QUIZ 2 STUDY GUIDE- EHDA
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
the function of the temperomandibular ligament
prevents excessive retraction or backward moving of the mandible
How to primary molar roots differ from permanent molars?
They are shorter, smaller, narrower, and flare out.
If a tooth has not erupted within three months of its contralateral sister tooth...
Efforts to diagnose should be made
What forms the TMJ?
An articulation between the temporal bone and the condyle of the mandible
articular eminence of temporal bone
Raised portion of the temporal bone just anterior to the glenoid fossa.
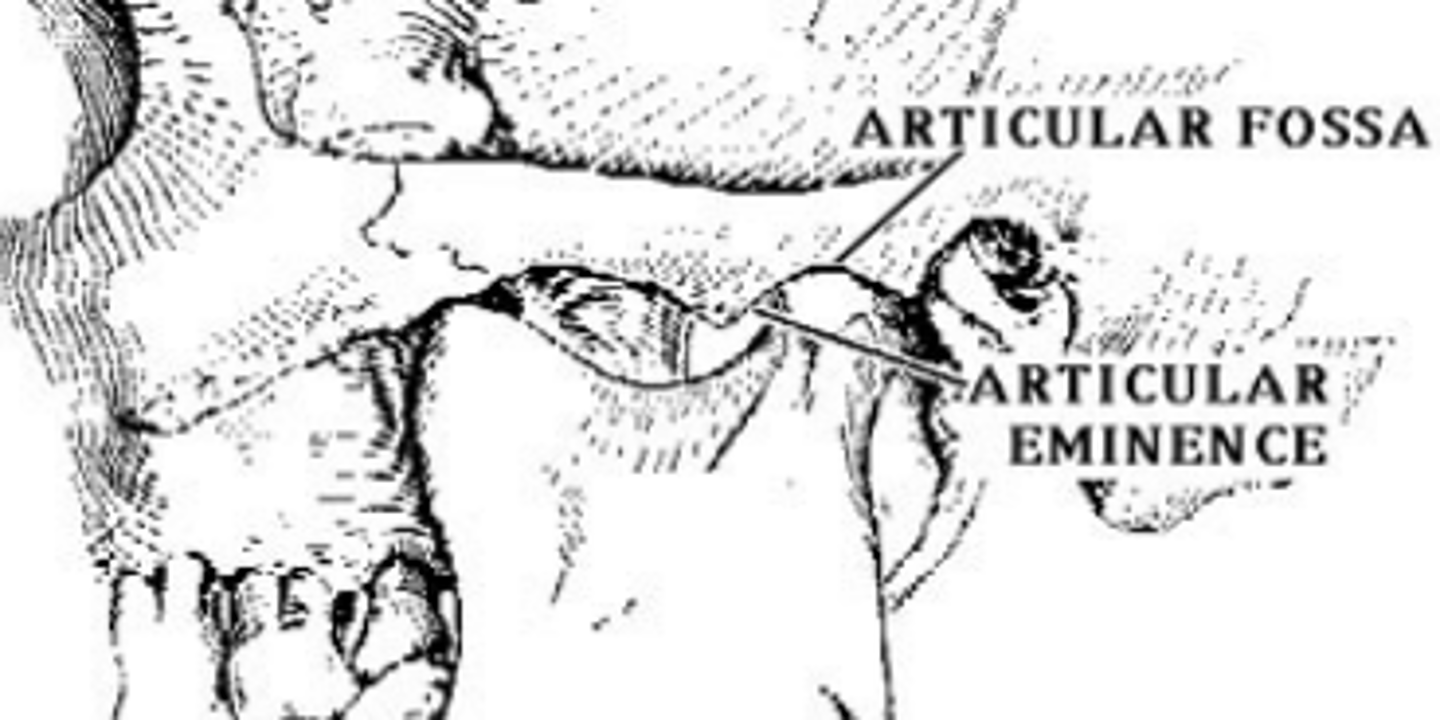
articular fossa of temporal bone
also called glenoid fossa: is posterior to the articular eminence
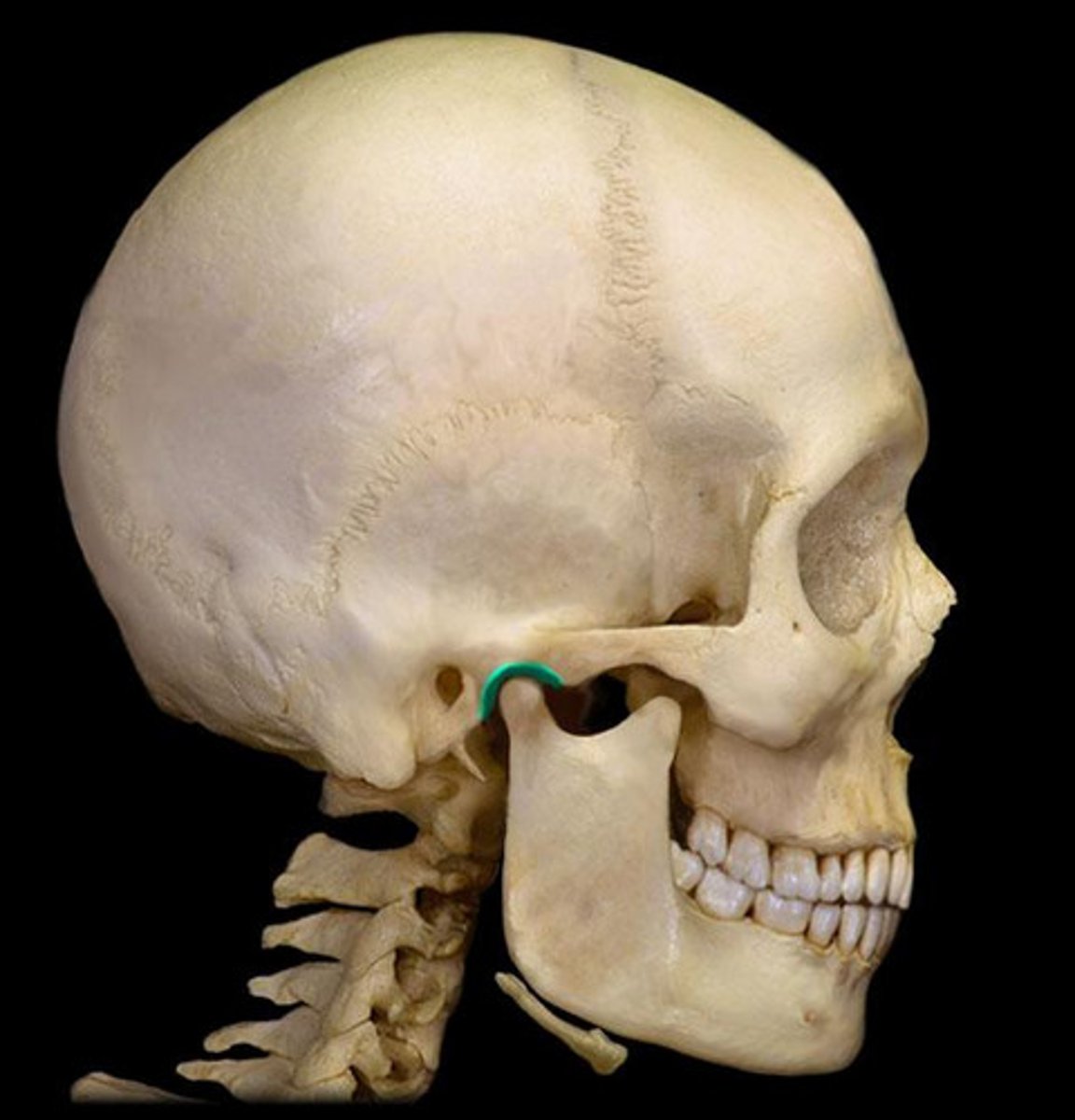
fibrous joint capsule
completely encloses the TMJ
what do the fibers of the inferior portion of the capsule do
they connect the condyle of the mandible to the articular disc
what does the upper portion of the fibrous capsule of the tmj do
it is looser and attaches the articular disc to the temporal bone
where does the articular disc get its nourishment
the synovial fluid that the surrounding cells exctrete
What is synovial fluid?
Lubricates and nourishes the cartilage covering the bones at movable joints
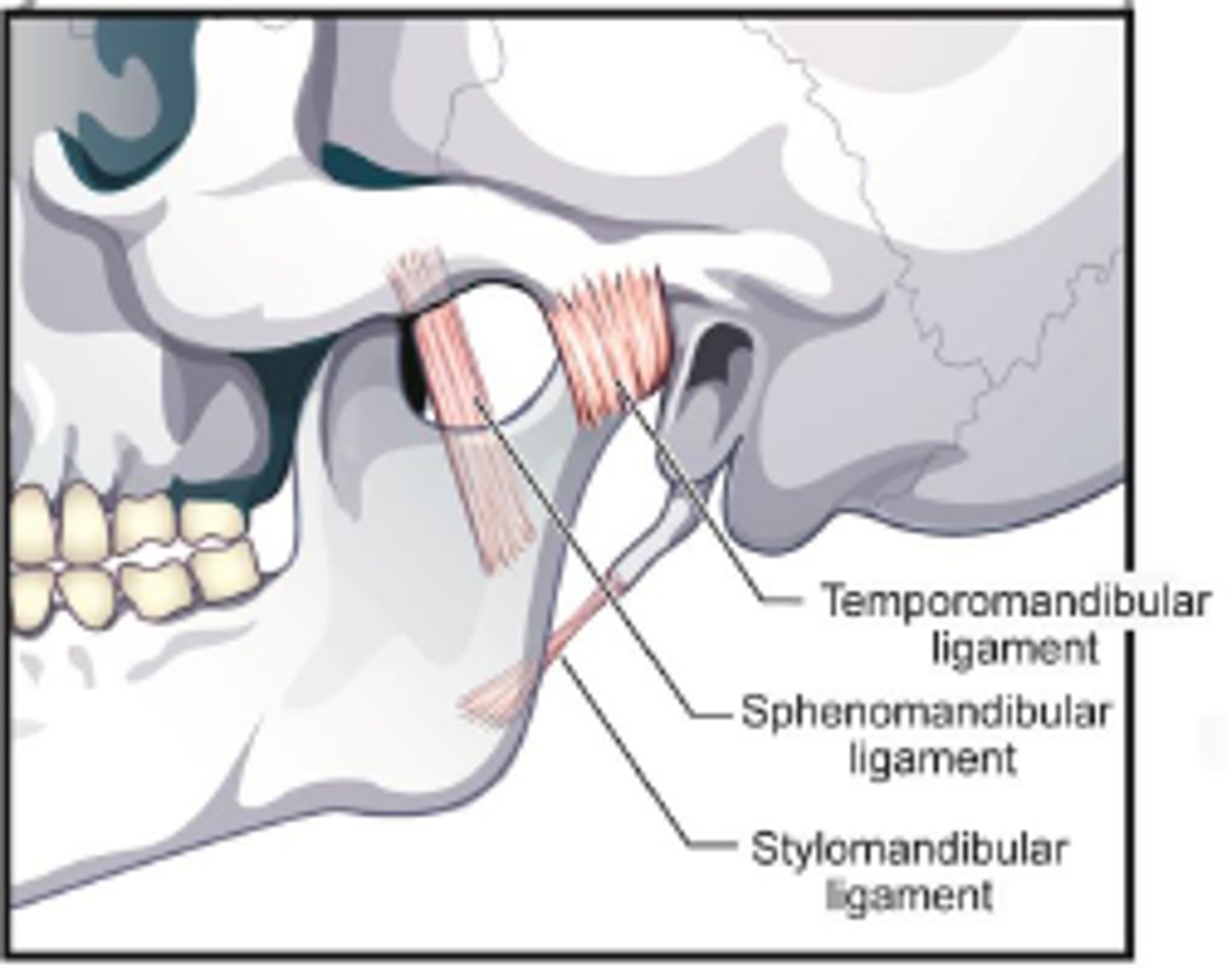
what are the 3 ligaments associated with the TMJ
Temporomandibular, stylomandibular, and sphenomandibular
Compared to the permanent teeth, how thick is the enamel on primary teeth?
0.5 mm
How thick is the enamel on a permanent tooth?
1.00 mm or more
True or false: primary teeth tend to erupt in pairs
True- a tooths contralateral sister should erupt along with or soon after
Is a baby whose molar erupts before the incisor normal?
No. This is a highly abnormal situation
Preservation of the primary teeth is important because
primary teeth act as space maintainers
True or false: preservation of primary teeth isn't important because the teeth with be lost anyway
FALSE
What is the TMJ innervated by?
mandibular division of trigeminal nerve (V)
Where does the TMJ get its blood supply?
branches of external carotid artery
Function of stylomandibular ligament
limits excessive protrusion of mandible
the function of the sphenomandibular ligament
Suspends the mandible and limits excessive anterior motion
what is important about the sphenomandibular ligament
it is used as a landmark for the administration of the inferioir alveolar block
what are the two movements that the tmj performs
gliding and roation
Rotational movement of TMJ
occurs mainly between the disc and the mandibular condyle in the lower synovial cavity
gliding movement of TMJ
allows jaw to move forward and backward
occurs between disk and articular eminence in the upper synovial cavity
what are the muscles of mastication involved in elevating the mandible during closing of the jaws
the bilateral contraction of the masseter, temporalis, and pterygoid muscles
what does the contraction of one of the lateral pterygoids cause
the mandible to deviate to the contralateral side
what is lateral excursion
side to side movement of the mandible
masseter
closes jaw by elevating mandible AND protrudes the mandible
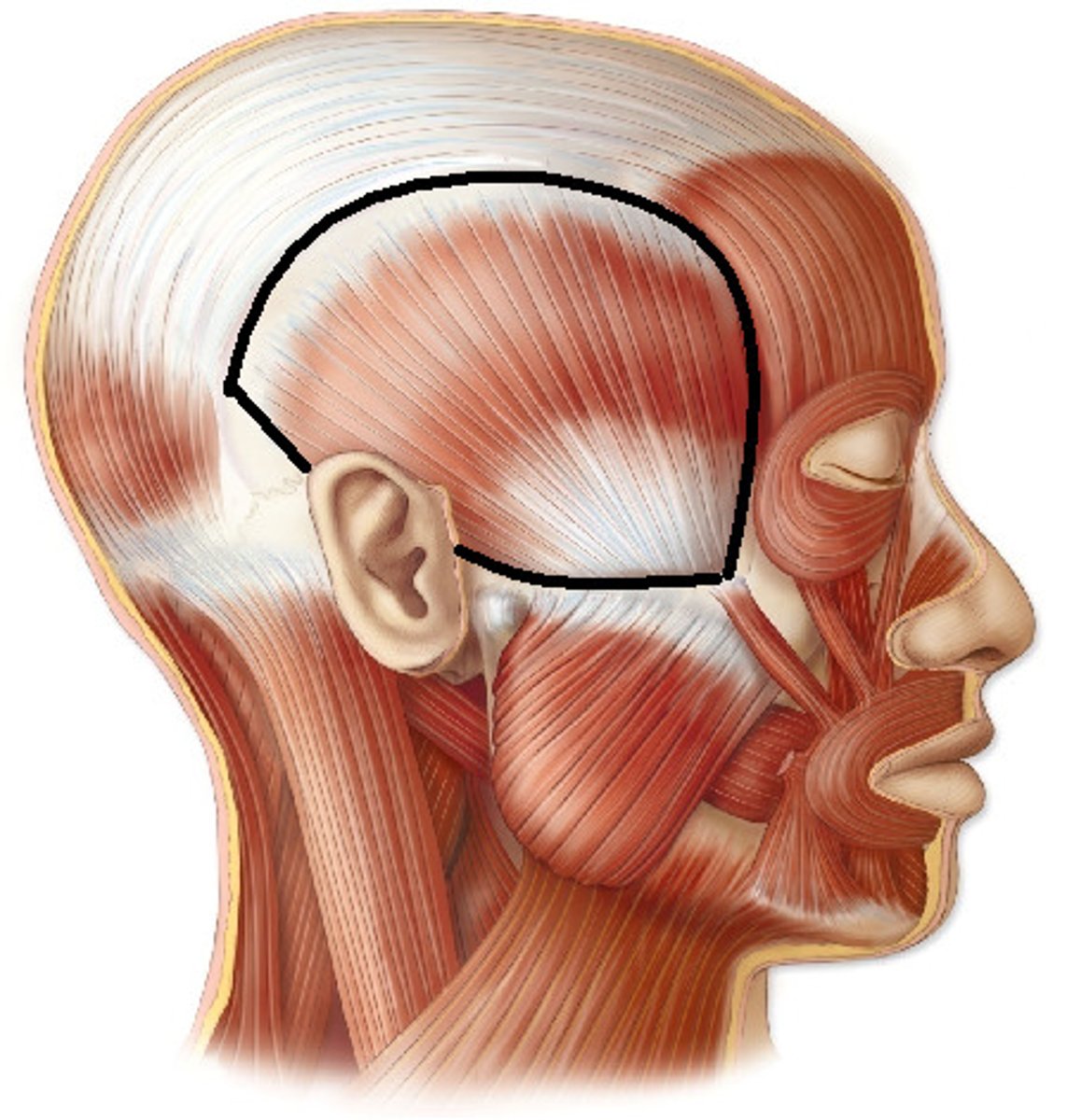
what is the function of the anterior and mid fibers of the temporalis
closes jaw and elevates mandible to help chew
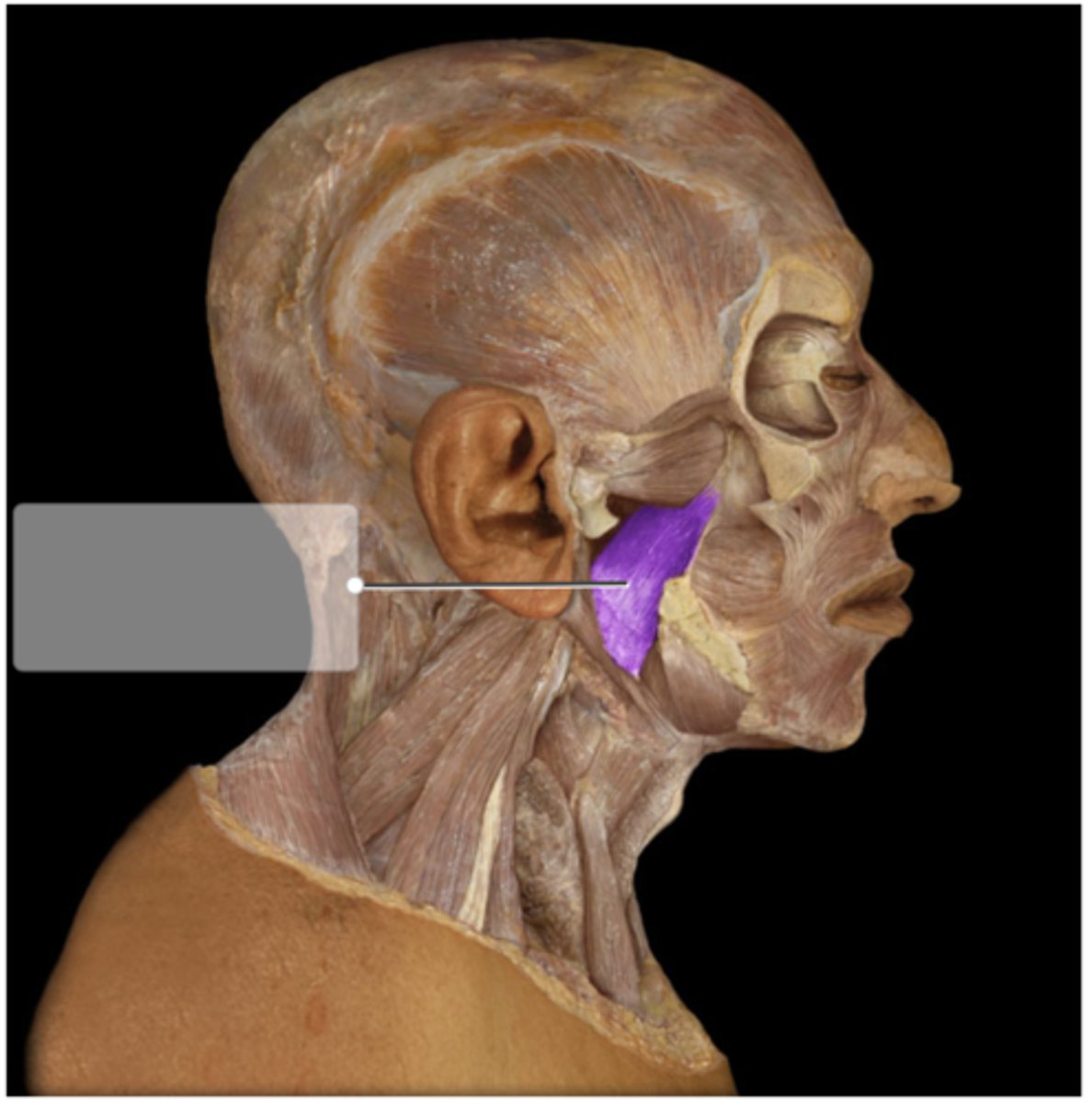
medial ptyergoid muscle
closes jaw, lifts the mandible, helps protrude the mandible, and helps with side to side movement
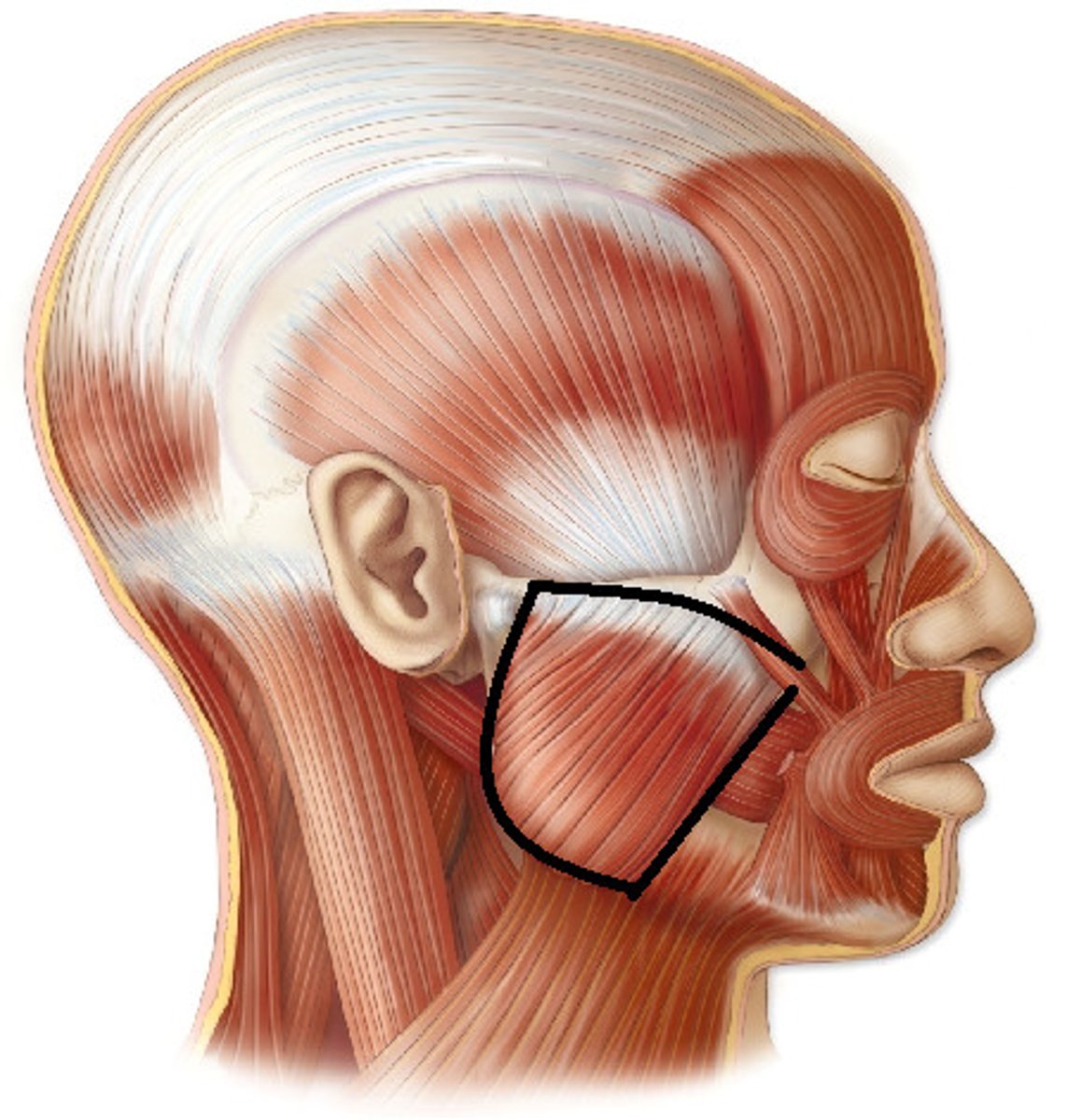
what is special about the lateral ptergoid
it is the only muscle of mastication that can elevate and depress the mandible
anterior digastric muscle
opens the jaw
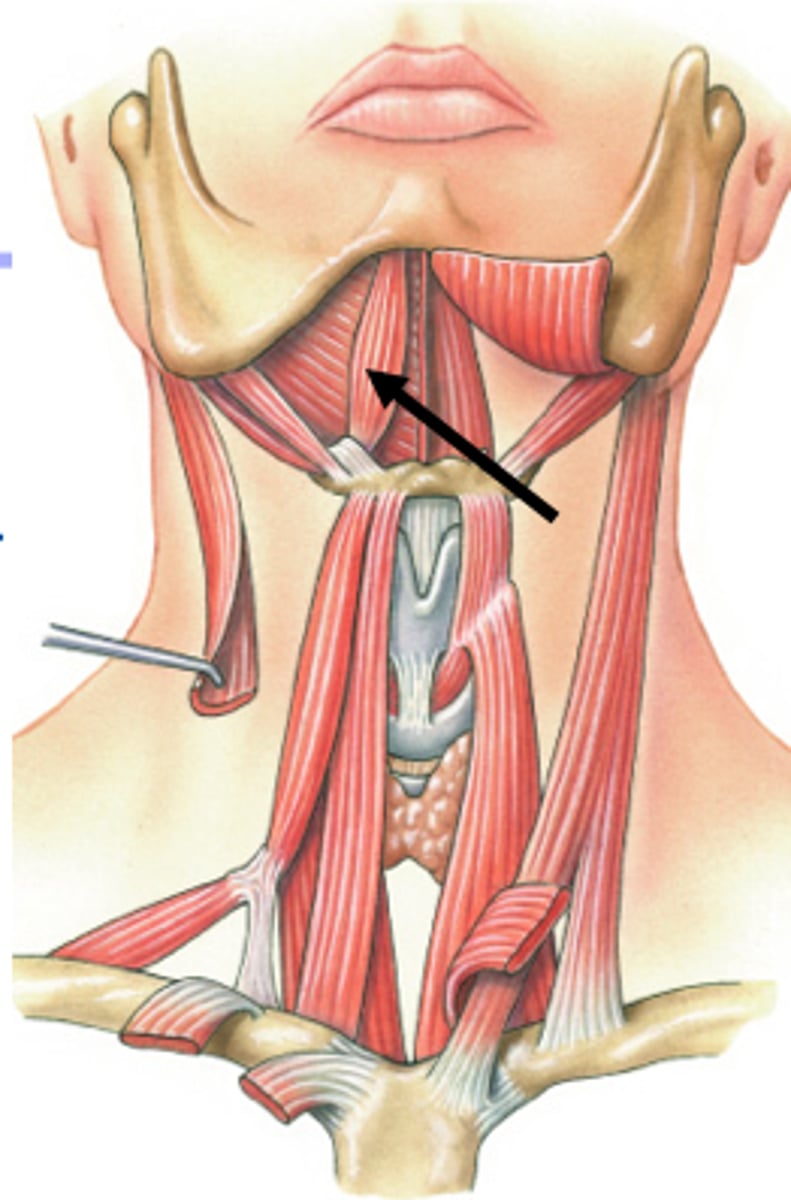
mylohyloid muscle
opens the jaw
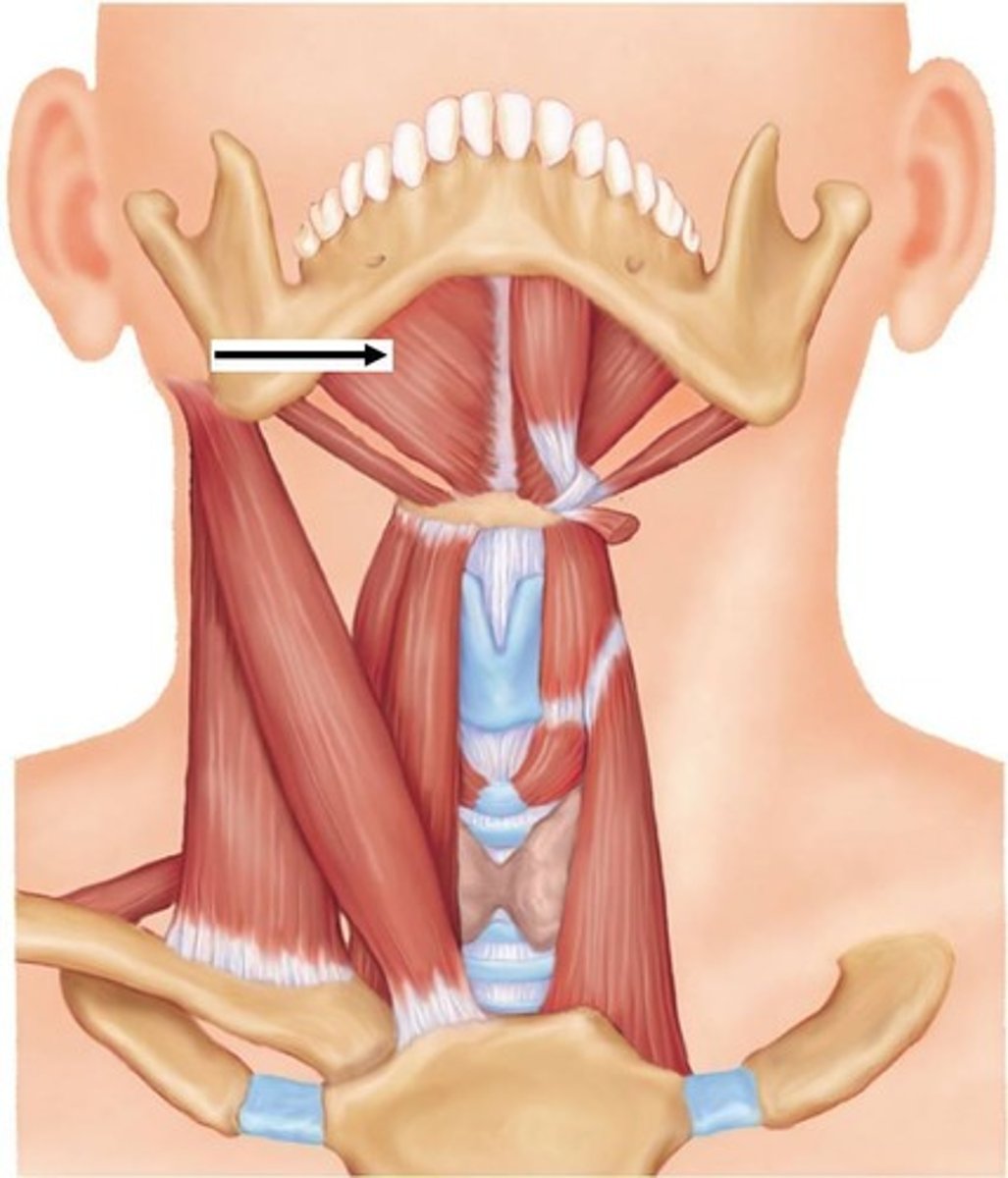
lateral pterygoid muscle
protrudes the mandible, pulls the articular disk forward, and contributes to lateral (side to side) movement of mandible
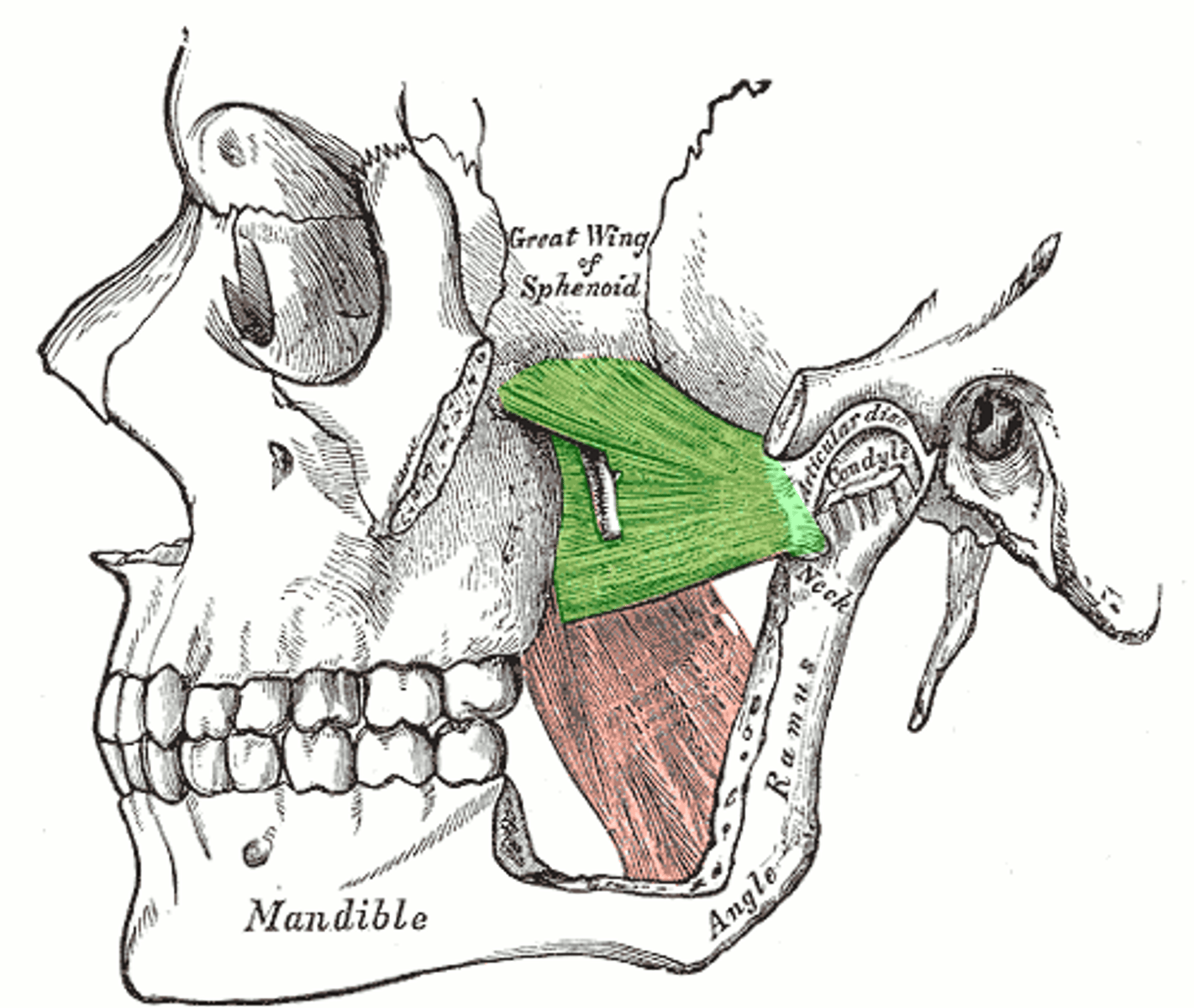
what is the function of the posterior fibers of the temporalis
retract the mandible
when the jaw is at rest where is the condyle positioned
centered on its fossa (the teeth are not in occlusion)
What is freeway space?
The space between your maxillary teeth and mandibular teeth when you are fully relaxed
what is a nightguard designed for
to reestablish natural freeway space, which protects from grinding
what is subluxation of the tmj
partial dislocation of a joint
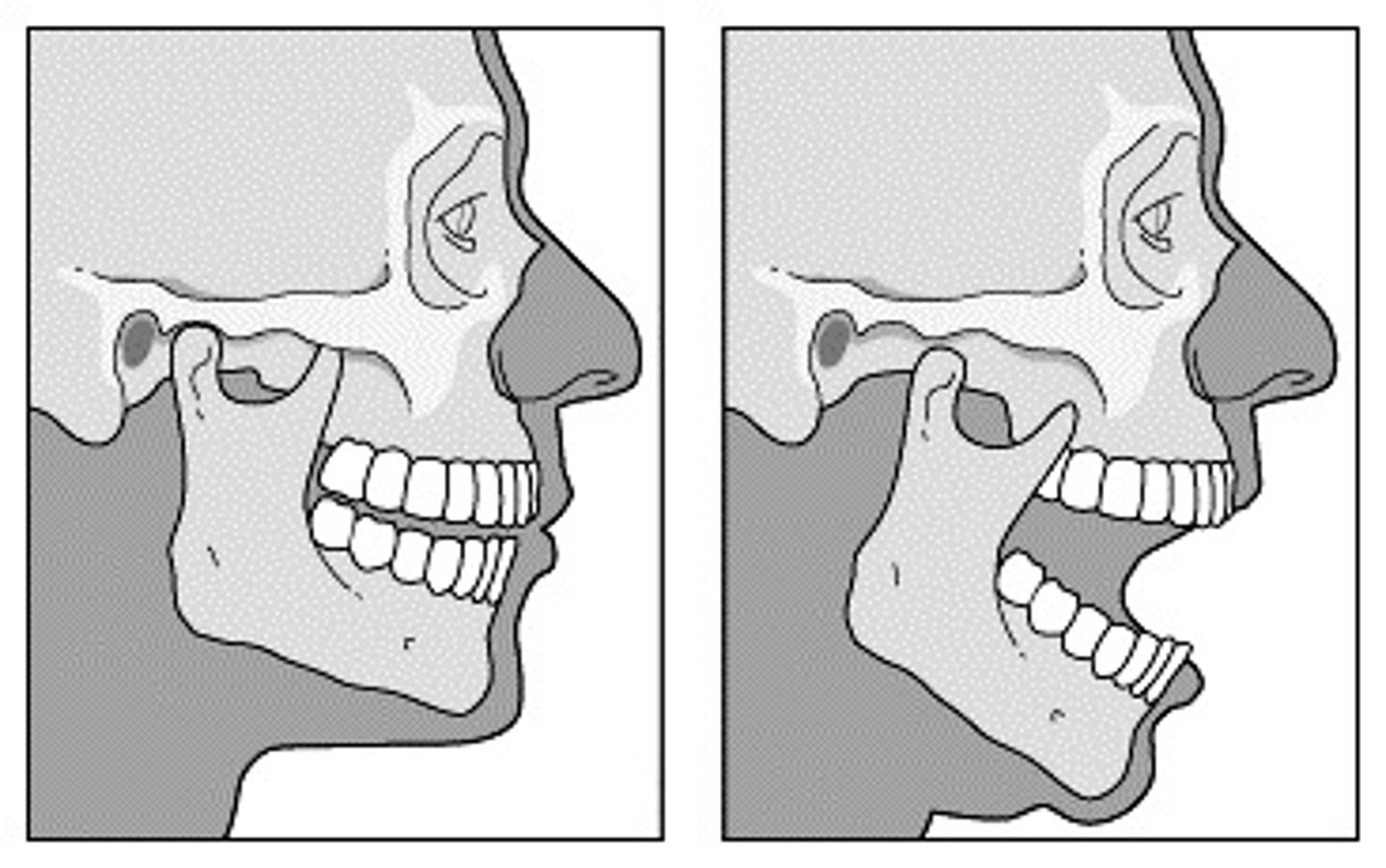
is dislocation of the tmj a medical emergency
yes
What is trismus?
LOCKJAW
inability to open the mouth due to a contraction/spasmsof the chewing muscles