Nucleotide Metabolism Exam 1 BioC
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
What are the 2 ways that nucleotides can be synthesized?
De novo or by salvage pathways
If nucleotides are synthesized de novo then they are derived from?
simple precursors such as amino acids
If nucleotides are synthesized via salvage pathways they are derived from?
recovered nitrogenous bases attached to an activated ribose (PRPP)
What does PRPP stand for?
phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate
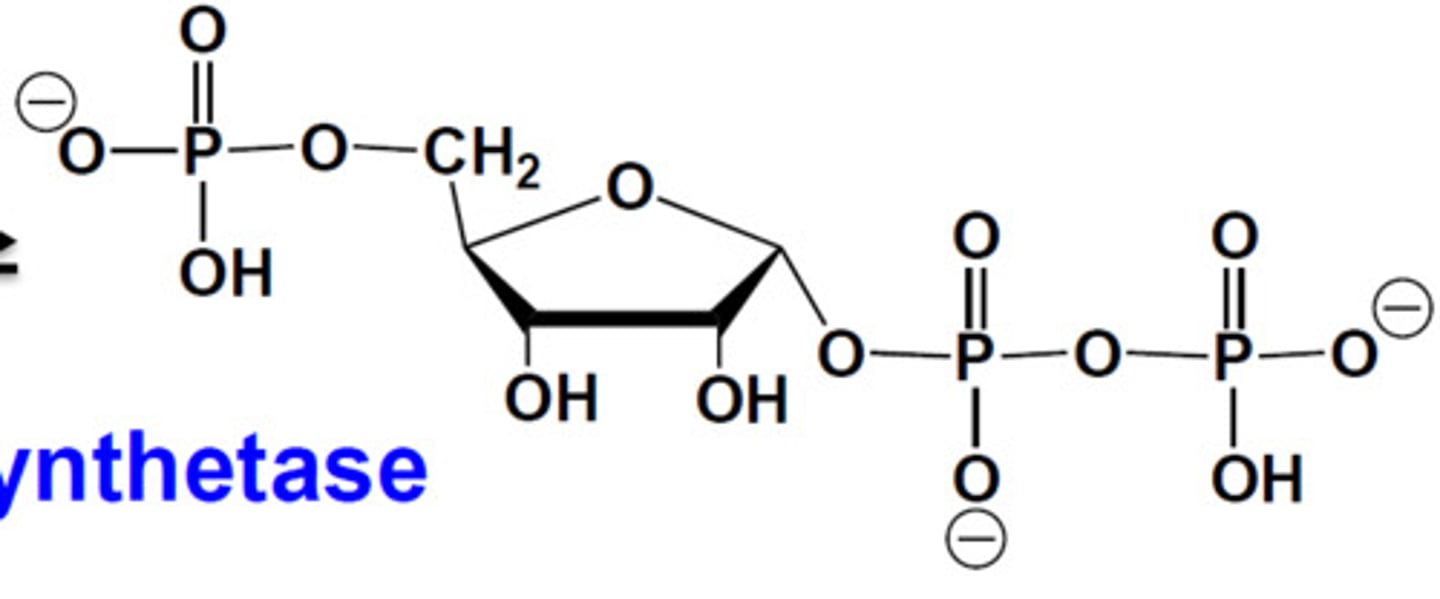
What are the 3 precursors of the pyrimidine ring?
bicarbonate, NH3 and aspartate
What are the precursors of the purine ring?
glycine, glutamine, aspartate, CO2 and tetrahydrofolate
What molecule are purines synthesized on in the de novo pathway?
A. phosphate
B. deoxyribose
C. ribose
D. ribonucleotide
C. ribose
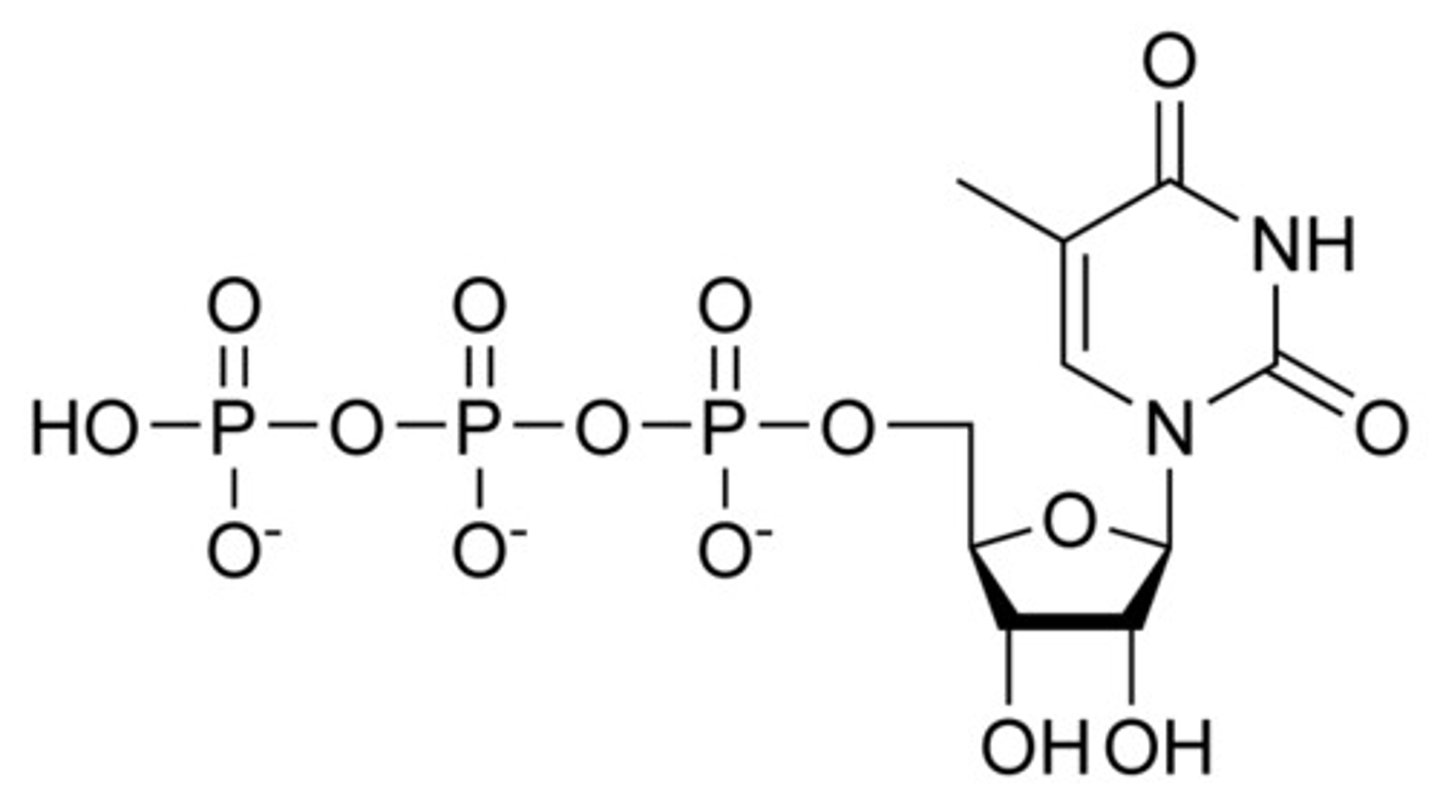
If UTP is methylated it turns into what?
TTP
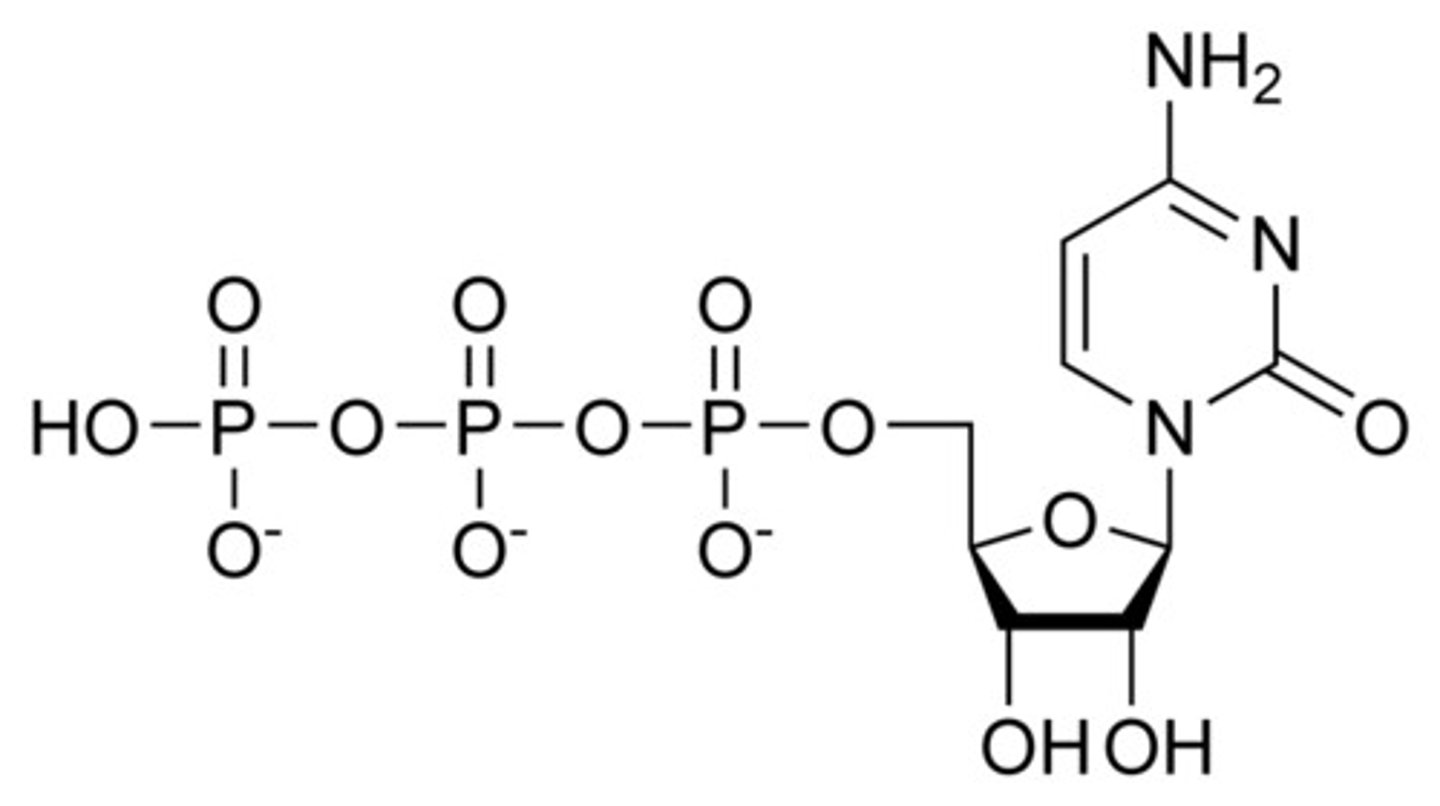
If UTP gets aminated it turns into what?
CTP
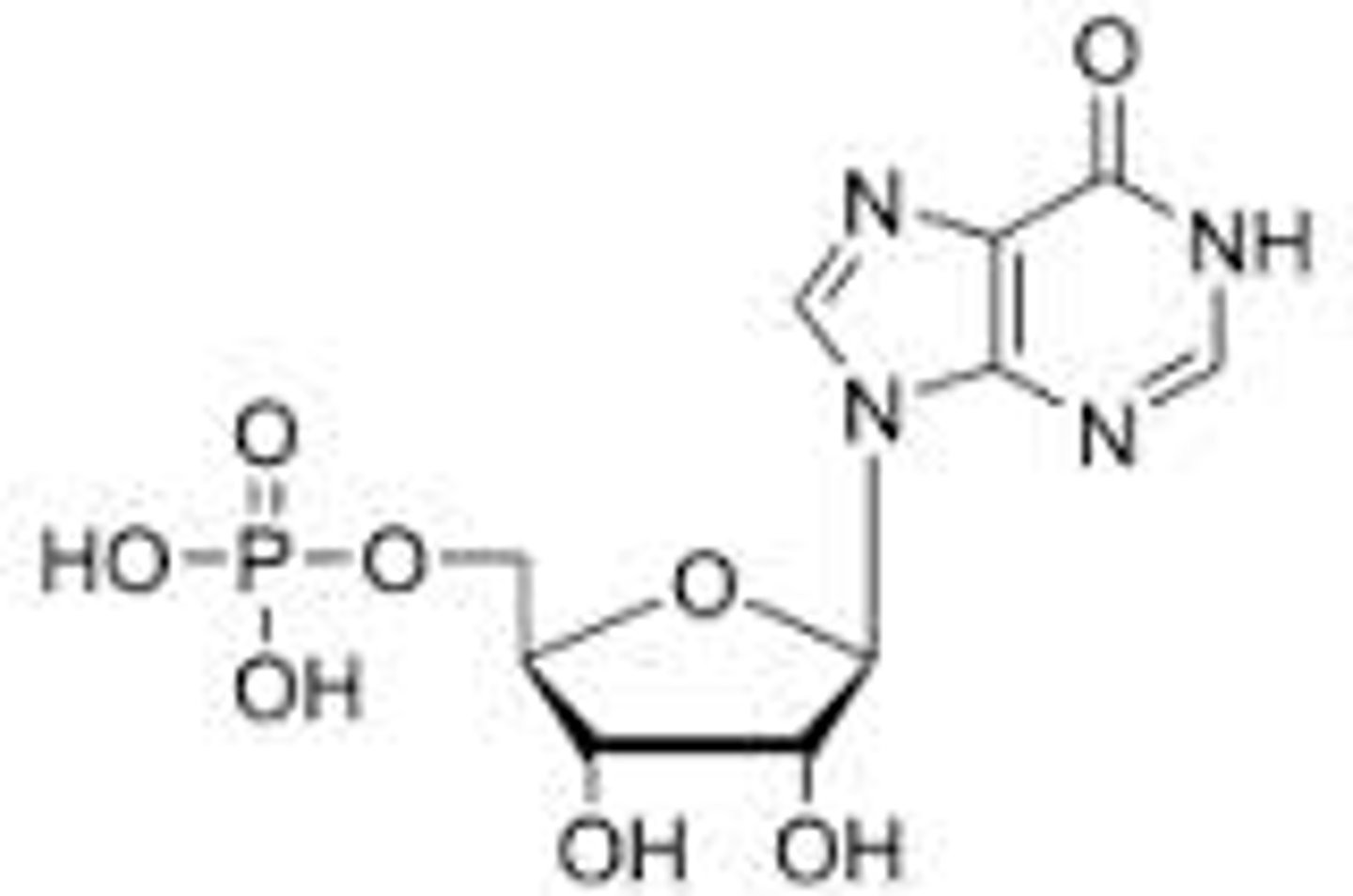
What is the product of 5-phosphoriobsyl-1-amine after nine steps in the de novo purine biosynthesis?
IMP (inosinate)
IMP can be converted into ____ and ____ for RNA and then turned into ____ and ____ for DNA
ATP and GTP; dATP and dGTP
In the de novo pathway purines are synthesized on a ____ molecule
ribose
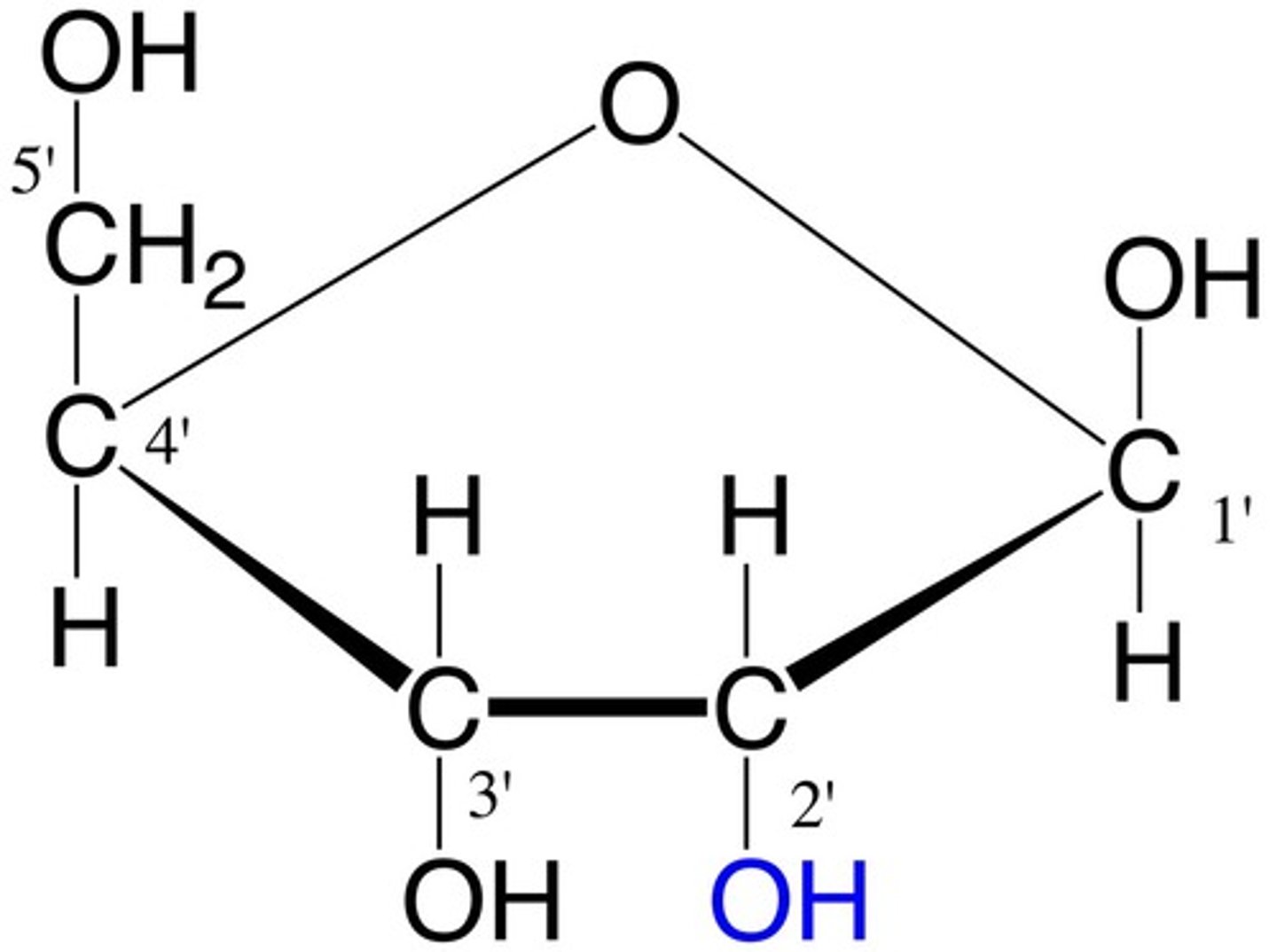
What enzyme catalyzes the reaction of PRPP and glutamine into 5-phsophoribosyl-1amine?
glutamine phosphoribosyl amidotransferase
What is the leaving group when 5-phosphoribosyl-1-amine forms from PRPP and glutamine?
PPi (pyrophosphate)
How many steps does it take to convert 5-phosphoribosyl-1-amine into IMP (inosine monophosphate)?
9
IMP is converted into ____ and ____
AMP and GMP
IMP is converted into adenylate (AMP) in a pathway that requires:
A. GMP
B. GTP
C.AMP
D.ATP
B. GTP
IMP is also metabolized to guanosine monophosphate (GMP or guanylate) in a pathway that requires:
A. GMP
B. GTP
C.AMP
D.ATP
D.ATP
What amino acid is used to convert IMP to AMP?
A. D
B. G
C. E
D. Q
E. A
A. D ... Asp Aspartate
What amino acid is used to convert IMP to GMP?
A. D
B. G
C. E
D. Q
E. A
D. Q Gln Glutamine
What are the 2 salvage enzymes that recycle purine bases?
APRT (adenine phosphoribosyl transferase) and HGPRT (hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase)
In the regulation of purine biosynthesis what 3 end products inhibit the enzyme glutamine-PRPP amidotransferase?
IMP, AMP and GMP
What does excess GMP inhibit?
It inhibits IMP dehydrogenase which inhibits the formation of xanthylate
What is PRPP synthesis inhibited by?
ADP and GDP
What is formed in the first step in the pyrimidine synthesis that consists of a 3-step reaction?
carbamoyl phosphate
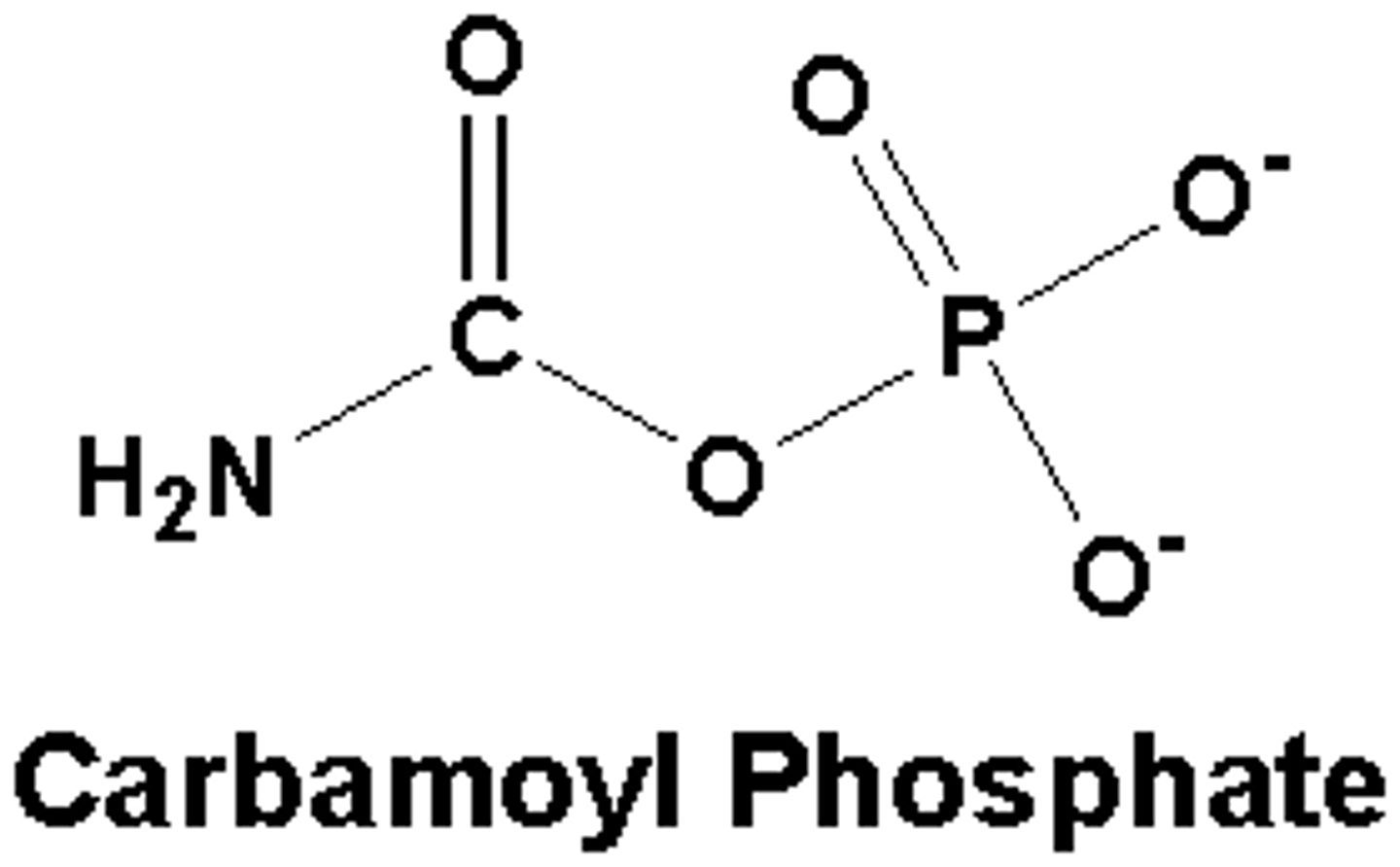
What enzyme catalyzes bicarbonate to carbamoyl phosphate?
carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II (CPS II)
Carbamoyl phosphate reacts with aspartate to form carbamoylaspartate and is catalyzed by what enzyme?
A. carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II
B. PRPP synthetase
C. aspartate transcarbamolyase (ATCase)
D. carbamoyl synthetase
C. aspartate transcarbamolyase (ATCase)
What is the key regulatory enzyme in pyrimidine synthesis?
A. PRPP synthetase
B. aspartate transcarbamolyase (ATCase)
C. glutamine-PRPP amidotransferase
D. Ribonucleotide reductase
B. aspartate transcarbamolyase (ATCase)
Carbamoylasparate is metabolized to what?
orotate
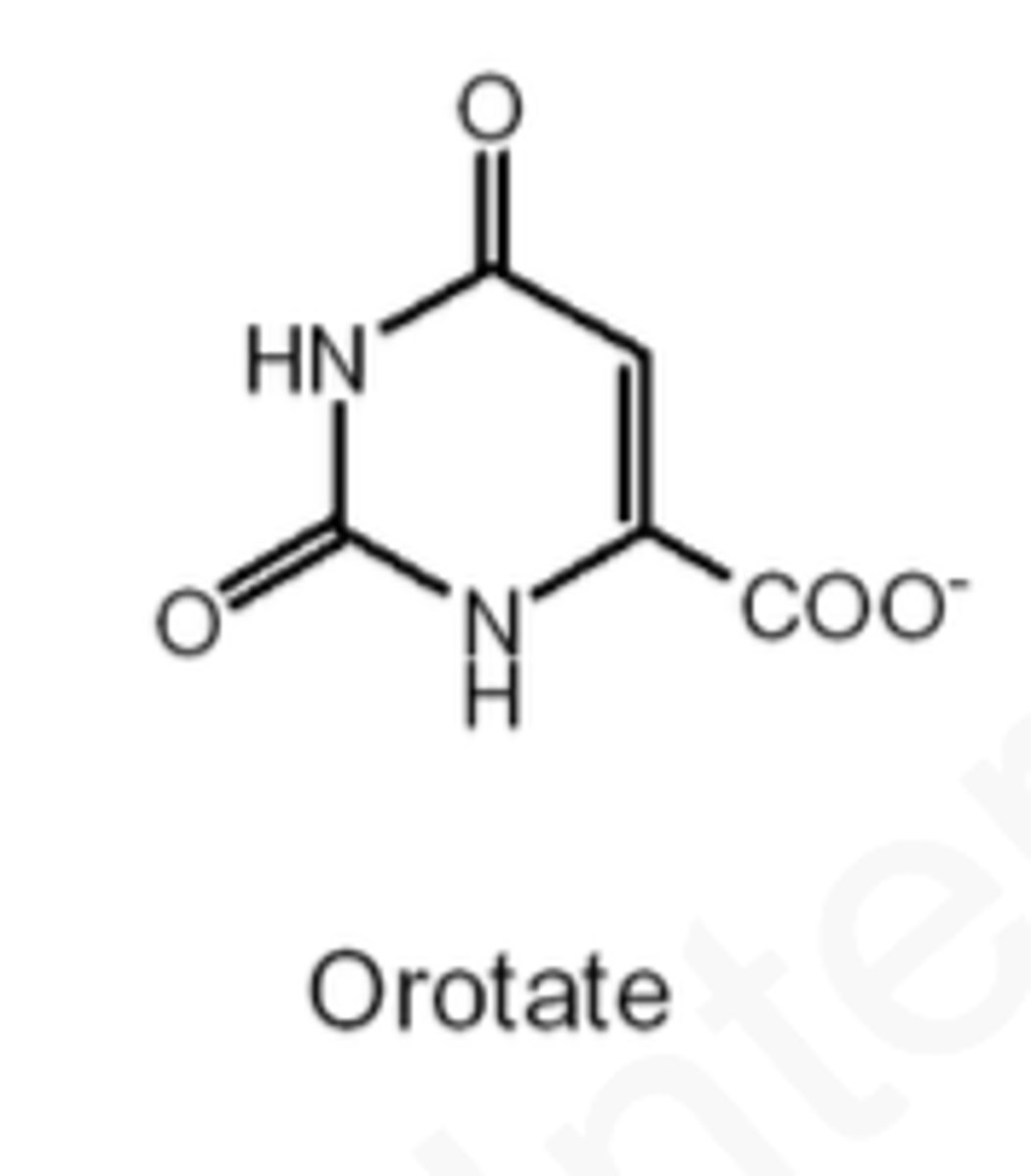
What is the intermediate molecule of carbamoylasparate and orotate?
dihydroorotate
Orotate reacts with PRPP to form what?
orotidylate
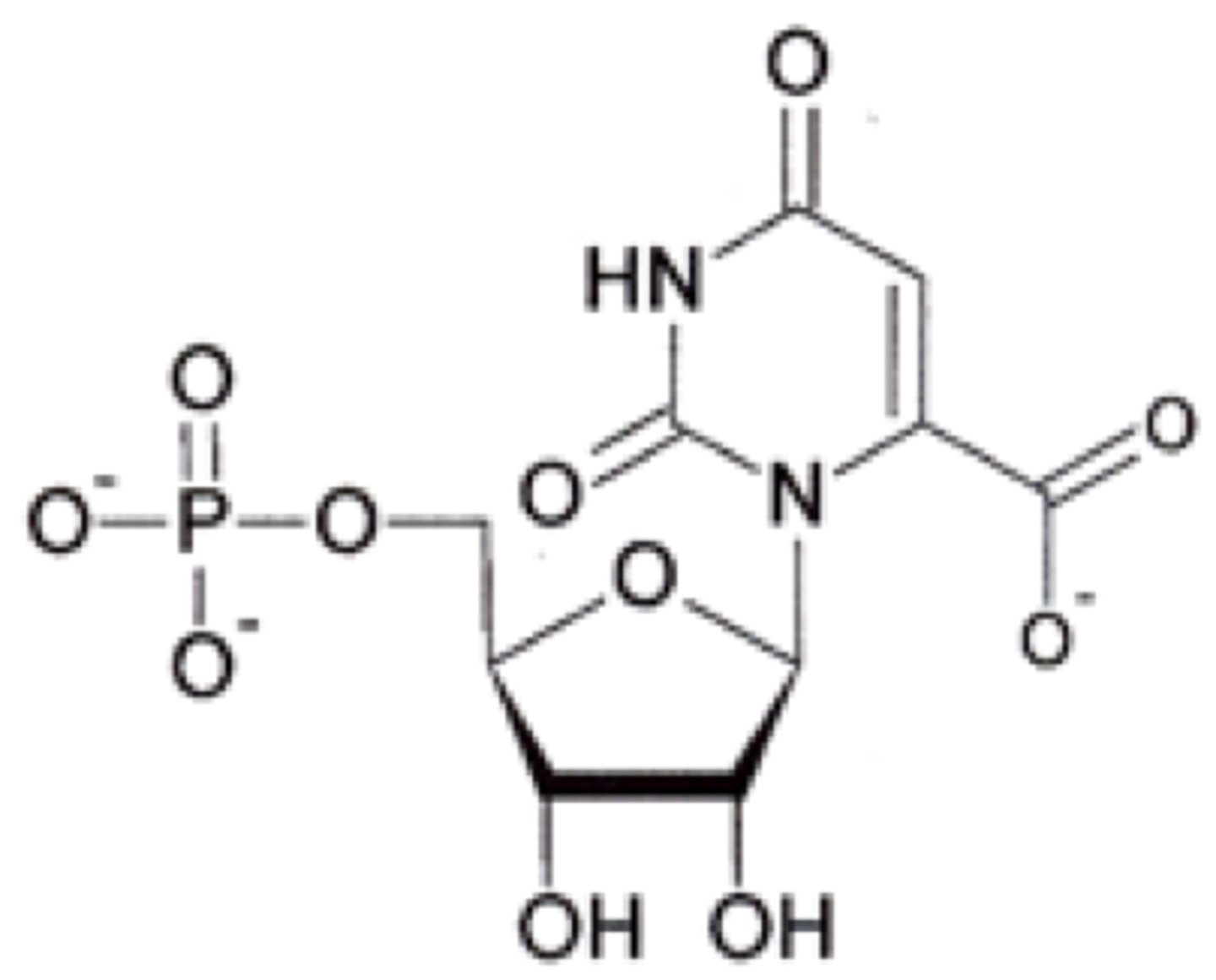
What is the leaving group when orotate reacts with PRPP to form OMP (orotidylate)?
PPi
Orotidylate is converted to uridylate (OMP to UMP) by what enzyme?
orotidylate decarboxylase
UMP is converted to UDP and UTP via what type of enzyme?
kinases because they add phosphates
What type of enzymes remove phosphates?
phosphatases
What enzyme catalyzes UTP to CTP?
Cytidylate synthetase
Rising levels of CTP inhibits what enzyme?
A. carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II
B. cytidylate synthetase
C. ACTase
D. PRPP synthetase
C. ACTase
What amino acid provides the amino group for the replacement of the carbonyl group with an amino group of UTP to CTP?
A. D
B. E
C. Q
D. N
E. R
C. Q, Gln Glutamine
What enzyme incorporates the salvaged thymine into a nucleoside thymidine?
thymidine phosphorylase
What enzyme generates the nucleotide of thymidine?
thymidine kinase
Ribonucleotides are precursors to deoxynucleotides how?
The 2' carbon of the sugar is reduced from OH to H (ribose to deoxyribose)
What enzyme catalyzes the reduction of ADP to dADP?
ribonucleotide reductase converts ribonucleotides to deoxynucleotides (NDP -> dNDP)
Oxidation is the addition of _____ atom, the loss of _____ and the removal of ___.
Oxygen; electrons; H+
Reduction is the removal of _____ atom, the addition of _____ and the gain of _____
Oxygen; H+; electrons
What is the amino acid attached to ribonucleotide reductase that become oxidized when the reduction ribonucleotides to deoxynucleotides takes place?
cysteine (thiol) -SH oxidized to S-S
What is the enzyme that catalyzes dCTP to dUTP?
A. ribonucleotide reductase
B. deaminase
C. thymidylate synthase
D. cytidylate synthetase
B. deaminase
What is the enzyme that catalyzes dCDP to dCTP and dUDP to dUTP?
A. nucleoside diphosphate kinase
B. ribonucleotide reductase
C. thymidylate synthase
D. PRPP synthase
A. nucleoside diphosphate kinase
What enzyme catalyzes dUTP to dUMP?
A. PRPP synthase
B. orotidylate decarboxylase
C. dUTPase
D. nucleoside diphosphate kinase
c. dUTPase
What enzyme catalyzes dUMP to dTMP?
A. dUTPase
B. thymidine kinase
C. thymidine phosphorylase
D. thymidylate synthase
D. thymidylate synthase
What is the enzyme that catalyzes tetrahydrofolate to N5, N10 -methylenetetrahydrofolate?
A. dihydrofolate reductase
B. tetrahydrofolate reductase
C. serine hydroxymethyl-transferase
D. thymidylate synthase
C. serine hydroxymethyl-transferase
What is the enzyme that catalyzes 7,8-dihydrofolate to tetrahydrofolate?
A. dihydrofolate reductase
B. tetrahydrofolate reductase
C. serine hydroxymethyl-transferase
D. thymidylate synthase
A. dihydrofolate reductase
Thymidylate is formed by the ____ of deoxyuridylate.
methylation
What enzyme catalyzes the reaction of IMP to adenylosuccinate?
A. adenylosuccinate ligase
B. adenylosuccinate lyase
C. adenylosuccinate synthetase
D. adenylosuccinate transferase
C. adenylosuccinate synthetase
Whay enzyme catalyzes the reaction of adenylosuccinate to adenylate?
A. adenylosuccinate synthetase
B. adenylosuccinate ligase
C. adenylosuccinate transferase
D. adenylosuccinate lyase
D. adenylosuccinate lyase
What enzyme catalyzes inosinate to xanthylate?
A. IMP transferase
B. IMP dehydrogenase
C. XMP-glutamine amidotransferase
D. XMP dehydrogenase
B. IMP dehydrogenase
What enzyme catalyzes xanthylate to guanylate?
A. GMP transferase
B. GMP dehydrogenase
C. XMP-glutamine amidotransferase
D. XMP dehydrogenase
C. XMP-glutamine amidotransferase
Write out of the name of CTP.
cytidine-5-triphosphate
Write out the name of GDP.
guanosine-5-diphosphate
Write out the name of ATP.
adenosine-5-triphosphate
What is the name of TMP also known as dTMP?
thymidylate or deoxythymidylate
What is the name of dAMP?
deoxyadenylate
What is the name of dCDP?
deoxycytidine-5-diphosphate
What is the name of CMP?
cytidylate or cytidine-5-monophosphate
What is A base name?
adenine
What is T base name?
thymine
What is C base name?
cytosine
Which base is strictly RNA?
Uracil (U)
Name the 4 ribonucleosides.
adenosine, guanosine, uridine, cytidine
Name the 5 nucleotides.
adenylate, guanylate, uridylate, cytidylate, thymidylate
What enzyme dephosphorylates guanylate to guanosine?
5'-nucleotidase (Mono ribonucleotide to nucleoside) (GMP to guanosine)
What enzyme dephosphorylates adenylate to adenosine?
5'-nucleotidase (Mono ribonucleotide to nucleoside) (AMP to adenosine)
Which enzyme catalyzes adenosine to inosine?
A. nucleosidase
B. adenosine deaminase
C. inosine deaminase
D. nucleotidase
B. adenine deaminase
What enzyme catalyzes inosine to hypoxanthine?
A. nucleosidase
B. adenosine deaminase
C. inosine deaminase
D. nucleotidase
A. nucleosidase
What enzyme catalyzes hypoxanthine to xanthine?
A. xanthine reductase
B. xanthine deaminase
C. xanthine oxidase
D. xanthine nucleotidase
C. Xanthine oxidase
What enzyme catalyzes guanine to xanthine?
A. guanine deaminase
B. guanine oxidase
C. guanine reductase
D. guanine nucleotidase
A. guanine deaminase
What enzyme catalyzes xanthine to uric acid?
A. xanthine reductase
B. uric acid reductase
C. xanthine oxidase
D. uric acid oxidase
C. xanthine oxidase
Which enzymes are used to in the production of uric acid from GMP? Select all the apply:
A. xanthine reductase
B. xanthine oxidase
C. guanine deaminase
D. nucleosidase
E. xanthine synthetase
B, C, D
Which statement is true of the biosynthetic pathway for purine nucleotides?
A. Inosinate is the purine nucleotide that is the precursor of both adenylate and guanylate.
B. Deoxyribonucleotides are formed from 5-phosphodeoxyribosyl 1-pyrophosphate.
C. The amino acid valine is one of the precursors contributing to purine nucleotides.
D. Orotidylate is an essential precursor for purine nucleotides.
E. CO2 does not participate in any of the steps in this pathway
A.
In purine biosynthesis, which contributes two of the ring nitrogen's?
A. aspartate
B. urea
C. glycine
D. asparagine
E. glutamine
E. glutamine
Precursors for the biosynthesis of the pyrimidine ring system include:
A. glycine and succinyl-CoA.
B. carbamoyl phosphate and aspartate.
C. glutamate, NH3, and CO2.
D. glutamine and aspartate.
E. glycine, glutamine, CO2, aspartate and tetrahydrofolate
B. carbamoyl phosphate and aspartate
The ribosyl phosphate moiety needed for the synthesis of orotidylate, inosinate, and guanylate is provided by:
A. guanosine 5'-phosphate.
B. cytosine 5'-phosphate.
C. ribulose 5-phosphate.
D. 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate.
E. ribose 5-phosphate.
D. PRPP
5-Fluorouracil is used for the treatment of cancer. It inhibits this enzyme
A. dihydrofolate reductase
B. thymidylate synthase
C. thymidylate phosphorylase
D. thymidylate kinase
B. thmidylate synthase
Glutamine is a nitrogen donor in the synthesis of:
A. inosinate.
B. dTTP.
C. UMP.
D. CTP.
E. orotate.
A. inosinate (IMP)
Which is the immediate precursor of thymidylate (dTMP)?
A. dUMP
B. dCTP
C. dGMP
D. dATP
E. UTP
A. dUMP
Which is the product of purine degradation in humans?
A. uric acid
B. succinate
C. urea
D. glutamate
E. NH4+
A. Uric acid
What is the direct precursor of uric acid in the catabolism of purines?
A. hypoxanthine
B. inosine
C. xanthine
E. xanthosine
C. xanthine
What is the enzyme that catalyzes the first step in thymine breakdown to dihydrothymine?
A. thymine dehydrogenase
B. dihydrothymine dehydrogenase
C. dihydrouracil dehydrogenase
D. uracil dehydrogenase
C. dihydrouracil dehydrogenase
What is the cofactor that is oxidized when dihydrouracil dehydrogenase reduces thymine to dihydrothymine?
A. NADH
B. NAD+
C. NADPH + H+
D. NADP+
E. FADH
C. NADPH + H+
Painful joints due to deposits of sodium urate crystals often in extremities like the toes is known as ______
Gout
The drug known as _____ is used to treat gout to prevent the formation of uric acid.
Allopurinol
What enzyme does Allopurinol inhibit?
A. hypoxanthine oxidase
B. xanthine reductase
C. hypoxanthine reductase
D. xanthine oxidase
D.
What human organ is especially dependent on salvage pathways?
The brain
What enzymes do the drugs azaserine and acivicin inhibit?
A. thymidylate synthase
B. dihydrofolate reductase
C. glutamine amidotransferases
D. cytidylate synthetase
C. glutamine amidotransferases
What drugs inhibit dihydrofolate reductase? Select all that apply:
A. Methotrexate
B. azaserine
C. aminopterin
D. acivicin
E. trimethoprim
A,C,E
What drug is converted into a molecule by the salvage pathway to inhibit thymidylate synthase?
A. Fluoroquinolones
B. Fluorouracil
C. Fluorine
D. Trimethoprim
B. Fluorouracil