Limiting Factors in an Ecosystem
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
a resource or environmental condition that limits the growth, abundance, or distribution of an organisms or a population of organisms in an ecosystem
biotic and abiotic factors that prevent the continuous growth of a population
may be physical or biological
limiting factor
limiting factors control population?
limiting factors control population growth
populations would continue to increase if they had all the resources they require in unlimited amounts, but there are always factors that limit their increase
the success of an organisms is determined by one crucial ingredient in the environment that is in short supply
law of minimum (Justus von Liebig 1840)
example what the law of minimum is
The Law of Minimum, also known as Liebig's Law of the Minimum, states that the growth of an organism or a plant is limited by the factor that is in the shortest supply, even if other factors are abundant.
For example, imagine a plant needs water, sunlight, nutrients, and air to grow. If it has plenty of water, sunlight, and air, but very little of a specific nutrient (like nitrogen), the plant's growth will be limited by that nutrient, even if the other needs are met. Essentially, the least available resource is what holds back growth.
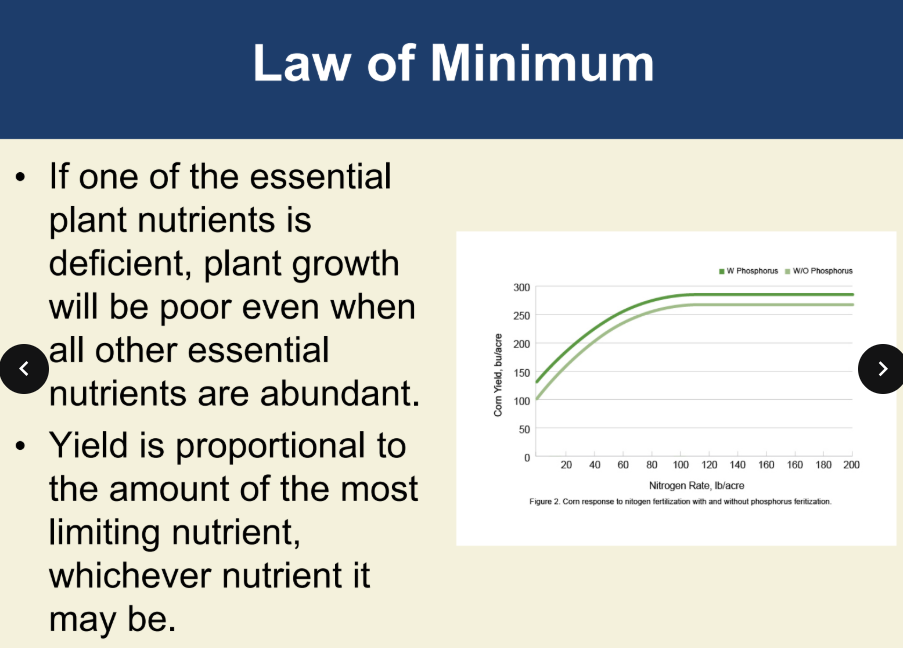
what is the limiting factor principle
too much or too little of any physical or chemical factor can limit or prevent growth of a population, even if all other factors at or near the optimal range of tolerance
examples of limiting factor principle
precipitation
nutrients
sunlight
exposure to too many competitors, predators or infectious diseases

In this case, the Great South Bay had more duck farms, which added extra fertilizer to the water. This fertilizer helped more algae (tiny plants in the water) grow. However, the types of algae that grew changed. Instead of the usual bigger algae, tiny green algae grew. These small algae weren’t as good for the oysters to eat, and the oysters ended up starving.
This situation is related to the limiting factor principle, which means that living things grow best when they have enough of the things they need. For the oysters, the problem wasn't just having too many nutrients but having the wrong type of algae to eat. Even though there was more food (nutrients), the oysters couldn’t use it properly, so they didn't survive.

explain the range of tolerance
The range of tolerance means that every species can only live in certain conditions, like temperature or amount of food. There are certain “good” conditions where they survive best, but they can also survive in conditions that are a little worse or a little better
However, if the conditions get too bad (either too hot, too cold, or not enough food) the species can’t survive anymore. So there are “limits” to how much change a species can handle, and those limits are called critical minimal and maximal thresholds. Outside of these limits, the species won’t survive
what are the ranges of tolerance
a. optimal zone
b. zones of stress
c. zones of intolerance
central portion of curve which has conditions that favor maximal reproductive success and survivability
optimal zone
- this is the “sweet spot” where things are just right for the species to grow, reproduce, and survive the best. They thrive here
regions flanking the optimal zone, where organisms can survive but with reduced reproductive success
zones of stress
- these are areas that are a little too harsh but not too bad. Organisms can still survive, but they don’t do well in terms of growing or reproducing
outermost regions in which organisms cannot survive (represents extremes of the limiting factor
zones of intolerance
these are the areas where conditions are so extreme (too hot, too cold, etc) that the species can’t survive at all. Its like the “danger zone”
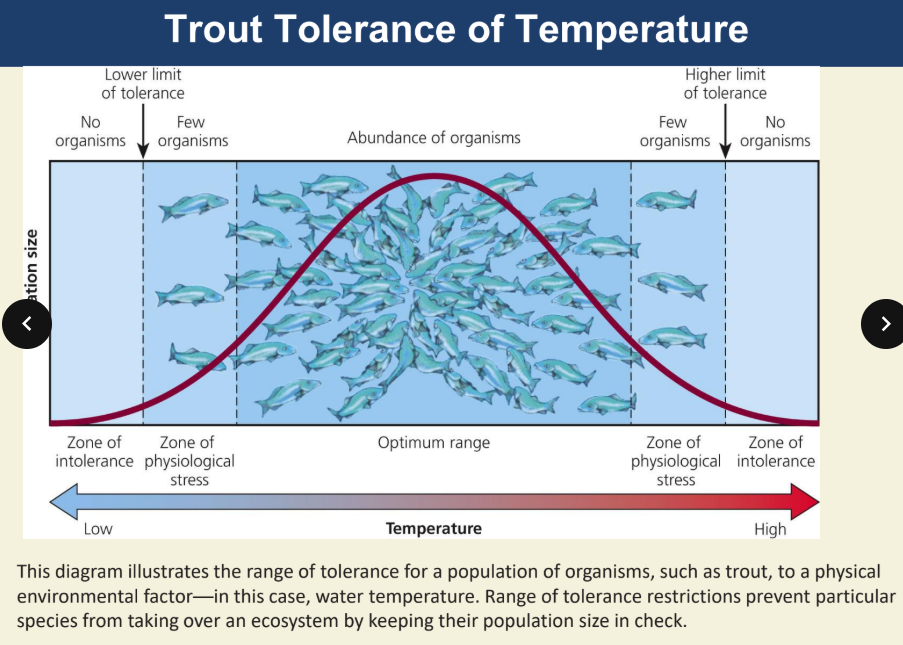
Trout have a specific range of temperatures where they can live and grow. They do best in cool water, typically between 10°C and 20°C (50°F to 68°F). If the water gets too warm, above 20°C (68°F), they start to get stressed, and their survival or reproduction can be affected. If the water gets too hot, above 25°C (77°F), they can't survive at all. So, trout have a "comfort zone" with cool water, and if it gets too hot or too cold, it can be harmful to them.
refers to narrow and wide tolerance respectively, of temperature
Stenothermal-eurythermal
refers to narrow and wide tolerance respectively, of water
Stenohydric-euryhydric
refers to narrow and wide tolerance respectively, of salinity
stenohaline-euryhaline
refers to narrow and wide tolerance respectively, of food
Stenophagic-euryphagic
refers to narrow and wide tolerance respectively, of habitat selection
Stenoecious-euryecious
why is the concept of limiting factors valuable?
the concept of limiting factors is valuable because it give the ecologist an entering wedge into the study of complex ecosystems
ecologists can usually discover the probable weak links and focus attention on those environmental conditions most like to be critical or limiting