Physical Science and Engineering
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Spontaneous Reaction
A chemical reaction that occurs when elements are combined even when no extra energy is present.
Neutral (Charge)
a material without a net positive or negative charge
Example.
neutrons
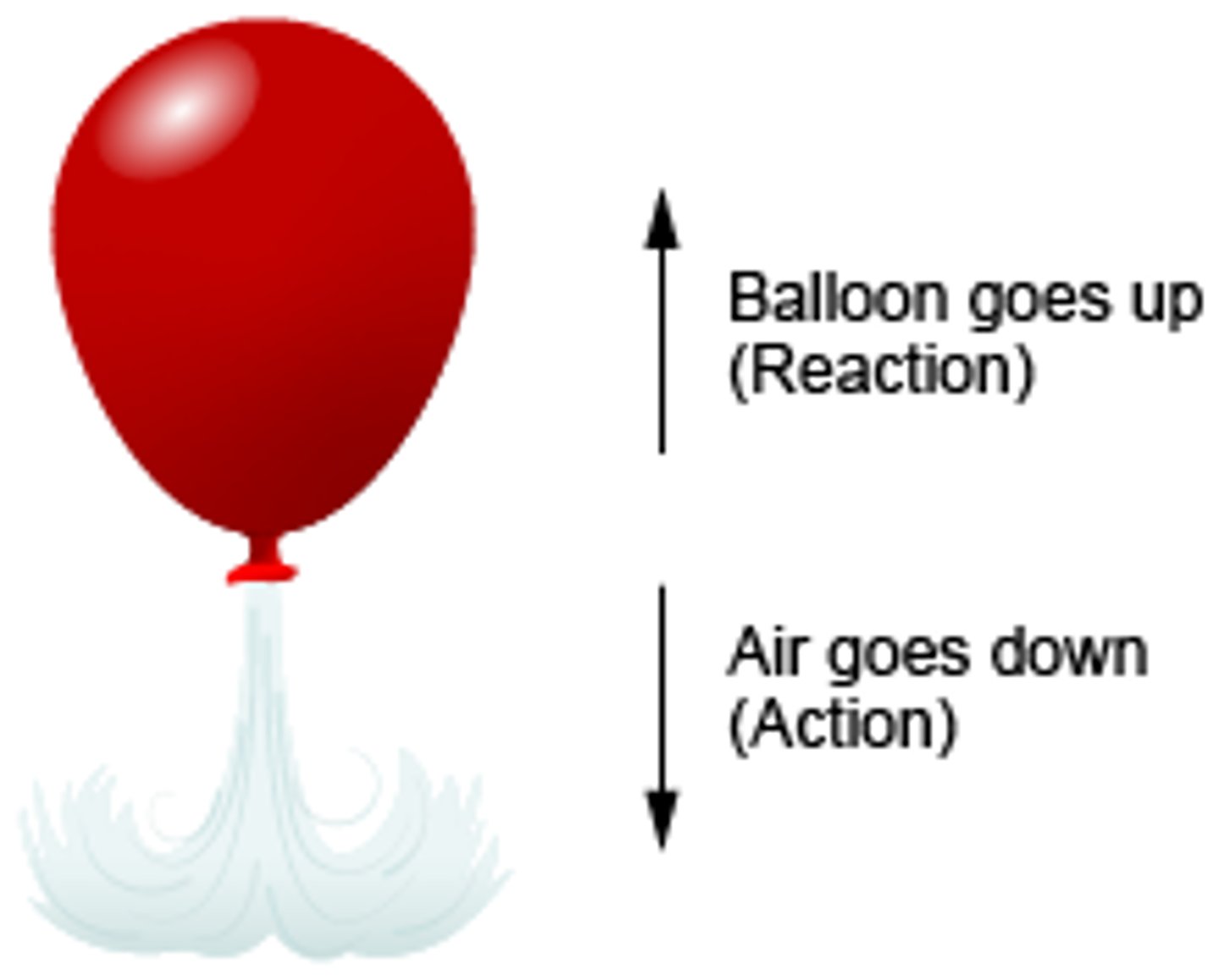
Newton's Third Law
the law that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
Example.
If you release the bottom of a balloon, the air rushes out. This movement causes an equal and opposite reaction and the balloon moves up.
Natural Gas
a fossil fuel byproduct formed with coal and oil
Electron Affinity
the ability to accept an electron and become a more negative ion
Example.
Fluorine (group 17) has a higher electron affinity than Oxygen (group 16)
Generator
A device that uses electromagnetic induction to produce an electrical current (mechanical energy to electrical energy).
Example.
Generator within a windmill
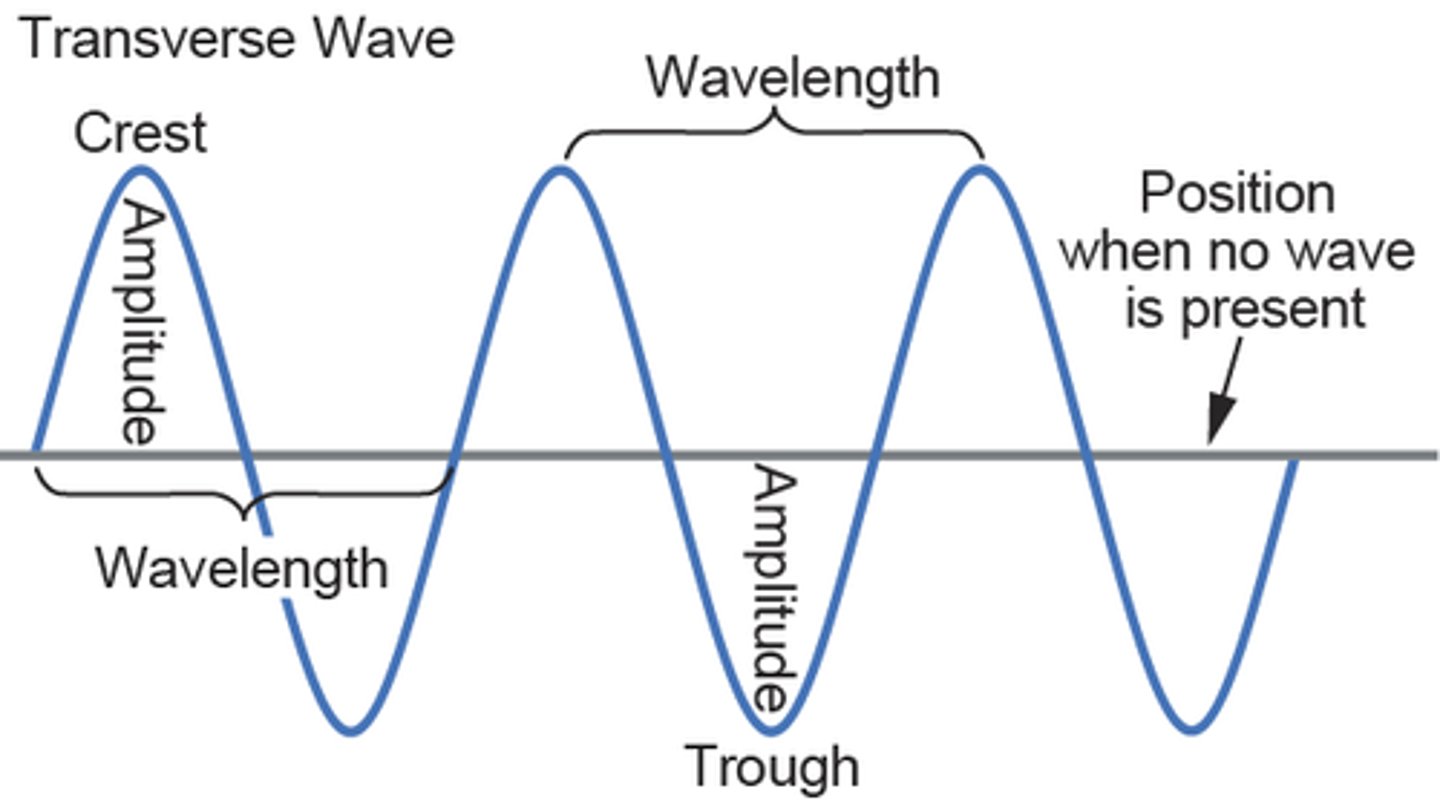
Transverse Wave
a wave in which the direction of the vibration is perpendicular to the direction the energy travels
Example.
light, vibrating guitar string
Gravity
a force that pulls all masses towards each other, with or without touching; Earth's gravity pulls all objects near its surface downward
Acceleration
a measure of how quickly something changes its speed or direction, calculated from change in velocity/time
Example.
slowing down, turning a corner
Greenhouse Gases
gases which, when present in elevated quantities in Earth's atmosphere, trap solar radiation and cause the planet to warm
Example.
carbon dioxide
Gravitational Force
the force of attraction of all masses toward each other due to gravitational pull
Example.
Earth pulls on Moon
Solar Energy
energy from the sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation
Weak Nuclear Force
a force that resists particle decay in the nucleus
Example.
radioactive decay
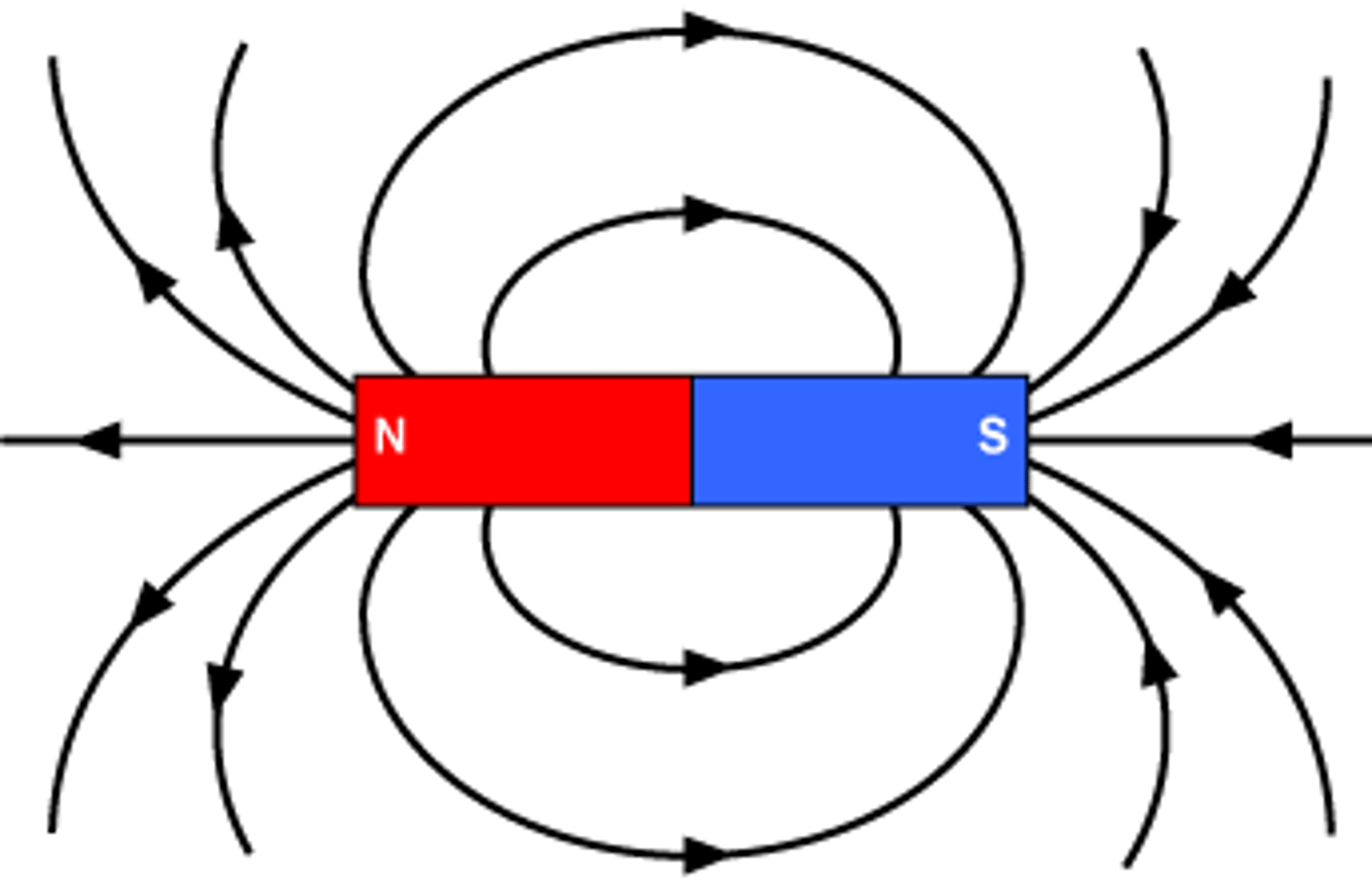
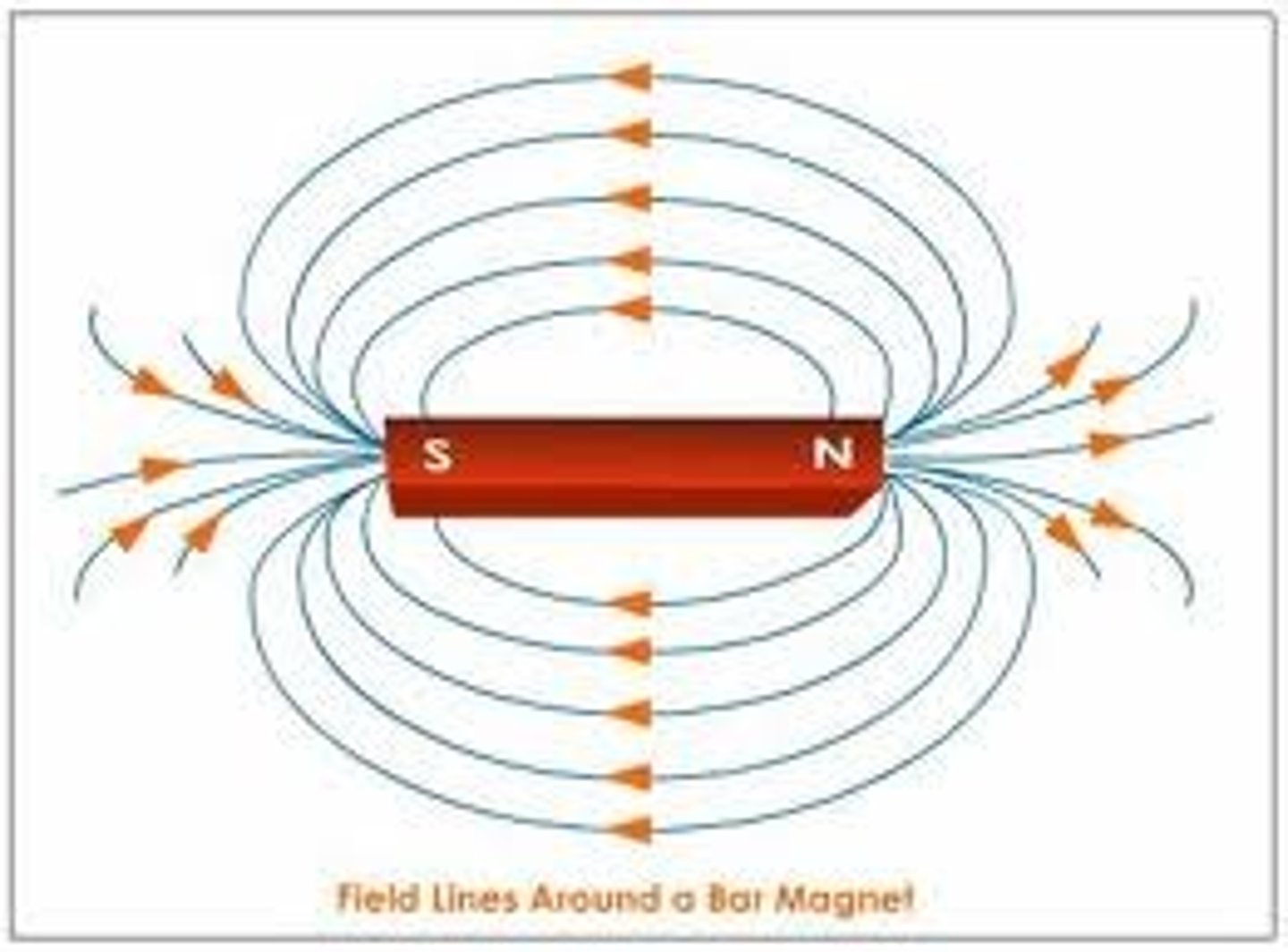
Magnetic Poles
the north and south ends of a magnet
Inertia
the tendency to resist changes in state of motion
Example.
objects at rest stay at rest and objects in motion stay in motion
Electronegativity
the tendency of an atom to attract electrons toward itself
Example.
Fluorine, Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Chlorine are the most electronegative elements, while Francium is the least.
Wave Speed
a measure of how fast the wave energy moves from one place to another
Example.
speed of light
Chemical Reactivity
a measure of the tendency of an atom, molecule, or compound to undergo a chemical change
Solid
a state of matter with particles fixed in place and packed closely together; has a definite shape and volume
Example.
ice
Metallic Character
Elements that show stronger metallic properties such as conductivity, malleability, ductility, and luster; greater in elements that easily lose their valence electrons.
Wave
a disturbance that transports energy as it moves through space and time
Example.
water wave, electromagnetism, sound
Medium
the material that carries a mechanical wave
Example.
air for sound wave, a string for a violin
Metallic Qualities
Qualities typically associated with metals such as magnetism, conductivity, malleability, and ductility
Electromagnetic Waves
Waves consisting of vibrating electric and magnetic fields. Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum because they do not require a medium. Emitted by all objects with a temperature above absolute zero.
Example.
light, radio waves, x-rays
Newton's First Law / The Law of Inertia
the law that objects resist changes in their state of motion
Example.
a rolling bowling ball keeps moving at constant speed
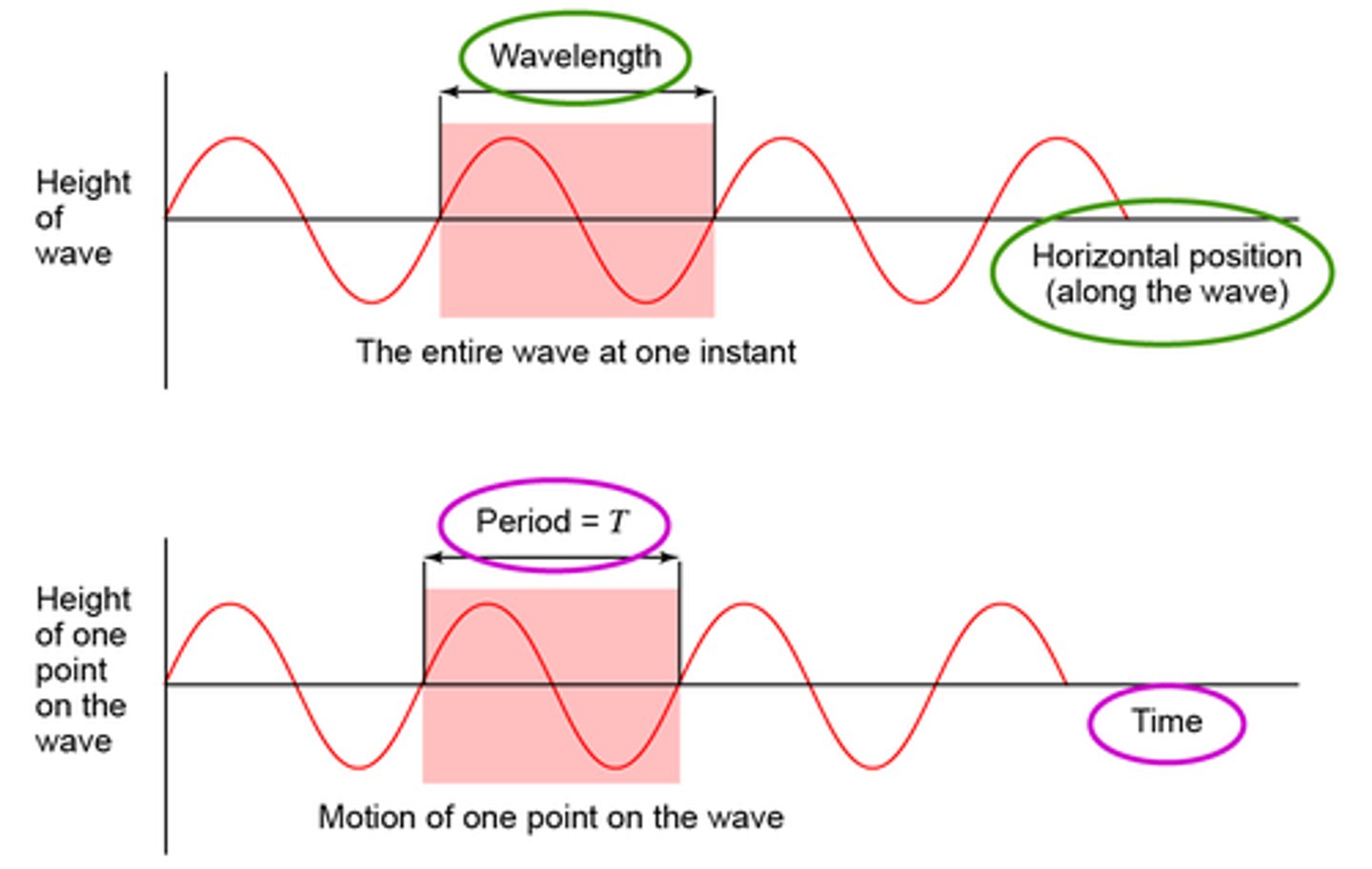
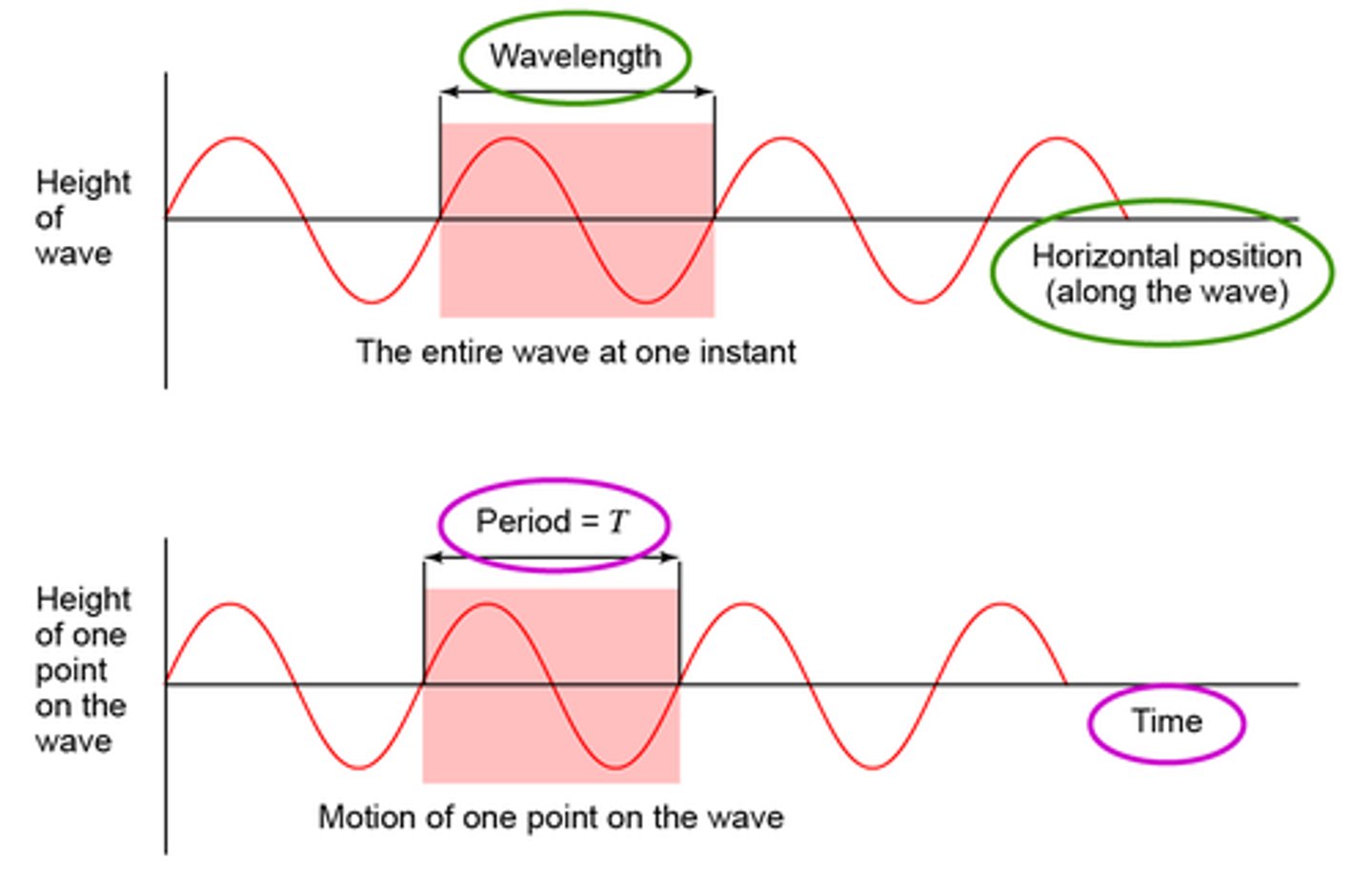
Period
the time it takes to complete one full wave cycle, measured in seconds
Example.
a 17 second stop-light cycle
Combustion Motor
a device that transforms chemical energy into mechanical energy
Example.
car engine
Troughs (of a Wave)
the valleys, or lowest points, of a vertically vibrating transverse wave
Liquid
a state of matter with particles close together but not fixed in place; has a definite volume, but takes the shape of the container
Example.
water
Coal
a fossil fuel formed from land plants
Force
an interaction (push or pull) of one object with another that resists other forces or causes acceleration
Example.
There are only four kinds of forces, called universal (or fundamental) forces: gravitational, electromagnetic, strong nuclear, and weak nuclear
Acid Rain
rain with a lower pH than neutral, corrosive to many substances including rocks, often caused by pollution
Example.
sulfur dioxide dissolves in the water droplets of clouds to make sulfuric acid
Ionization Energy
the amount of energy needed to remove an outer electron to make a positive ion
Example.
Alkali metals have low ionization energies, making them highly reactive.
Mechanical Waves
Physical waves that travel through a medium.
Example.
sound, water waves
Conservation of Energy
in a closed system, the total amount of energy is constant, even if it changes form or moves from one place to another
Example.
girl diving off board into water
Longitudinal Wave
a wave in which the direction of the vibration is parallel to the direction the energy travels
Example.
sound

Charge
an electric property of matter that produces interactions with an electric field; can be positive or negative
Example.
protons, electrons
Amplitude
the maximum displacement of a particle of the medium during a vibration (measured from non-vibrating position to one crest)
Example.
height of an ocean wave above the ocean's normal surface height
Conservation of Matter
Matter cannot be created or destroyed; it only changes form
Example.
chemical reaction

Magnetic Field
the potential magnetic force in the space surrounding a magnet; proportional to the force on a magnetic pole in the space around the magnet
Fossil Fuels
a natural non-renewable fuel source. derived from underground, fossilized (petrified) remains of living organisms.
Example.
natural gas, petroleum, coal
Frequency
the number of ocurrences of an observed behavior over a set time period
Example.
A teacher counting the number of times Jacob sticks his tongue out at a classmate during a one-hour class would be collecting frequency data.
Strong Nuclear Force
a force that holds protons and neutrons together in the nucleus
Example.
fission and fusion
Photovoltaics
panels collect sunlight and turn the energy into electricity
Oil
a fossil fuel formed from marine organisms
Renewable Resources
resources which replenish at the same (or faster) rate than the rate at which they are used
Example.
wind energy, solar energy, hydroelectric power
Electromagnetic Force
interactions (pushes and pulls) of electrically charged particles with other charged particles and magnetic poles
Example.
like charges repel, opposite charges attract
Net Force
The vector sum of all forces acting on an object.
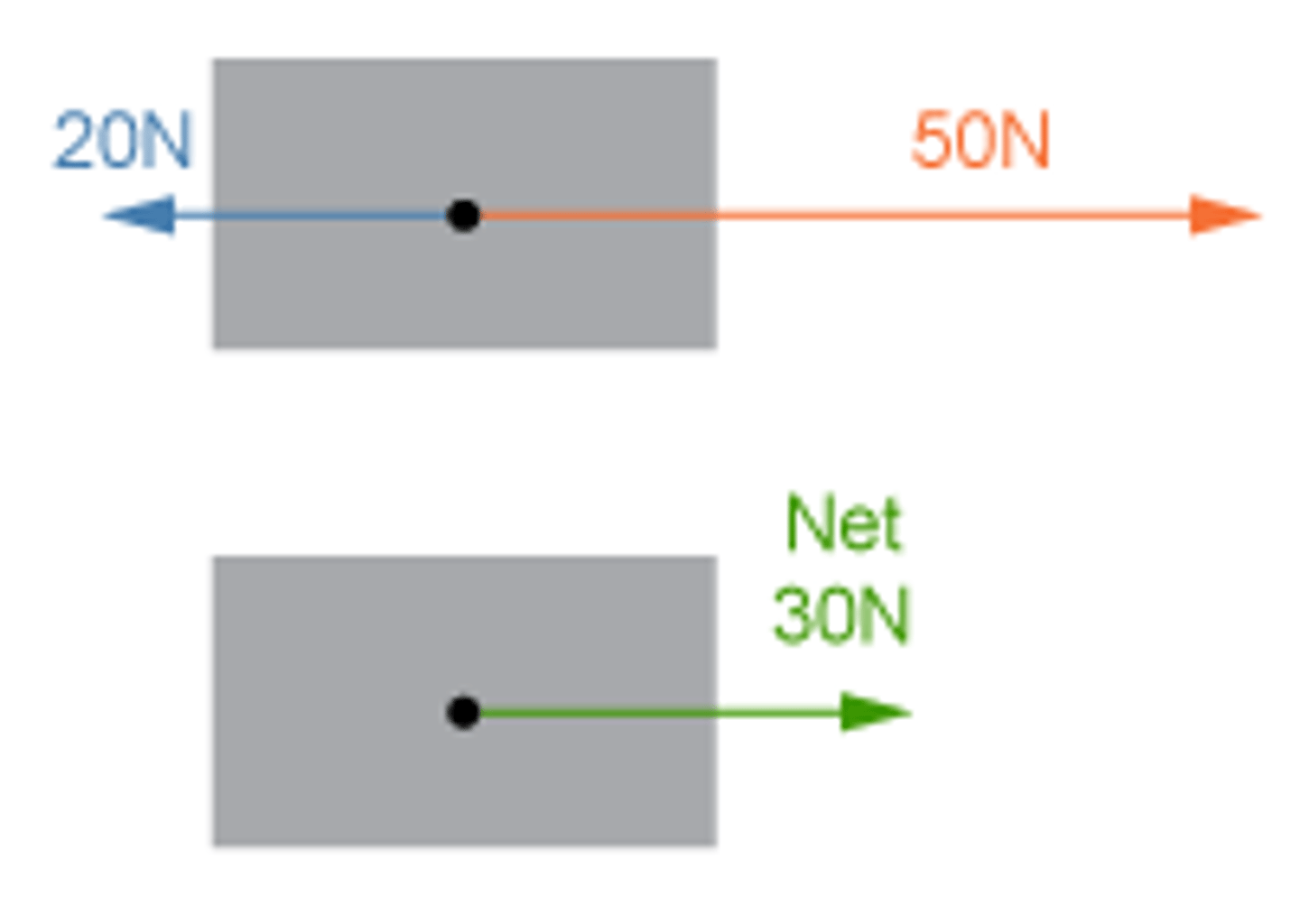
Mass
The amount of matter in an object, measured in kg in the SI system of units.
Turbine
a device that transforms kinetic energy into mechanical energy
Example.
Blades of a windmill
Atomic Radius
the distance from the nucleus to the outer electron shell
Gas
a state of matter with quickly-moving particles that are farther apart than in a liquid; has no definite volume and takes the shape of the container
Example.
water vapor
Ion
an atom with a net electrical charge because it lost or gained an electron
Example.
H+ ion has a +1 charge
Non-Renewable Resources
resources which will be depleted faster than they can be replenished
Example.
natural gas, petroleum
Hydroelectric Energy
energy collected as gravity pulls water from higher elevations to lower elevations
Example.
Hoover Dam
Crests
the peaks, or highest points, of a vertically vibrating transverse wave
Newton's Second Law
the law that greater masses require a greater force to achieve the same acceleration, F = ma
Example.
force needed to stop a bowling ball vs baseball rolling at same speed
Wavelength
the length (in space) of one complete wave cycle, measured in distance units
Example.
crest to crest distance on a water wave