Module 25 APES
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Soil triangle questions removed - easier to answer w/photo
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
1. Base saturation of soil is a measure of the:
a. particulate matter in lakes.
b. percentage of water to particles in a sample.
c. ability of nutrients to adhere to clay particles.
d. proportion of soil bases to acids.
D
2. Soil drains most rapidly when it is made up of:
a. primarily clay.
b. primarily sand.
c. roughly equal proportions of silt and clay.
d. roughly equal proportions of sand, silt, and clay.
3. Plant roots cause:
a. both physical and chemical weathering.
b. only erosion.
c. only chemical weathering.
d. only physical weathering.
4. Which is NOT a service provided by soil?
a. Breaks down inorganic material
b. Provides a habitat for various organisms
c. Recycles nutrients
d. Filters water
5. Acid precipitation is destructive to:
I. limestone gravestones
II. marble statues
III. granite outcrops
a. I and III
b. II only
c. I only
d. I and II
6. Mineral nutrients are present primarily in the:
a. C horizon, the parent rock.
b. A horizon, the zone of eluviation.
c. E horizon, the zone of leaching.
d. B horizon, the subsoil.
10. Which is NOT a function of soil?
a. Filters water and atmospheric chemical compounds
b. Binds with greenhouse gases
c. Provides a habitat for organisms
d. Provides an anchor for plants
11. Chemical weathering:
a. Is part of the cycle that renews soil nutrients
b. Is the result of wind, water, and ice
c. May reduce atmospheric carbon dioxide
d. Is detrimental to soil
a. Is part of the cycle that renews soil nutrients
12. The E horizon is:
a. Present in all soils
b. The zone which receives dissolved organic acids that pass from overlying horizons
c. The least weathered zone
d. The zone through which iron and aluminum pass from overlying horizons
13. The soil that yields the greatest productivity for agriculture has:
a. Low cation exchange capacity and high porosity
b. More soil bases than acids
c. High cation exchange capacity and low porosity
d. An equal amount of soil acids and bases
14. Soil is more fertile when:
a. It contains few organisms or other biotic components
b. The parent rock has a high quartz content
c. It has been farmed for many years
d. The parent material has a high calcium carbonate content
15. Humus is the most fully decomposed organic matter in the lowest level of which soil horizon?
a. O horizon
b. B horizon
c. A horizon
d. E horizon
16. When surface area of a rock increases:
a. The rock weathers more rapidly
b. The rock is less vulnerable to chemical weathering
c. The rock is less vulnerable to physical weathering
d. The rock weathers less rapidly
17. Topsoil is the:
a. A horizon
b. O horizon
c. B horizon
d. C horizon
18. Soil degradation is caused by:
a. Compaction from heavy machinery
b. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria
c. Animal waste
d. Burrowing animals such as earthworms
19. Which practice does NOT accelerate erosion of soil?
a. Planting trees
b. Road building
c. Logging
d. Construction
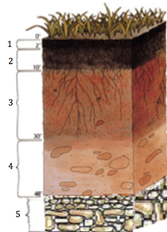
20. Identify the zone labeled 1 in the figure:
a. B horizon
b. C horizon
c. O horizon
d. A horizon
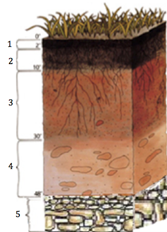
21. Identify the zone labeled 5 in the figure:
a. O horizon
b. C horizon
c. B horizon
d. A horizon
22. Which is NOT associated with ore formation?
a. Deposited by animals
b. Collected in veins
c. Deposited igneous rock
d. Precipitated when magma comes into contact with water
23. The porosity of soil is a measure of:
a. How quickly it drains
b. How much biological material it contains
c. Its cation exchange capacity
d. The depth of its topsoil layer
24. Which chemical reaction is involved in the creation of acid precipitation?
I. Sulfur dioxide and water vapor combine to create sulfuric acid
II. Hydrogen and chlorine combine to create hydrochloric acid
III. Sulfur and oxygen combine to create sulfur dioxide
a. III only
b. II only
c. I and III
d. I and II
25. Select the correct order of physical size of sediment particles from largest to smallest.
a. Loam, sand, silt
b. Silt, sand, clay
c. Sand, silt, clay
d. Loam, silt, clay
26. What is the difference between chemical and physical weathering of rock?
a. Physical weathering creates new substances; chemical weathering does not
b. Chemical weathering results in new substances; physical weathering does not
c. Physical weathering results in erosion; chemical weathering does not
d. Chemical weathering results in erosion; physical weathering does not
27. Which four elements make up more than 88 percent of Earth's crust?
a. Gold, copper, nickel, silicon
b. Oxygen, gold, aluminum, iron
c. Oxygen, silicon, nickel, iron
d. Oxygen, silicon, aluminum, iron
28. Soil is:
a. Most fertile nearest to the poles because it contains high amounts of decomposed organic matter
b. Thickest on steep slopes in very dry areas because nutrients do not get leached away
c. Nutrient poor in the humid tropics because high rain leaches nutrients from the ground
d. Richest in the humid tropics because warm temperatures and high rain causes rapid decomposition
29. The infiltration of pollutants into groundwater:
a. Is more likely in regions that contain basaltic bedrock
b. Is common in areas with clay soils because water flows through these soils easily
c. Is rare in areas with sandy soils because water flows through these soils easily
d. Is common in areas with sandy soils because water flows through these soils easily
30. Cation exchange capacity in clay:
a. Is low, meaning that it cannot absorb positively charged ions
b. Is high, meaning that it retains water efficiently
c. Is low, meaning that it releases ions with a negative charge
d. Is high, meaning that it absorbs and releases positively charged ions
31. Which material is best as a liner for a landfill?
a. Silt
b. Basalt
c. Sand
d. Clay
32. The soil that is best for growing most plants is composed of:
a. A mixture of sand, silt, and clay that promotes water drainage and retention
b. Silt, because it is a medium-sized particle
c. Sand, because water drains most easily
d. A mixture of sand for drainage and clay to hold nutrients
33. Rocks comprise primary minerals that erode to secondary minerals and then to ionic forms of these minerals. An example is:
a. Feldspar → clay → marble → calcium carbonate
b. Basalt → feldspar → clay → nitrogen
c. Granite → feldspar → clay → potassium ions
d. Basalt → granite → feldspar → magnesium
34. What role do lichens play in weathering?
a. Lichens play a role in chemical weathering because they produce weak acids
b. Lichens play a role in chemical weathering only when they are in contact with limestone
c. Lichens play a role in chemical weathering because they create carbon dioxide
d. Lichens play a role in physical weathering because their roots contribute to erosion
35. Which type of mine would be most dangerous for humans to work?
a. Gold placer mining
b. A subsurface diamond mine
c. Mountaintop removal for coal
d. An open-pit copper mine
36. The A horizon of soil is:
I. a zone of organic material
II. also known as topsoil
III. Created artificially
a. I and II
b. II only
c. I only
d. III only
37. Erosion is NOT caused by:
a. Water
b. Wind
c. Gravity
d. Acid rain
38. What is the difference between weathering and erosion?
a. Weathering refers to the breakdown of rock; erosion refers to the removal of rock from its landscape.
b. Erosion refers to the breakdown of rock; weathering refers to the removal of rock from its landscape.
c. Weathering is a chemical process; erosion is strictly physical.
d. Weathering happens in the tropics; erosion happens in temperate climates.
39. The freeze-thaw cycle is an example of:
a. Chemical weathering
b. Physical erosion
c. Chemical erosion
d. Physical weathering
40. The least weathered zone in a soil is the:
a. E horizon
b. A horizon
c. C horizon
d. O horizon
c. C horizon
41. The soil that is best for growing most plants is composed of:
a. Sand, because water drains most easily.
b. Silt, because it is a medium-sized particle.
c. A mixture of sand, silt, and clay that promotes water drainage and retention.
d. A mixture of sand for drainage and clay to hold nutrients.
42. When minerals within a rock respond differently to temperature changes, it results in:
a. Physical weathering.
b. Chemical weathering.
c. Differential cracking of the rock.
d. Both A and C.
d. Both A and C
43. What is the difference between the physical weathering of rocks and erosion of rocks?
a. Physical weathering requires water to break apart rocks, while erosion relies solely on wind.
b. Physical weathering happens over a few days, while erosion occurs over centuries.
c. Physical weathering leads to deposition, while erosion leads to chemical weathering.
d. Physical weathering breaks down rocks, while erosion removes rock from an ecosystem.