Chapter 5: Form Perception
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
bottom up processing
physical stimuli influence how we perceive them
ex. eyes detect a reflected long wavelength and we see it as red
top down processing
existing knowledge of objects influences how we perceive them
ex. perceive a rose because we know roses are red and have this specific shape
recognition
ability to match a presented item with an item in memory
representation
storage and/or reconstruction of information in memory when the information isn’t actively being used
perceptual organisation
objects in our environment are grouped so we can identify multiple objects in complex scenes
allows us to separate similarly shaped objects like books vs bricks
grouping
elements are brought together in common unit
segregation
distinguishing 2 objects as distinct
figure-ground organisation
divide world in 2 parts: foreground (object of interest) and background
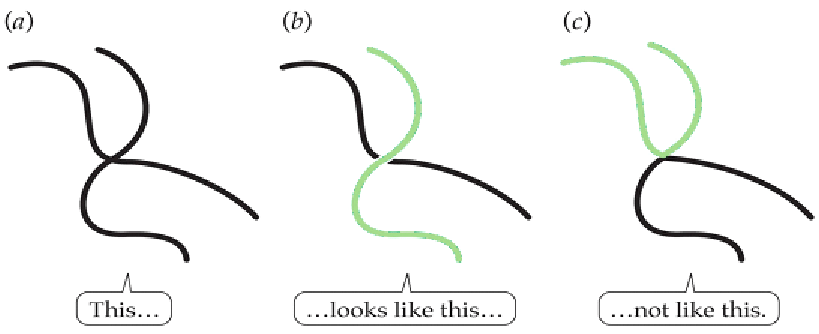
law of good continuation
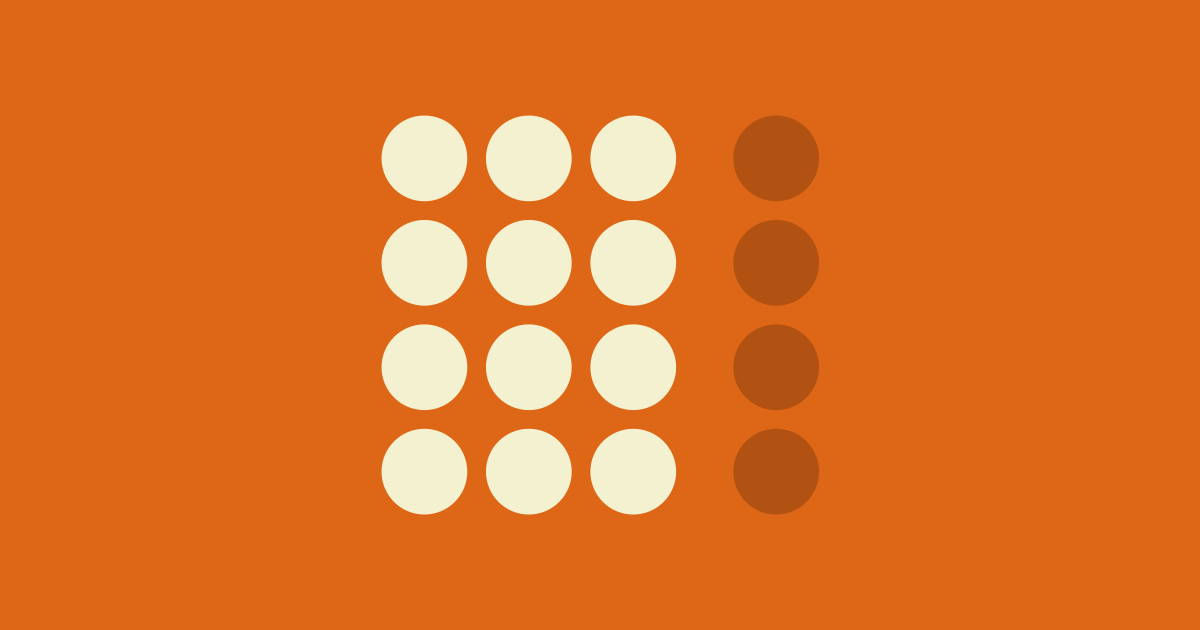
law of proximity

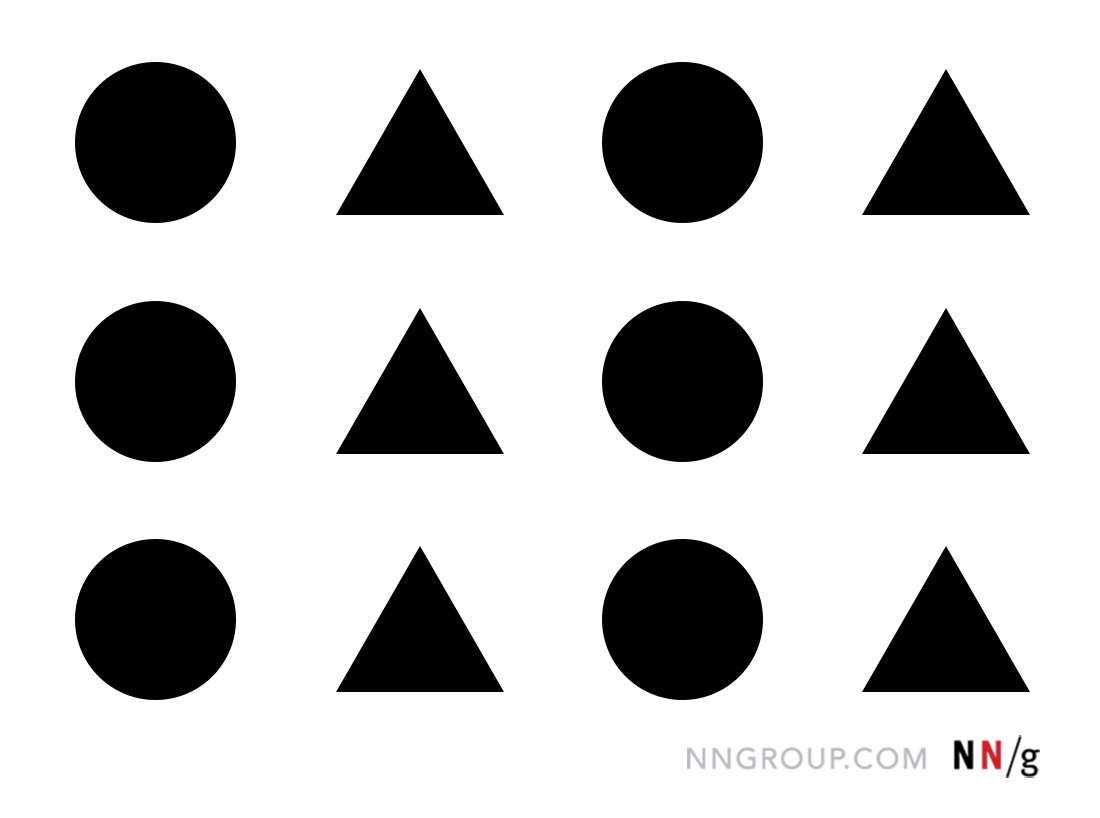
law of similarity
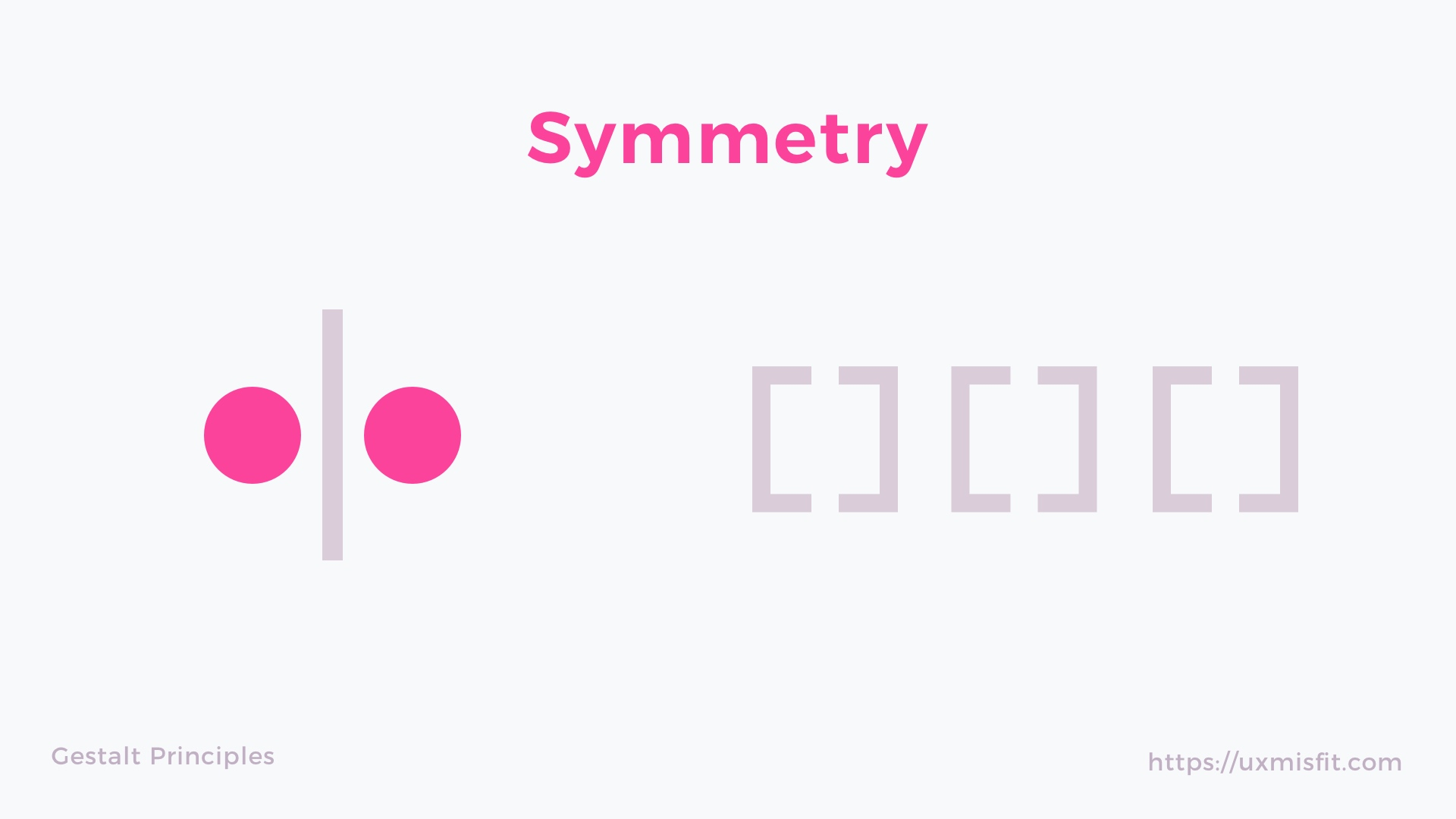
law of symmetry
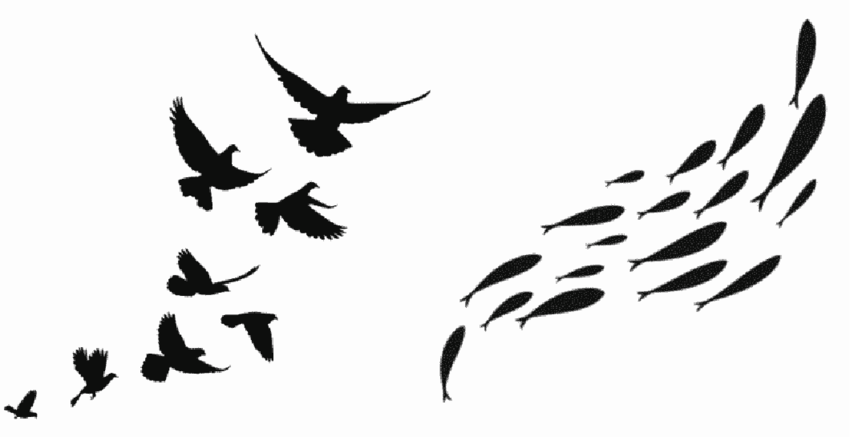
law of common fate

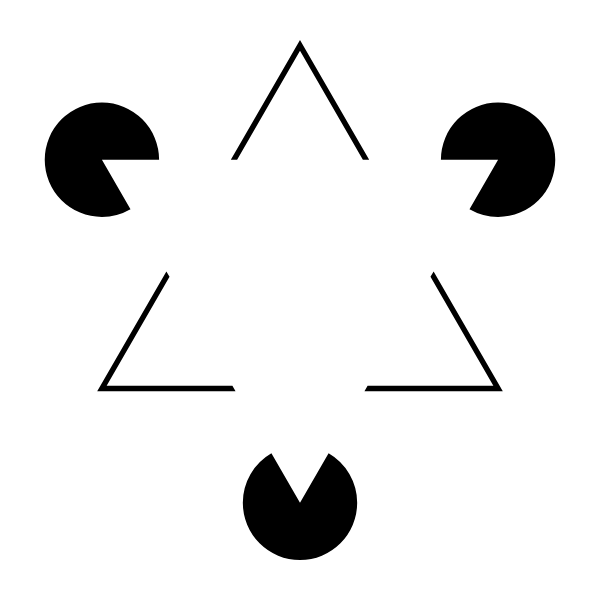
edge completion (closure)
creates illusory contours
geons
basic units of objects
simple shapes like pyramids and cylinders
recognition by component theory
object recognition occurs by representing each object as a combination of basic units (geons) that make up an object
viewpoint invariance
perception of an object doesn’t change when we look at it from different angles
V4
area of brain concerned with colour vision and shape perception
inferotemporal area
area of the temporal lobe involved in object perception
gets input from v4
fusiform face area
in inferotemporal area
recognises familiar faces
occipital face area
recognises faces as distinct from other objects
Parahippocampal place area PPA
inferotemporal cortex
scene recognition
topographic agnosia
can’t recognise spatial landscapes
damage to parahippocampal place area
extrastriate body area
inferotemporal cortex
activated when its cells view bodies or body parts but not faces
dull target cost
as the # of objects searched for increases, the likelihood of detecting one of those objects decreases
→ we stop looking once we’ve found the first
issue for cancer readings