3.2.3 gas exchange (plants)
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
How are the leaves of plants adapted for gas exchange
many stomata (high density) which provides a large surface area for gas exchange when opened by the guard cells
The spongy mesophyll contains air spaces which provides a large surface area for gases to diffuse through
The leaves are thin to provide a short diffusion distance
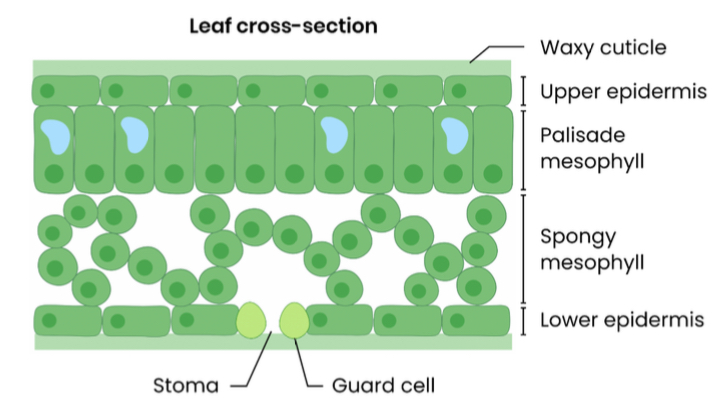
Draw the cross section of a leaf
waxy cuticle
Upper epidermis
Palisade mesophyll
Spongy mesophyll
Lower epidermis
Stoma and guard cells
What is taken in/ out through the stomata
CO2/ oxygen is taken in
Water vapour is taken out
What is a xerophyte
A plant adapted to live in very dry conditions
Explain how xerophytic plants allow gas exchange and limit water loss — thick waxy cuticle
increases diffusion distance so less evaporation
Explain how xerophytic plants allow gas exchange and limit water loss — Sunken stomata, rolled leaves and hairs
trap water vapour/ protect stomata from wind
So reduced water potential gradient between the leaf and air
So less evaporation
Explain how xerophytic plants allow gas exchange and limit water loss — Spines/ needles
reduces surface area to volume ratio