AP Euro Full Topic 2
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
Primogeniture
A system of inheritance in which the eldest son in a family received all of his father's land.
House of Lords
the upper house of the British parliament whose members are members of the Peerage (established nobility)
House of Commons
Lower House of Parliament including wealthy landowners and rich business leaders that represent the middle class and are elected to office
patriarchal
relating to a society in which men hold the greatest legal and moral authority
dowry
money or property brought by a woman to her husband at marriage
La Querelle des Femmes
Literally, "the question of women," a literary debate which began amongst intellectual elites and religious leaders around 1500 about the nature and status of women
Black Death
A deadly plague that swept through Europe, first between 1347 and 1351 and multiple outbreaks after through the 1600s.
Carnival
a festival marked by merrymaking and processions that happens just before the season of Lent.
penance
voluntary self-punishment in order to atone for (make up for) some wrongdoing or sin.
blood sports
Events such as bull-baiting, bear-baiting and cockfighting that involved inflicting violence and bloodshed on animals and that were popular entertainment with European masses. (grrr)
Charivari
Degrading public rituals (often a parade where the offender rides backwards on a donkey) used by village communities to police personal behavior and maintain moral standards. Often done on a man whose wife had cheated on him.
stocks
public punishment where offender sat on a bench with ankles closed in holes for several hours while passers-by threw garbage at them.
pillory
public punishment where offender stood with hands and head locked in a wooden bar for hours while passers-by threw garbage at them.
pranger
public punishment where an offender's neck and feet were chained together, leaving them standing in an uncomfortable half kneeling position for hours.
flogging
Also called whipping, a public punishment where an offender is beaten with a whip, usually accompanying being chained to pillory. The event attracted many spectators.
branding
Searing of the skin with a mark that indicates a person does not believe in the same things as the community, or committed a terrible crime or sin.
maleficium
harm believed to be caused by Witches in their attempt to please the Devil.
Malleus Maleficarum
German book published in 1487 outlining the nature and appearance of witches. Became the go-to book for determining guilt in a Witchcraft Trial.
Laura Cereta
A radical feminist in her time (1469-1499) who had enough education to write about her ideas. She defended women's right and ability to be scholars. She wrote a series of letters defending this.
peerage
Lords or Ladies, with a nobility rank that is higher than knighthood
vernacular bibles
Bibles written in the common language of the people, rather than Latin.
Puritans
Protestant sect in England hoping to "purify" the Anglican church by getting rid of of Roman Catholic traces in practice and organization.
Huguenots
French Protestants influenced by John Calvin
New Testament
The second part of the Christian Bible, containing descriptions of the life and teachings of Jesus and of his early followers
Old Testament
first part of the Bible that is about the early history of the Jews and Judaism
Elizabethan Settlement
The attempt by Elizabeth to settle England's religious problems through compromise
Thirty-nine Articles
The official statement of the beliefs of the Church of England. They established a moderate form of Protestantism and created the Anglican Church
Concordat of Bologna
Treaty under which the French Crown recognized the supremacy of the pope and obtained the right for the government to nominate all French bishops and abbots (1516)
Schmalkaldic Wars
Wars in 1540s between Catholic Charles V and the Protestant German princes
Peace of Augsburg
1555 agreement declaring that the religion of each German state would be decided by its ruler
Schmalkaldic League
Protestant alliance formed by Lutherans against the Catholic Holy Roman Empire/Charles V.
Cuius regio, eius religio
Whose realm, his religion--basic idea behind Peace of Augsburg
Catherine de' Medici
The wife of Henry II of France, who exercised political influence after the death of her husband and during the rule of her weak sons, instigating several religious conflicts in France.
Henry of Navarre
Leader of Huguenot forces during French Religious wars and head of Bourbon family. Became Henry IV, first Bourbon monarch.
St. Bartholomew's Day Massacre
Mass slaying of Huguenots (Calvinists) in Paris, on Saint Bartholomew's Day, 1572.
Henry III
son of Henry II of France and the last Valois to be king of France, killed in War of the Three Henrys
War of the Three Henrys
This was the last of the wars that occurred over the religious differences in France, between the Catholics (Henry III of France and Henry of Guise) and Protestants (Henry of Navarre)
Henry IV
(1589-1610) - Formerly Henry of Navarre; ascended the French throne as a convert to Catholicism. First Bourbon family monarch.
Edict of Nantes
Issued by Henry IV, granted religious freedom to the Huguenots in France--said you caaan't hurt the protestaaaants in fraaaaance.
religious pluralism
an attitude or policy regarding the diversity of religious belief systems co-existing in society
Charles V
Holy Roman Emperor during Reformation. Abdicated in 1555 and split his empire, giving his son Spain and the Americas and his Brother the HRE.
Ottoman Empire
A Muslim empire based in Turkey that lasted from the 1300's to 1922. Threatened Europe, especially the HRE in 1500s.
Thirty Years War
last religious war between Catholics and Protestants in Europe that devastated the region that is now Germany
Cardinal Richelieu
Regent for Louis XIII in France. Weakened power of Protestants in France while secretly supporting Protestants against the Holy Roman Emperor during the 30 Years' War.
Peace of Westphalia
the peace treaties that ended the Thirty Years' War in 1648. Increased power of France. Allowed Catholic, Lutheran, and Calvinism as acceptable religions.
Philip II
King of Spain from 1556 to 1598. Absolute monarch who helped lead the Counter Reformation by persecuting Protestants under his power. Zealous Catholic.
politiques
Rulers who put political necessities above personal beliefs. For example, Henry IV of France and Elizabeth I of England made religious compromise in order to achieve political unity.
"Paris is Worth A Mass"
The reason Henry IV gave when he converted to Catholicism as king of France.
indulgences
Selling of forgiveness by the Catholic Church. It was common practice when the church needed to raise money.
Reformation
a 16th century movement for religious reform, leading to the founding of Christian churches that rejected the pope's authority
Martin Luther
a German monk who became one of the most famous critics of the Roman Catholic In 1517, he wrote 95 theses, or statements of belief questioning some church practices.
95 Theses
Martin Luther's ideas that he posted on the church door at Wittenberg which questioned some Roman Catholic Church practices.
Diet of Worms
This was the conference that Charles V called to question/prosecute Martin Luther
Charles V
This was the Holy Roman Emperor that called for the Diet of Worms. He was a supporter of Catholicism.
Sola Scriptura
Belief that the Bible is the sole source of religious truth
Sola Fide
Belief in Justification by faith alone--faith alone is needed to get to heaven.
Priesthood of All Believers
Luther's revolutionary idea that every believer had the ability to read and interpret the Bible, that all people of faith were viewed by God as equals.
John Calvin
religious reformer who believed in predestination and a strict sense of morality for society
Predestination
Calvinist belief that God long ago determined who would gain salvation and nothing someone does will change that.
The Elect
In Calvinist doctrine, those who have been chosen by God for salvation.
Geneva
Swiss city-state which became a Calvinist theocracy in the 1500s;
German Peasants' War
revolt of German lower classes calling for social/political change based on ideas of Luther (rejected by Luther, in reality).
Anabaptists
A Protestant sect that believed only adults could make a free choice regarding religion; they also advocated pacifism, separation of church and state, and democratic church organization.
Edict of Worms
declared Martin Luther an outlaw within the Holy Roman Empire and his works were to be burned and luther himself captured and delivered to the emperor
Theocracy
A government controlled by religious leaders using their religious text (such as the Bible) as the source of law.
pacifism
the belief that any violence, including war, is unjustifiable under any circumstances, and that all disputes should be settled by peaceful means.
Mannerism
an artistic movement that emerged in Italy in the 1520s and 1530s; it marked the end of the Renaissance by breaking down the principles of balance, harmony, and moderation
Tintoretto
Venetian Mannerist painter
El Greco
Spanish Mannerist painter (born in Greece) remembered for his religious works characterized by elongated human forms and dramatic use of color (1541-1614)
Baroque
An artistic style of the late 16th through 17th century characterized by complex forms, bold ornamentation, and contrasting elements and intense emotion. The art of the Catholic Reformation
Caravaggio
Italian Baroque painter noted for his realistic depiction of religious subjects and his use of Chiaroscuro
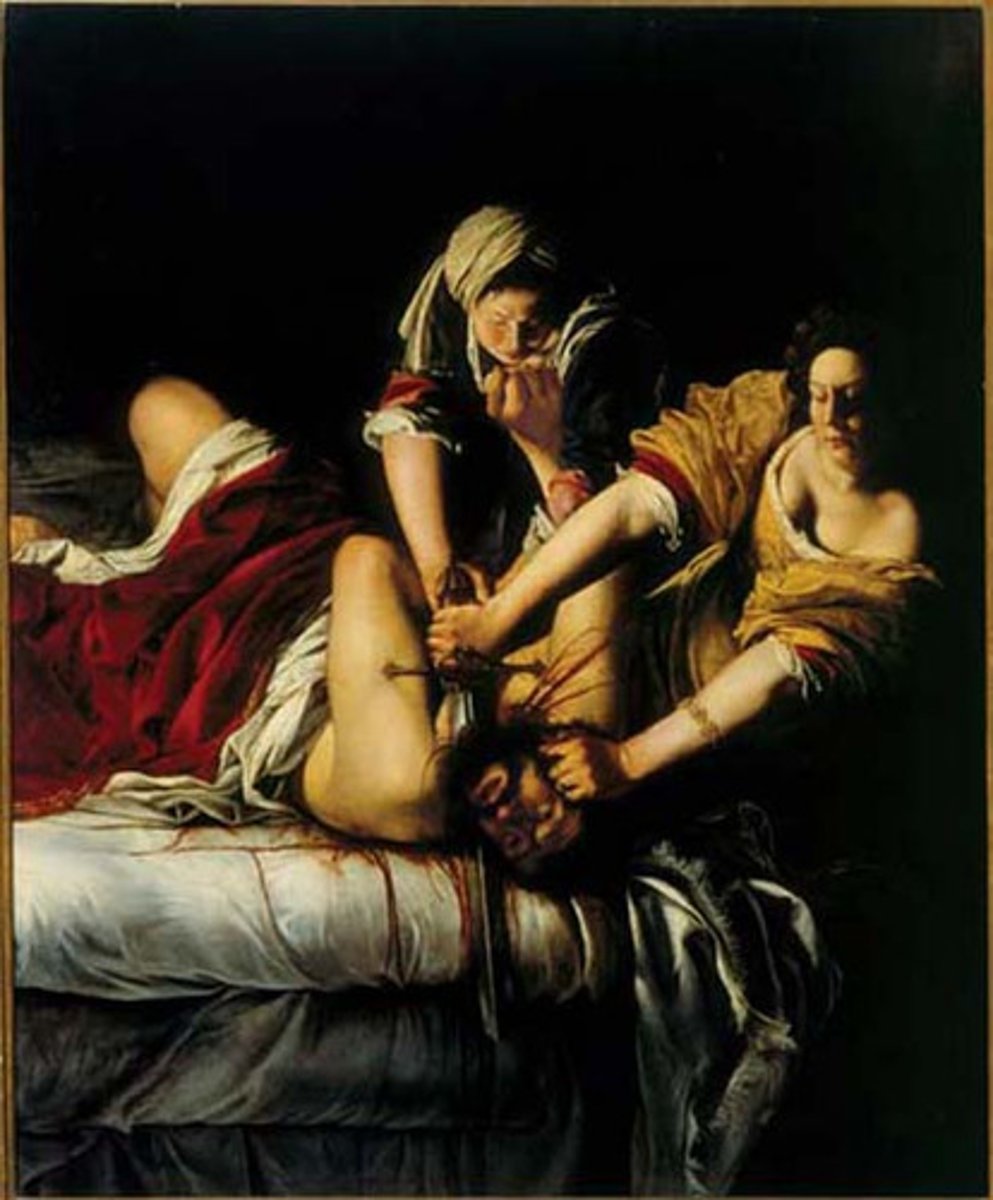
Artemisia Gentileschi
Baroque painter famous for vivid depictions of dramatic Old Testament scenes esp her Judith paintings
Gian Lorenzo Bernini
Italian architect and sculptor, famous for Saint Peter's Basilica, Ecstasy of St Teresa. Is sometimes called artist of the Catholic Reformation.
Peter Paul Rubens
is the most famous Baroque artist who studied Michelangelo in Italy and took that Renaissance style to the next level of drama, motion, color, religion and animation, which is portrayed in his paintings
Chiaroscuro
The treatment of light and shade in a work of art, especially to give an illusion of depth or to focus the eyes on a certain aspect of the painting.

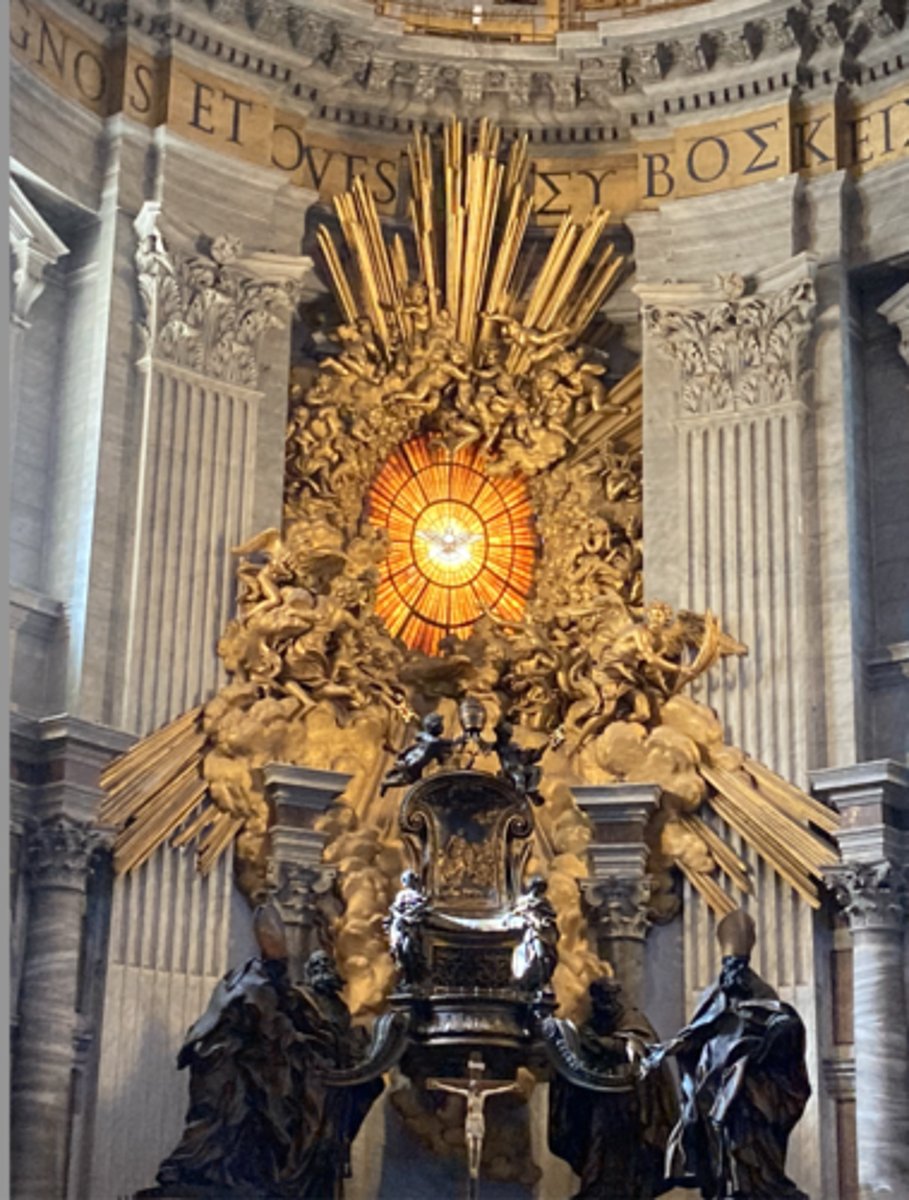
Gian Bernini, Throne of Saint Peter

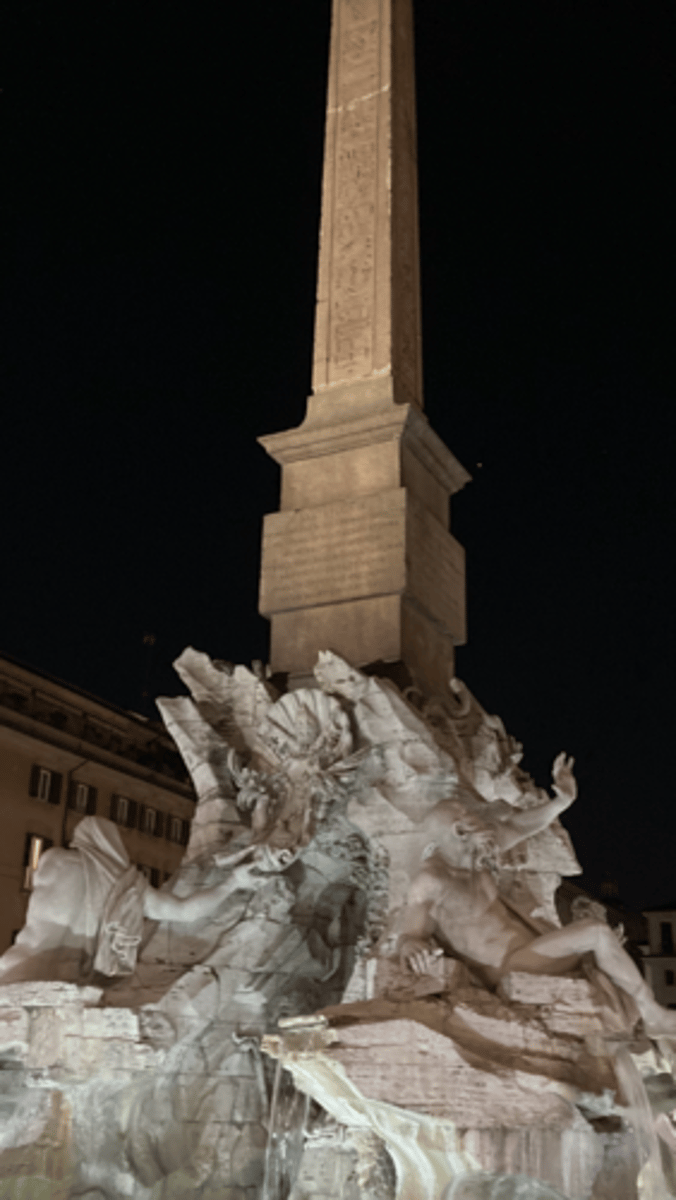
Gian Bernini, Fountain of the Four Rivers

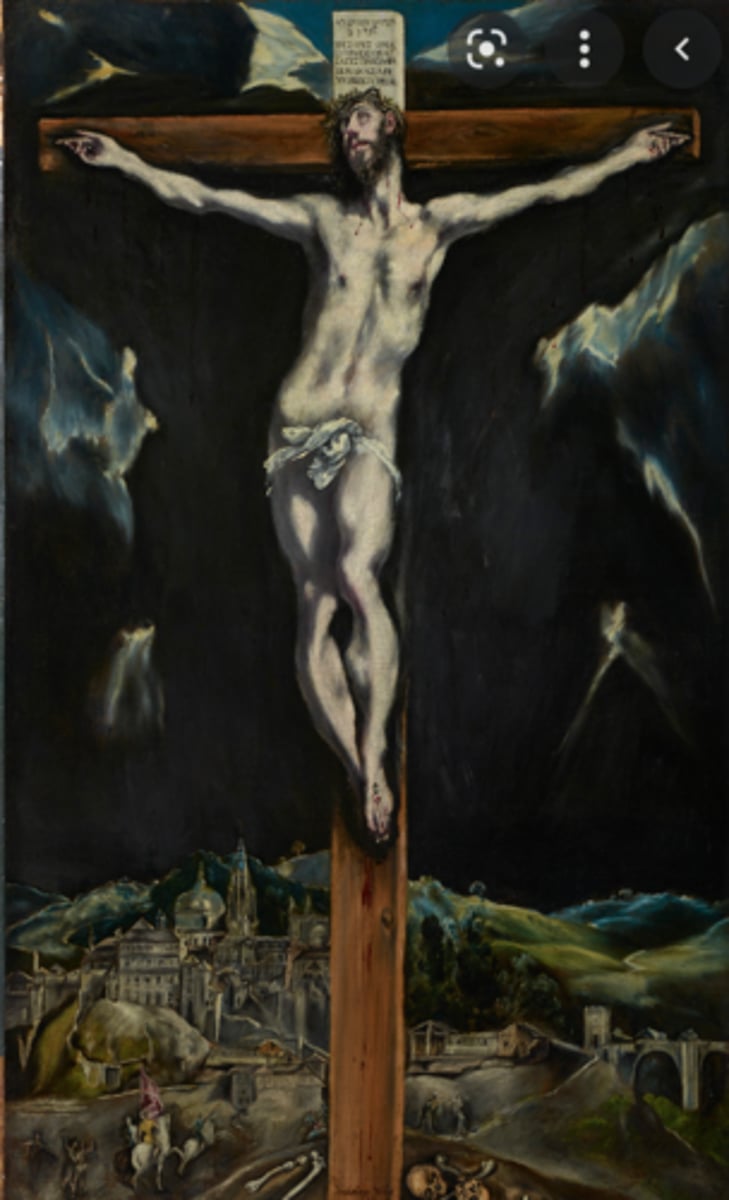
El Greco, Christ Crucified with Toledo background

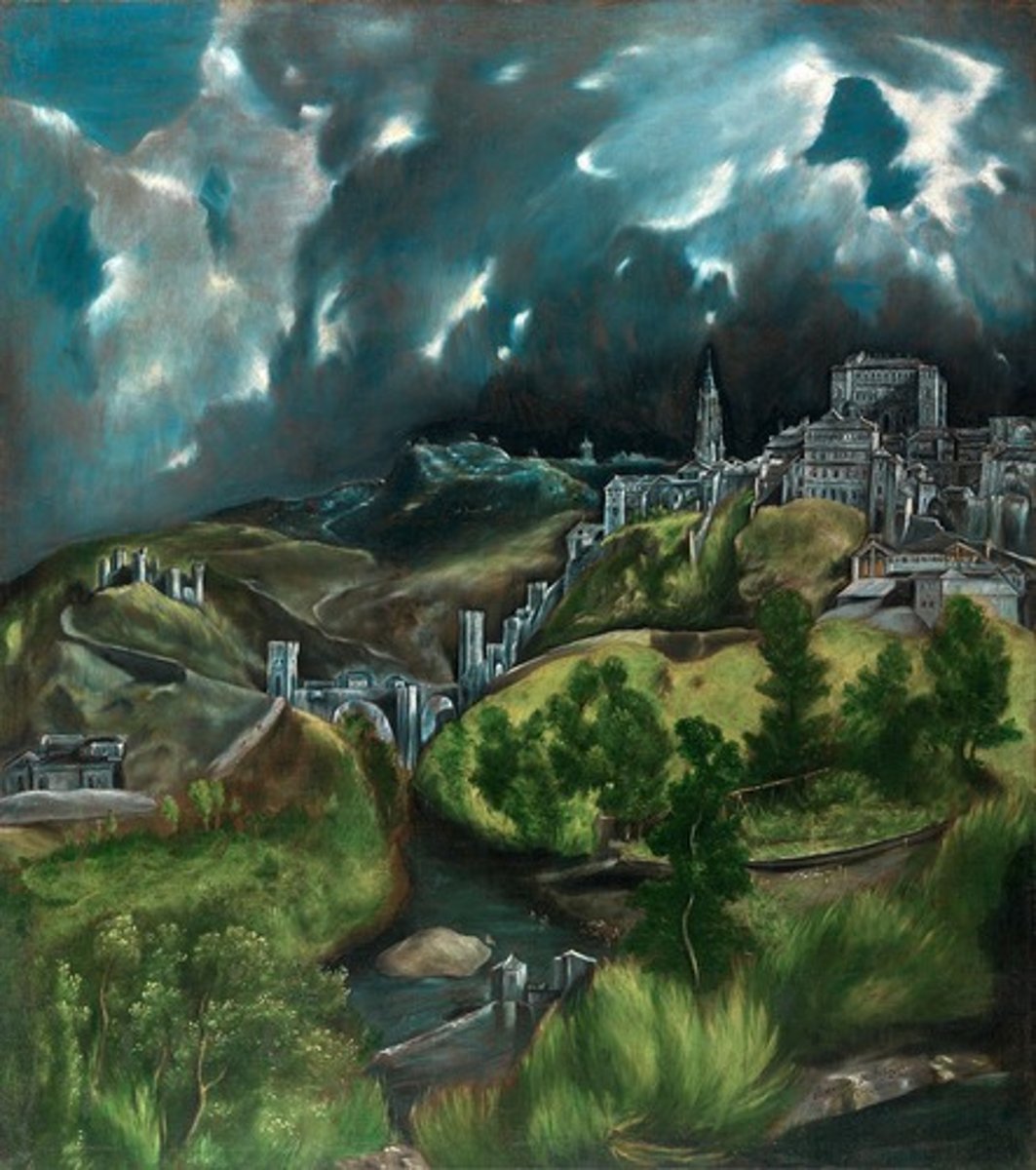
El Greco, View of Toledo

Tintoretto, Last Supper

Tintoretto, Judith and Holofernes

Artemesia Gentileschi, Judith Slaying Holofernes
Artemesia Gentileschi, Susanna and the Elders, 1610

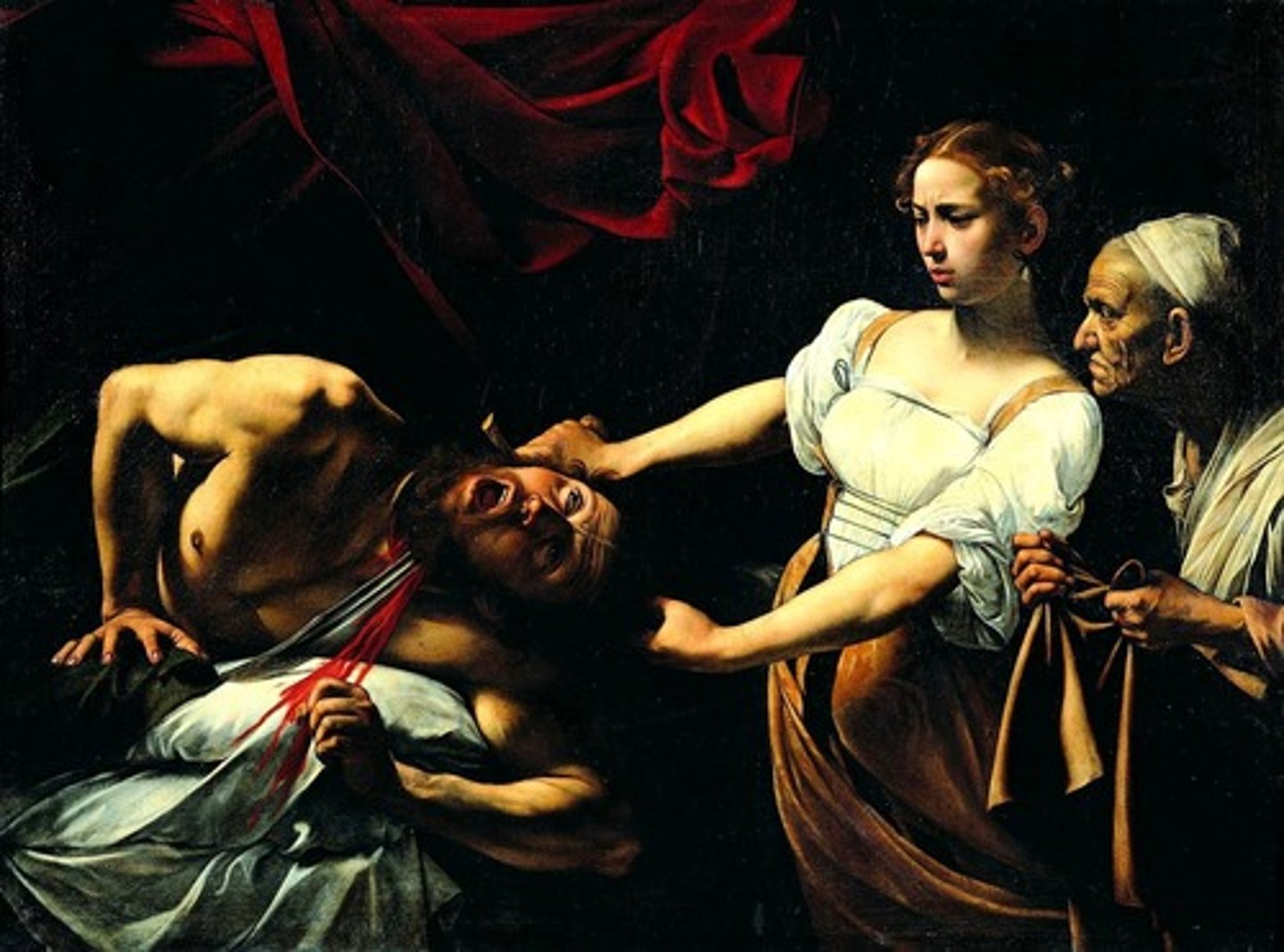
Caravaggio, Judith Beheading Holofernes

Peter Paul Rubens, The Three Graces

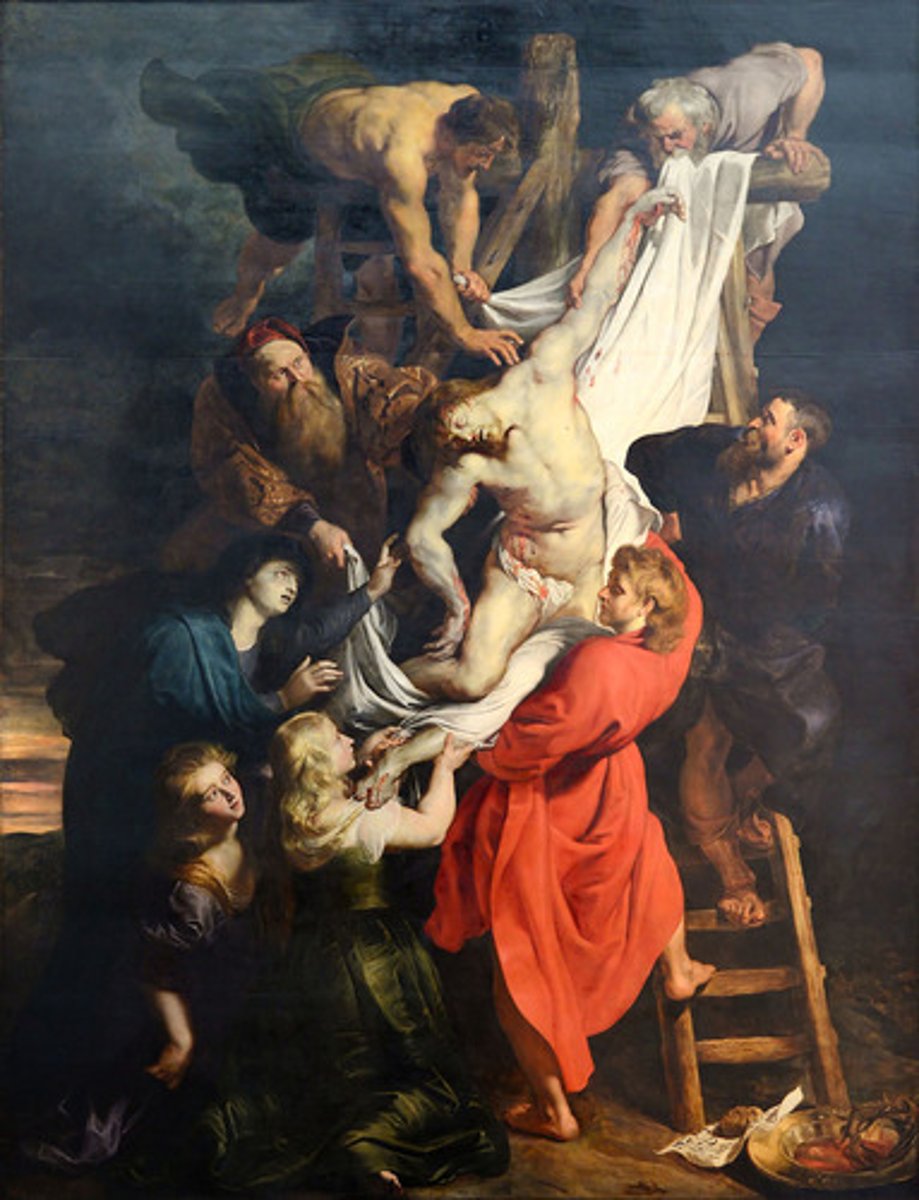
Peter Paul Rubens, Descent from the Cross

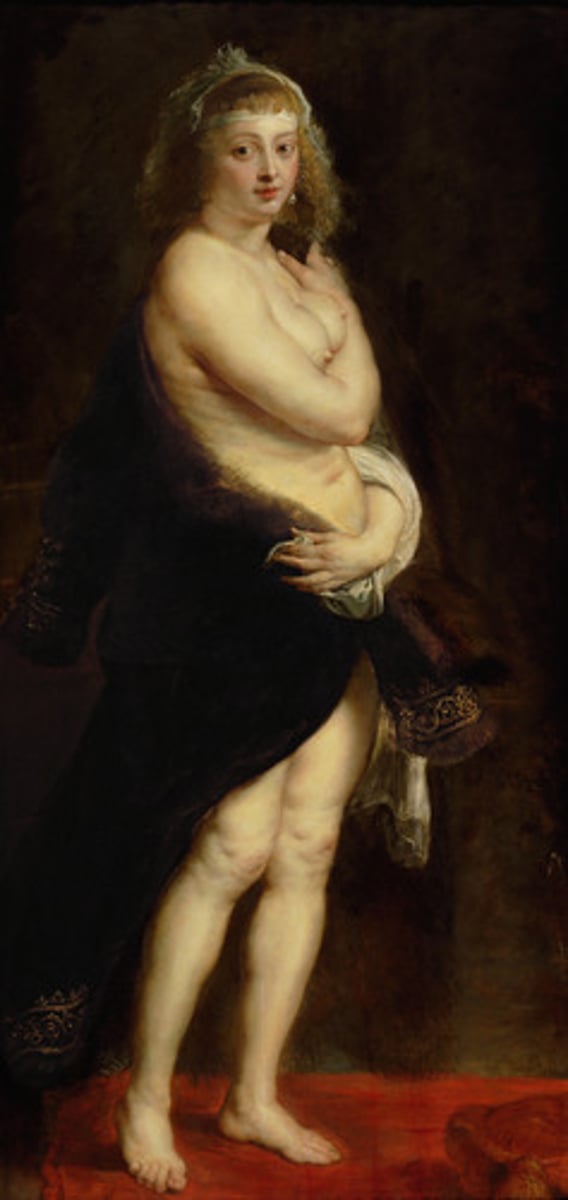
Rubenesque
Used to describe art that depicts full-figured female bodies, a polite way to refer to a tubby woman. ;) based on the work of Peter Paul Rubens.

Catholic Reformation
Religious reform movement within the Latin Christian Church, begun in response to the Protestant Reformation. It clarified Catholic theology and reformed clerical training and discipline.
Roman Inquisition
A religious committee of six Roman cardinals that tried heretics and punished the guilty by imprisonment and execution

Index of Prohibited Books
Books that supported Protestantism or that were overly critical of the Church were banned. Possession could be severely punished (even death)
Ignatius Loyola
Founded the Society of Jesus (Jesuits), resisted the spread of Protestantism, wrote Spiritual Exercises.
Jesuits
Also known as the Society of Jesus; founded by Ignatius Loyola (1491-1556) as a teaching and missionary order to resist the spread of Protestantism.
Ursulines
groups of nuns that dedicated themselves to caring for the needy and educating young girls as a way to strengthen Catholicism.
Teresa of Avila
Carmelite nun who reformed Spanish convents and monasteries insisting on strict return to personal prayer and vows of poverty among the nuns.
Council of Trent
Called by Pope Paul III to reform the church and secure reconciliation with the Protestants (but failed to do both instead it mostly reaffirmed traditional Catholic teachings.)
Carmelite Order
This order was revived by St. Teresa of Avila and her disciples who attempted to de-secularize the order and bring back intense devotional prayer and absolute vows of poverty.
Paul III
This was the Pope that called the Council of Trent
Simony
the buying and selling of church offices
Clerical Celibacy
The requirement that all members of the clergy remain unmarried and celibate (no hanky panky)
1509
Erasmus writes In Praise of Folly