Biology 2: Reproduction
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
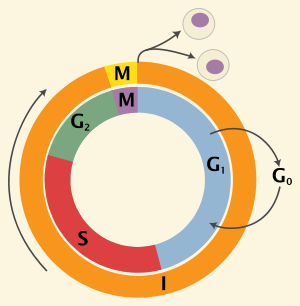
During the [cell cycle phase], cells synthesize mRNA and proteins
G1 phase
this is to prepare for subsequent steps leading to mitosis
g1 stands for “Ga 1”
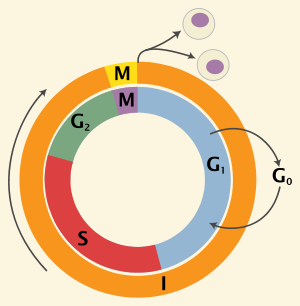
A cell will enter [cell cycle phase] if it does not need to divide
the G0 phase
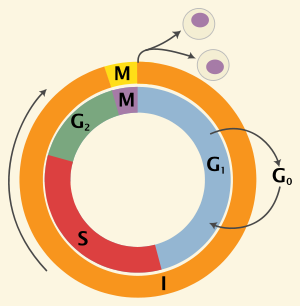
At the [...] checkpoint, cells choose whether or not to divide
the G1 checkpoint
p53 is in charge
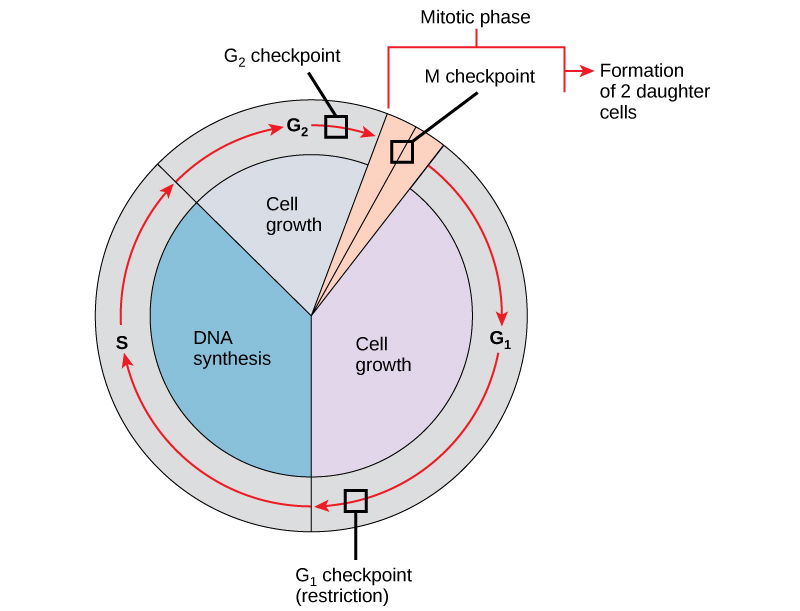
DNA is replicated in the [cell cycle phase]
S phase
s= synthesis phase
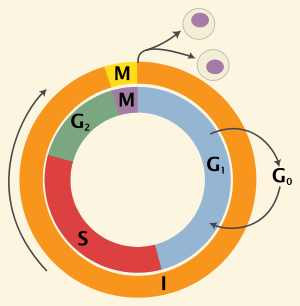
In the [cell cycle phase], cells grow and make organelles
g2 phase
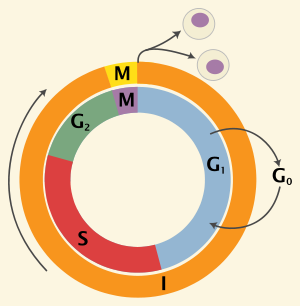
At the [...] checkpoint, the cell will check that the DNA has replicated correctly
G2 checkpoint
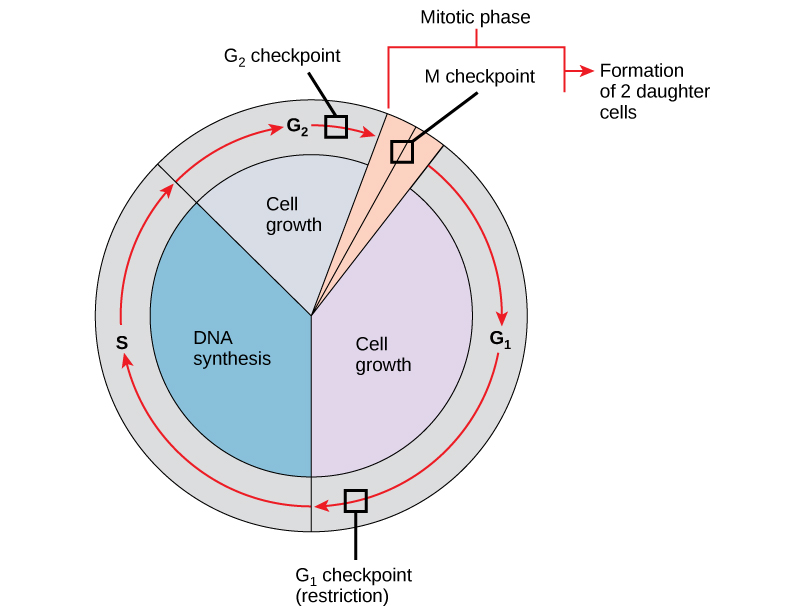
Mitosis and cytokinesis occur in the [cell cycle phase]
M phase
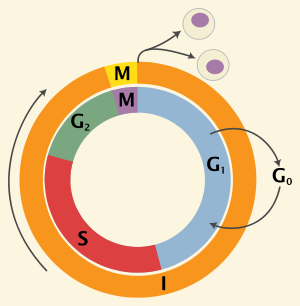
The four phases of Mitosis:
[...]
[...]
[...]
[...]
prophase
metaphase
anaphase
telophase
PMAT
note: interphase precedes mitosis, it is not apart of mitosis
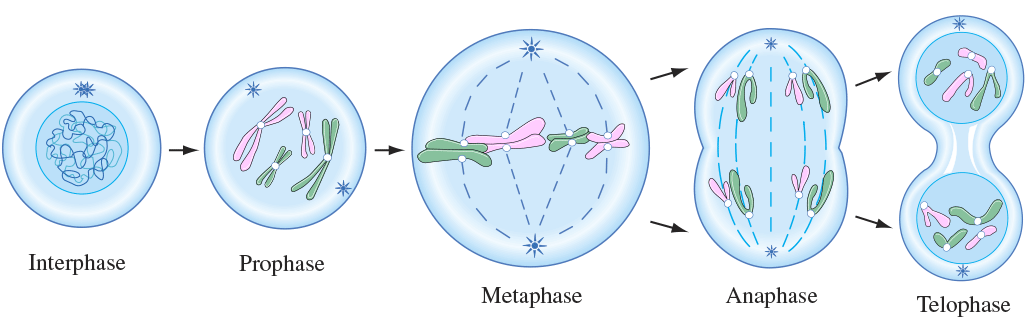
Interphase includes [cell cycle phases]
G1, S, ang G2 phases
phases where the cell spends most of its life
In [mitosis phase], the DNA condenses, centrioles migrate to opposite poles, and microtubules form
prophase
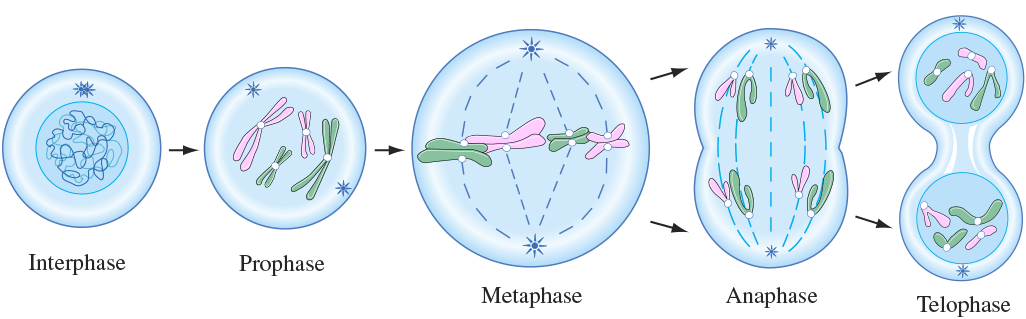
In [mitosis phase], chromosomes meet in middle of the cell
metaphase
metaphase =”meet in middle” at the metaphase plate
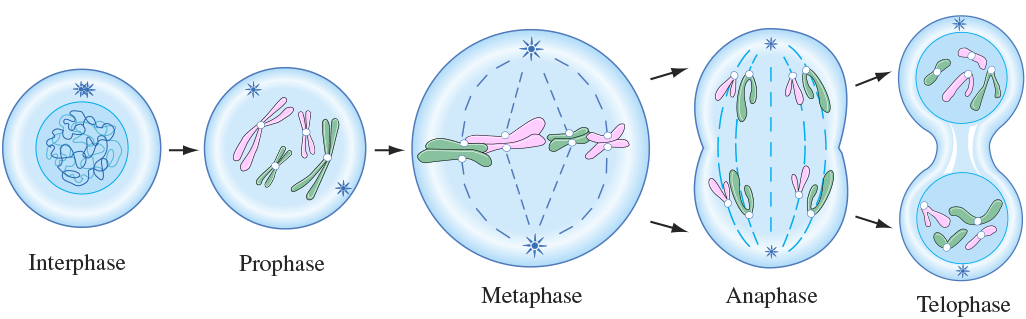
In [mitosis phase], sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles
anaphase
anaphase=apart
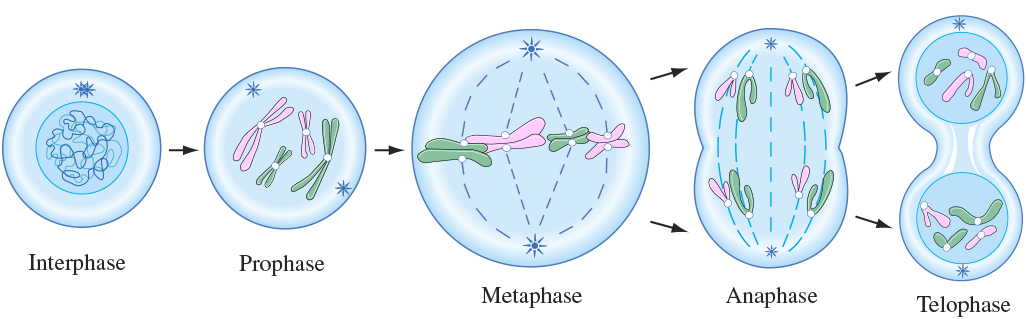
In [mitosis phase], chromosomes decondense, the nuclear membrane forms, and cytokinesis occurs
telophase
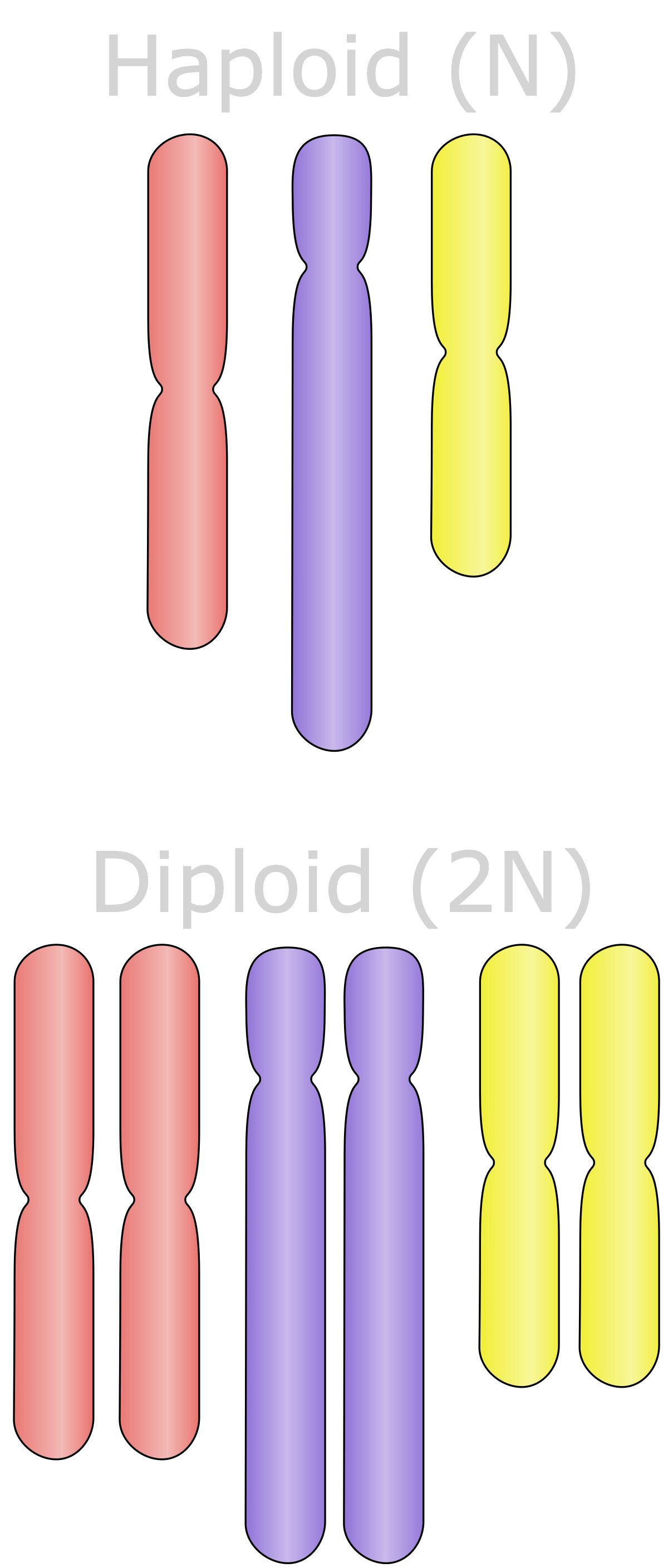
The number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell is referred to as the [...] of a cell
ploidy
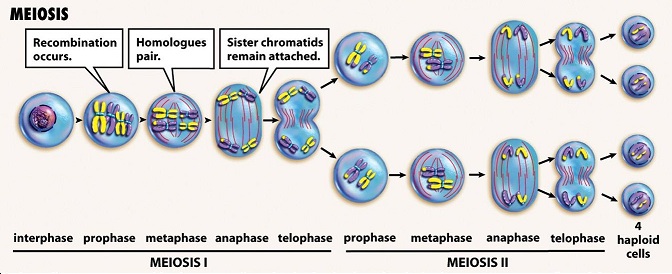
The phases of meiosis:
[...]
Prophase I
Metaphase I
Anaphase I
Telophase I
Prophase II
Metaphase II
Anaphase II
Telophase II
PMAT x 2
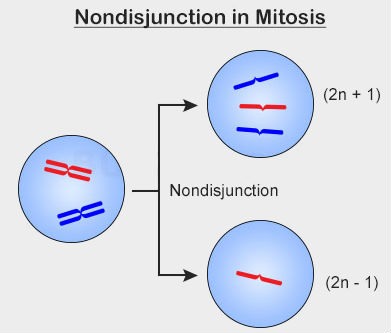
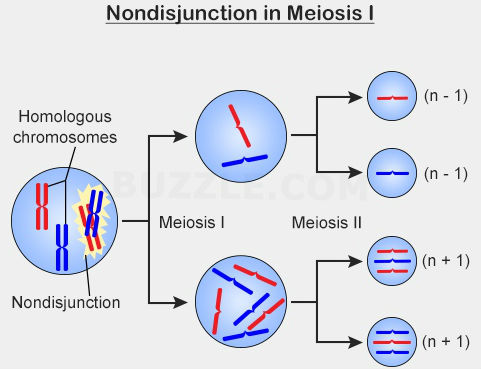
[...] is when sister chromatids don’t separate properly during anaphase
nondisjunction
results in aneuploidy
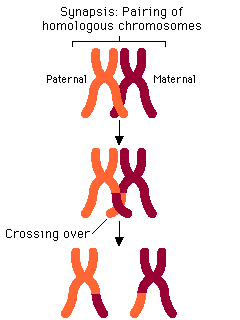
[...]is when two chromosomes of a homologous pair exchange segments with each other
crossing over
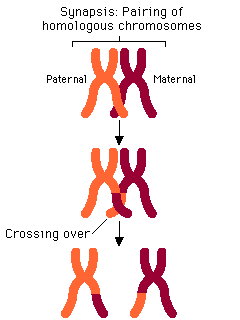
Crossing over occurs in [meiosis phase]
Prophase I
[...] states that two alleles of each gene become separated and only one allele from each parent will be passed to the offspring
the law of segregation
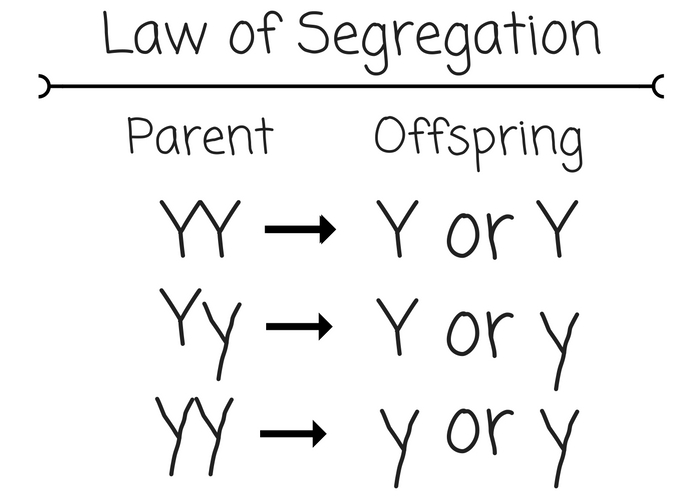
The law of segregation occurs in [meiosis phase]
anaphase I
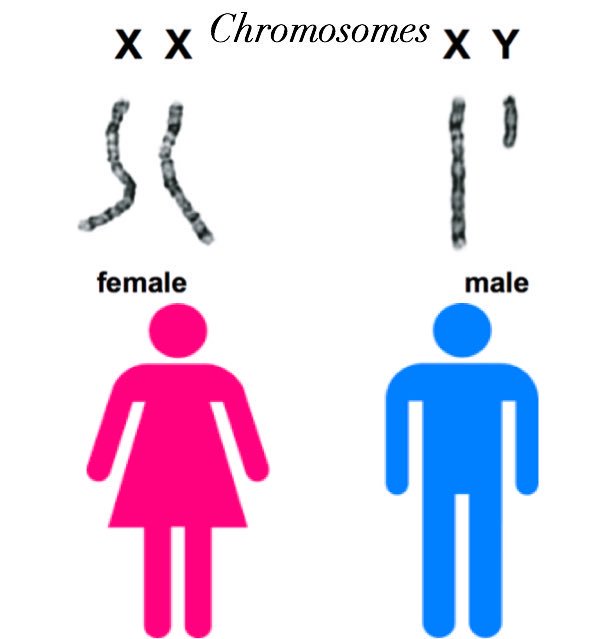
Female chromosome pairs are [XX or XY]
xx
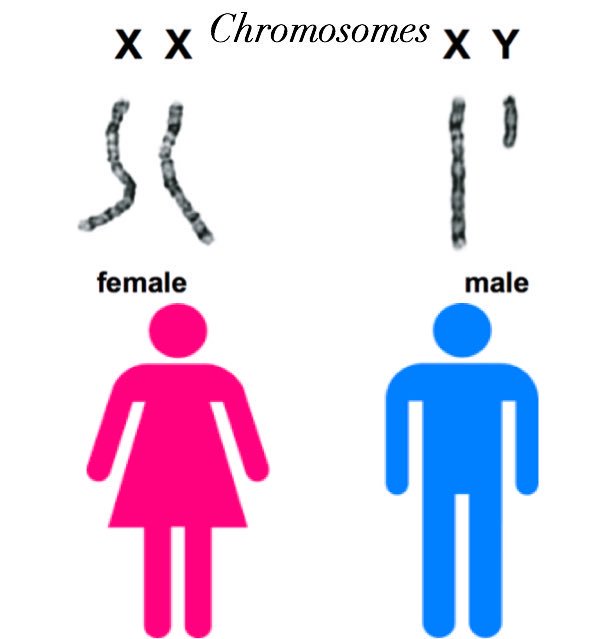
Male chromosome pairs are [XX or XY]
xy
[...] refers to genetic conditions associated with mutations in genes on the X chromosome
x-linked recessive inheritance
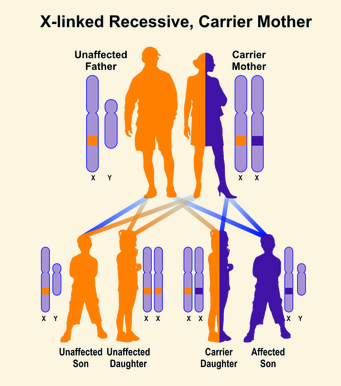
In males with an X-linked recessive mutation, the mutation [will or will not] be expressed
will
this is because males only have one x chromosome
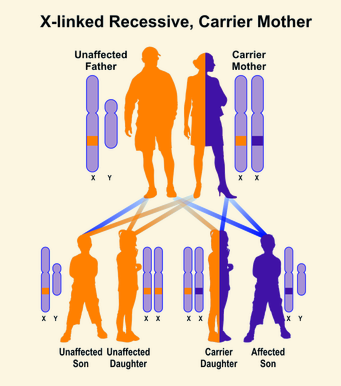
In females with an X-linked recessive mutation, the mutation [will or will not] be expressed
will not
females have two x chromosomes, so the mutation is carried but not expressed. the normal x chromosomes will be expressed because this is a recessive trait
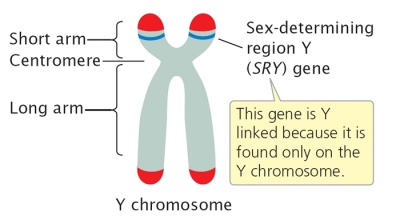
The [gene] is responsible for initiation of male sex determination and codes for testicles
SRY gene
sorry your a male
Semen is a combination of [...] and [...]
sperm and seminal fluid
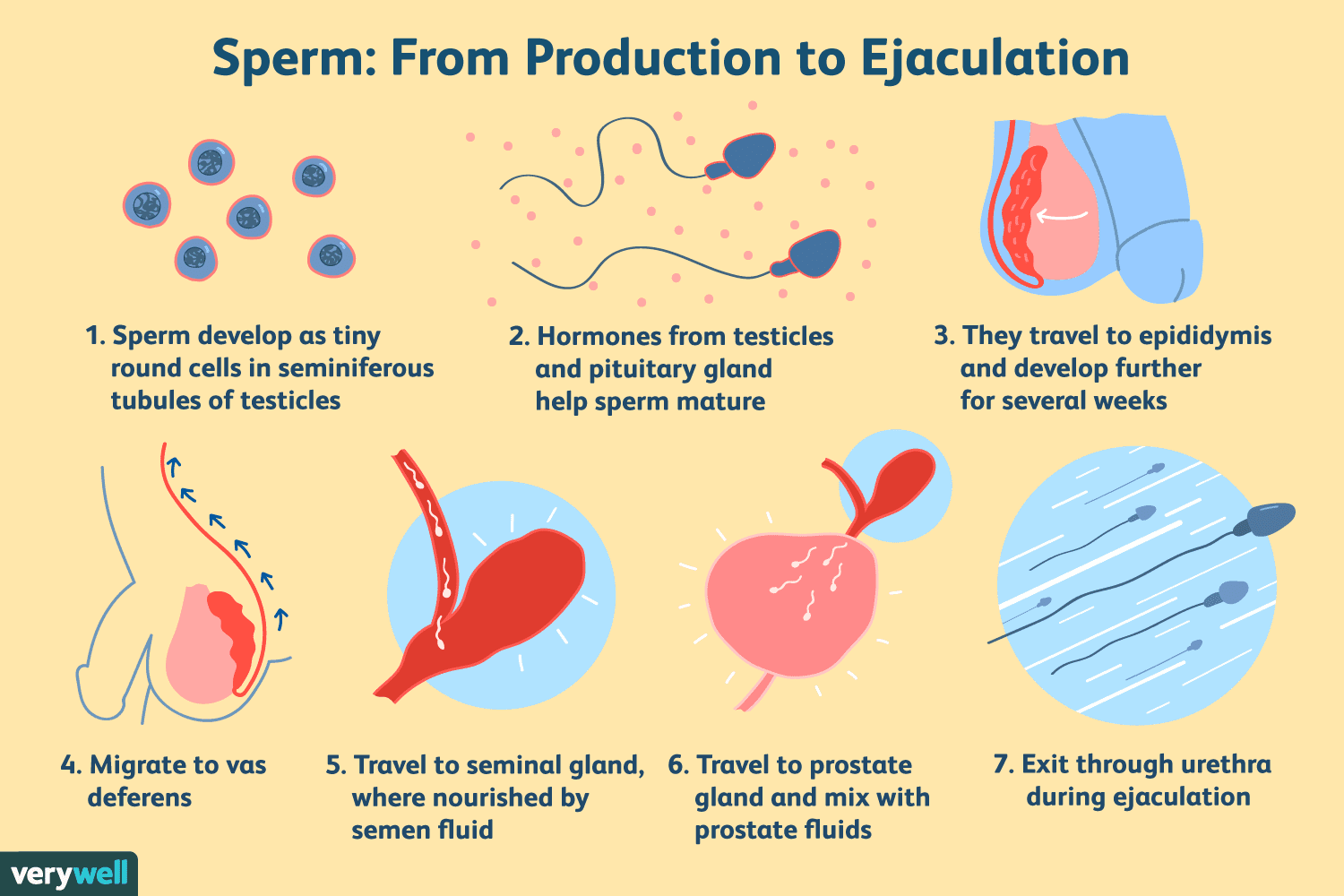
The [...] makes viscous fluid to clean out the urethra
bulbourethral gland
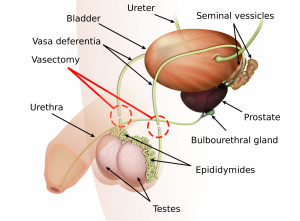
[...] and the [...] make alkaline fluid to help sperm survive the acidic environment of the female reproductive tract
seminal vesicles and prostate gland
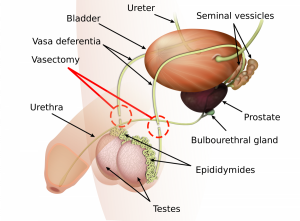
Pathway of sperm during ejaculation:
seven (N) up

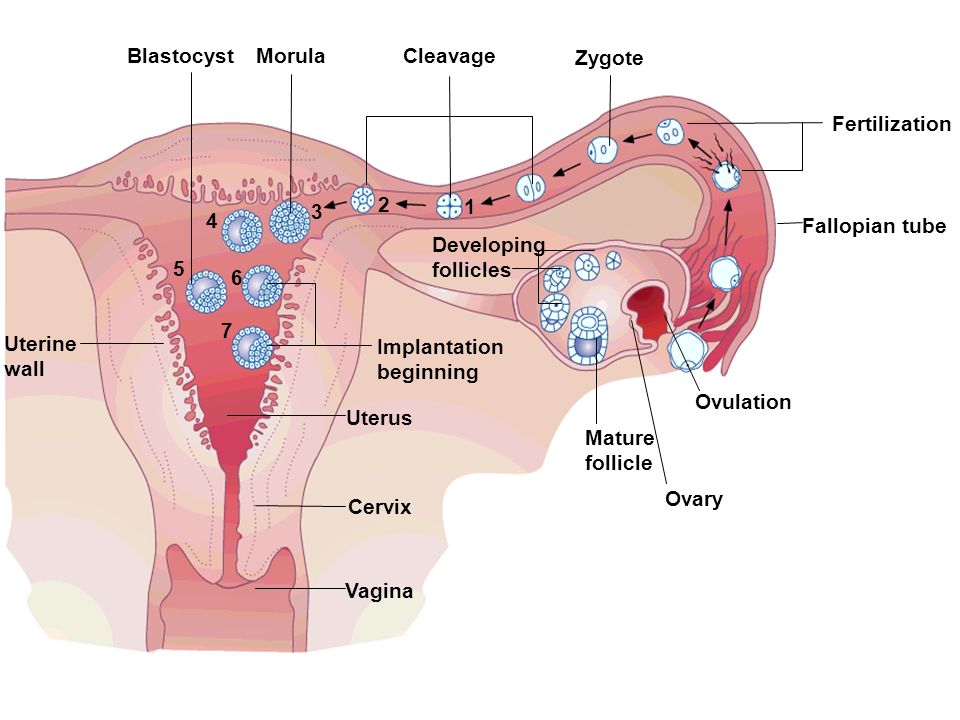
The [...] have follicles that produce ova
ovaries
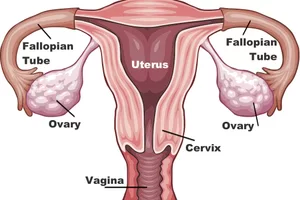
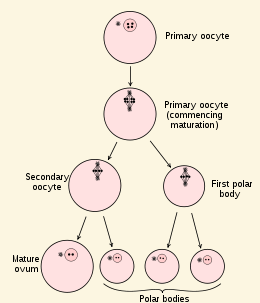
[...] is the production of female gametes
oogenesis
[Hormone] develops the female reproductive tract and thickens the uterine wall
estrogen
estrogen estabiles and progesterone protects the endometrium
estrogen response to FSH
[...] maintains and protects the endometrium
progesterone
estrogen establish and progesterone protects the endometrium
progesterone respond to LH
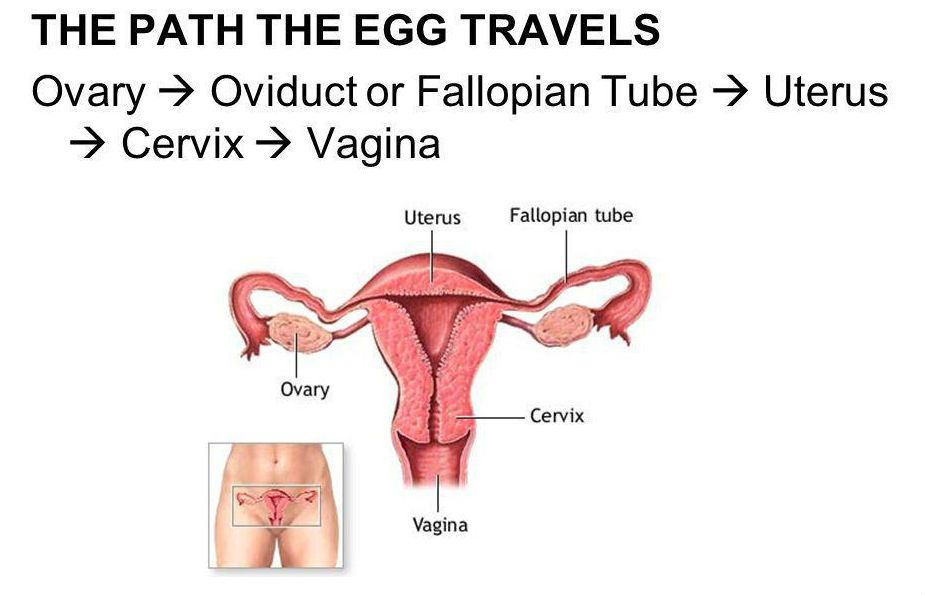
Female egg pathway:
[...]
note: if unfertilized, the egg will leave thruough the cerivix and vgina, otherwise it implant into the uterus as an embryo
[...] induces ovulation in females and, in males, it initiates the production of testosterone
luteinizing Hormone (LH)
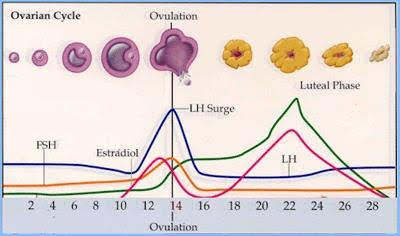
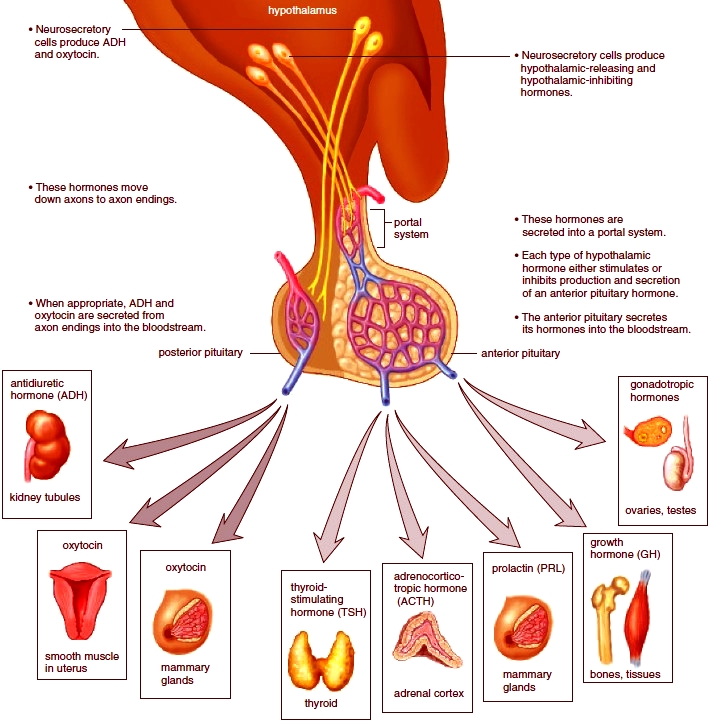
GnRH stimulates the anterior pituitary to release [...] and [...]
FSh and LH
gonadotropin-releasing hormone
Fertilization occurs in the [...]
fallopian tube