week 09
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/32
Earn XP
Last updated 7:23 PM on 4/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
1
New cards
quantizing video colour: YUV
Y = luminance/brightness (changes more easily seen by human eyes)
UV = chrominance (colour/hue), not needed for black and white TV
4:1:1 method:
same brightness (4), but taking the average colour
* reduces storage
UV = chrominance (colour/hue), not needed for black and white TV
4:1:1 method:
same brightness (4), but taking the average colour
* reduces storage
2
New cards
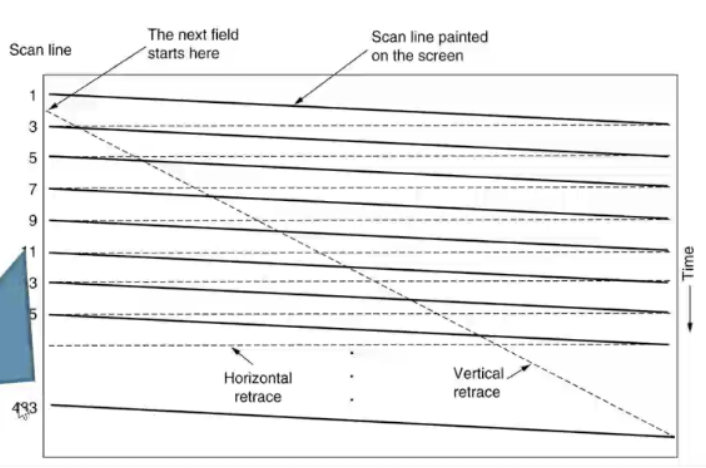
old TVs
interlaced display
* our eyes see phosphor dots on the screen
* an electron beam (gun) activates the dots
* the gun scans through the dots horizontally
* each pass = a field
* our eyes see phosphor dots on the screen
* an electron beam (gun) activates the dots
* the gun scans through the dots horizontally
* each pass = a field
3
New cards
2000s TVs
* 4k TVs have vertical scan lines
* standard definition resolution was 480 or 576
* now companies are beginning to make 8k TVs
* standard definition resolution was 480 or 576
* now companies are beginning to make 8k TVs
4
New cards
2010 small devices
* Apple says small devices should be held 10-12 inches away
* screen resolution should be at least 300ppi to look crisp
* screen resolution should be at least 300ppi to look crisp
5
New cards
retina display
* more pixels = crisper images
* 326ppi (300 is the limit for human retina)
* need to consider pixel density, viewing distance, and display size
* 326ppi (300 is the limit for human retina)
* need to consider pixel density, viewing distance, and display size
6
New cards
editing before digital video
* had to copy from one tape to another
* had to load up tapes on a machine copy
* loss of quality after each copy made
* had to load up tapes on a machine copy
* loss of quality after each copy made
7
New cards
editing video now
* can easily move clips around
* no loss of quality
* slight compression occurs in the camcorder when the video is captured
* no loss of quality
* slight compression occurs in the camcorder when the video is captured
8
New cards
pre 1967
camcorders were not portable
9
New cards
1967
Sony came up with black and white camcorder (it was big)
10
New cards
1971
first cassettes
11
New cards
1982
combine videos, sound, recording and playback (camera recorder)
12
New cards
2001
most camcorders record at 5fps
13
New cards
2019
iPhoneX records 4k at 60fps
14
New cards
things to think about before exporting video
where?
* on the web compression is important
* on CD playback speed is an issue
* DVD video must be in mpeg2 format
who?
* will they be on different platforms
* how old will their computer be
why?
* videos have a lot of stuff (colour, sound, motion, etc…)
* 1 second video could be 133MB without compression
* on the web compression is important
* on CD playback speed is an issue
* DVD video must be in mpeg2 format
who?
* will they be on different platforms
* how old will their computer be
why?
* videos have a lot of stuff (colour, sound, motion, etc…)
* 1 second video could be 133MB without compression
15
New cards
data and bit rate
* amount of video processed per second
* average bitrate = file size/length in seconds of video
* normally measured in bit (Mb = megabit and MB = megabytes)
* average bitrate = file size/length in seconds of video
* normally measured in bit (Mb = megabit and MB = megabytes)
16
New cards
compression: lower frame size
change the frame size for each frame in the video
17
New cards
compression: lower frame rate
* hold the frame on the page for longer
* depends on the type of video (not good for high action)
* depends on the type of video (not good for high action)
18
New cards
compression: pick a codec that does higher compression
codec: coder/decoder
* compression decompression software
* compresses a video or audio as it is created
* decompresses the video or audio as it is displayed to the user
* YouTube uses H.264
* often relates to file format
* sometimes can’t get a video if you don’t have to right codec
* compression decompression software
* compresses a video or audio as it is created
* decompresses the video or audio as it is displayed to the user
* YouTube uses H.264
* often relates to file format
* sometimes can’t get a video if you don’t have to right codec
19
New cards
compression: lower picture quality
can be done with a codec
20
New cards
compression: lower the colour depth
* not popular because video looks best in 24 bit colour
* some compressors won’t compress colour
* some compressors won’t compress colour
21
New cards
compression: play with the audio
not super helpful
22
New cards
spatial compression
* compresses each frame individually
* same are JPG compression
* same are JPG compression
23
New cards
temporal compression (e.g., H.264)
* only saves info on keyframes
* all other frames just save the differences from the previous keyframe
* good when the difference between current frame and keyframe is small
* all other frames just save the differences from the previous keyframe
* good when the difference between current frame and keyframe is small
24
New cards
lossy vs lossless compression (depends on codec)
lossless:
* looks for large blocks that are the saem and do run length encoding (RLE)
lossy:
* lower video quality but get better file size and bitrate
* looks for large blocks that are the saem and do run length encoding (RLE)
lossy:
* lower video quality but get better file size and bitrate
25
New cards
html5 (2008)
* a new standard for the html in web pages
* includes a way to watch video on a website that does not require a plug-in
* supports MP4, WebM, and Ogg (not Flash)
* goal was good, royalty free compression that handles hardware issues
* includes a way to watch video on a website that does not require a plug-in
* supports MP4, WebM, and Ogg (not Flash)
* goal was good, royalty free compression that handles hardware issues
26
New cards
Ogg, WebM, and MP4
* originally wanted to use codec .ogg but Apple didn’t want it
* WebM another royalty free file format used by Google and YouTube
* Apple and Microsoft use H.264 which creates .mp4 files
* WebM another royalty free file format used by Google and YouTube
* Apple and Microsoft use H.264 which creates .mp4 files
27
New cards
how to add video in html5
*
28
New cards
soft vs hard subtitles
hard: embedded in the video and cannot be turned on/off
soft: stored in a separate file and can be turned on/off (.vtt files)
soft: stored in a separate file and can be turned on/off (.vtt files)
29
New cards
downloading video on the web
* used to be the only option for viewing video
* progressive download: start watching the video as soon as it has enough bits to stay ahead of the download
* data is sent to be permanently stored on the machine
* progressive download: start watching the video as soon as it has enough bits to stay ahead of the download
* data is sent to be permanently stored on the machine
30
New cards
streaming video on the web
true streaming
* file is never permanently on the hard drive and plays as soon as it gets enough packets to stay ahead
* not as high quality video
* don’t have to wait for download
* uses buffering: download speed depends on bandwidth
* unicast: each user gets their own stream of video
* multicast: sends the same stream but people can’t pause
* file is never permanently on the hard drive and plays as soon as it gets enough packets to stay ahead
* not as high quality video
* don’t have to wait for download
* uses buffering: download speed depends on bandwidth
* unicast: each user gets their own stream of video
* multicast: sends the same stream but people can’t pause
31
New cards
adaptive streaming
* when you upload a 4k video to YouTube, it makes several quality versions of it
* if the viewer picks “auto” it will select the best quality video depending on the current bandwidth
* people find buffer much more annoying than low quality
* if the viewer picks “auto” it will select the best quality video depending on the current bandwidth
* people find buffer much more annoying than low quality
32
New cards
YouTube and adaptive streaming
* accepts several video formats
* uses many codecs, but mostly H.264
* convert every video into .mp4
* always compresses your video so it’s bets to always upload your highest quality video (but it’ll take a while)
* uses many codecs, but mostly H.264
* convert every video into .mp4
* always compresses your video so it’s bets to always upload your highest quality video (but it’ll take a while)
33
New cards
bitrate and quality
* going from 1080p to 4k will not always improve quality
* the video with the least compression will have the best quality
* over 75% of videos are viewed on phones
* smartphones are capable of recording in 4k but cannot display in 4k (not enough pixels)
* the video with the least compression will have the best quality
* over 75% of videos are viewed on phones
* smartphones are capable of recording in 4k but cannot display in 4k (not enough pixels)