SCIE Impact of Science Human Population
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Climate Change
a change in the average atmospheric conditions, such as temperature and rainfall, over a long period of time
Greenhouse effect
Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas, meaning it blocks heat from escaping the atmosphere causing surface and ocean temperatures to rise through a process called
Climate Change Effects
increased average global temperature
shrinking glaciers
rising sea levels
melting polar ice caps
more frequent severe weather events like tornadoes, flooding, and hurricanes
increased drought and disruption of rainfall patterns
Deforestation
occurs when trees are removed from an area to convert the land for other purposes
forests are responsible for removing a significant amount of carbon dioxide
Deforestation effect
less removal of atmospheric carbon dioxide by trees
excess carbon dioxide is emitted into the atmosphere by burning wood
decreased biodiversity by habitat destruction
accelerated soil erosion
displacement of indigenous people
increases in regional temperatures from loss of atmospheric moisture
disruption of global rainfall patterns from changes in atmospheric moisture
Desertification
a permanent reduction in the productivity of land. Land is desertified when it can no longer support the same level of plant growth
Effects of Desertification
destruction of habitat to create landfills
pollution of water, soil, and air
global climate change
production of acid rain by gaseous wastes
Acid Rain
occurs when sulfur dioxide or nitrogen oxides are emitted into the atmosphere and react with water, oxygen, and other chemicals
Acid rain has a lower pH than normal precipitation.
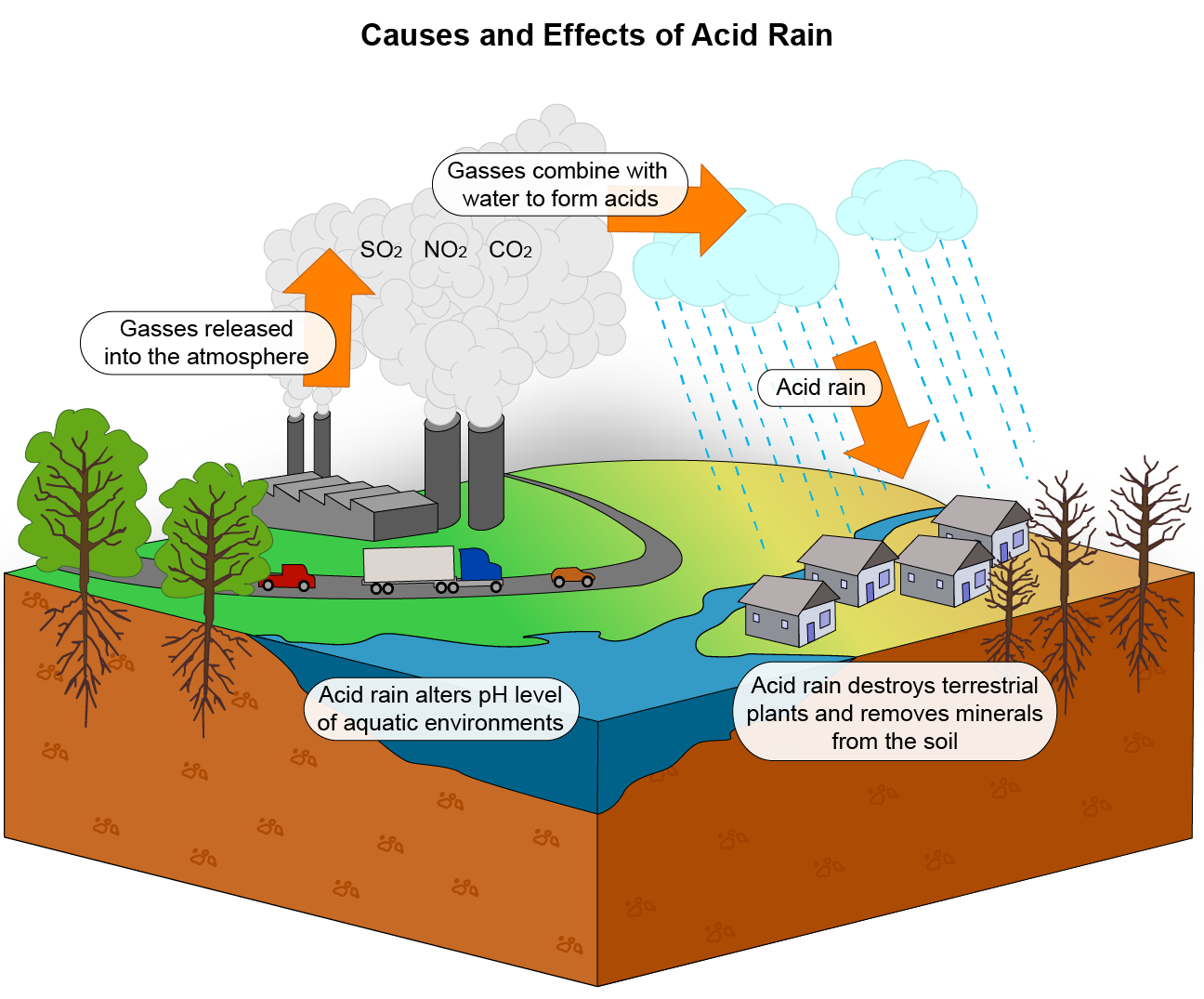
Acid Rain Effects
loss of biodiversity
decreased air quality due to damaged plants and trees
decreased crop yields due to acidic soil
poor water quality due to acid rain and runoff of acidic soil
eye and respiratory issues when acidic fog is inhaled
Waste Disposal
landfills can leach harmful chemicals into the water supply, and burning waste contributes to lower air quality and acid rain production
disposal of plastic is the greatest issue
Effects of Disposal
destruction of habitat to create landfills
pollution of water, soil, and air
global climate change
production of acid rain by gaseous wastes
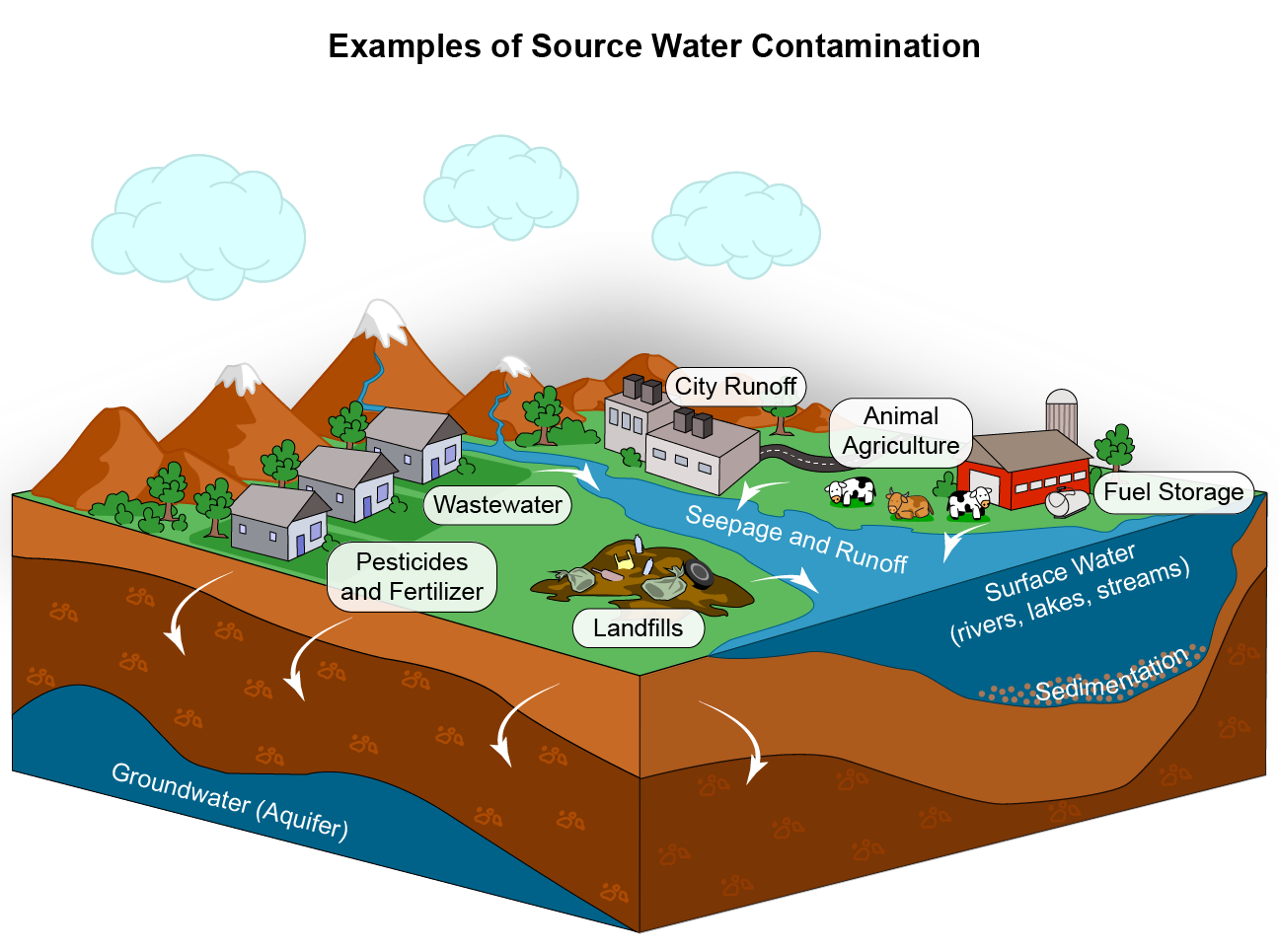
Water Quality and Availability
only 4% is freshwater available for human use and consumption.
Effects of decreased WATER:
destruction of aquatic habitats
depletion of local surface and groundwater reserves
reduced mountain snowmelt to feed surface and groundwater reservoirs
potential loss of biodiversity
illness from consumption of polluted water
decreased crop yields
Ozone Depletion
Earth's atmosphere layer is composed of O3 molecules called ozone
Emissions of chlorine and bromine released by manufactured chemicals are the primary cause of ozone depletion. These chemicals are commonly referred to as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
decreased rate of photosynthesis for plants and phytoplankton
inhibited growth of many plants and trees
decreased food supply from UV-B damaged crops
eye and skin damage to animals and humans