PHA611: Plant Tissues and Arbituary Classification
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
TISSUE
A group of cells that perform specific function
Meristem
Tissues where the cells are in the mitotic state; actively dividing
Promeristem (primordial meristem)
Young meristamatic cells of a growing organ
Occupies a small area at the tip of a stem or a root
Divide in order to form primary meristem
Primary meristem
First derivative of promeristem
Tip of the stem, root, or appendiges
Divide repeatedly, develop and mature, to form the primary structure
Apical meristem
Secondary meristem
Secondary tissue
Eg. Lateral and intercalary meristems, vascular cambium
Apical
Growth region found in root tips and tips of new shoots and leaves
Differeniate into different cell type
Intercalary
Growth in length and elongation
Rapid growth and regrowth
Lateral
Grow in diameter, girth, thickness
Vascular and Core Cambium
Protoderm
Dermatogen
produces the epidermis, a dermal tissue.
Procambium
Plerome
produces the Vascular tissue; xylem and pheolem
Fundamental or Ground
produces Ground tissue hypodermis
PERMANENT
Cells are stable, no longer dividing; matured
SIMPLE PERMANENT TISSUE
Composed of one type of cell
Differentiates into dermal or protective and ground or fundamental
Parenchyma Tissue
A mass of parenchyma cells; most common type of tissue constituting all soft parts of a plant
Least specialized permanent tissue composed of living thin-walled cell
Parenchyma Cells
Most common type of cell
Has thin primary walls; large vacuole (storage)
Active matebolically and alive at maturity
Numerous subtypes are specialized for particular tasks
Eg. geranium
Chlorenchyma Cells
Involved in photosynthesis: chloroplast
The thinnest of the wall allows light and carbon dioxide to pass through to the chloroplasts
Eg. a leaf of privet
Elongated cylindrical cells with their long axis at the right angle to th surface of the organ
Cell contains numerous chloroplast for photosynthesis
Glandular Cells
Secrete nectar, fragrances, mucilage, resins, and oils
Contain few chloroplasts but have high amounts of dictyosomes and endoplasmic reticulum
Eg. A resin canal in pine leaf
Aerenchyma cells
Specialized in gas exchange; large interceullar space
Irregular cell surrounded with large air space
Found in stems of aquatic plant
Collenchyma Tissue
A mass of collenchyma cells
Collenhyma cells
Unevenly thickened primary walls (thin in some areas, thick most often in the corners)
Typically alive at maturity
Provide plasticity (the ability to be deformed by pressure or tension and to retain the new shape even if the pressure or tension ceases).
Present in elongating shoot tips as a layer just under the epidermis or as bands located next to vascular bundles
Usually produced only in shoot tips and young petioles (connects leaf to stem).
Living cell with thickening in corner leaving the lateral wall thinning
May be either short and prismatic, elongated and tapering or polygonal in transverse section
plasticity
the ability to be deformed by pressure or tension and to retain the new shape even if the pressure or tension ceases
petioles
connects leaf to stem
Sclereids
under Mechanical (nonconducting)
Brittle and inflexible
Form hard, impenetrable surfaces
Eg. shells of walnuts and coconuts or the “pits” or “stones” of cherries and peaches
more or less isodiametric; often dead at maturity
Fibers
under Mechanical (nonconducting)
flexible; found in areas where strength and elasticity are important (wood of flowering plant, trunk, and branches)
Resists insects, fungi, pests (bark)
Elongates as the internode increases in length (node - where leaves grow)
Long; many types are dead, other types remain alive and are involved in storage
Tracheids
under Conducting (tracheary elements)
Water-conducting long cells with tapered ends, no perforations
Only type of water conducting cells in ferns, conifers and most other nonflowering plants
Dead at maturity (hollow tubular wall)
Secondary wall has bordered pits (to keep sclereid alive)
Found in all vascular plants
Vessel Elements
under Conducting (tracheary elements)
Forms large hole called a perforation which greatly reduces the friction = water moves much more easily than through pits of tracheids.
short and wide with rather perpendicular end walls;
most contain one or two perforations.
Dead at maturity.
Found almost exclusively in flowering plants. Among nonflowering plants, only few ferns, horsetails, and gymnosperms have vessels
Sclerenchyma Tissue
Has both a primary wall and a thick secondary wall that is almost always lignified
Many dead at maturity
Provides elasticity ( the ability to be deformed, but snap back to their original size and shape when the pressure or tension is released)
May or may not be living
Occurs in cluster or group among parenchymatour cells surrounding vascular tissue
Fiber - elongated cells with pointed end walls
Sclera’s or Stone Cell - roundish or polygonal cell with walls varying in thickness
Scelerenchyma Cells
Some are involved in water transport
Develop mainly in mature organs that have stopped growing (non-extending parts) and have achieved their proper size and shape)
EPIDERMIS
Outermost surface of a herbaceous stem, leaf and root
Uses
Protection; regulate exchange of materials
Encrusted with cutin (cuticle)
Contains guard cells, trichomes, and root hairs
Cutin
inhibits the entry of Co2 needed for photosynthesis = plant’s starvation -> pairs of guard cells with a hole (stomatal pore) between them to permit gas entry
Guard + stomatal pore = stoma/ stomata
Stomatal pores are open during daytime
Accessory cells
Serves as reservoir of water and ions
Bulliform cells
Longitudinal rows of vacuolated cells
Epidermal hair
For the elongation of the epidermal cell outward (trichome and root hairs); increase surface area
Trichomes
aka epidermal outgrowths/hairs
Functions:
Protection from insects and excessive sunlight
Aids in nutrient uptake
Spread of seeds
Economic Importance
Threads -> cloth
Glandular
Glandular or Secretory
Aratiles
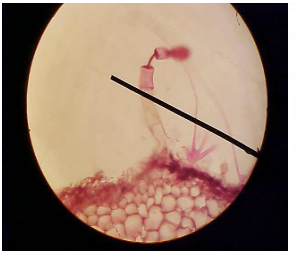
Stinging
Glandular or Secretory
Lipa
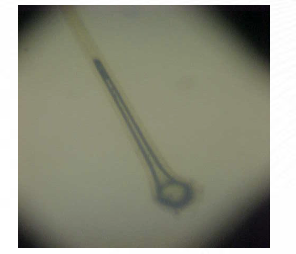
Branching
Non-glandular/Non-secretory
velvet dock
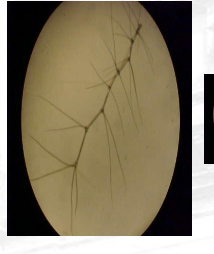
Bristle
Non-glandular/Non-secretory
(Lipai); thinner
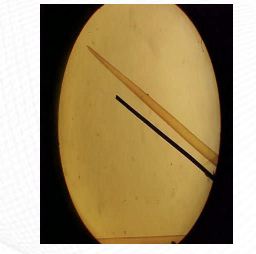
Scale
Non-glandular/Non-secretory
(Lingaro); finer, flower
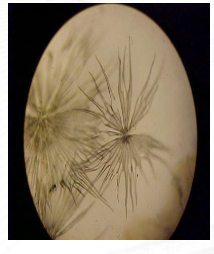
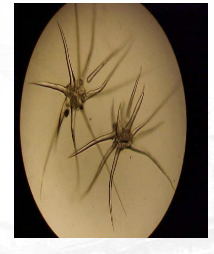
Stellate
Non-glandular/Non-secretory
(Mallotus); star
Root hair
epidermal outgrowth of root’s epidermis
increase surface area for absorption
Cork or Phellem
Outer covering of woody stems and roots
Cell wall is impregnated with suberin
Produced by the cork cambium (secondary meristem)
No intercellular spaces (avoid water loss)
COMPLEX PERMANENT TISSUE
Composed of different kinds of cell but perform similar function
Xylem
Brings water and minerals salts from the roots to the rest of the plants
tracheids & vessels - transport water and minerals from roots to all part of the plant
Principal water conducting tissue composed of lignified dead cells located in the stellar (Vascular) region of stem, root, or leaves
Various patterned secondary walls called tracheids, vessel, fiber, and parenchyma
Xylem parenchyma
under xylem
stores water
Xylem Fibers
under xylem
help in support
Phloem
Moves sugar and other organic nutrients (food) and minerals
Principal food conducting tissue composed of different type of cells located in the stellar region
Composed of fibers, parenchyma, sieve cell or tube and companion cells
Sieve tubes and companion cells
transport food from leaves to all parts of the plant
Phloem parenchyma
under phloem
stores food
Phloem fibers
under phloem
help in support
ARBITRARY CLASSIFICATIONS
Easily classify plants; less time consuming; not universal applicable; characteristics (what we observe)
Bryophytes
(mosses, hornworts, and liverworts)
Lacks vascular tissue but some have water conducting tube
Multicelluar embryo remains attached to mother plant nourished and protected
Lack leaves, stems, roots (no support)
Limited habitats (near water; moisture)
Pteridophytes
Have vascular tissue
Seedless but embryo nourished by parent cell (spores)
Eg. Lycophytes, fern, horsetail, whiskfern, Salvinia Natans
Gymnosperms
Non-flowering
Vascular, have seeds which are not enclosed inside an ovary
Male (smaller) or Female (larger) cones
Eg. Gingko, Cycas, Gnetae, confider, Giant Sequioa Tree, Sago Palm
“Naked seeds”
Angiosperms
Flowering plants (largest family)
Vascular, seed within ovaries
Eg. Water lily, Cosmos flower, Sunflower
Tree
More than 5 heights
Usually with woody main trunk or stem
Lives for several years
Shrubs
Less than 5 meters
With short main trunk or stem
Lives for several years
With numerous lateral branches
Herbs
Plants with little or no woody tissue; soft stem
Spices (basil, aragon, celery)
Vine
Plants with climbing or training or trailing stem, maybe herbaceous vine or woody vin
Lianas
Plants with woody climbing or training stems
Long flexible; rooted in the grown; Tropical rainforest
Eg. grapevine
Annual
Plants that live for only one year or completes the vegetative and reproductive cycle in one growing season
Seed to flower = one growing season
Eg. rice
Biennial
Plants that lives for two year or two growing season
Vegetative growth is completed during first year and reproductive or flowering takes place in the second year
First season - vegetative parts; Second season - flower and seeds
Perennial
Plants that live for several years
Mesophytes
Backyard plants
plants that can survive in moderate environments that are neither particularly dry nor particularly wet.
Hydrophytes
Big amount of water
Eg. Water lily, aquatic plant
Halophytes
Watery but salty environment
Eg. cerop stagal, mangrove
Xerophytes
Little water, special structure for them to store water to survive droughts
Eg. cactus
Terrestrial
land or soil
Aquatic
water
Aerial or Epiphytes
air (eg. orchids
Autotrophic
Plants that can manufactured their own food
Usually green due to the presence of chlorophyll
Heterotrophic
Plants that are non-chlorophyllus
They get their nourishment from other plants by living as parasite, absorbing nutrient from tissue of their host.