Ap physics semester 1 ( unit 1 - 3) review
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All of these are predictions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What force causes centripetal motion for a car on a flat (unbanked) curve?
The force providing centripetal motion for a car on a flat (unbanked) curve is static friction between the tires and the road surface.
Max speed on a curve ( unbanked) without skidding ?
square root of (g* r* coefficient of static friction)
mass does not determine if the car skids. all that determines it is radius and and coefficient of friction
On a frictionless banked curve, what provides the centripetal force?
normal force * sinθ
Equation for frictionless banked curve?
normal force = mg* cosθ
fc=(Fn)*cosθ
v=square root of ( r*g*tan θ)
Conceptual question for frictionless banked curve?
If you speed up, in what direction will you head ? You will go up the rampIf you speed up, in which direction will you head? You will go up the ramp.
If you slow down, in which direction will you head? You will go down the ramp.
If you speed up on a frictional banked curve, in which direction is friction pointing? Down the ramp.
If you slow down on a frictional banked curve, in which direction is friction pointing? Up the ramp.
Horizontal string question?
velocity = 2πR/T tension = Mv²/r
speed increases but radius remains the same - tension will increase (vice versa
radius increase but spead remains the same - tension will decrease ( vise versa)
Vertical swinging block (algebraic equations )
At the top of the circular motion, tension, mg, and fc all point down, so you set the equations (Fn + Mg = Mv² / r )
At the bottom of the circular motion, tension and Mv²/r points up, but mg points down, so you set the equation ( T - mg = Mv²/r)
Vertical swinging block ( conceptual questions )
At which point is tension the greatest? the bottom
At which point is tension the smallest? At the top ,
minimum speed at the top to keep swinging? square root of g*r
Mass On Table + String Through A Hole
M1 = mass hanging; M2 = mass moving in circular motion on a table
. Find the tension? M1*g = M2*v²/r
. You can also you that equation to find: radius, masses, and velocity
it is the only equation to memorize in these scenarios, and most of the time it is in equilibrium
Conical Pendulum ( Algebraic equations )
radius = length sinθ velocity = squarer root of ( R*G*tan θ )
tension = Mg/cosθ centripetal force = mg*tan θ = mv²/r
2πr/( velocity )
Conical Pendulum ( conceptual question)
Horizontal component of tension = centripetal force
Vertical component of tension balances weight
Centripetal force is not a separate force
Mass often cancels in calculations
Increasing θ → increases radius, speed, tension
Period increases with radius
Tension always points along the string
2 vehicles crash with different masses, what force do they exert on each other?
Will always be equal. but for frq explanation “ newtons third law” as there mass are different but so are their accelerations due to that. so when they crash their force will be the same.
Maximum static friction on an incline
θmax = tan-1 (μs)
If you push the bottom box and there’s another box on top, what is the same?
Both boxes will have the same acceleration but different forces
To calculate the maximum acceleration, the top box can experience before sliding, the equation is: μsg
1 D motion equations
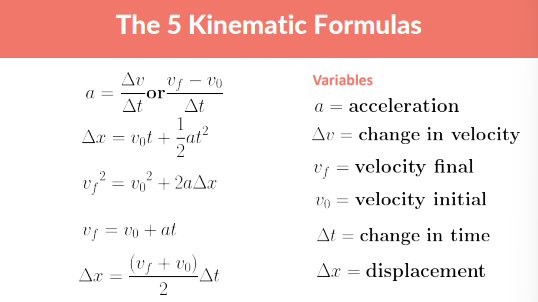
1 D motion Uniform motion position over time
slope if 0: the person is not moving
slope is positive: they are moving, positive velocity, and 0 acceleration,
slope is negative: they are moving, negative velocity, and 0 acceleration
Position vs. Time graph: Curvature indicates changing slope → velocity is changing → acceleration ≠ 0.
Direction of acceleration: If the curve is concave up → acceleration is positive; if concave down → acceleration is negative.