a gene pool?
all alleles at all loci in a population
What is polymorphism?
a difference in the nucleotide sequence of a given gene in different individuals of a species. the gene occurs in different “forms” in the population (ex. the gene has different alleles in the population)
What does SNP stand for? what is an examples
single nucleotide differences. ex looking at an individual with a disease and looking at the SNPs to associate with certain diseases
What are the two potential sources of genetic variation?
production of new alleles
rearrangement of existing alleles into new combinations
What can cause production of new alleles?
mutations
migrations
What is genotype frequency?
percentages of individuals possessing a genotype (genotypes have to add up to 100%)
what is allele frequency? how is it calculated?
How common dominant allele is or recessive allele is. calculated from genotype in diploid organisms. p and q are two different alleles at a locus
What are null models?
conceptual models that serve as theoretical reference points to observations
what is the hardy-weinburg principle?
conditions where diploid organisms have genetic equilibrium (no evolution, static)
What conditions must be met for population to be in Hardy-Weinberg equillibrium?
no mutations occurring
populations closed to migration
population infinite in size
all genotypes free of selection
random mating with respect to genotype (only condition measured over 2 generations)
What are the fundamental conclusion of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
allele frequencies in a population will not change generation after generation
if allele frequencies in a population are given by pq then the genotypic frequencies will be given by P², 2pq, q²
Why do biologists use HW equilibrium?
proof no evolution has occurred
provides null model (but you need to take sampling issues into account)
HW rest on several key assumptions (deviation means you look back to try to find out which of the four mechanisms is causing evolution)
if violated HW conclusions may not hold
What does it mean if it is assumed there is no natural selection?
all individuals survive at equal rates
individuals contribute equal number of gametes to the gene pool
what happens if the assumption no natural selection is violated?
some individuals with some genotypes survive and reproduced better than others, allele frequencies will change
What does it mean if it is assumed there is no mutation?
no copies of existing alleles were converted by mutation into copies of other existing alleles
no new alleles were/are created
small effect, only important long term
what happens if the assumption no mutation is violated
some alleles have higher mutation rates than others, allele frequencies will change
What does it mean if it is assumed there is no migration?
no individuals move into or out of the population
assume isolated population with no gene flow
what happens if the assumption no migration is violated?
individuals carrying some alleles move out of the population at higher rates than individuals carring other alleles, allele frequencies will change
what are the two types of migration
emmigration (leaving)
immigration (coming)
What does it mean if it is assumed there is no chance events?
nothing happens that causes individuals with some genotypes to pass more of their alleles to the next generation than others (no blind luck) and is avoided if the population is infinitely large (no bottle neck)
what happens if the assumption no chance events is violated
genetic drift, allele frequencies will change from one generation to the next
What does it mean if it is assumed individuals choose their mates at random?
gametes find each other randomly
what happens if the assumption individuals choose their mates at random is violated
individuals will prefer to mate with other individuals with the same phenotype (F0), during F1 no change will happen to the allele frequencies but during F2 the genotypic frequencies may change (due to inbreeding)
true or false the eggs dont screen against inbreeding
false, the eggs screen against inbreeding and seek the sperm least likely to result in inbreeding
true or false HW identifies what conditions cause evolution
true
what are the four agents of microevolution
gene flow
genetic drift
mutation
natural selection
gene flow
introduces new alleles into populations, may occur from individuals or gametes (plant sperm or birds). life history/behavour may enhance gene flow (behaviours of migrations or something else).
genetic drift
reduces genetic variability within populations, most important in smaller populations and reduces genetic variability NON SELECTIVE MECHANISM. doesn’t lead to adaption but does change allele frequencies
mutations
random and create genetic novelty. only two things make it matter, small populations and long periods of time
natural selection
shapes genetic variability by favouring some traits over others
what can enhance gene flow? example?
dispersal agents. ex bluejays moving seeds around
What is migration
movement of alleles between populations, not the same as seasonal movements of individuals, a form of gene flow. varies depending on mobility of individuals with propagules
what should frequencies be under HW?
A1A1=0.64, A1A2=0.32, A2A2= 0,04
true or false after migration a single bout of random mating will put the population back to HW
true
population bottleneck
reduction in alleles due to population reduction. loss of genetic diversity, some alleles totally gone, only common make through the rare are usually lost completely
founder effect
allele frequencies likely different from the older large population due to chance (very important in conservation biology)
is genetic drift a selective mechanism?
no it is a non-selective mechanism
is genetic drift random?
yes
does genetic drift impact large populations?
only unless it is over many many generations otherwise it only effects small populations
what is sampling error?
random discrepancy between theoretical expectations and actual results
sampling error +evolution=
founder effect
What was the founder effect prediction for silvereye birds?
birds on different islands have different allele frequencies so everytime they jump from on island to another allele variation gets smaller and smaller.
What is mutation?
change to double strand sequence of DNA, spontaneous or caused by other facts. deleterious mutations are harmful to organism
what are the types of mutations
point mutation
insertion
deletion
inversion
duplication
point mutation (substitution)
a single nucleotide (base) is changed
insertion
one or more nucleotide base pairs are introduced into a DNA sequence
deletion
one or more nucleotide base pairs are removed from a DNA sequence
inversion
a segment of DNA breaks and is inserted back into its original position in the reverse orientation
duplication
DNA is copied twice; the duplication can be part of a gene, a whole gene, or an entire genome
what are the different modes of selection?
directional selection (most common)
stabilizing selection (semi common)
disruptive selection (relatively rare)
what is directional selection
favors individuals near one end of the phenotypic spectrum
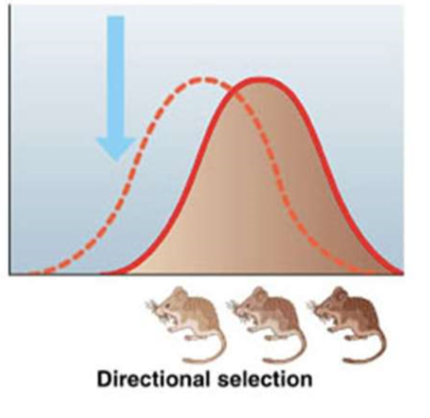
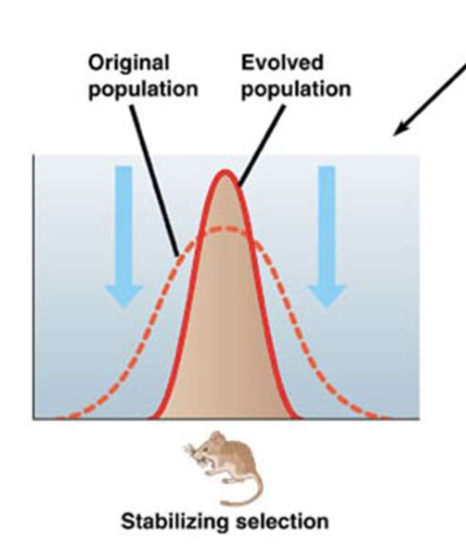
what is stabilizing selection?
favors individuals with intermediate phenotypes (favors average value)
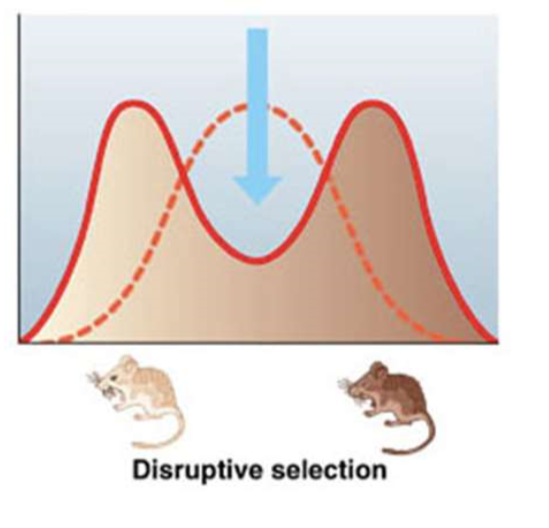
what is disruptive selection
favors individuals with extreme phenotypes (bimodal peak disruptive selection)
inbreeding reduced _______
heterozygosity
what effect does inbreeding have on the percentege of heterozygotes and homozygotes
the % of heterozygotes will decline by 50% each generation, whereas homozygotes will increase 25% each generation, however from one generation to the next allele frequency does not change
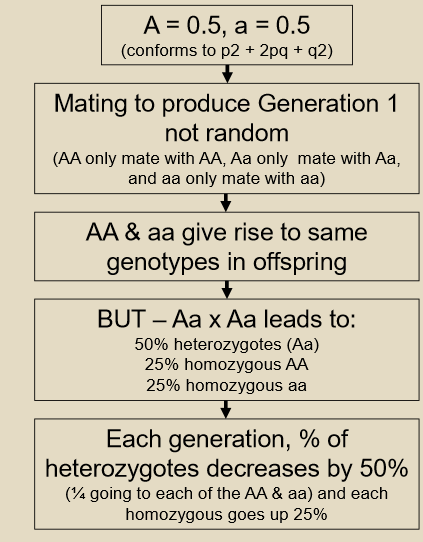
does the deviation in HW equilibrium from inbreeding mean evolution is occuring?
no because allele frequencies do not change from generation to generation, it simply affects how genotypes are packaged into diploid zygotes
true or false inbreeding changes proportion of alleles in a population
false it simply moves them from heterozygote to homozygote genotypes
what is inbreeding depression
decrease in the average fitness of inbred individuals. deleterious alleles tend to be “unmasked” more in an inbred population more homozygous recessive) which is typically harmful or even lethal
what can resolve inbreeding depression
outbreeding (genetic rescue)
inbreeding depression=
loss of fitness
what is purging
something being wiped out
interbreeding coefficient leads to loss in _____
fitness
true or false animals and plants have evolved mechanisms to avoid inbreeding?
true, eggs actively seek sperm that is least likely to cause inbreeding and mate choice is genetically controlled (example with the smells)
when is inbreeding unavoidable?
some small populations, common for rare or endangered species and captive breeding problems
what is hybridization
mating between individuals of two genetically distinct populations (can be between species, or the same species)
interspecific hybridization
hybridization between species
intraspecific hybridization
hybridization within a species
hybrid sink
situation where immigration of locally unfit genotypes produces hybrids with low fitness that reduces local abundance
Hybrid vigour (heterosis)
hybrid offspring have higher offspring than either of the parents (or parental organisms)
what poses threats to biodiversity
environmental change, invasive species, overharvesting, habitat loss
genetic rescue
“aggressive” effort to conserve decline population by using hybridization (either very good or very bad)
outbreeding depression
loss of fitness due to parents genetic differences
how does genetic rescue reduce extinction risk
by increasing absolute fitness, increasing population size or growth rate often owing to immigration of new alleles
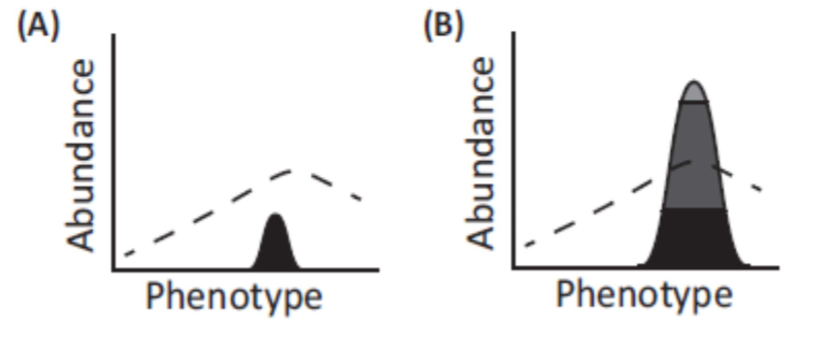
fitness of individuals of a given phenotype indicated via relation between distribution of ____ (abundance) and _____ (broken line)
phenotypes, fitness function
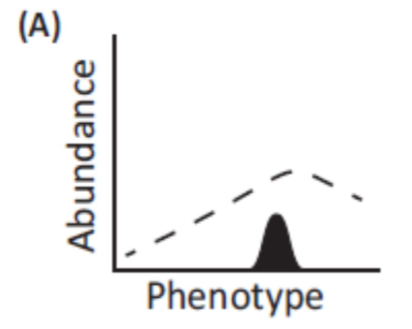
What does this graph represent?
small at risk population with reduced phenotypic and genetic variation that could benefit from genetic rescue
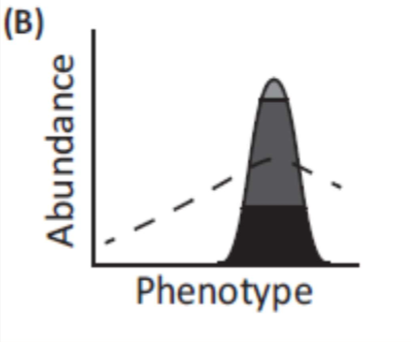
What does this graph represent
successful genetic rescue with an increase in fitness following prescribed gene flow
How do you perform genetic rescue and why do you perform it that way?
you bring in few key individuals with different alleles because too many would cause outbreeding depression, low levels of immigration should be enough to decrease frequency of deleterious alleles and provide genetic variation