P5: Electricity in the home
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
Current
Flow of electrons
Type of current from a cell
DC
Why is the current from a cell DC?
Moves in 1 direction
Leaves cell from 1 end, goes around circuit + returns to cell at the another end
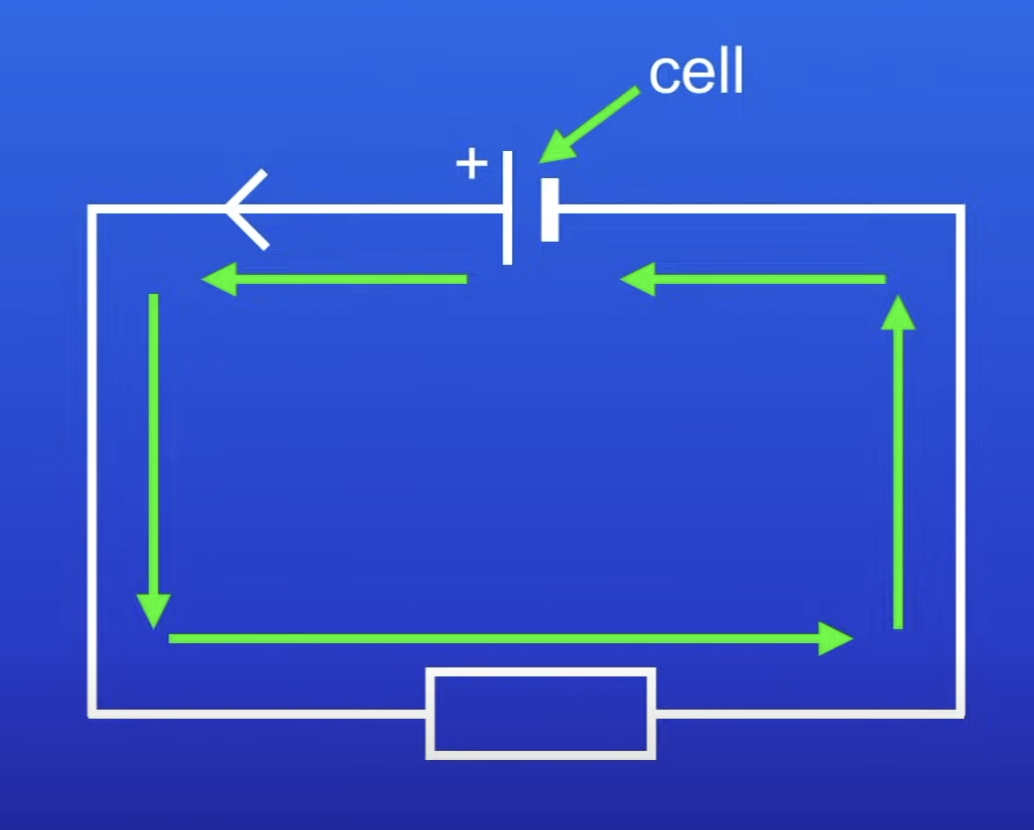
Direct current (DC)
Current only moves in 1 direction
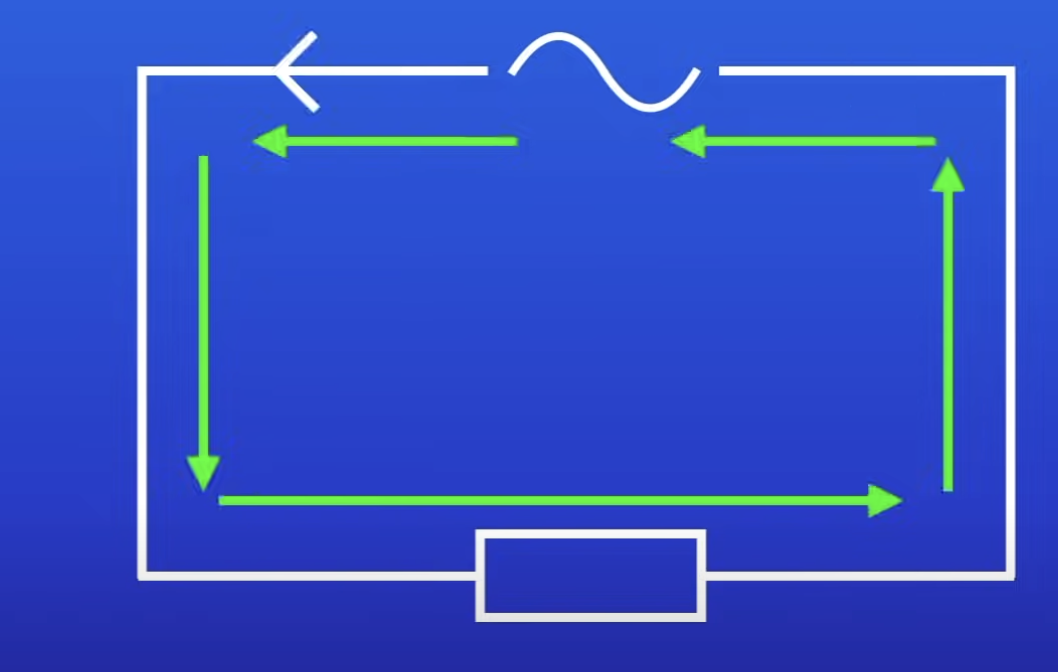
What type of supply is mains electricity?
Ac supply
Alternating current (AC)
Current constantly changes direction
Benefit of using AC
Easy to use transformer to increase or decrease PD
When are transformers used?
When electricity is transferred from power stations to homes
Frequency of AC (domestic electricity supply) in UK
50 Hz
What is meant by frequency of AC is 50 Hz
AC switches direction 50 times per second
PD of AC in UK
230 V
What does an oscilloscope show?
Pattern of electrical current
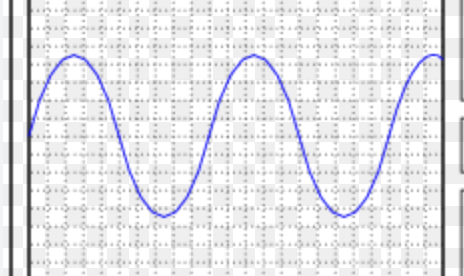
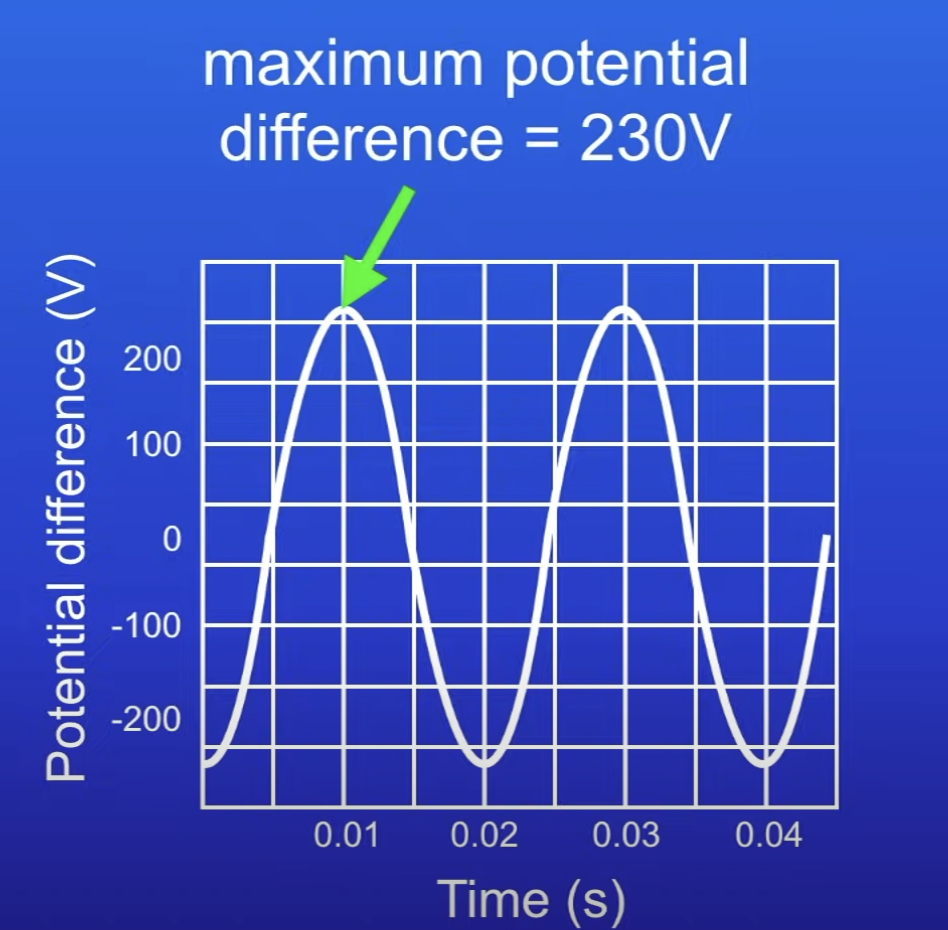
What type of current does this show and why?
AC
PD rising + falling (shows current going back + forwards)
What does the height of peak show?
Max PD (230 V)
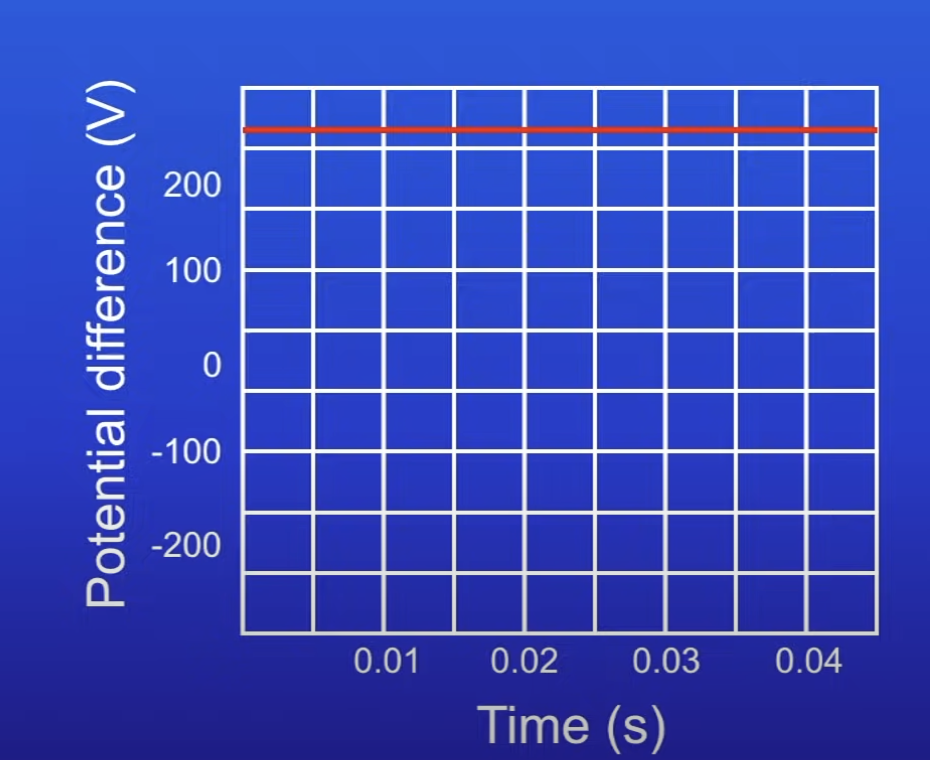
What type of current does this show and why?
DC
PD doesn’t change
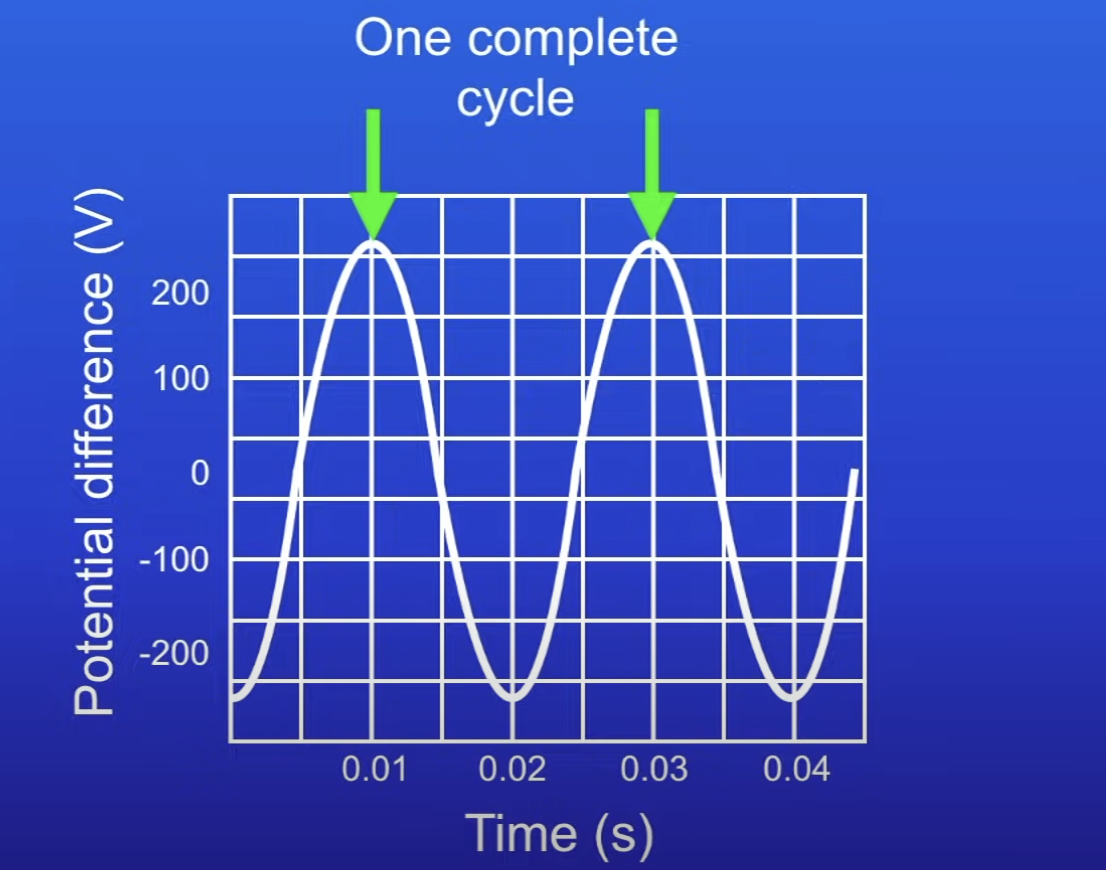
How to use the oscilloscope trace to calculate frequency of AC
From 1 peak to the next, current has changed direction + changed back again
Time from 1 peak to the next peak = 1 complete cycle
1 / time taken = freq
Frequency
Number of cycles AC changes direction in 1s
Rate at which AC reverses direction
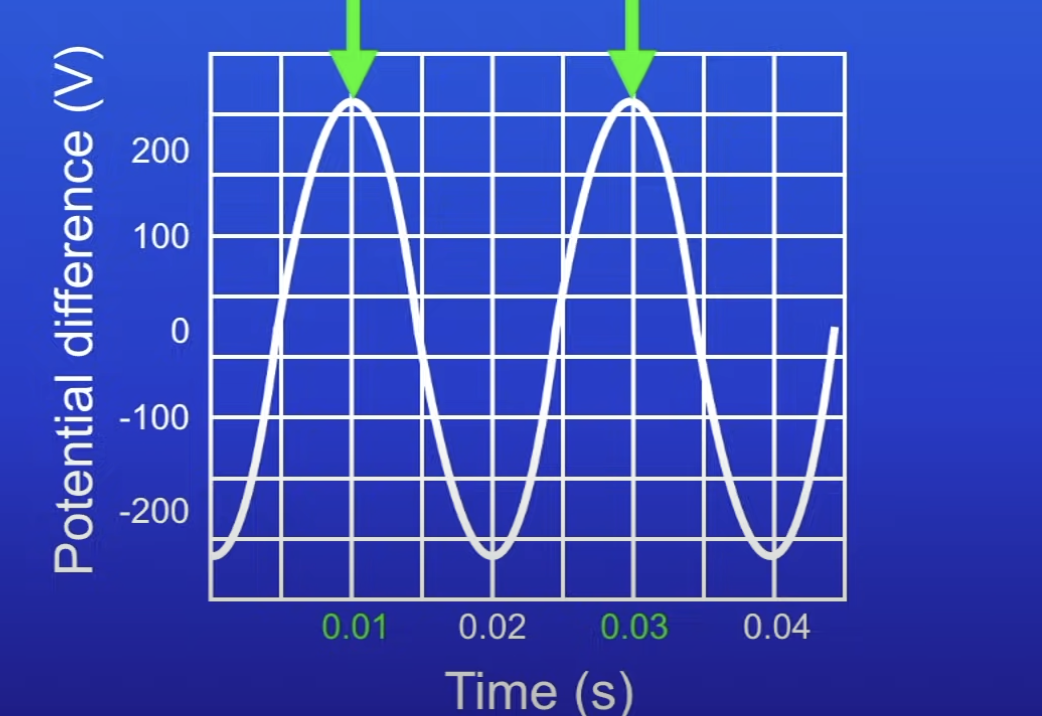
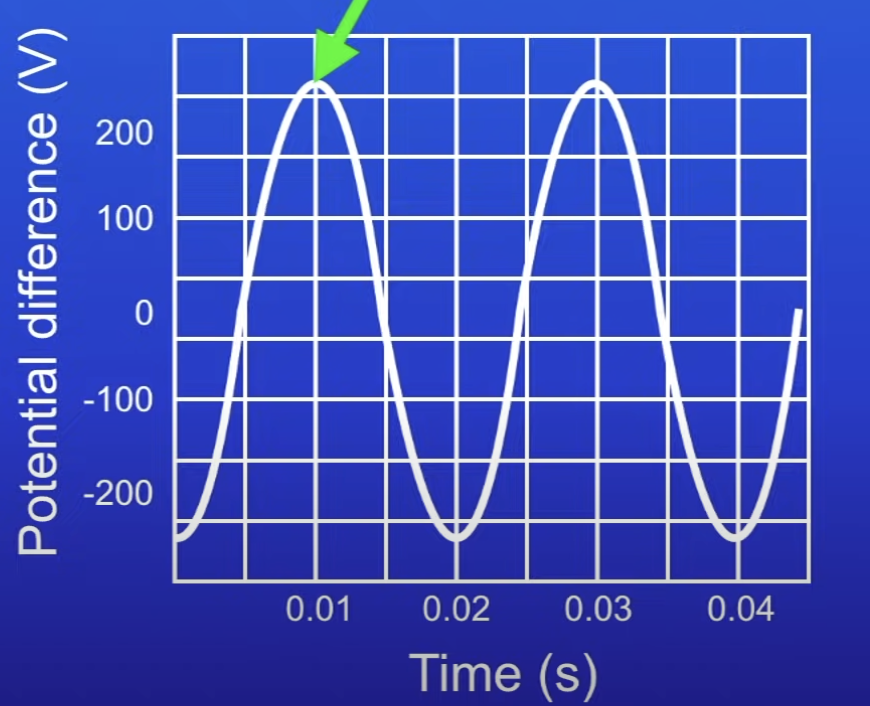
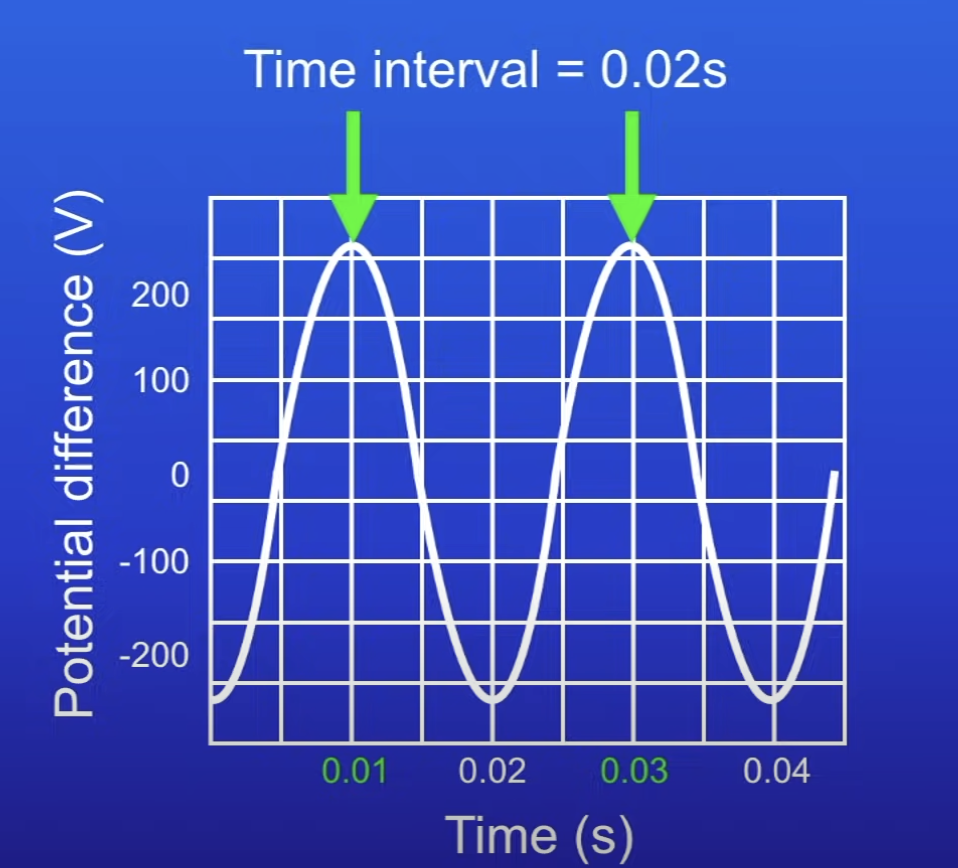
Calculate the frequency of this
50 Hz
0.03 s - 0.01 s = 0.02 s
1 / 0.02 s = 50 Hz
DC vs AC
DC
PD doesn’t change
Current flows in 1 direction
AC
PD reverses (positive - negative)
Current constantly changes direction
How are most electrical appliances connected to the mains electricity?
Using three-core cable
What are the wires in a three-core cable made of and why?
Copper
Good conductor of electricity
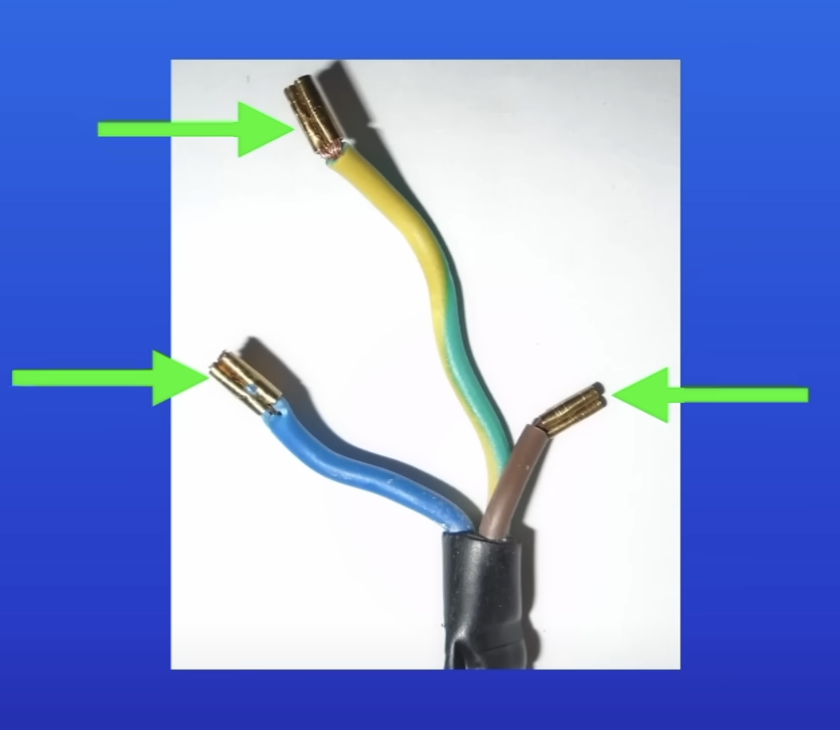
What are the coatings of wires in a three-core cable made of and why?
Plastic
Doesn’t conduct electricity
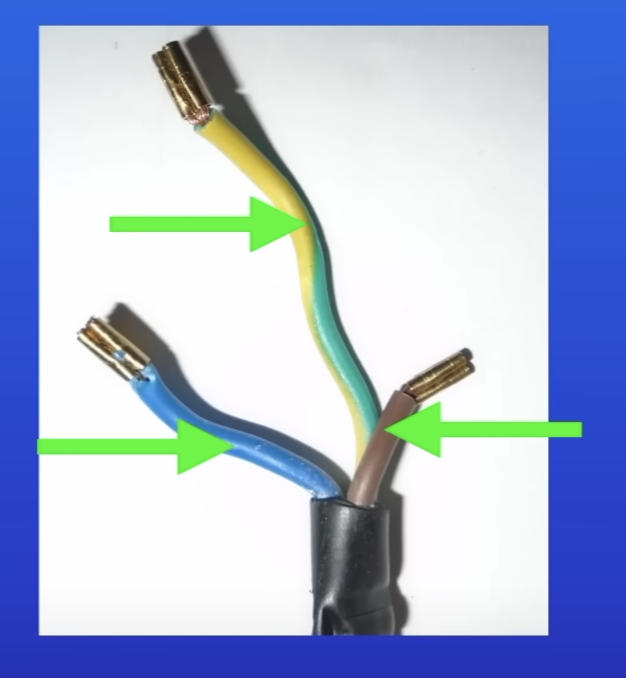
Why is the insulation covering each wire colour coded?
For easy identification
3 types of wires in a three-core cable
Live wire
Neutral wire
Earth wire
Color of each wire in a three-core cable
Live wire = brown
Neutral wire = blue
Earth wire = green + yellow stripes
Live wire
Carries the alternating PD from the supply
At 230 V
Neutral wire
Completes the circuit (w live wire)
0V (compared to live wire)
What is the earth wire for?
Safety wire
Earth wire
Safety wire
To stop the appliance becoming live
What is the live wire connected to?
A fuse in the plug
Voltage of the live and neutral wire
Live: 230 V
Neutral: 0V (earth potential)
PD between live and neutral wire
230V
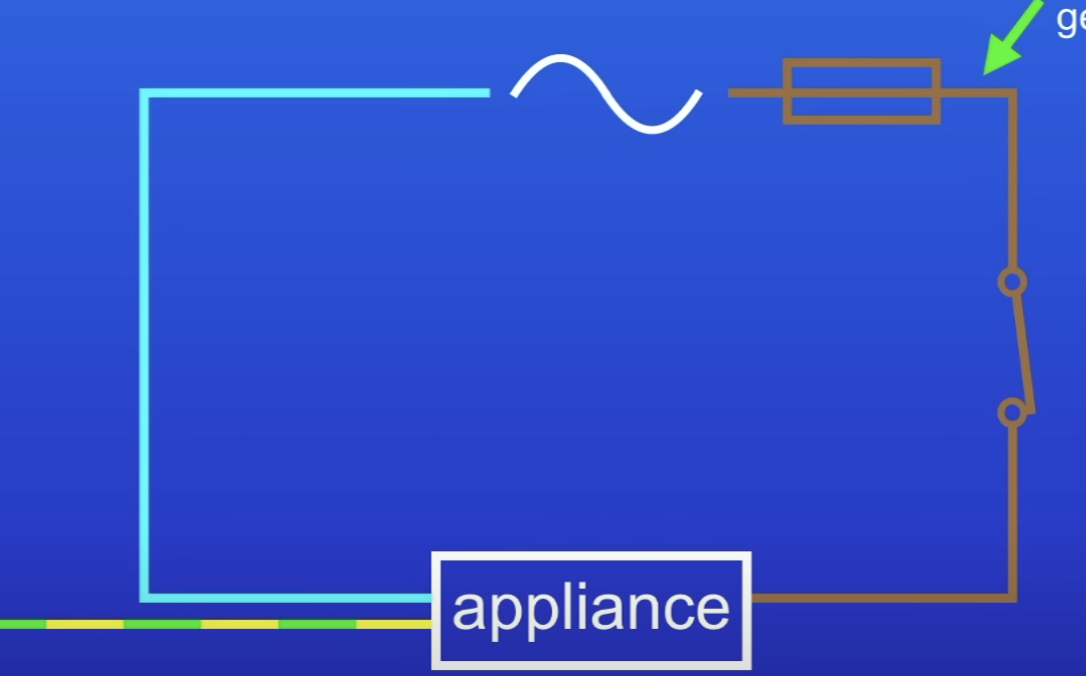
Explain this circuit wired to the main supply
Live wire- carried 230V electricity from generators, connected to fuse
ET as electrical current passes thru appliance
Neutral wire- completes circuit
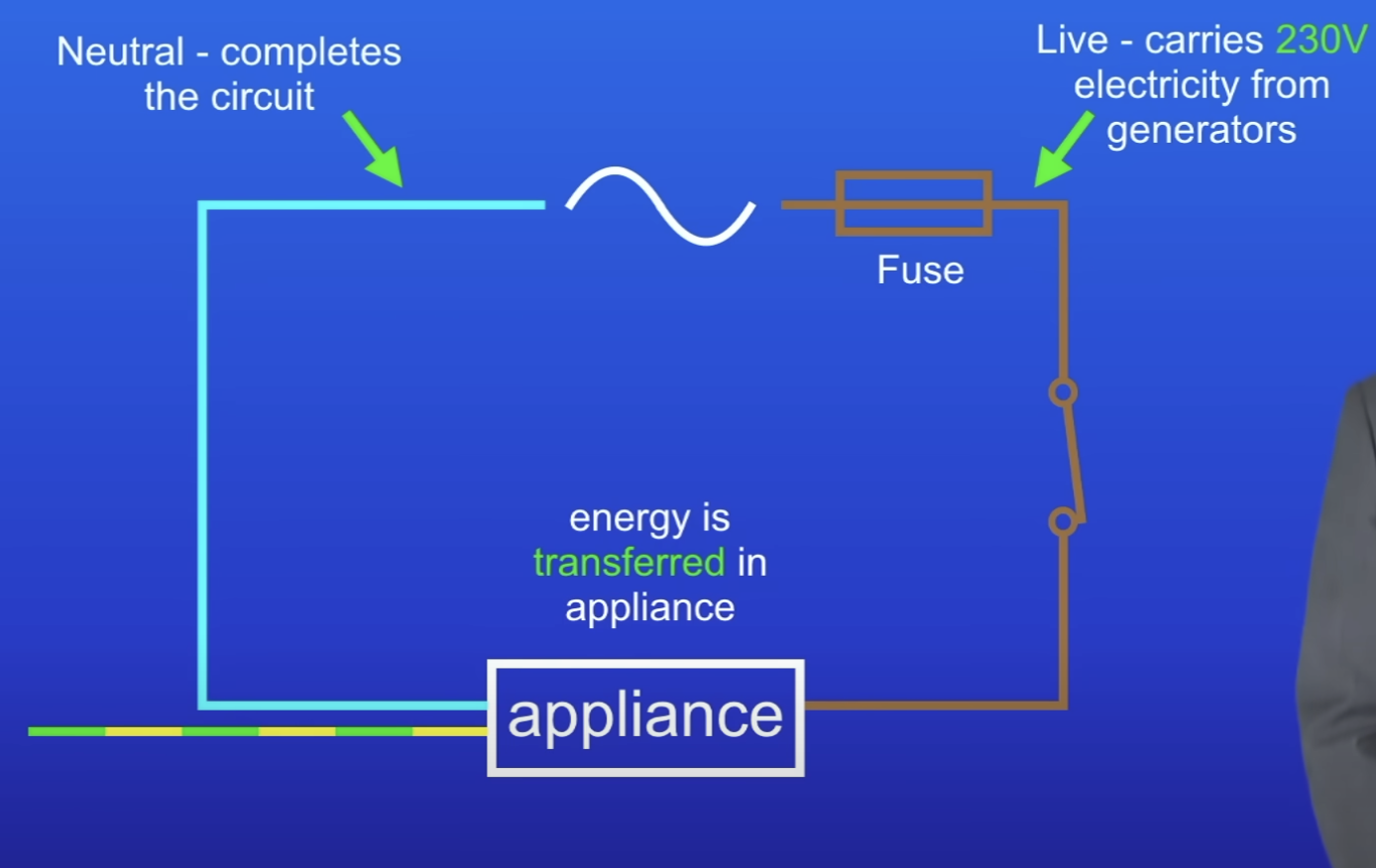
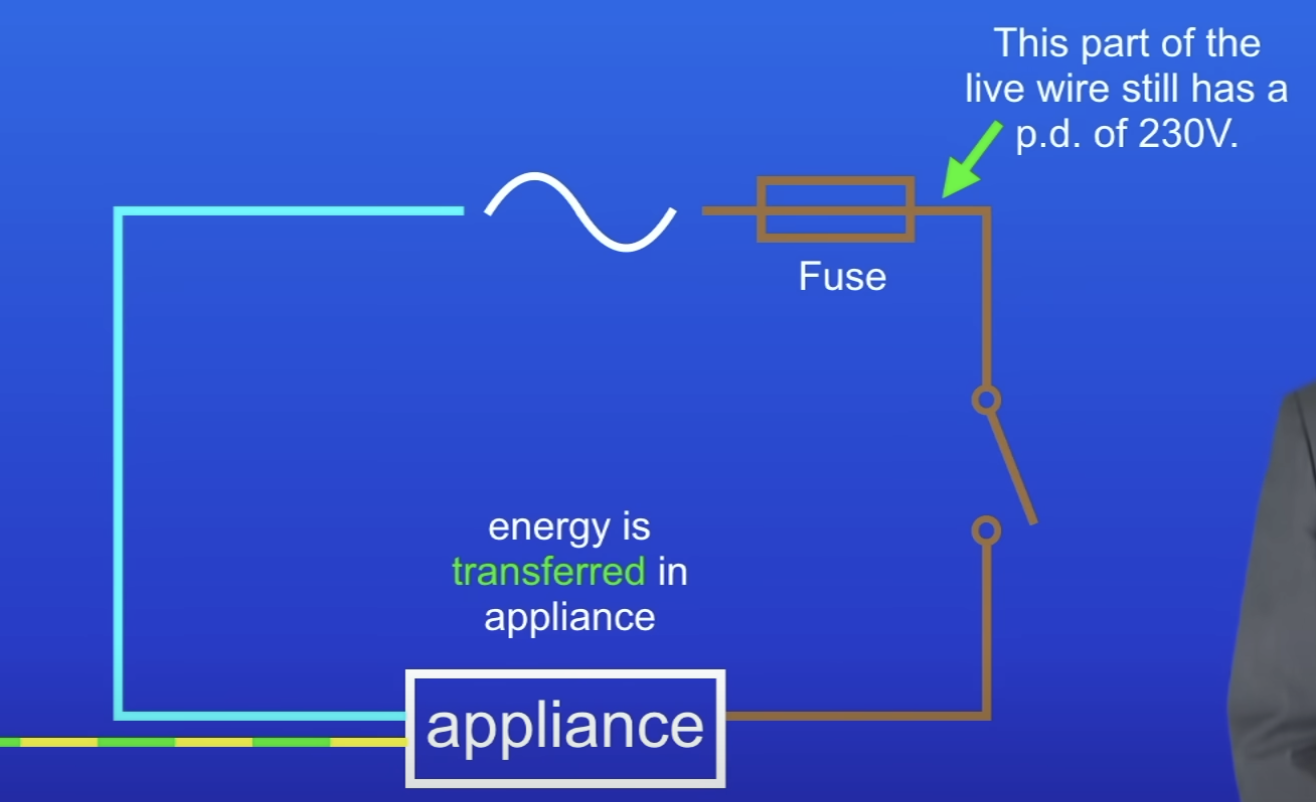
Why is the live wire dangerous + fatal if touched, even if off (switch is open)?
First part of live wire running to switch still has PD of 230V
PD of earth is 0V
Person touched live wire → current flows thru person, into the earth + they would be electrocuted
Why are appliances with a metal case dangerous?
If live wire comes loose + touches metal case → case becomes live (gets PD of 230V)
Person touches live case → fatal electric shock
Why are most appliances, especially those with metal cases, connected to an earth wire?
Metal case attached to earth wire
Earth wire connected into ground w a metal rod
If case becomes live → huge current flows to Earth
Fuse melts + shuts off current
Prevents person from getting electric shock from touching the case
Power
Rate at which energy is transferred
1 W =
Energy transferred at 1 Joule per second
10 V =
10 J of energy transferred per coulomb of charge passing thru component
1 A
1 coulomb of charge flowing per second
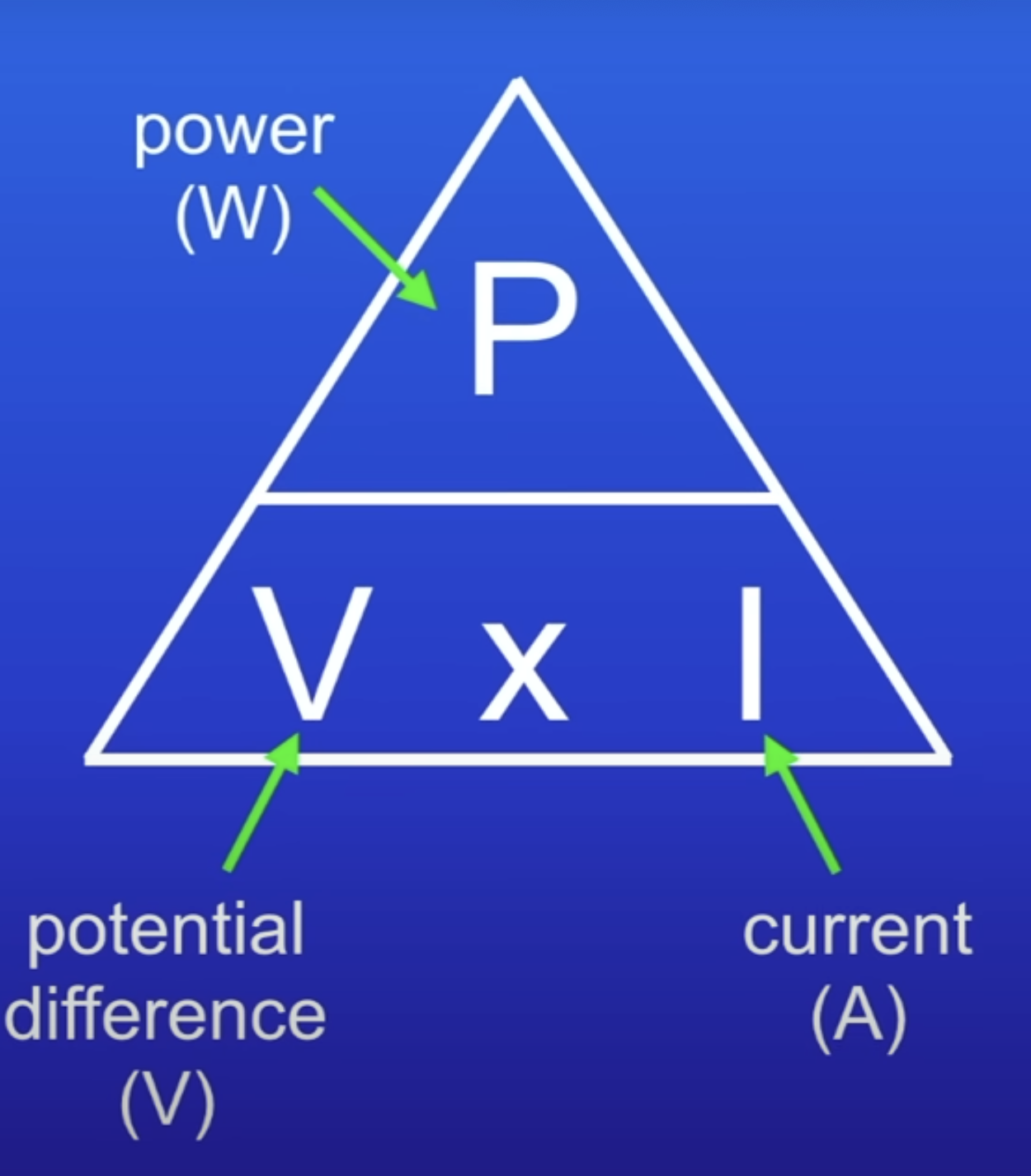
Power equation (using voltage)
P = VI
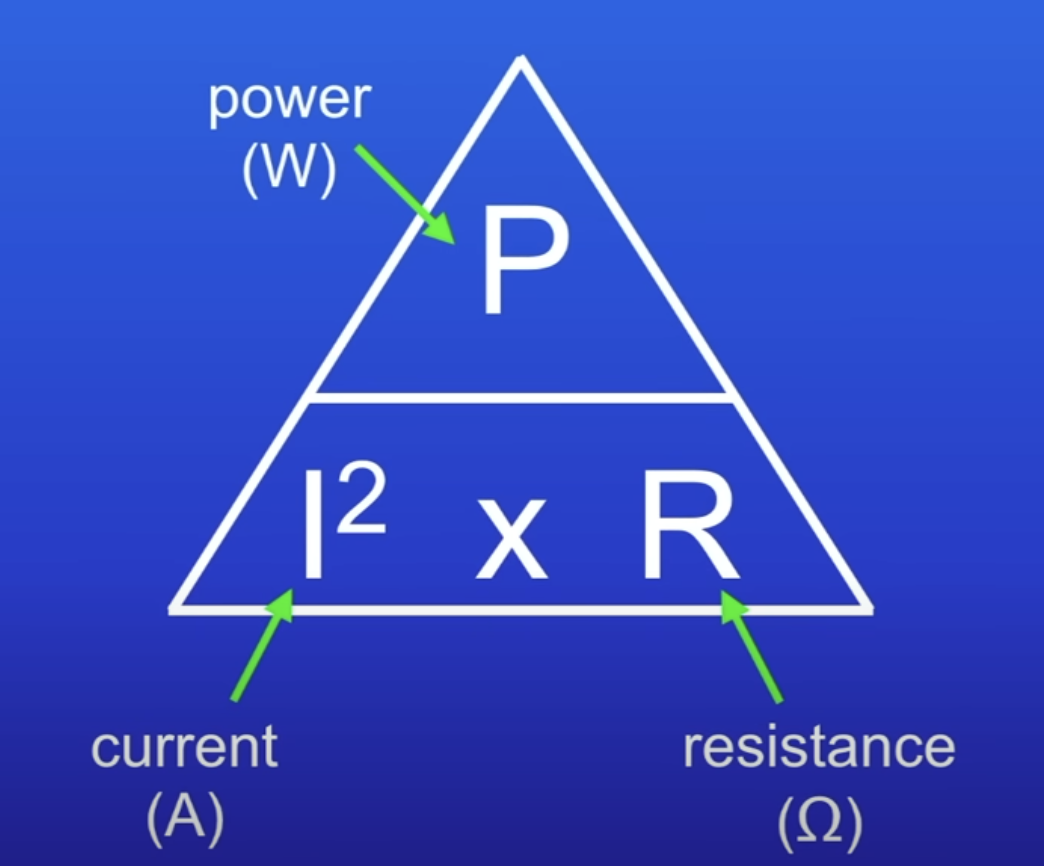
Power equation (using resistance)
P = I2R
What do everyday electrical appliances do?
Transfer electrical energy into other forms of energy (thermal, kinetic)
What do blenders + fans transfer electrical energy into?
Kinetic energy of electric motors
Main purpose of these appliances is movement
What do irons + kettles transfer electrical energy into?
Thermal energy
Both designed to get hot
What categories can appliances be divided into?
Those that transfer EE into:
KE
TE
What do hair dryers transfer electrical energy into?
KE of electric motors
TE (heating element heats air)
What do washing machines transfer electrical energy into?
KE of electric motors (turns drum)
TE (heating element heats water)
Which appliances have a higher power rating?
Those that are designed to generate TE
Over those designed to generate KE
What does the amount of energy an appliance transfers depends on?
How long the appliance is switched on for
Power of the appliance
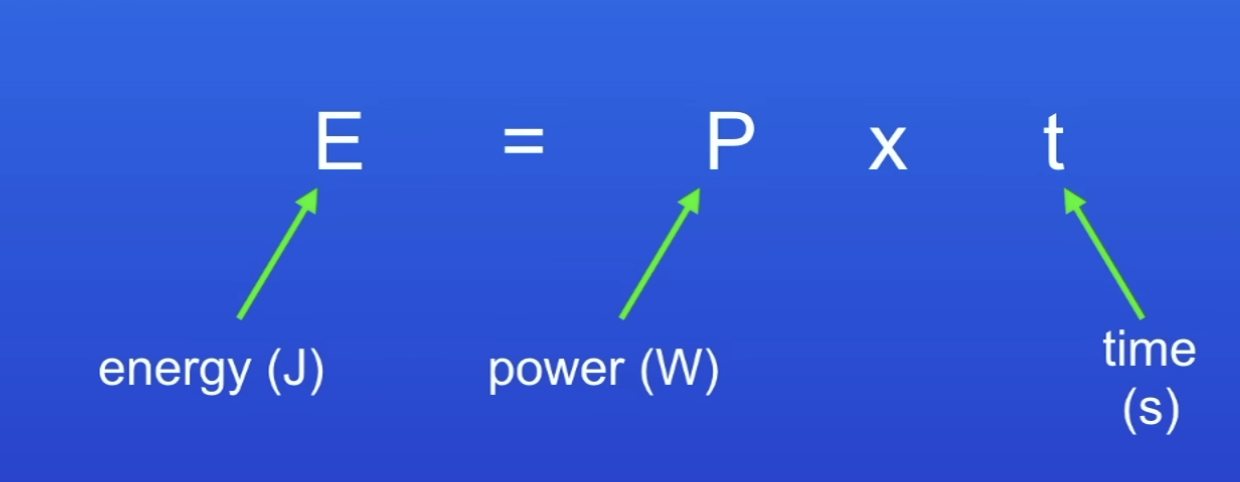
Energy transferred equation (power)
E = P t
Energy transferred equation (charge)
E = Q V
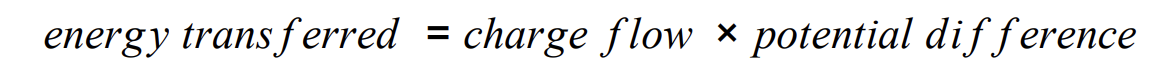
Work is done when…
Charge flows in a circuit
How does charge flowing thru a resistor make it hot?
ET to resistor
TE store of resistor increases
Resistor becomes hotter
TE transferred to surroundings
Why do all electrical appliances waste energy?
Heating effect of current in wires
Why do electric appliances with an electric motor waste energy?
Friction betw moving parts
Max efficiency
100% (1)
Efficiency equation
Output power / input power x 100
Domestic energy meter
Measures how much energy is supplied
What happens when electrical charge flows thru an appliance?
Electrical energy transferred by appliance to another energy store
Simple answer: why does a resistor become hotter when charge flows thru it?
ET to resistor
Fuse
Safety device that breaks the circuit if a fault in an appliance causes too much current to flow
What does a fuse contain?
Piece of metal wire that melts easily
How to choose a fuse?
Fuse current rating is slightly higher than current thru appliance
What happens if fuse size is smaller or a lot larger than the normal current thru the appliance?
Smaller: wire inside will melt as soon as the appliance starts
Larger: current will continue to increase → leads to overheating
What wire does a 2 core cable not have?
Earth wire
What happens if the current thru a fuse becomes too big?
Melts + cuts of current to live wire
How are appliances with a metal case earthed?
Case attached to earth wire in cable
How does earthing an appliance increase safety?
Stops metal case becoming live if live wire breaks + touches case
Do appliances with plastic cases need to be earthed- why or why not?
No
They are double insulated so only connected to live + neutral wire
Cables of different thicknesses are used for?
Diff purposes
The larger the current to be carried…
The thicker the cable must be
Examples of DC supply
Cells
Battery
Frequency equation
1/time taken for 1 cycle
When does a earth wire carry and not carry a current?
Not carry: normally
Carry: if fault occurs in appliance → so current will flow to ground
Energy transfers in battery powered torch
Battery converts chemical to electrical energy
Bulb converts EE to light
+ waste energy (heating)
Energy transfers in battery powered motor
Battery converts chemical to electrical energy
Motor converts EE to KE
+ waste energy (heating due to friction
National grid
A system of cables + transformers linking power stations to consumer
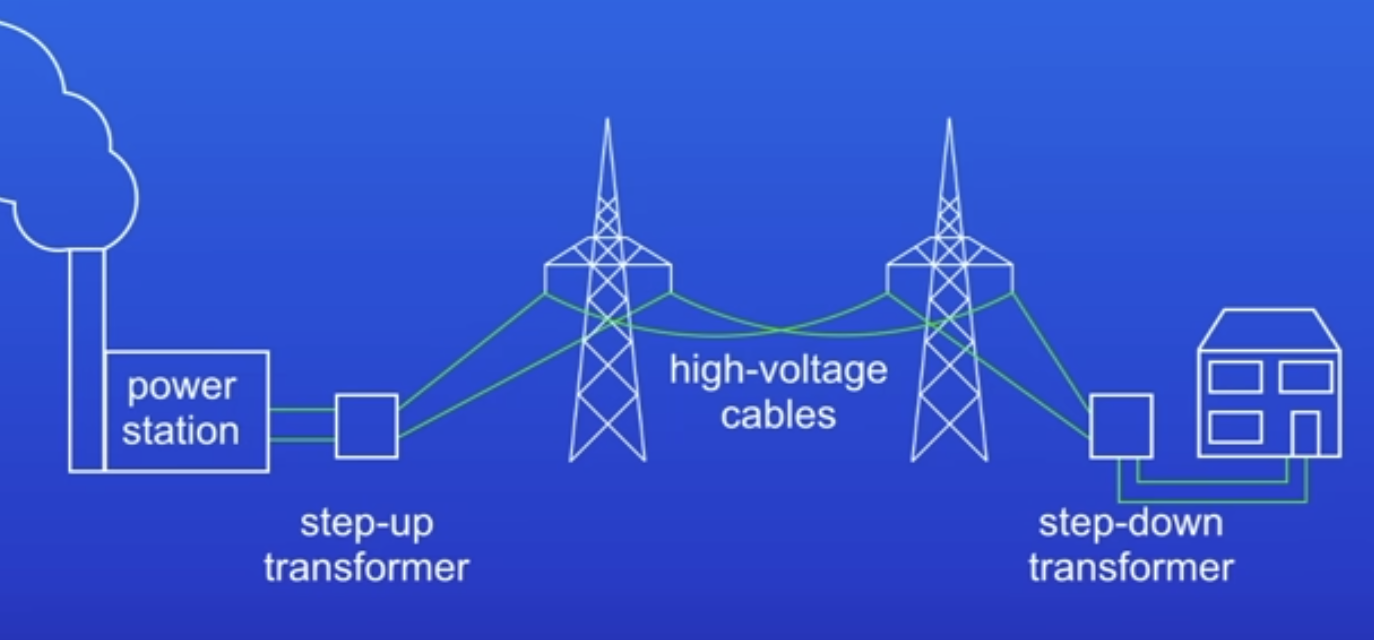
Issue with getting electricity to homes
Energy always lost in power cables due to resistance of wires
Purpose of national grid
To link power stations to consumers so they have access to electricity
Bigger the distance between power stations + homes…
Greater the energy lost
How can you reduce energy loss due to resistance of wires?
Build power stations near homes
Use transformers
What is transferred from power stations to consumers using the National Grid?
Electrical power
2 types of transformers
Step up
Step down
Step up transformers
Increase the PD from the power station to the transmission cables
Step down transformers
Decrease, to a much lower value, the PD for domestic use.
How do step up transformers help?
Reduce energy lost in transmission cables
Do step up + down transformers increase or decrease PD?
Up: increase
Down: decrease
How do transformers work?
Electricity fm power station passes thru step up transformers (increase PD)
High PD = less energy lost in power cables
Electricity passes thru step down transformers (reduce PD, 230 V)
To what PD do step down transformers reduce PD to?
230V
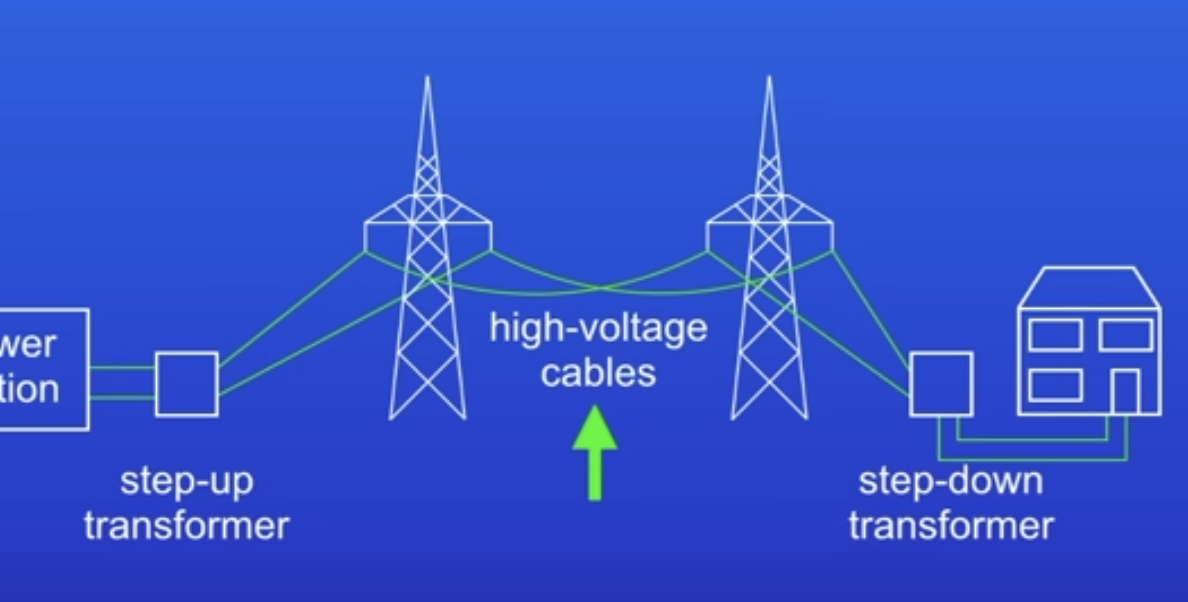
Why is it efficient that national grids transfer electricity at high potentials?
High PD → low current
Lower current = lesser energy wasted as heat
Why does PD need to be decreased between transmission lines + houses?
Lower PD safer for domestic use
+ reduces chance of electrocution
Where do step up transformers increase PD from?
Power stations to transmission cables
Good conductors of electricity
Metals
Why are metals good conductors of electricity?
Electrons can easily flow thru them
Good insulators
Plastic
Glass
Insulators
Don’t conduct electricity
Why can’t insulators conduct electricity?
Electrons can’t move thru them
What happens when insulating materials are rubbed against each other?
They become electrically (statically) charged
Why do insulators become electrically charged when rubbed against each other? (static electricity)
Negatively charged electrons rubbed from 1 material to another
Material that gains electrons becomes negatively charged
Material that loses electrons becomes equally positively charge