AP Chem
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
If given grams and asked for moles,
Divide grams by molar mass.
If given moles and asked for molecules,
Multiply moles by Avogadro's number.
If asked to identify an element from average atomic mass,
Pick the element closest to that amu value on the periodic table.
If given percent composition and asked for empirical formula,
Assume 100g, convert % to grams, divide by molar mass for moles, divide by smallest mole value, and round to whole numbers.
If asked why different samples of a compound have the same element ratios,
Use the Law of Definite Proportions — same mass ratio in all samples.
If given the percent of a component in a mixture and asked for percent of the pure compound,
Divide the mixture component's percent by the pure compound's percent composition, then multiply by 100.
If asked for number of valence electrons,
Count electrons in outermost s and p orbitals based on group number for groups 1, 2, 13-18.
If asked which electrons are removed first when forming cations,
Then refer to outermost s and p orbitals first, then from d orbitals.
If asked to compare force between charged particles,
Greater charge = stronger force, greater distance = weaker force
If asked what the height of a peak represents,
It's the number of electrons in that sublevel.
If asked to identify an element from PES data,
Add up the electrons and match to electron configuration.
If asked about binding energy,
Higher binding energy = electrons are closer to the nucleus (core electrons).
If asked to rank ionization energy or electronegativity,
Increase across a period (left to right) and decrease down a group.
If asked to rank atomic radius,
Decrease across a period and increase down a group.
If asked why atomic trends occur,
Across a period: higher effective nuclear charge. Down a group: greater distance between nucleus and valence electrons.
If asked to compare sizes of ions,
Cations are smaller, anions are larger (due to electron-proton ratio and repulsion).
If asked how an ionic compound forms,
Metals lose electrons to form cations, nonmetals gain electrons to form anions, and opposites attract.
If asked whether a molecule has a dipole moment,
Check for polar bonds and asymmetric shape; if both, it has a net dipole.
If asked to rank bond polarity,
Compare electronegativities — if difference is ≥ 0.5, bond is polar.
If asked to rank bond polarity,
Greater electronegativity difference = more polar bond.
If asked to compare bond strength or bond enthalpy,
Triple > Double > Single.
If asked to compare bond length,
Triple < Double < Single.
Ionic
high melting point, brittle, conducts when molten or aqueous
Covalent Network
very high melting point, hard, non-conductive
Metallic
conductive, malleable, ductile, variable melting points
Molecular
low melting point, soft, non-conductive
If asked while solute will dissolve in a solvent
Use “like dissolves like” — polar dissolves polar, nonpolar dissolves nonpolar
If asked if a particle diagram is correct for a balanced reaction
Check that it satisfies the mole ratios from the balanced chemical equation.
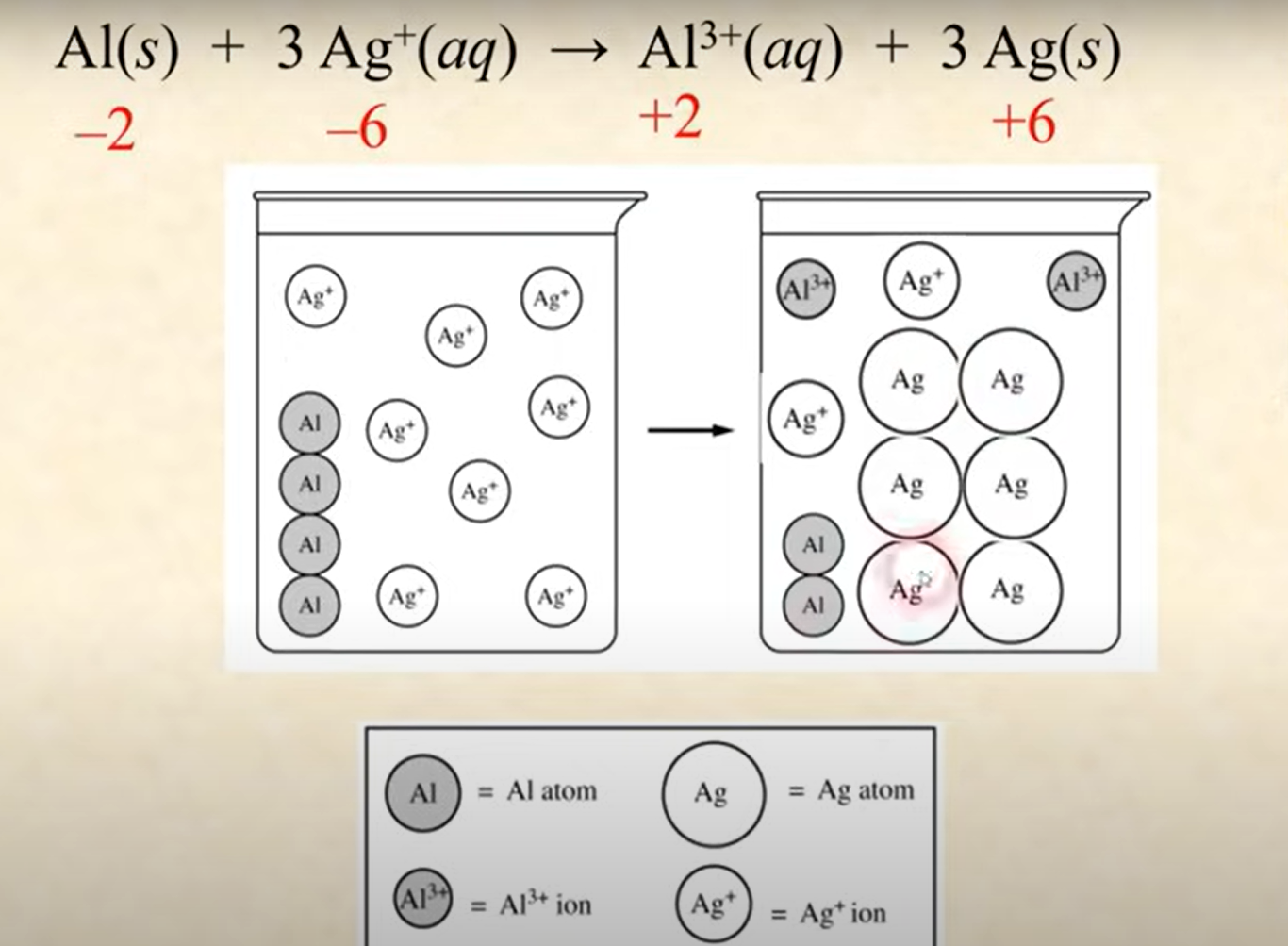
If asked to identify the limiting reactant,
Convert given amounts of each reactant to moles of product, whichever makes less product is limiting.
If asked how much of a product forms in a reaction,
Use mole ratios from balanced equation to convert from moles of limiting reactant to moles of product.
If asked how much of an excess reactant remains,
Convert limiting reactant to moles of excess used (via mole ratio), subtract from initial moles of excess reactant.
If asked to find gas volume at certain conditions,
Use PV = nRT to solve for V when given moles, pressure, and temperature.
If asked what the endpoint of a titration is,
It’s when moles of acid = moles of base (or vice versa) according to balanced equation
If asked about the effect of a reactant’s concentration a in terms of kinetics
Then state that the frequency of collisions.
If asked what temperature effects in terms of kinetics
Then state that the activation energy and the rate constant
If you mix two different solutions and desire the concentration of the molecule present in both solutions
Then find the moles of each compound with desired molecule, with respect to mole ratio, then divide by total volume
If asked for the rate constant from a graph of [A], ln[A], or 1/[A]
Then state the absolute value of the slope is the rate constant, k.
If asked to identify intermediates in a reaction mechanism,
Intermediates appear as products first, then as reactants in a later step.
If asked to identify catalysts in a reaction mechanism,
Catalysts appear as reactants first, then as products in a later step.
If asked to identify the rate-determining step in an energy profile diagram,
The slow step is the one associated with the highest peak (activation energy barrier) on the energy profile.
If asked whether the temperature change is high or low during heat transfer
Use q = mcΔT and remember that a larger mc value = larger temperature change, and a lower mc value is a smaller temperature change
If asked how to calculate overall enthalpy change for a reaction using multiple steps
Manipulate given equations so reactants and products align with the target reaction, then add their ΔH values