Biology 2- Animal Science 1.2
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
nine major phyla names
porifera, cnidaria, platyhelminths, nematodes, annelids, mollusca, arthropoda, echinoderms, chordates
non-bilateral animals
no bilateral symmetry, most ancient
complex life cycle
switches between asexual and sexual reproduction, polyps and medusas
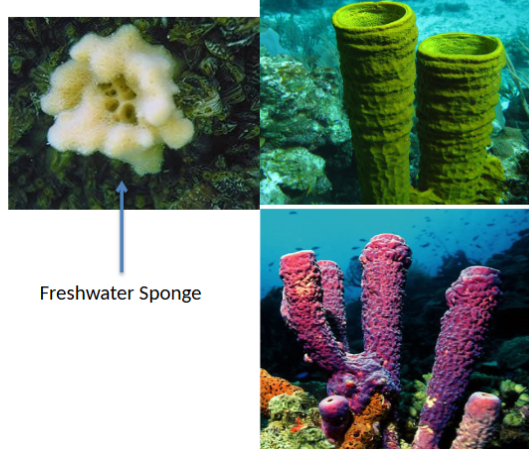
phylum porifera
sponges - no organized tissues or structures, no symmetry, filter feeders, in through pores and out through osculum, three functional layers: choanocytes, mesophyll, outer epithelial layer, spicules for structure and defense

phylum cnidaria
jellyfish and anemones - diploblastic, specialized tissues in two levels, radial symmetry, incomplete digestive tract, complex life cycle

go back to non major phyla starting at 49 and classes
go back to non major phyla starting at 49 and classes
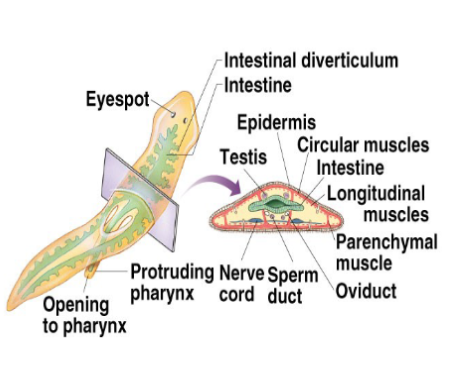
phylum platyhelminths
flatworms, flukes - parasitic, triploblastic, acoelomate, organ level organization, bilateral symmetry, incomplete digestive tract, lack specialized structure for gas exchange, complex life cycle
phylum nematoda
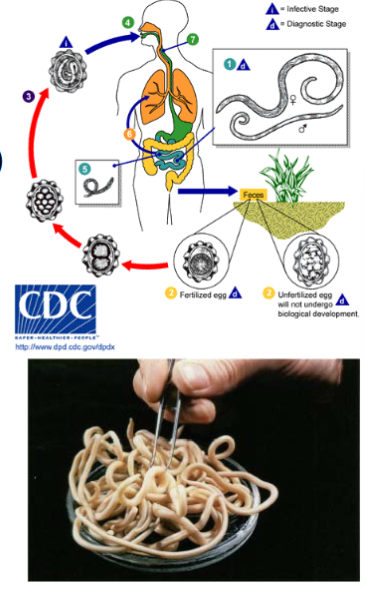
roundworms - pseudocoelom, organ level organization, no circulatory system, bilateral symmetry, unsegmented
phylum mollusca
snails, clams, octopuses - complex organs and mantle, coelom present but reduced, filter feeders with complete digestive tracts, open circulatory system with a few large vessels

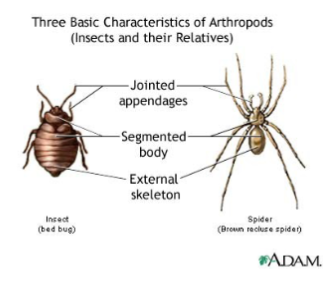
phylum arthropoda
insects - most successful and 75% of species, chitin exoskeletons, segmented, coelom, organs, open circulatory system, respiratory system with trachea, complete digestive tract, joints, nervous and respiratory systems
phylum echinodermata
starfish - coelom, organs, endoskeletons, water vascular systems, bilaterally symmetrical larvae and radial adults, spiny skin marine, bilateral larval stage and radial adults, endoskeletons made of ossicles plates

phylum chordata
everything else, humans - four principle features are dorsal nerve chord, notochord, pharyngeal slits and postanal tail at some stage of life, organs, complete digestive system

internal and external fertilization
internal happens in animal body and external happens outside
cleavage patterns
protosome spirals, deuterostomes radial
what is the closest ancestor to animals
protists
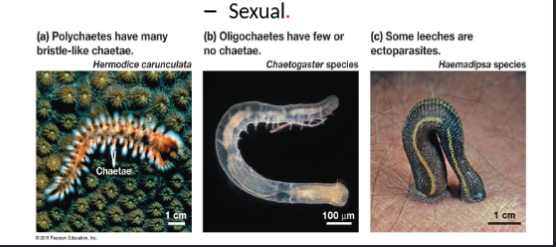
phylum annelida
segmented worms- most have bristles or setae, coelomates, organ level organization, complex and complete digestive tract, closed circulatory system, bilaterally symmetric
hemimetabolous vs holometabolous
three stage incomplete metamorphosis, egg, nymph, adult vs full metamorphosis with larval stage
traits of deuterostome animals
large and complex, pore development mouth second, 2 major phyla of echinodermata and chordata
diversity of ray fin fish
evolution of protrusible jaw that can be extended to bite
membranes of amniotic egg
chorion (gas exchange) amnion (encases embryo) yolk sac (surrounds yolk) allatois (surrounds waste cavity)
kinetic skull
lower jaw not directly attached to skull
hooves and horns
mammal trait, horns permanent and antlers temporary