Stem Cells (BN)
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Self renewal
stem cells can continually divide and replicate
Potency
stem cells have the capacity to differentiate into specific cell types
stem cell supplies are typically limited
When a cell differentiates to become specialised, it loses its capacity to form alternative cell types
Totipotent
Can form any cell type and develop into entirely new organisms
Pluripotent
Can form any cell type arising from the three germ layers
Multipotent
Can only form a number of closely related cell types
embryonic stem cells
Totipotent stem cells (e.g. zygotes) and pluripotent stem cells (inner cell mass of blastocyst)
adult stem cells
multipotent stem cells (e.g. bone marrow)

Embryonic and adult stem cells
can be used therapeutically to treat diseases by replacing damaged cells with healthy ones
Embryonic stem cells have a greater potency
can treat more conditions) but there are ethical issues associated with their use (involves the generation and destruction on an embryo)
Adult stem cells have less ethical issues and a lower chance of graft rejection
(involves use of patient’s own cells), but have lower potency and are therefore limited in their potential use
Stem cell niches
sites within the body where a pool of adult stem cells are maintained in preparation for future proliferation and differentiation
Locations of stem cell niches
bone marrow, hair follicles, heart, intestines and brain
Bone Marrow
Haemopoietic stem cells are located within the bone marrow and give rise to the different types of blood cells (e.g. erythrocytes, leucocytes and thrombocytes)
Hair Follicles
contain a range of epidermal stem cells that are involved in cyclic bouts of hair growth, skin innervation, vascularisation and wound repair
Differentiation
the process during development whereby newly formed cells become more specialised and distinct from one another as they mature
genome
each cell contains the entire set of genetic instructions for that organism
Differential Gene Expression
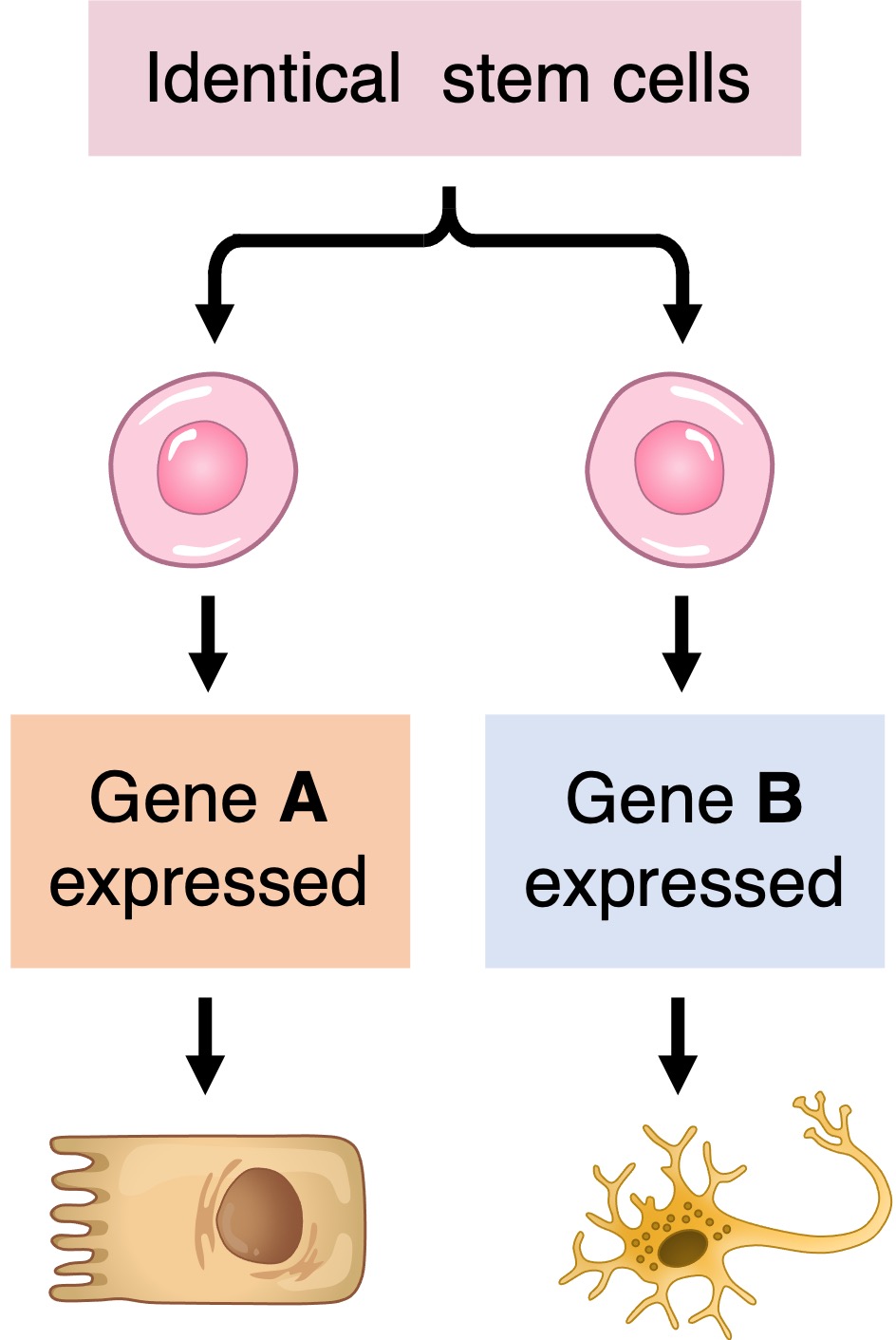
early zygote
unspecialised zygote will divide and develop into a mass of specialised cells
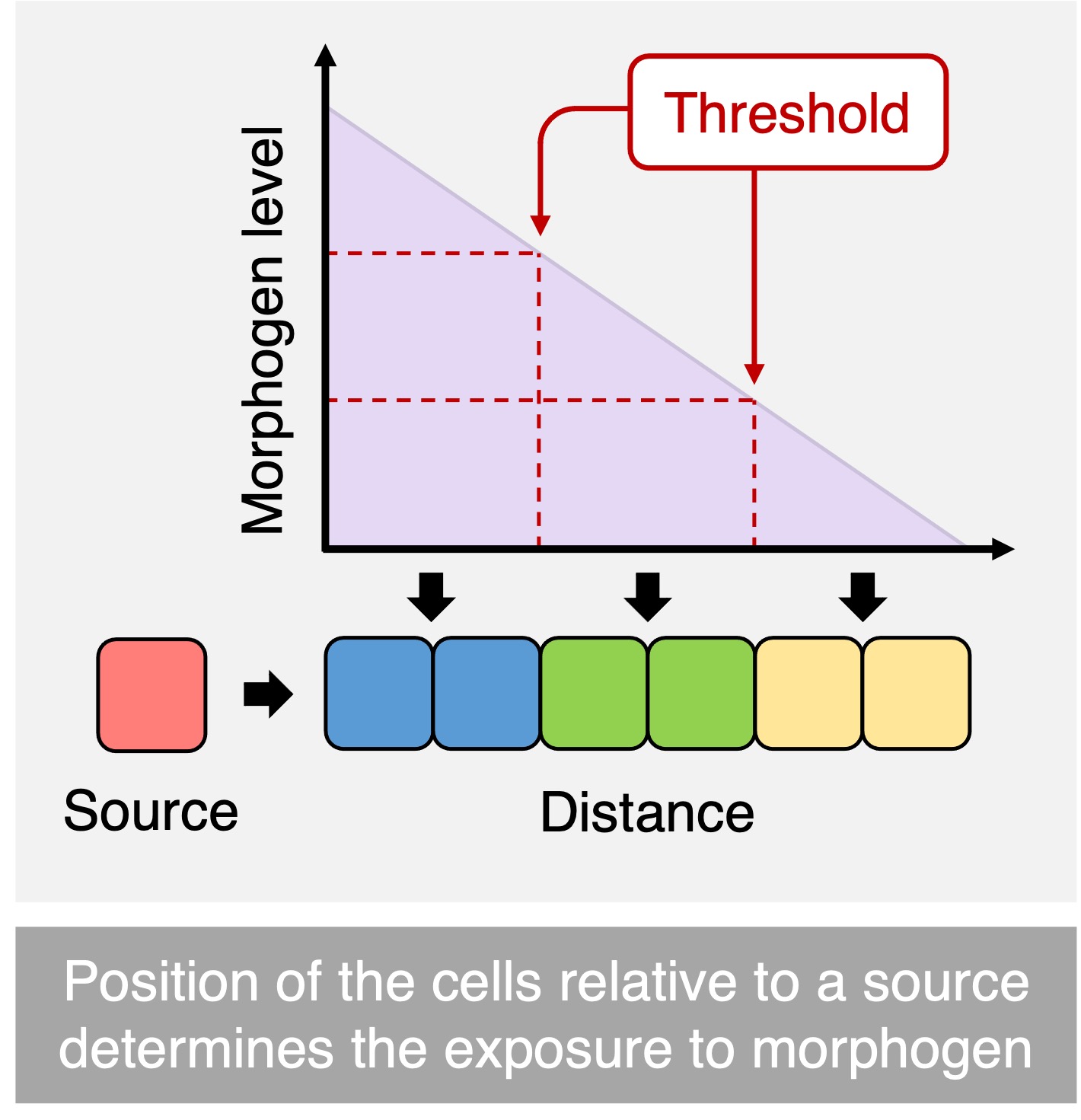
morphogens
release of gene regulating chemicals (transcription factors)
cells closer to the morphogen source
receive higher concentrations of morphogen, resulting in the activation of more genes
Cells further away from the morphogen source
receive lower concentrations of morphogen, resulting in the expression of fewer genes
morphogen gradients
control the differential expression of genes within an early-stage embryo
Morphogen Gradients
rate of metabolism
is a function of its mass / volume (larger cells need more energy to sustain essential functions)
rate of material exchange
function of its surface area (large membrane surface equates to more material movement)
cell will die
metabolic rate exceeds the rate of exchange of vital materials and wastes (low SA:Vol ratio)
ratio suitable for survival
growing cells tend to divide and remain small in order to maintain a high SA:Vol
SA:Vol Ratio

size of cells
vary significantly in multicellular organisms in order to optimise the specific function of a cell